Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Waves
Transféré par
HimanshuMathurCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electromagnetic Waves
Transféré par
HimanshuMathurDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes
Chapter-08: Electromagnetic Waves
Displacement Current:
It is due to time-varying electric field is,
d
id = 0 E
dt
Displacement current acts as a source of magnetic field in exactly the same way as
conduction current.
Electromagnetic Waves:
a) Electromagnetic waves are produced only by charges that are accelerating, since
acceleration is absolute, and not a relative phenomenon.
b) An electric charge oscillating harmonically with frequency , produces
electromagnetic waves of the same frequency .
c) An electric dipole is a basic source of electromagnetic waves.
d) Electromagnetic waves with wavelength of the order of a few metres were first
produced and detected in the laboratory by Hertz in 1887. He thus verified a basic
prediction of Maxwells equations.
Oscillation of Electric and Magnetic Fields:
These oscillate sinusoidally in space and time in an electromagnetic wave. The
oscillating electric and magnetic fields, E and B are perpendicular to each other and to
the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave.
For a wave of frequency , wavelength , propagating along z-direction,
E = E X (t ) = E0 sin(kz t )
z
z t
= E0 sin 2 vt = E0 sin 2
T
B = BY (t ) = B0 sin(kz t )
z
z t
= B0 sin 2 vt = B0 sin 2
T
E
They are related by o = c
Bo
Relation between 0 and 0 :
The speed c of electromagnetic wave in vacuum is related to 0 and 0 (the free space
permeability and permittivity constants) as
C = 1/ 0 0
The value of c equals the speed of light obtained from optical measurements. Light is an
electromagnetic wave; c is, therefore, also the speed of light. Electromagnetic waves
other than light also have the same velocity c in free space.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Speed of Light:
The speed of light, or of electromagnetic waves in a material medium is
v = 1/
Where is the permeability of the medium and its permittivity
Electromagnetic waves carry energy as they travel through space and this energy is
shared equally by the electric and magnetic fields.
Energy Per Unit Volume:
If in a region of space in which there exist electric and magnetic fields E and B , there
exists Energy Density (Energy per unit volume) associated with these fields is,
2
1 2
U= 0E +
B
2
2 0
where we are assuming that the concerned space consists of vacuum only.
Electromagnetic waves transport momentum as well. When these waves strike a surface,
a pressure is exerted on the surface.
If total energy transferred to a surface in time t is U, total momentum delivered to this
surface is p = U/c.
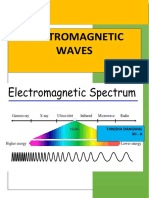
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
The spectrum of electromagnetic waves stretches, in principle, over an infinite range of
wavelengths.
The classification of electromagnetic waves according to frequency is the
electromagnetic spectrum.
There is no sharp division between one kind of wave and the next.
The classification has more to do with the way these waves are produced and detected.
Different Regions of Spectrum:
Different regions are known by different names; -rays, X-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible
rays, infrared rays, microwaves and radio waves in order of increasing wavelength from
10-2 or 10-12 m to 106 m.
(a)Radio Waves:
These are produced by accelerated motion of charges in wires.
These are used in radio and television communication systems.
These are generally in the frequency range from 500 kHz to about 1000 MHz.
(b)Microwaves:
These are short wavelength radio waves with frequencies in the gigahertz range.
Due to their short wavelengths, they are suitable for radar systems used in
aircraft navigation.
Microwave ovens use them for cooking.
(c) Infrared Waves:
These are produced by hot bodies and molecules.
They lie in the low frequency or long wavelength end of the visible spectrum.
(d)Visible Light:
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
The spectrum runs from about 4 x 1014 Hz to about 7 x 1014 Hz.
Our eyes are sensitive to this range of wavelengths.
(e)Ultraviolet light:
It covers wavelengths ranging from 400 nm to 0.6 nm.
The sun is an important source of UV rays.
(f) X-rays:
These cover the range 10 nm to about 10-4 nm.
(g)Gamma Rays:
These lie in the upper frequency range of the spectrum, and have wavelengths in
the range 10-10 m to 10-14 m.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electromagnetic Waves: QUICK REVISION (Important Concepts & Formulas)Document10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: QUICK REVISION (Important Concepts & Formulas)haleem ghaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Speed GuideDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Speed GuideKaushik KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesalyxsmh01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Notes Xii Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics Notes Xii Electromagnetic WavesSuman RathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - WatermarkDocument16 pagesChapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - WatermarkRajath S KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Wave Notes and Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Wave Notes and Important Questionsmuddiknp7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas For Electromagnetic WavesDocument3 pagesFormulas For Electromagnetic WavesNitish ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EM WavesDocument10 pagesEM WavesShaurya JainPas encore d'évaluation
- E.M. WavesDocument11 pagesE.M. WavesSatish Sharma100% (1)
- Optoelectronics DaDocument7 pagesOptoelectronics DaZarif HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 (Assignment)Document6 pagesChapter 8 (Assignment)asmaaysha121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves: Displacement CurrentDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Displacement CurrentMoses AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves: y Z y ZDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: y Z y Zmaruthi cyber19Pas encore d'évaluation
- EMW Notes CLASS 12 CBSEDocument5 pagesEMW Notes CLASS 12 CBSEShabnam ZakirPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 1Document13 pagesPhysics 1bort kortPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 EM WavesDocument9 pagesModule 1 EM WavesALTHEA ANN TUPASPas encore d'évaluation
- 95-126 Electromagnetic WavesDocument32 pages95-126 Electromagnetic WavesStockPlusIndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves ExplainedDocument44 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Explainedvenom ePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1fundamentals of ElectromagneticDocument91 pagesUnit-1fundamentals of Electromagneticmuvin236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module EM Waves 22-23 (1) Class 12 chpt7Document4 pagesModule EM Waves 22-23 (1) Class 12 chpt7Sheetal VatsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 24Document47 pagesChapter 24sairahhannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic WavesReddyvari VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- EM Waves Study GuideDocument7 pagesEM Waves Study GuidePreethiPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSSurya A S100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Waves PresentationDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Waves PresentationCyril CauilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion On Electromagnetic Waves Under The Circumstances of Total Internal Reflection and Optical TunnelingDocument6 pagesDiscussion On Electromagnetic Waves Under The Circumstances of Total Internal Reflection and Optical TunnelingJulio CaceresPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisika Gelombang: (Electromagnetic Waves - 3)Document11 pagesFisika Gelombang: (Electromagnetic Waves - 3)ROMA DHONPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Physics Assignment 1Document9 pagesApplied Physics Assignment 1areejPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument5 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksGlen CutinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Em WavesDocument20 pagesEm WavesVershaPas encore d'évaluation
- Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236: Electromagnetic Radiation and PolarizationDocument64 pagesSatellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236: Electromagnetic Radiation and PolarizationAnonymous E7tRVUPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class 11Document6 pagesPhysics Class 11mmohnishvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99Document35 pagesStudy Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99budgies2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Displacement CurrentDocument10 pagesDisplacement Currentojhamunesh388Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic WavesamazingPas encore d'évaluation
- Emw 1Document4 pagesEmw 1aditya43soniPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 2 4.1 Maxwell'S EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics 2 4.1 Maxwell'S EquationsNanzkie Andrei SamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Spectrum ExplainedDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum ExplainedElle Segovia SungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Techniques - Wireless Channel and Radio Wave PropagationDocument251 pagesWireless Techniques - Wireless Channel and Radio Wave PropagationJorma KekalainenPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic WavesHannah VsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lessonsections 2Document12 pagesLessonsections 2Ghazi DallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Batch Basic MathsDocument75 pagesBatch Basic Mathssoumava palitPas encore d'évaluation
- Week1-2 DoneDocument6 pagesWeek1-2 DoneLienh Mhil P. CajigasPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument63 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAleia Amano100% (2)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Wavessimon mamboPas encore d'évaluation
- CHPT 26 PacketDocument8 pagesCHPT 26 Packethongling240% (2)
- CH 8Document12 pagesCH 8terasaini77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8c WavesDocument26 pagesChapter 8c WavesBibha KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- MK Fisika Dasar 2 - Bab14Document26 pagesMK Fisika Dasar 2 - Bab14Josua ChristantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 30Document60 pagesChap 30noscribdyoucantPas encore d'évaluation
- TE Pbs8 PDFDocument2 pagesTE Pbs8 PDFJoseMiguelMenchacaRodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Notes on Electromagnetic Waves ChapterDocument4 pagesClass 12 Notes on Electromagnetic Waves ChapterDDDPPPas encore d'évaluation
- Em WavesDocument4 pagesEm WavesKoushal MazumderPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Instrumental Analysis 2Document90 pagesPharmaceutical Instrumental Analysis 2Ayat AborassPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of ElementsDocument12 pagesElectronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elementszekarias wondafrashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayuub Microwave IDocument55 pagesAyuub Microwave IPeter ParkerPas encore d'évaluation
- 203 3 Electromagnetic WavesDocument19 pages203 3 Electromagnetic WavesSudipta GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsD'EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7D'EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics Notes Ch07 Alternating CurrentDocument4 pages12 Physics Notes Ch07 Alternating CurrentMayank SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- VersionofstwDocument1 pageVersionofstwHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo C++ FILELISTDocument7 pagesTurbo C++ FILELISTJivtesh KhuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scan Codes of SwfpsDocument3 pagesScan Codes of SwfpsHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationAtif AteeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert Solutions: Probability QuestionsDocument2 pagesClass - Xii Mathematics Ncert Solutions: Probability QuestionsHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Railway Reservation in CDocument33 pagesRailway Reservation in CJASPER WESSLYPas encore d'évaluation
- Himanshu Project PhysicsDocument19 pagesHimanshu Project PhysicsHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Project File: Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Sanatan Dharma Vidhyalaya, KanpurDocument1 pageComputer Project File: Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Sanatan Dharma Vidhyalaya, KanpurHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Polarization of LighttrDocument11 pagesPolarization of LighttrHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- 3the Function of IafDocument1 page3the Function of IafHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- jAI HODocument1 pagejAI HOHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- FlipkrtDocument1 pageFlipkrtHimanshuMathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Food AdulterationDocument15 pagesFood AdulterationPrateek UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB TECHNIQUE: SPATIAL FILTERINGDocument2 pagesLAB TECHNIQUE: SPATIAL FILTERINGdoug_jones_36Pas encore d'évaluation
- Information & Instructions Model Xsp-2Ca Biological MicroscopeDocument3 pagesInformation & Instructions Model Xsp-2Ca Biological Microscopescribd birdPas encore d'évaluation
- Open-End Air ColumnsDocument4 pagesOpen-End Air ColumnsNovevacche DemoncowsPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EDocument9 pagesWeek 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EInstituto Centro de Desenvolvimento da GestãoPas encore d'évaluation
- GCE-Physics-574-Summer2022-AS 2, Waves, Photons and Astronomy-Paper-2Document28 pagesGCE-Physics-574-Summer2022-AS 2, Waves, Photons and Astronomy-Paper-2David McFaulPas encore d'évaluation
- LaserDocument6 pagesLaserShubhankar KhandaiPas encore d'évaluation
- McDonough (Ed.), 2020 - Teleology. A HistoryDocument315 pagesMcDonough (Ed.), 2020 - Teleology. A HistoryLeinadPas encore d'évaluation
- VT500Document77 pagesVT500Husen TravadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Document4 pagesMechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Shivam JaggiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: Wave: 6.1 Understanding WavesDocument34 pagesChapter 6: Wave: 6.1 Understanding WavesMohd Khairul Anuar100% (2)
- 2017-Ultra-Thin Metasurface Microwave Flat Lens For Broadband Applications-AIPDocument6 pages2017-Ultra-Thin Metasurface Microwave Flat Lens For Broadband Applications-AIPYumna SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Electromagnetic: Course 180Document2 pagesEngineering Electromagnetic: Course 180Eward KenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolex Camera h8 h16 User Manual PDFDocument38 pagesBolex Camera h8 h16 User Manual PDFCarolina SourdisPas encore d'évaluation
- M32 10torsionDocument12 pagesM32 10torsionRyan Jhay YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection of Light: Multiple Choice Questions: (MCQS)Document4 pagesReflection of Light: Multiple Choice Questions: (MCQS)Arushi100% (3)
- Aharonov-Bohm Effect: Seminar - 4. LetnikDocument14 pagesAharonov-Bohm Effect: Seminar - 4. Letnikilg1Pas encore d'évaluation
- SVET Overview: Add To Quote RequestDocument3 pagesSVET Overview: Add To Quote RequestthuronPas encore d'évaluation
- LensesDocument41 pagesLensesjanithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Micro BiologyDocument15 pagesAssignment Micro BiologyManasvi MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- ARC MainbookDocument65 pagesARC MainbookgowdamandaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument18 pagesPhysics Project Moving Coil GalvanometerShàùryà Priyanshu100% (1)
- Microscope LPDocument1 pageMicroscope LPElma Ortega Camion100% (1)
- Tarek Elhaik - Aesthetics and Anthropology - Cogitations-Routledge (2021)Document169 pagesTarek Elhaik - Aesthetics and Anthropology - Cogitations-Routledge (2021)Anamaría Garzón MantillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leica APO-TELYT-R 400mm f/2.8 LensDocument7 pagesLeica APO-TELYT-R 400mm f/2.8 LensNikonRumorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Amateur Photography, Candid PhotographyDocument4 pagesAmateur Photography, Candid PhotographySameera BommisettyPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 02 SolutionsDocument16 pagesHW 02 SolutionsLuis Gutierrez MelgarejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12 - Frictional Forces PDFDocument19 pagesLecture 12 - Frictional Forces PDFFolker sPas encore d'évaluation
- Toilet Paper TieDocument12 pagesToilet Paper Tieapi-331780332100% (1)
- Accu Scope 3075 SeriesDocument7 pagesAccu Scope 3075 SeriesRosa ArcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Exploration: Potential Energy On ShelvesDocument3 pagesStudent Exploration: Potential Energy On ShelvesShe.luv. cruz0% (1)