Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
EppCHII Negligence and Liabilities
Transféré par
Sujan SinghCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EppCHII Negligence and Liabilities
Transféré par
Sujan SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CH2- Profession and Ethics
2.1 Profession: Definition and Characteristics
2.2 Professional Institutions
2.3 Relation of an Engineer with Client, Contractor
and Fellow Engineers
2.4 Ethics, Code of Ethics and Engineering Ethics
2.5 Moral Dilemma and Ethical Decision Making
2.6 Detailed Duties of an Engineer and Architect
2.7Liability and Negligence
epp
negligence and liabilities
Concept of reasonable skill and care:
Every person who wants enter in to
learned profession undertakes to bring to
the exercise of it a reasonable degree of
care and skill.
The degree of skill that required is the skill
of
an
ordinary
component
person
exercising that particular art.
Breach: failure to perform an obligation
undertaken
Tort: civil mistake
epp
negligence and liabilities
Some times while performing engineering duties,
engineers happen to harm or damage to other
unconcerned, non related person or property.
The engineers perform jobs more attentively
towards their client/ organisation/ employer but
even doing so they happen to cause damages or
harms to these who are not concerned to the jobs
at all.
That happens because of unnecessary incidental
negligence is doing jobs. Incidental negligence
seeks compensations for the jobs.
This type of compensation to unconcerned
parties/ property is tort liability.
epp
negligence and liabilities
Liability is a troublesome responsibility.
It is a legal, binding or an obligation.
Liability: is legal responsibility, accountability,
responsibility, and burden
Engineers/ professionals are active actors in
the society
attention towards all likely to be affected
parties are not paid, liability are likely to occur.
Liabilities occur because of negligence in
performance.
The liability that most engineers face is Tort
liability and
organizational liability is called vicarious
liability.
epp
negligence and liabilities
Two types of liabilities that must
engineers face
Tort liability ; tort is something wrong but not
criminal
Organizational liability or vicarious liability
Vicarious liability:
A person who commits a tort is a liable for the damage that he
causes. What about a person who did not commit a tort?
When an employee commits a tort in the course of his / her
employment, his/her employer will be liable for the tort of his
/her employee, which is called a vicarious (explicit) liability.
For example, during the course action if a servant commits a
tort his master will be liable for the tort of his employee.
epp
negligence and liabilities
Tort liability is private wrong or civil
wrong for which a person may have to pay
compensation. Torts is any act or not act
(omission) that infringes (break) an
responsibility imposed by laws which gives
injured party the right to bring an action
for the damages or loss.
epp
negligence and liabilities
Negligence:
Careful, care free
Careless
Types
Subjective (state of mind) and objective (conduct
absence of skill and care )
Heedlessness
(without
willingness)and
recklessness (ignores consequence)
Advertent (intentionally)and inadvertent
Contributory (conduct of doing job)
Reasonable person
Professional standard
Employer liability
Occupiers liability
Trespass (infringe)
epp
negligence and liabilities
Elements of TORT:
Duty: a plaintiff in a tort case must establish that the
defendant (a person accused in a legal case) had a duty
(moral or legal obligation) to the plaintiff. (The
questions is not whether the defendant tried in good
faith, to be careful, but whether his conduct was up to
the standard of a reasonable persons conduct under the
circumstances)
Breach: a plaintiff must prove that the defendant had
breached the duty. (The defendant act fell below the
standard of care of reasonable persons
Proximate / legal case: the plaintiff must prove that the
acts of defendant actually caused the physical harm or
injury to the plaintiff.
Damages: A plaintiff must prove damage.
Damage without injury
Injury without damage
epp
negligence and liabilities
Principles of tort law:
In order to succeed in action in a tort, a plaintiff
must prove :
The defendant owed to the plaintiff
The defendant was in breach of that duty by his/her
conduct and
The plaintiff has suffered damage or injury as a
result of that breach.
Objective of tort law: Appease (settle) , Deter
(prevent), justice (fair dealing)
Compensation to victims
Transferring the cost of injury from victims to the
person responsible for that
epp
negligence and liabilities
DUTIES/ LIABILITIES/ of designers or
professional
Negligent, misstatement.
Statutes, bylaws, and standards
Examination of site above or below ground
surface
Public and private rights
Plans. drawings/ specification
Suitability of materials
Suitability of Method of execution
Novel/
risky
design
and
employers
interference in design
Revision of design during execution
epp
negligence and liabilities
Delegation of authority
employer
designer
specialist
epp
negligence and liabilities
Delegation of authority
employer
Main
designer
Expert/
specialist
epp
negligence and
liabilities
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture 4 Elements of TortsDocument38 pagesLecture 4 Elements of TortsAnonymous Th1S33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap # 2: Responsibility in EngineeringDocument32 pagesChap # 2: Responsibility in EngineeringZuha Nadeem Nadeem NawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Professional Practice Chapter 2: Ethics and ProfessionalismDocument22 pagesEngineering Professional Practice Chapter 2: Ethics and ProfessionalismStc StcPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 Professional NegligenceDocument53 pagesTopic 4 Professional NegligenceAlamgir kabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics and ProfessionalismDocument33 pagesEthics and ProfessionalismYSheng ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fin CHPTR 7 - 2Document35 pagesFin CHPTR 7 - 2Siti HawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts, Negligence and Product Liability Chapter 7 (2ed)Document32 pagesTorts, Negligence and Product Liability Chapter 7 (2ed)api-522706100% (5)
- Ethics Chapter 1: The Responsibility of EngineersDocument24 pagesEthics Chapter 1: The Responsibility of EngineersNguyễn QuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of Responsibility Accountability LiabilityDocument95 pagesTheories of Responsibility Accountability Liabilityankit boxer100% (1)
- Business Law 2024 Week3Document38 pagesBusiness Law 2024 Week3zakaria ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Duty To Take CareDocument15 pagesDuty To Take Careim.mariyam13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - Torts PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Torts PDFMyke BarnetsonPas encore d'évaluation
- ProfessionNegligence PortsmouthPresentationDocument18 pagesProfessionNegligence PortsmouthPresentationAnonymous JJhHAdY5HzPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Ethics and ResponsibilitiesDocument58 pagesProfessional Ethics and ResponsibilitiessaifPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Semester OutlineDocument12 pagesMid Semester OutlineLindsay E. DealPas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS Assignment SolutionDocument6 pagesETHICS Assignment SolutionkatendejohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics 2Document28 pagesEthics 2ParthivPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Values and EthicsDocument19 pagesEngineering Values and EthicsRaven CabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety ElementsDocument49 pagesSafety ElementsRocksonPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 NegligenceDocument29 pages17 Negligencetse maPas encore d'évaluation
- Tete 2206 Engineering Ethics - AssignmentDocument6 pagesTete 2206 Engineering Ethics - AssignmentkatendejohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Ethics Responsability Profesional EthicsDocument4 pagesEngineering Ethics Responsability Profesional EthicsAdrian Adalberto GarayPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Professional Practice Chapter 2: Ethics and ProfessionalismDocument18 pagesEngineering Professional Practice Chapter 2: Ethics and ProfessionalismivyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tort Law Lectures BarbriDocument6 pagesTort Law Lectures BarbriKarthik Shetty100% (1)
- Director and Officer Liability Insurance - It's Not Just For Ds&OsDocument10 pagesDirector and Officer Liability Insurance - It's Not Just For Ds&OsAbhishek GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 03Document27 pagesChapter 03leksalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture#10 Liability in EngineeringDocument3 pagesLecture#10 Liability in EngineeringKashif AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS PART II RevDocument46 pagesETHICS PART II RevNeib Kriszah AlbisPas encore d'évaluation
- Related-Injury-Cases: Act of Omission: Failing To Act Responsibly. Example: A Trainer Who Fails ToDocument5 pagesRelated-Injury-Cases: Act of Omission: Failing To Act Responsibly. Example: A Trainer Who Fails ToJerald CañetePas encore d'évaluation
- Tort LawDocument3 pagesTort LawkovalitskajaninaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment NEGLIGENCEDocument2 pagesAssignment NEGLIGENCEsaiful ramadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Ethics: Lecture by Md. Raihan Goni Southeast UniversityDocument28 pagesEngineering Ethics: Lecture by Md. Raihan Goni Southeast Universityanon_451662750Pas encore d'évaluation
- Torts II Outline - Bisom-Rapp - Spring 2012Document26 pagesTorts II Outline - Bisom-Rapp - Spring 2012jonkurz6757Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME 303 Engineering Ethics Lectures Set 4 2020Document17 pagesME 303 Engineering Ethics Lectures Set 4 2020GeckoPas encore d'évaluation
- TORT (Civil Wrong) : Negligence and LiabilityDocument24 pagesTORT (Civil Wrong) : Negligence and LiabilityMohammad Arif Hasan100% (2)
- Module Two: Legal Responsibilities For Engineers: Welfare of The Public in The Performance of Their Professional Duties"Document8 pagesModule Two: Legal Responsibilities For Engineers: Welfare of The Public in The Performance of Their Professional Duties"nyanzi arthur victor wPas encore d'évaluation
- US Torts CANsDocument112 pagesUS Torts CANsBob MorrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics in EngineeringDocument23 pagesEthics in Engineeringdish16Pas encore d'évaluation
- E 1Document7 pagesE 1MD AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Moral Reasoning and Codes of EthicsDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Moral Reasoning and Codes of EthicszahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Ethics Assignment # 01: Submitted To: Engr. M. KhalidDocument4 pagesEngineering Ethics Assignment # 01: Submitted To: Engr. M. Khalidrizwan ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Report 9 Honesty TruthfulnessDocument48 pagesReport 9 Honesty TruthfulnessMiggy ArangoPas encore d'évaluation
- (1932) AC 562. Ginger-Beer Manufacturer, The Defendant Has Sold Ginger-Beer To A RetailerDocument3 pages(1932) AC 562. Ginger-Beer Manufacturer, The Defendant Has Sold Ginger-Beer To A Retailersaiful ramadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Ethics Notes 1st YearDocument8 pagesEngineering Ethics Notes 1st Yearsupermusician12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- L2 ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesL2 ResponsibilityMd. Nuh Islam 210041108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labout 5 SSB1207 Labour LawDocument23 pagesLabout 5 SSB1207 Labour LawEugene TeoPas encore d'évaluation
- NegligenceDocument2 pagesNegligenceMehreen NaushadPas encore d'évaluation
- Code of Ethic GuidesDocument39 pagesCode of Ethic GuidesFaiz MechyPas encore d'évaluation
- Law Question PDFDocument29 pagesLaw Question PDFlimin zhang70% (10)
- The Law of Tort NotesDocument19 pagesThe Law of Tort NotesJohntehPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts-Negligence-lecture #6Document29 pagesTorts-Negligence-lecture #6Omar Al-lheebiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Studies Ethics-AnswersDocument12 pagesCase Studies Ethics-AnswersCalvin Joshua LacsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Full VersionDocument18 pagesEthics Full VersionSebastian CarterPas encore d'évaluation
- EthicsFull VersionDocument18 pagesEthicsFull VersionCharbel RahmePas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Responsibility: Summary of Different Senses of ResponsibilityDocument44 pagesProfessional Responsibility: Summary of Different Senses of ResponsibilityarchitbumbPas encore d'évaluation
- Law NotesDocument39 pagesLaw NotesHanny KeePas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Grievance Redressal: What Is Grievance ? Causes of Grievance Grievance Redressal ProcedureDocument32 pagesEmployee Grievance Redressal: What Is Grievance ? Causes of Grievance Grievance Redressal ProcedureAnamika VatsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal SuccessDocument4 pagesPersonal SuccessAnshuman TagorePas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Ethics Chapter Three Responsibility in EngineeringDocument22 pagesEngineering Ethics Chapter Three Responsibility in EngineeringCaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Lok Sewa Aayog (First Part Exam) For Engineering Buildng and ArchitectDocument4 pagesSyllabus of Lok Sewa Aayog (First Part Exam) For Engineering Buildng and ArchitectKiran Basu100% (2)
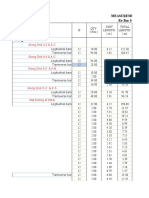
- BeamDocument1 pageBeamSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BOQ NDocument2 pagesBOQ NSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- ND 4may2016 Endoscopy Cad-ModelDocument1 pageND 4may2016 Endoscopy Cad-ModelSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Candidate Instruction ManualDocument21 pagesCandidate Instruction ManualSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Basement Wall Design: Check For DepthDocument1 pageBasement Wall Design: Check For DepthSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- FNDDocument3 pagesFNDSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- NBD Eq6Document80 pagesNBD Eq6Sujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Saiwzuzzr 06 V 7Document3 pagesSaiwzuzzr 06 V 7Bibek BasnetPas encore d'évaluation
- List Of: S.No. ParticularsDocument21 pagesList Of: S.No. ParticularsSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Disaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationDocument9 pagesDisaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Slab PDFDocument2 pagesSlab PDFSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Building and Architecture TheoryDocument3 pagesBuilding and Architecture Theoryशंकर थापाPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Wall SystemDocument1 pageWall SystemSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- FNDDocument3 pagesFNDSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- JOSHI Bar ScheduleDocument40 pagesJOSHI Bar ScheduleSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Disaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationDocument9 pagesDisaster Resilience and Safety:: A) Site ConsiderationSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- List Of: S.No. ParticularsDocument21 pagesList Of: S.No. ParticularsSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure Dhan BDR LasiwaDocument37 pagesStructure Dhan BDR LasiwaSujan Singh100% (1)
- Staircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsDocument3 pagesStaircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Pilla System PDFDocument1 pagePilla System PDFSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Staircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsDocument3 pagesStaircasedesigncalculation: I I Material Properties DimensionsSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseDocument2 pagesGeometry of Staircase: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000) Design of Stair-CaseSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
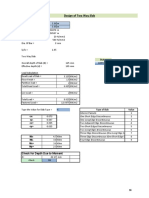
- Structural Design OF: The Proposed Residential BuildingDocument2 pagesStructural Design OF: The Proposed Residential BuildingSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Two Way Slab: StatusDocument2 pagesDesign of Two Way Slab: StatusSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Final RepDocument32 pagesFinal RepSujan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
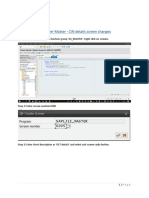
- Customer Master - CIN Details Screen ChangesDocument4 pagesCustomer Master - CIN Details Screen Changespranav kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Government of IndiaDocument13 pagesGovernment of Indiavikash_kumar_thakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Analysts - Occupational Outlook Handbook - U.S. Bureau of Labor StatisticsDocument6 pagesFinancial Analysts - Occupational Outlook Handbook - U.S. Bureau of Labor StatisticsHannah Denise BatallangPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 Written ReportDocument21 pagesGroup 4 Written ReportEm Bel100% (1)
- Account STDocument1 pageAccount STSadiq PenahovPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4, 5, 6 Adjustments and Financial Statement Prep - ClosingDocument61 pagesWeek 4, 5, 6 Adjustments and Financial Statement Prep - ClosingAarya SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Villareal vs. PeopleDocument11 pagesVillareal vs. PeopleJan Carlo SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Project22Document10 pagesTorts Project22Satyam SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternative Approaches and Best Practices Potentially Benefiting TheDocument54 pagesAlternative Approaches and Best Practices Potentially Benefiting Thechiffer venturaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument41 pagesChapter 1 - Electricity and MagnetismDarwin Lajato TipdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Strain Curve For Ductile and Brittle MaterialsDocument13 pagesStress Strain Curve For Ductile and Brittle MaterialsDivyeshkumar MorabiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- The People Who Matter Most: P. SainathDocument9 pagesThe People Who Matter Most: P. SainathkannadiparambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Peavey Valveking 100 212Document12 pagesPeavey Valveking 100 212whitestratPas encore d'évaluation
- Barandon Vs FerrerDocument3 pagesBarandon Vs FerrerCorina Jane Antiga100% (1)
- PCA Case No. 2013-19Document43 pagesPCA Case No. 2013-19Joyen JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th MAILING - Validation Letter - SampleDocument6 pages4th MAILING - Validation Letter - SampleJeromeKmt100% (20)
- Practice Tests Electrical Potential Energy PDFDocument9 pagesPractice Tests Electrical Potential Energy PDFFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (2)
- Demand Letter WiwiDocument1 pageDemand Letter WiwiflippinturtlePas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Modeling in Finance: Assignment # 01Document10 pagesMathematical Modeling in Finance: Assignment # 01Shahban ktkPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Colander Test BankDocument45 pagesMacroeconomics 10th Edition Colander Test Bankmichaellopezxsnbiejrgt100% (36)
- Role of The Head of Internal AuditDocument28 pagesRole of The Head of Internal Auditsaiful2522Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biografi Pahlawan IndonesiaDocument20 pagesBiografi Pahlawan Indonesiasafar banunPas encore d'évaluation
- Florentino V SupervalueDocument2 pagesFlorentino V SupervalueVener Angelo MargalloPas encore d'évaluation
- City of Fort St. John - COVID-19 Safe Restart GrantDocument3 pagesCity of Fort St. John - COVID-19 Safe Restart GrantAlaskaHighwayNewsPas encore d'évaluation
- October 2010 Business Law & Taxation Final Pre-BoardDocument11 pagesOctober 2010 Business Law & Taxation Final Pre-BoardPatrick ArazoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Site Crisis Management Plan TemplateDocument42 pages2 - Site Crisis Management Plan Templatesentryx1100% (7)
- Motion For Preliminary InjunctionDocument4 pagesMotion For Preliminary InjunctionElliott SchuchardtPas encore d'évaluation
- Celebration of International Day For Street ChildrenDocument3 pagesCelebration of International Day For Street ChildrenGhanaWeb EditorialPas encore d'évaluation
- 2000 CensusDocument53 pages2000 CensusCarlos SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.7 Industrial and Employee RelationDocument65 pages2.7 Industrial and Employee RelationadhityakinnoPas encore d'évaluation