Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Audit Strategy Planning Programming
Transféré par
Suhag PatelDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Audit Strategy Planning Programming
Transféré par
Suhag PatelDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
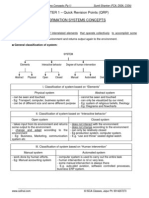
Audit Strategy, Planning and Programming
Meaning
Meaning
Matters to be
considered
Audit Programming
Acquiring knowledge of client
accounting system, policies and
internal control procedures.
Establishing the expected degree
of reliance on internal control.
Determining the NTE of audit
procedures.
Coordinating the work to be
performed.
Identification of significant audit areas.
Setting of materiality levels.
Degree of reliance on internal control.
First Time Audit
Subsequent Engagement
Terms of engagement
Nature & timing of reports /
Communications
Legal or statutory requirements.
Accounting policies & changes therein.
Effects of new accounting/auditing
pronouncements.
Detailed plan of work
comprises of techniques and
procedures,
may also contain objectives for
each audit step.
Nature of business.
Overall Plan
System of internal control and
accounting procedures.
Size and structure of
organization.
Information regarding the
organization.
Accounting policies followed.
To devote attention to important areas
Identify & resolve potential
problems.
Organized and managed audit.
Selection of suitable engagement
team.
Coordination of work done
Direction and supervision of
engagement team.
Development of Audit programme
Importance of planning
Factors to be
considered
Steps involved in Audit Strategy
Compiled by: Pankaj Garg (CA, CS, CMA(I) All India Topper, Gold Medalist)
Audit Planning
Developing an overall plan for the
expected scope and conduct of the
audit and
Developing an audit programme
showing NTE of Audit procedures
Aspects to be covered
Audit Strategy
Meaning: Designing Audit Approaches to achieve necessary audit assurance
at the lowest cost.
1. Obtaining knowledge of business:
It provides a frame of reference within which the auditor exercises
his professional judgement to assess risk, to plan audit, to evaluate
audit evidence and providing quality services.
2. Performing Analytical Procedures at Initial Stages:
To assess the potential for material misstatement in the financial
statements as a whole.
3. Evaluating Inherent Risk:
On the basis of prior audit experience, controls exercised by
management, significant changes since last assessment.
Factors to be evaluated to assess inherent risk
At the level of F.S.
At the level of A/c Balance
Management experience
Quality of Accounting System.
Changes in management
Susceptibility to Misstatement
/ Misappropriation of assets.
Unusual pressures
on
Complexity of transactions.
Management
Nature of entity business.
Degree of judgement involved.
Factors affecting industry.
Unusual transactions
4. Evaluating Internal Control System:
By documenting the extent of computerization, preparing/updating
flowcharts to record the transactions.
5. Formulating Audit Strategy:
Requires consideration of:
Engagement objective
Knowledge of clients business
Preliminary judgements as to materiality
Identified inherent risks
Extent of compliance testing
NTE of Substantive testing
Points relating to planning and controlling the audit.
Draw a broad outline
Filled up the details on a
consideration
of
deficiencies in internal
control.
Determine the special
procedures needs to be
applied.
Review earlier programme
and modified on account of:
Experience gained during
the previous audit.
Important
changes
in
internal control system,
accounting procedures etc.
Evaluation of internal
control for current year.
Page 1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Power Chords & InversionsDocument1 pagePower Chords & InversionsSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prepare An Audit PlanDocument8 pagesHow To Prepare An Audit PlanJay Ann100% (1)
- IG AT IO N: Audit PlanningDocument19 pagesIG AT IO N: Audit PlanningAmeer ShafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- HOLT Notes - FadeDocument3 pagesHOLT Notes - FadeElliott JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Audit PlanningDocument31 pages5 Audit PlanningEliza BethPas encore d'évaluation
- Controllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantD'EverandControllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantPas encore d'évaluation
- Starbucks 4Document59 pagesStarbucks 4Amirul Irfan100% (3)
- Final Zayredin AssignmentDocument26 pagesFinal Zayredin AssignmentAmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT. Chapter 2 AuditingDocument21 pagesPPT. Chapter 2 AuditingJerlmilline Serrano Jose100% (1)
- Nhóm 4 - In-Class Exercise BOP - 2020Document36 pagesNhóm 4 - In-Class Exercise BOP - 2020Thảo Hoàng PhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Tata Performance Management System: Presented By: Mahima Suri Aman Sharma Bhanuj SharmaDocument19 pagesTata Performance Management System: Presented By: Mahima Suri Aman Sharma Bhanuj SharmaAman SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit PlanningDocument26 pagesAudit PlanningDev PipilPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT& Financial Data Pakistan Petroleum LimitedDocument13 pagesSWOT& Financial Data Pakistan Petroleum LimitedFarah Nawaz QabulioPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Procedure-5Document4 pagesAudit Procedure-5yashPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit StepsDocument2 pagesAudit StepsDhana BalashanmugamPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Risk Alert: Employee Benefit Plans Industry Developments, 2018D'EverandAudit Risk Alert: Employee Benefit Plans Industry Developments, 2018Pas encore d'évaluation
- L3 Audit PlanningDocument7 pagesL3 Audit PlanningJun Guerzon PaneloPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit ProcessDocument2 pagesAudit Processrajahmati_28Pas encore d'évaluation
- At.1609 - Audit Planning - An OverviewDocument6 pagesAt.1609 - Audit Planning - An Overviewnaztig_017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Document10 pagesChap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Himanshu MorePas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Planning TechniquesDocument12 pagesAudit Planning TechniquesRahul KadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Planning MemoDocument9 pagesAudit Planning MemoJerald Oliver Macabaya100% (1)
- What Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Document6 pagesWhat Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Chris JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit ManualDocument80 pagesAudit ManualhaninadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Programme and Checklists For Completion of Audit Audit ProgrammeDocument26 pagesAudit Programme and Checklists For Completion of Audit Audit ProgrammejafarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Audit PlanningDocument17 pages6 - Audit PlanningJayson Manalo Gaña100% (1)
- Ferrari Case StudyDocument2 pagesFerrari Case StudyjamesngPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessDocument42 pagesOverview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessLorenzo RadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Planning MemoDocument10 pagesAudit Planning MemoChyrra ALed ZuRc100% (3)
- Audit PlanningDocument9 pagesAudit PlanninggumiPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Planing and DocumentationDocument4 pagesAudit Planing and DocumentationBharat LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Od Intervention With Case StudiesDocument13 pagesOd Intervention With Case StudiesArushi Kaul75% (8)
- Audit PlanningDocument15 pagesAudit Planningemc2_mcv75% (4)
- Final Project On Stock MarketDocument329 pagesFinal Project On Stock MarketAllan07563% (27)
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 300, 310, 320, 520 and 570Document5 pagesCpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 300, 310, 320, 520 and 570Ma Yra YmataPas encore d'évaluation
- Audting Chapter4Document12 pagesAudting Chapter4Getachew JoriyePas encore d'évaluation
- A&a L4 EditedDocument5 pagesA&a L4 EditedKimosop Isaac KipngetichPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing: Lecture # 8Document4 pagesAuditing: Lecture # 8Md Joinal AbedinPas encore d'évaluation
- QAR of FS in Accordance With PSADocument169 pagesQAR of FS in Accordance With PSAMarco Fernando Lumanlan NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer Sa AuditDocument6 pagesReviewer Sa Auditprincess manlangitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document4 pagesChapter 9Andrin LlemosPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTES - Audit Planning and Analytical ProceduresDocument9 pagesNOTES - Audit Planning and Analytical ProceduresDahlia BloomsPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing Theory: Audit Planning: An OverviewDocument31 pagesAuditing Theory: Audit Planning: An OverviewChristine NionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Planning & DocumentationDocument12 pagesAudit Planning & DocumentationMerlin Gey BlessingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Classnotes Important!!Document35 pagesClassnotes Important!!mansi patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit ProgrammeDocument34 pagesAudit ProgrammesurajPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2. Asuncion HandoutDocument8 pagesChapter 2. Asuncion HandoutCiel ArvenPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER5 AudTheoDocument18 pagesCHAPTER5 AudTheoadarose romaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Audit Evidence, Audit Objectives, Audit Programs and Working PapersDocument11 pagesChapter 6 - Audit Evidence, Audit Objectives, Audit Programs and Working PapersHolymaita TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit PlanningDocument2 pagesAudit PlanningMarconni B. AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Title: Assess The Effectiveness of The Organization and Key Management Audit Objectives: DescriptionDocument20 pagesTitle: Assess The Effectiveness of The Organization and Key Management Audit Objectives: DescriptionVera Magdalena HutaurukPas encore d'évaluation
- Engagement Letter and PlanningDocument17 pagesEngagement Letter and PlanningJoseph SimudzirayiPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing Study GuideDocument6 pagesAuditing Study GuideSelma KhiraouiPas encore d'évaluation
- AT-5908 - Audit PlanningDocument18 pagesAT-5908 - Audit Planningsanguyo_karenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 070804Document14 pagesChapter 6 070804Shahid Nasir MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Completing The AuditDocument27 pagesCompleting The AuditAlona Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Risk-Based AuditDocument8 pagesOverview of Risk-Based AuditMay Grethel Joy PerantePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer AuditingDocument3 pagesComputer AuditingTroy AJ GezyPas encore d'évaluation
- Brave BraveDocument20 pagesBrave BraveAnonymous F4E4myPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionJasmine Roberts MatorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit PlanningDocument12 pagesAudit PlanningDeryl GalvePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 06Document11 pagesCH 06Ekta Saraswat VigPas encore d'évaluation
- Alan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Document28 pagesAlan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Alan FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Cooperative AuditingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Cooperative AuditingJedidiah ManglicmotPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 - Audit PlanningDocument15 pagesModule 6 - Audit PlanningMAG MAGPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit PlanningDocument16 pagesAudit PlanningAnnieka PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 3 2021 B RevisedDocument40 pagesTOPIC 3 2021 B Revisedkitderoger_391648570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important NotesDocument4 pagesImportant NotesSojo VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsD'EverandAnnual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsPas encore d'évaluation
- Engagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsD'EverandEngagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsPas encore d'évaluation
- Invoice: Invoice Id Purchase Key Payment Status Payment Method Paypal ExpressDocument1 pageInvoice: Invoice Id Purchase Key Payment Status Payment Method Paypal ExpressSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Question - Bank - Costing (Old and New) Syllabus PDFDocument245 pagesQuestion - Bank - Costing (Old and New) Syllabus PDFSuhag Patel100% (1)
- SFM Equity Additional Practice QuestionsDocument23 pagesSFM Equity Additional Practice QuestionsSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldine Ca: Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 103 Business CombinationsDocument21 pagesAldine Ca: Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 103 Business CombinationsSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- FInancial ReportingDocument2 pagesFInancial ReportingSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Amendment PArveen Sharma NotesDocument59 pagesAmendment PArveen Sharma NotesSuhag Patel0% (1)
- 27 EtdsDocument29 pages27 EtdsSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ca Final VatDocument34 pagesCa Final VatSuhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ca Final Exam Capsule Practical Questions May 14Document98 pagesCa Final Exam Capsule Practical Questions May 14Suhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Set II CA Final ISCA Summary Notes 2012Document99 pagesSet II CA Final ISCA Summary Notes 2012Suhag PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Audit Notes For CA Final by CA Ashish GoyalDocument159 pages13 Audit Notes For CA Final by CA Ashish GoyalSuhag Patel100% (3)
- Tender Process - Queensland GovernmentDocument4 pagesTender Process - Queensland GovernmentsaimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock Control and InventoryDocument8 pagesStock Control and Inventoryadede2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Settlement CaseDocument14 pagesSettlement CaseSsseven GODPas encore d'évaluation
- Compensation Management at Tata Consultancy Services LTDDocument4 pagesCompensation Management at Tata Consultancy Services LTDNishaant S Prasad0% (2)
- Eldenburg 4e PPT Ch06Document6 pagesEldenburg 4e PPT Ch06StaygoldPas encore d'évaluation
- GE Countrywide Case StudyDocument2 pagesGE Countrywide Case StudyPratyush Jaiswal100% (1)
- An Introduction Abt Cement IndustryDocument6 pagesAn Introduction Abt Cement IndustrySiddharth ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Abbott Laboratories (ABT)Document8 pagesAbbott Laboratories (ABT)Riffat Al ImamPas encore d'évaluation
- Foreign Exchange MarketDocument73 pagesForeign Exchange MarketAmit Sinha100% (1)
- Formation of The Shariah Supervisory CommitteeDocument3 pagesFormation of The Shariah Supervisory Committeeapi-303511479Pas encore d'évaluation
- AISAN CanopyDocument46 pagesAISAN CanopyAmirul AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Awareness2021Document14 pagesRisk Awareness2021HansPas encore d'évaluation
- A Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessDocument8 pagesA Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessmoussumiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigned Problems FinmarDocument8 pagesAssigned Problems FinmarTABUADA, Jenny Rose V.Pas encore d'évaluation
- E3 Operating AuditingDocument21 pagesE3 Operating AuditingPaupauPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2023 For BPOI - 105 (005) (DBPOFA Prog)Document1 pageAssignment 2023 For BPOI - 105 (005) (DBPOFA Prog)Pawar ComputerPas encore d'évaluation
- 4global Capital Market 2Document11 pages4global Capital Market 2rosePas encore d'évaluation
- Price Action TradingDocument1 pagePrice Action TradingMustaquim YusopPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Quizbowl QuestionsDocument7 pagesAccounting Quizbowl QuestionsChabby ChabbyPas encore d'évaluation
- DB 1 - Marketing Management - V2Document3 pagesDB 1 - Marketing Management - V2NanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit 2, PENSION-EQUITY-INVESTMENT-LONG-QUIZDocument3 pagesAudit 2, PENSION-EQUITY-INVESTMENT-LONG-QUIZShaz NagaPas encore d'évaluation