Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Nitrogen Family Ques
Transféré par
Kamal Kishore0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
157 vues2 pagesp-block
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentp-block
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
157 vues2 pagesNitrogen Family Ques
Transféré par
Kamal Kishorep-block
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Group 15
Very short answer type question:
1. Give the oxidation state of nitrogen in N2H4.
2. Name the oxide of a nitrogen which is blue solid. Give one method of its
preparation.
3. Draw the structure of P4O10.
4. Which compound is formed during ring test for nitrates in qualitative
analysis?
5. What is the reaction of water on P4O6?
6. Give the formula of laughing gas.
7. Which oxide of phosphorus is used as a powerful dehydrating agent?
8. Carry out autoxidation of nitrous acid.
9. What is diazo reaction?
10.Give the composition of aqua regia.
11.What happens when PCl5 is hydrolyzed in excess of water?
12.What is geometry of pent halides of phosphorous?
13.Which oxide of nitrogen is obtained by heating ammonium nitrate at 250 c?
14.What is the formula of hydrazoic acid?
15.H3PO2 is a good reducing agent. Why?
16.How many unpaired electrons are present in valance shell of VA group
elements?
17.How many covalent bonds nitrogen can form?
18.What are minimum and maximum oxidation states of nitrogen?
19.Which oxy acids of nitrogen behaves both as an oxidising and a reducing
agent?
20.Why NH3 exists as liquid whereas other hydrides of the same group exist as
gases?
21.Which oxide of nitrogen is paramagnetic and coloured?
22.What is the basicity of hypo phosphorous acid?
23.What is the shape of phosphorous molecule?
24.How will you obtain PH3 form mixture of PH3 and NH3?
25.Why water has highest boiling point among NH3,PH3 and H2O?
26.Why NH3 acts as a ligand?
27.Which product is obtained on dehydration of HNO3?
28.What is the basicity of phosphorous acid?
29.What is the shape of PO4- ion?
30.What is the bond angle HPH in phosphine?
General Questions:
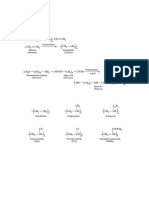
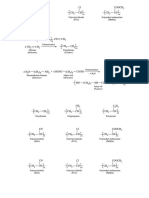
1. Give the preparation of hydrazine. How does it reacts with:
a) Air
b) Nitrous acid
c) Silver nitrate
d) Hydrogen peroxide
2. Draw the structure of any two oxides of phosphorous. How do they react
with water?
3. Give reasons for the following:
a) H3PO3 is dibasic acid.
b) NO is paramagnetic.
c) HNO2 is weaker acid than HNO3.
4. Complete the following reactions:
5. Nitric oxide becomes brown when released in air. Explain?
6. Nitric acid acts only as an oxidising agent while nitrous acid can act both
as oxidising and reducing agent. Why?
7. Why concentrated nitric acid becomes yellow on exposure to sunlight?
8. What is the hybridization of N in NO2- and which has larger bond angle out
of NO2- and NO2?
9. Give two properties to show that H2SO4 acts as an oxidising agent.
10.How is nitric oxide prepared in laboratory and on commercial scale?
11.Give the chemical reactions of nitric oxide with:
a) Phosphorous
b) Sulphurous acid
c) Chlorine
d) Oxygen
e) Ferrous sulphate
12.How does hydrazine reacts with
a) AgNO3
b) HONO
13.Give preparation and structure of phosphine and phosphoric acid.
14.Nitrogen forms NCl3 but not NCl5. Why?
15.Name six important oxoacids of phosphorous. Draw their structures.
16.What happens when:
a). Phosphorus burns in excess of air.
b). Hydrazine reacts with platinum chloride.
c). Hydroxylamine absorbs oxygen in the presence of an alkali.
d). Ammonia is oxidized with air in the presence of platinum gauze.
e). Nitric oxide reacts with phosphorus.
17. Draw and discuss the structures ofH 3PO4, H3PO3 and H3PO4.
18. Give reasons for the following:
a). Nitrogen is a gas whereas phosphorus is a solid.
b). Nitrogen does not form pentahalides.
c). HPO2 is not known.
19. Name any five oxoacids of sulphur and explain their structures.
20. What happens when:
a). Orthophosphonic acid is heated with ammonium molybdate solution.
b). Nitrous acid reacts with urea.
21. Discuss the nitrogen dependent equilibria of nitrogen dioxide and
nitrogen tetraoxide.
22.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chemistry P BlockDocument5 pagesChemistry P BlockAshok PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- P Block Give Reasons (Without Answers)Document6 pagesP Block Give Reasons (Without Answers)zxcvb100% (1)
- P-BLOCK EXAM QUESTIONSDocument19 pagesP-BLOCK EXAM QUESTIONSRishabh AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- P-Block Elements Part 2Document5 pagesP-Block Elements Part 2Aakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Document5 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Aakaash C.K.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements AssignmentDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements AssignmentManickam Gnanashekaran0% (1)
- 2nd Year Past Papers 2009 To 2019 by M ShehzadDocument18 pages2nd Year Past Papers 2009 To 2019 by M ShehzadMarvel StudioPas encore d'évaluation
- Reduced Syllabus 2020-21 P Block G 15 Important Questions Group 15Document3 pagesReduced Syllabus 2020-21 P Block G 15 Important Questions Group 15Kalpa DihingiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Halogen FamilyDocument14 pagesHalogen FamilyCharin KadianPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Chemistry Handguide by Ri DaDocument2 pagesInorganic Chemistry Handguide by Ri DaGAME DEVPas encore d'évaluation
- P-Block Elements Group 15Document24 pagesP-Block Elements Group 15SSSSSSSSSSSSPas encore d'évaluation
- Pratice Questions Class 10Document14 pagesPratice Questions Class 10Dps BhangraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonding Practice Test 2Document3 pagesBonding Practice Test 2ゆかりPas encore d'évaluation
- Past PapersDocument12 pagesPast PapersMarvel StudioPas encore d'évaluation
- 12th-class-guess-papers-2024-chemistry-short (2)Document7 pages12th-class-guess-papers-2024-chemistry-short (2)tahajalil1074Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 07: P Block: PART - A (MCQ Based)Document4 pages12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 07: P Block: PART - A (MCQ Based)Bloody DemonPas encore d'évaluation
- TERM I CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL EXAMDocument9 pagesTERM I CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL EXAMHarishankar SPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN CHEM - Module 2 - Answer KeyDocument1 pageGEN CHEM - Module 2 - Answer KeyMa. Alyzandra G. LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN CHEM - Module 2 - Answer KeyDocument1 pageGEN CHEM - Module 2 - Answer KeyMa. Alyzandra G. LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 07Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 07Tuff HammonsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry exam questionsDocument2 pagesChemistry exam questionsParesh ModiPas encore d'évaluation
- SRI SRI RAVISHANKAR VIDYA MANDIR CHEMISTRY WORKSHEETDocument3 pagesSRI SRI RAVISHANKAR VIDYA MANDIR CHEMISTRY WORKSHEETVaradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 QuizDocument10 pagesChapter 7 QuizSuny100% (1)
- P Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationDocument13 pagesP Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationSrijan ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- SNC2D Chemistry ReviewDocument2 pagesSNC2D Chemistry ReviewLindsay KennedyPas encore d'évaluation
- P-Block Elements and Group TrendsDocument5 pagesP-Block Elements and Group TrendsSnehashish PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques1 67abe1mcDocument8 pagesQues1 67abe1mcKerimberdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 16Document4 pages16Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Full BookDocument12 pagesFull Bookamnaliaqat0009Pas encore d'évaluation
- P Block ElementDocument5 pagesP Block ElementrshirayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Test # 3Document2 pagesChemistry Test # 3dania.siddiqui195Pas encore d'évaluation
- Level 0 PhosphorousDocument10 pagesLevel 0 PhosphorousTimothy SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 14: Acids and Bases: Assignment 3 (Formal Task) 100 MarksDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Chapter 14: Acids and Bases: Assignment 3 (Formal Task) 100 MarksPhantom BloodPas encore d'évaluation
- VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT PROVIDES QUALITY SCIENCE LESSONSDocument4 pagesVAISHALI EDUCATION POINT PROVIDES QUALITY SCIENCE LESSONSLavanya Priya SathyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMDocument3 pagesActivity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMClarise CanAPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Important Topics and Tips in ChemistryDocument23 pagesSome Important Topics and Tips in Chemistrysanits591Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2Document32 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2Shaurya 5116jPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 2,3, BIO 8, PHY 12 CompressedDocument135 pagesCHEM 2,3, BIO 8, PHY 12 CompressedDiana AmeryPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: KEY Nomenclature - Covalent (Molecular) Compounds Part A: Name The Following Covalent Compounds. Part B: Write The Chemical Formula For Each of The Following CompoundsDocument2 pagesName: KEY Nomenclature - Covalent (Molecular) Compounds Part A: Name The Following Covalent Compounds. Part B: Write The Chemical Formula For Each of The Following CompoundsTrung LuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids and bases review quizDocument2 pagesAcids and bases review quizAnna DixonPas encore d'évaluation
- Possible Viva Questions Ak 4Document3 pagesPossible Viva Questions Ak 4akshat1aps100% (1)
- 8) Redox Reaction.Document1 page8) Redox Reaction.B9 Adi JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Sureshkumar DevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Chemistry SynopsisDocument24 pagesInorganic Chemistry SynopsisAvi KedarrPas encore d'évaluation
- The P Block Elements-Anil-hssliveDocument3 pagesThe P Block Elements-Anil-hssliveMathew YoyakkyPas encore d'évaluation
- ch10 Nomenclature ReportDocument3 pagesch10 Nomenclature Reportapi-233552637Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Sri Vagdevi AcademyDocument6 pagesChem Sri Vagdevi AcademyTammudu Abhay100% (2)
- Sharjah Chemistry Worksheet on p-Block ElementsDocument3 pagesSharjah Chemistry Worksheet on p-Block ElementsTania LizPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch14 Study QuestionsDocument3 pagesCh14 Study QuestionsКанат ТютеновPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Document2 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Worksheet 1api-251783882100% (3)
- 16.p Block Element ExerciseDocument27 pages16.p Block Element ExerciseKIRAN ALLUPas encore d'évaluation
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Question Bank em 218992Document71 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Question Bank em 218992TharaneshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Himanshu Raj 1118163 PDFDocument12 pagesChemistry Himanshu Raj 1118163 PDFHimanshu rajPas encore d'évaluation
- JR Chemistry Imp Vsaq 2023-24Document4 pagesJR Chemistry Imp Vsaq 2023-24masarathbegum94Pas encore d'évaluation
- P Block Elements II WorkbookDocument53 pagesP Block Elements II WorkbookStudy BuddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Galaxonia Classes Surface Chemistry Revision Sheet 40TITLE Galaxonia Classes Cell Structure and Function Revision Sheet 38 TITLE Galaxonia Classes P-Block Elements Revision Test 35Document5 pagesGalaxonia Classes Surface Chemistry Revision Sheet 40TITLE Galaxonia Classes Cell Structure and Function Revision Sheet 38 TITLE Galaxonia Classes P-Block Elements Revision Test 35Vishesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet on p-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet on p-Block ElementsveenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Ch4 Part IIDocument2 pagesChemistry Ch4 Part IIkhushbakht.dania6336Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsPas encore d'évaluation
- Monohydric Alcohols Their Ethers and Esters Sulphur Analogues Nitrogen Derivatives Organometallic Compounds: A Modern Comprehensive TreatiseD'EverandMonohydric Alcohols Their Ethers and Esters Sulphur Analogues Nitrogen Derivatives Organometallic Compounds: A Modern Comprehensive TreatisePas encore d'évaluation
- OCR TextDocument6 pagesOCR TextKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions, Phase Equilibrium, Conductance, Electrochemistry & Functional Group Organic Chemistry-IiDocument1 pageSolutions, Phase Equilibrium, Conductance, Electrochemistry & Functional Group Organic Chemistry-IiKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- QuantumDocument2 pagesQuantumKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageElectrochemistryKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Ii) A Six-Proton Singlet at The Highest Field (: C CH CHDocument1 pageIi) A Six-Proton Singlet at The Highest Field (: C CH CHKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Four Probe MethodDocument1 pageFour Probe MethodVita Efellina100% (3)
- Pectros 4Document1 pagePectros 4Kamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions DineshDocument110 pagesSolutions DineshKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Spectros 6Document1 pageSpectros 6Kamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- What Do We Mean by Black Body Radiation ?Document2 pagesWhat Do We Mean by Black Body Radiation ?Kamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer IntroductionDocument1 pagePolymer IntroductionKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions, Phase Equilibrium, Conductance, Electrochemistry & Functional Group Organic Chemistry-IiDocument1 pageSolutions, Phase Equilibrium, Conductance, Electrochemistry & Functional Group Organic Chemistry-IiKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Four Probe MethodDocument1 pageFour Probe MethodVita Efellina100% (3)
- Resistivity of Semiconductors by Four Probe MethodDocument23 pagesResistivity of Semiconductors by Four Probe MethodK.H. TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphic1 PDFDocument1 pageGraphic1 PDFKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- CN CH CH CL CH CH CoochDocument1 pageCN CH CH CL CH CH CoochKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer Structure 1Document1 pagePolymer Structure 1Kamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology Unitization Syllabus Guide BSC PapersDocument5 pagesZoology Unitization Syllabus Guide BSC PapersKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Natural and Vulcanized RubberDocument2 pagesNatural and Vulcanized RubberKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Natural RubberDocument1 pageNatural RubberKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Applications of Porous Transition-Metal Oxide Systems For The Conversion of BiomassDocument38 pagesSynthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Applications of Porous Transition-Metal Oxide Systems For The Conversion of BiomassKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Synthetic RubbersDocument3 pagesTypes of Synthetic RubbersKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- PaperDocument2 pagesPaperKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Two Problems NMRDocument1 pageTwo Problems NMRKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- B.Sc. IIDocument252 pagesB.Sc. IIKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- V K AhluwaliaDocument19 pagesV K AhluwaliaKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acids and Proteins IntroductionDocument1 pageAmino Acids and Proteins IntroductionKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Date Relaxation For Attending Orientation and Refresher CoursesDocument4 pagesDate Relaxation For Attending Orientation and Refresher CoursesKamal Kishore100% (2)
- Requirements For NDocument1 pageRequirements For NKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclo Al KanesDocument1 pageCyclo Al KanesKamal KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Terminología Sobre Reducción de Riesgo de DesastresDocument43 pagesTerminología Sobre Reducción de Riesgo de DesastresJ. Mario VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 NumberSystemsDocument49 pages01 NumberSystemsSasankPas encore d'évaluation
- Vydyne® R533H NAT: Ascend Performance Materials Operations LLCDocument4 pagesVydyne® R533H NAT: Ascend Performance Materials Operations LLCJames FauncePas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesDocument4 pagesExercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesPriyanshu SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- MTS Material Testing SolutionsDocument34 pagesMTS Material Testing SolutionskarthegrePas encore d'évaluation
- CaseHistoriesOnTheApplication of Vacuum PreloadingDocument25 pagesCaseHistoriesOnTheApplication of Vacuum PreloadingvaishnaviPas encore d'évaluation
- BILL OF SALE Pre ApproveDocument1 pageBILL OF SALE Pre ApprovedidinurieliaPas encore d'évaluation
- RS-RA-N01-AL User Manual of Photoelectric Total Solar Radiation TransmitterDocument11 pagesRS-RA-N01-AL User Manual of Photoelectric Total Solar Radiation TransmittermohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- 34 Annual Report 2019 20Document238 pages34 Annual Report 2019 20Rahul N PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermediate Accounting Testbank 2Document419 pagesIntermediate Accounting Testbank 2SOPHIA97% (30)
- Air Cycle Refrigeration:-Bell - Coleman CycleDocument21 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration:-Bell - Coleman CycleSuraj Kumar100% (1)
- The Study of Accounting Information SystemsDocument44 pagesThe Study of Accounting Information SystemsCelso Jr. AleyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency Meter by C Programming of AVR MicrocontrDocument3 pagesFrequency Meter by C Programming of AVR MicrocontrRajesh DhavalePas encore d'évaluation
- Incident Report Form: RPSG-IMS-F-24 Accident and Investigation Form 5ADocument2 pagesIncident Report Form: RPSG-IMS-F-24 Accident and Investigation Form 5ARocky BisPas encore d'évaluation
- Broschuere Unternehmen Screen PDFDocument16 pagesBroschuere Unternehmen Screen PDFAnonymous rAFSAGDAEJPas encore d'évaluation
- Lirik and Chord LaguDocument5 pagesLirik and Chord LaguRyan D'Stranger UchihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Congress Policy Brief - CoCoLevyFundsDocument10 pagesCongress Policy Brief - CoCoLevyFundsKat DinglasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial ManagementDocument21 pagesFinancial ManagementsumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Whats The Average 100 M Time For An Olympics - Google SearchDocument1 pageWhats The Average 100 M Time For An Olympics - Google SearchMalaya KnightonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4 Adams Equity TheoryDocument1 page2.4 Adams Equity TheoryLorainePas encore d'évaluation
- Tita-111 2Document1 pageTita-111 2Gheorghita DuracPas encore d'évaluation
- City Gas Distribution ReportDocument22 pagesCity Gas Distribution Reportdimple1101100% (9)
- Rejoinder To Adom Ochere's Misrepresentation - FinalDocument3 pagesRejoinder To Adom Ochere's Misrepresentation - FinalFuaad DodooPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae 2010Document11 pagesCurriculum Vitae 2010ajombilePas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines Taxation Scope and ReformsDocument4 pagesPhilippines Taxation Scope and ReformsAngie Olpos Boreros BaritugoPas encore d'évaluation
- CELF Final ProspectusDocument265 pagesCELF Final ProspectusDealBookPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Magnet 43 Foolproof Strategies To Get More Leads, Win A Ton of New Customers and Double Your Profits in Record Time... (RDocument189 pagesLead Magnet 43 Foolproof Strategies To Get More Leads, Win A Ton of New Customers and Double Your Profits in Record Time... (RluizdasilvaazevedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Responsibility Centres: Nature of Responsibility CentersDocument13 pagesResponsibility Centres: Nature of Responsibility Centersmahesh19689Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 13 AminesDocument3 pagesUnit 13 AminesArinath DeepaPas encore d'évaluation
- Master StationDocument138 pagesMaster StationWilmer Quishpe AndradePas encore d'évaluation