Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
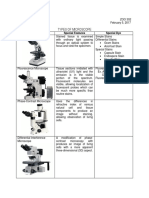
Microscope
Transféré par
Bryan Paul0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
149 vues4 pagesThe document discusses different types of microscopes and their uses. It describes several microscopes including compound microscopes, which have two lens systems for greater magnification up to 1000x; stereo microscopes which provide 3D viewing at up to 100x magnification; and optical microscopes which use visible light and have subcategories. It also outlines electron microscopes which use electron beams, as well as other specialized microscopes such as confocal, transmission, scanning, x-ray, helium ion, acoustic, neutron, and scanning probe microscopes.
Description originale:
Different kinds of Microscope :)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document discusses different types of microscopes and their uses. It describes several microscopes including compound microscopes, which have two lens systems for greater magnification up to 1000x; stereo microscopes which provide 3D viewing at up to 100x magnification; and optical microscopes which use visible light and have subcategories. It also outlines electron microscopes which use electron beams, as well as other specialized microscopes such as confocal, transmission, scanning, x-ray, helium ion, acoustic, neutron, and scanning probe microscopes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
149 vues4 pagesMicroscope
Transféré par
Bryan PaulThe document discusses different types of microscopes and their uses. It describes several microscopes including compound microscopes, which have two lens systems for greater magnification up to 1000x; stereo microscopes which provide 3D viewing at up to 100x magnification; and optical microscopes which use visible light and have subcategories. It also outlines electron microscopes which use electron beams, as well as other specialized microscopes such as confocal, transmission, scanning, x-ray, helium ion, acoustic, neutron, and scanning probe microscopes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Uy, Bryan Paul B.
2G-PH
January 25, 2016
Different types of microscope and their
uses
Aside from lens system classification,
microscopes are classified based on their
area of application and performance,
their cost, their versatile nature or any
other aspect.
Compound Microscope: The
compound microscope is built of
two systems of lenses for greater
magnification (an objective and
an ocular: eye piece). The utmost
useful magnification of a
compound microscope is about
1000x.
Stereo Microscope (dissecting
microscope): The
stereomicroscope is an optical
microscope, which magnifies up
to about maximum 100x and
provides a 3- dimensional view
of the specimen.
Stereomicroscopes are highly
useful for observing opaque
objects.
Optical Microscope: Optical
microscope uses visible light (or UV
light in the case of fluorescence
microscopy) to sharply magnify the
samples. The light rays refract with
optical lenses. Dating back to the first
microscopes that were invented, it is
found that they belonged to this
category. Optical microscopes can be
further subdivided into several
categories:
Confocal Laser Scanning
Microscope: Unlike compound
and stereomicroscope, Confocal
Laser scanning microscope are
reserved for research
organizations. Such microscopes
are able to scan a sample also in
depth. A computer can then
assemble the data to create a 3D
image.
Electron Microscopes: Electron
microscopes are the most advanced
microscopes used in modern sciences.
The electron microscopes essentially
function on the principle of a beam of
electrons that strikes any object that
comes to its path to magnify it. Electron
microscopes are designed specifically
for studying cells and small particles of
matter, as well as large objects.
Transmission Microscope:
Transmission microscopes are designed
for studying cells and tiny slices of
microorganisms like viruses, the
Transmission Microscope is an effective
device used for studying cells and tiny
slices of microorganisms that have been
stained with palladium and gold and
place upon a wire grid.
Scanning Electron Microscope:
Scanning Electron Microscope is
characterized as a microscope that has
lower magnifying power but can provide
3 dimensional viewing of objects. The
Scanning Electron Microscope captures
the image of the object in black and
white after being stained with gold and
palladium.
Reflection Electron Microscope:
Reflection electron microscopes are also
designed on the principle of electron
beams but they are characteristically
different from transmission and scanning
electron microscopes being that it is built
to detect electrons that have been
scattered elastically.
X-ray Microscope: An X-ray
microscope uses a beam of x-rays to
create an unparalleled high-resolution
3D image. Due to the small wavelength,
the image resolution is higher as
compared to optical microscopes. The
greatest useful magnification is therefore
also higher and it lies between the
optical microscopes and electron
microscopes. X-ray microscope holds
significant importance in science and
research and has got one special
advantage over electron microscopes is.
It allows observing the structure of the
living cells. It is adept at slicing together
thousands of images to generate a single
3D X-ray image
Scanning Helium Ion Microscope
(SHIM or HeIM): Scanning Helium Ion
Microscope is a new imaging
technology, which uses a beam of
Helium ions beams to generate an
image. This technology has several
advantages over the traditional electron
microscopes; one advantage lies in the
fact that the sample is left mostly intact
(due to the low energy requirements) and
that it provides a high resolution. The
first commercial systems were released
in 2007.
technology would use neutrons instead
of beams of light or electrons to generate
high-resolution images.
Scanning acoustic microscope (SAM):
Scanning acoustic microscope uses
focused sound waves to generate an
image. An acoustic microscope has a
wide range of applications in materials
science to detect small cracks or tensions
in materials. The scanning acoustic
microscope is a powerful tool, which can
also be used in biology to study the
physical properties of the biological
structure and help uncover tensions,
stress and elasticity inside the biological
structure.
Neutron Microscope: Still under an
experimental stage, Neutron microscope
generates a high-resolution image and
may offer better contrast than other
forms of microscopy. The new
Scanning Probe Microscopes:
Scanning Probe Microscope helps
visualize individual atoms. The image of
the atom is computer-generated,
however. It provides the researchers an
imaging tool for the future where a small
tip measures the surface structure of the
sample. These specialized microscopes
provide high image magnification to
observe three-dimensional specimens. If
an atom projects out of the surface, then
a higher electrical current flows through
the tip. The amount of current that flows
is proportional to the height of the
structure. A computer then assembles the
position data of the tip. An enhanced 3D
image is generated.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Different Types of Microscopes Are Used by The Microbiologists For Specific PurposesDocument15 pagesDifferent Types of Microscopes Are Used by The Microbiologists For Specific PurposessandeeptaraPas encore d'évaluation
- ZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeNini CioconPas encore d'évaluation
- Trimester One NotesDocument48 pagesTrimester One NotesHannah RossPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4Document6 pagesLesson 4doldol ocampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of MicroscopeDocument60 pagesTypes of MicroscopeAaf M100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology ModulesDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ModulesAllan IgbuhayPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Technology CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Technology CoursesAly Bint SmbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Zoology - Vol - 1 EM PDFDocument216 pagesBio-Zoology - Vol - 1 EM PDFSelvakapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Anachem PrelimsDocument20 pagesAnachem PrelimsMONICA VILLANUEVAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Chapter OneDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Chapter Oneapi-378592385Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHematology Lesson PlanGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam0% (1)
- 6 Microbial ControlDocument36 pages6 Microbial ControlGladish RindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Microscope: Micrometry and The Microbial WorldDocument3 pagesMicroscope: Micrometry and The Microbial WorldPatricia Hariramani100% (1)
- Lab Report in General Biology 1: Hay InfusionDocument2 pagesLab Report in General Biology 1: Hay InfusionDarren LaportezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypotonic Isotonic&hypertonic SolutionsDocument19 pagesHypotonic Isotonic&hypertonic SolutionsTanesh SelvarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Compendial Drug MonographDocument4 pagesCompendial Drug MonographPatricia Camryne AmbidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Micropara Lec Unit 1 LaDocument1 pageMicropara Lec Unit 1 LaGrace HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy ReproductiveDocument34 pagesAnaPhy ReproductiveTom Sing100% (1)
- Special Collections and Point of Care TestingDocument42 pagesSpecial Collections and Point of Care Testingmicah cajandabPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncm101 Microbiology Prelims (Lecture)Document31 pagesNcm101 Microbiology Prelims (Lecture)k78cwhs6v7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluorometry NotesDocument5 pagesFluorometry NotesHayna RosePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 01Document35 pagesChap 01Agita RakaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO024 Session-1 IGDocument6 pagesBIO024 Session-1 IGKenny McCormickPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesCell MembraneSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Human BodyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Human BodyHenie Louise HinanayPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryDocument42 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryBrythym Mojeca De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument8 pagesEnzymes Lab ReportMaizamPas encore d'évaluation
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument84 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsHey itsJamPas encore d'évaluation
- MEDT02 Lesson 2 - Safety in PhlebotomyDocument5 pagesMEDT02 Lesson 2 - Safety in PhlebotomySHELDY AGONCILLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Terminologies ReviewerDocument4 pagesMedical Terminologies ReviewerSav OliPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Health Care and The Philippine Health Care Delivery SystemDocument19 pagesPhilippine Health Care and The Philippine Health Care Delivery SystemJennifer Ledesma-PidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Economics: Teacher: Teresita Balgos Reporter: Group 4 MLS-II FDocument19 pagesHealth Economics: Teacher: Teresita Balgos Reporter: Group 4 MLS-II FThyrealle Frances Sorongon100% (1)
- Biochemistry: DR - Radhwan M. Asal Bsc. Pharmacy MSC, PHD Clinical BiochemistryDocument13 pagesBiochemistry: DR - Radhwan M. Asal Bsc. Pharmacy MSC, PHD Clinical BiochemistryAnas SeghayerPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelab Activity MPLDocument5 pagesPrelab Activity MPLAlthea Valenzuela100% (1)
- Std11 Zoo EMDocument303 pagesStd11 Zoo EMElangovan PalanisamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Culture MediaDocument7 pagesTypes of Culture MediaSurbhi GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide No. 1 Carbohydrates (Part 1) A. General Test For Carbohydrates 1. Molisch TestDocument2 pagesStudy Guide No. 1 Carbohydrates (Part 1) A. General Test For Carbohydrates 1. Molisch TestMichael Ralf SionosaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Microbiology Chapter 1Document10 pagesA Brief History of Microbiology Chapter 1eyearenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ched Memorandum Order No. 6 Series of 2008Document32 pagesChed Memorandum Order No. 6 Series of 2008MharamelAbellaPalamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Compund MicroscopeDocument6 pagesCompund MicroscopebellarosyPas encore d'évaluation
- LEC 4 - Blood Collection EquipmentDocument6 pagesLEC 4 - Blood Collection EquipmentJewel Jehd AlegriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyDocument27 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Pharmaceutical Microbiologynicole dela rosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2Document14 pagesLesson 2Jennifer Ledesma-PidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification and Nomenclature of EnzymesDocument12 pagesClassification and Nomenclature of EnzymesmcgilicuttyPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Senses NotesDocument3 pagesSpecial Senses NotesChelsa LeyritanaPas encore d'évaluation
- OJT Feedback Paper PatternDocument3 pagesOJT Feedback Paper PatternJen N. de ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 13: Reflex Arc and Reflexes: Learning Outcomes of The Lab ExercisesDocument6 pagesLab 13: Reflex Arc and Reflexes: Learning Outcomes of The Lab ExercisesNellyWataPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary System and Disorders IntroductionDocument23 pagesUrinary System and Disorders IntroductionHananya ManroePas encore d'évaluation
- Angelica New PRC Cases FormattedDocument7 pagesAngelica New PRC Cases FormattedDino CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro paraDocument7 pagesMicro paraAj MillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Ribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesChemistry of Ribonucleic AcidPrince DannPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 6 Microbial Nutrition and Growth Fall 2012Document21 pagesChap 6 Microbial Nutrition and Growth Fall 2012joiesupremoPas encore d'évaluation
- CALDERON Bacteriology Worksheet With AnswersDocument3 pagesCALDERON Bacteriology Worksheet With AnswersJames Belgira TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissecting A Whole ChickenDocument5 pagesDissecting A Whole Chickenbrianmore10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveDocument5 pagesSafety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveZabdiel Ann SavellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Report Blood Group SubDocument1 pageSample Report Blood Group SubNarayan ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Students Copy Taking A Health HistoryDocument35 pagesStudents Copy Taking A Health HistorySherinne Jane CariazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of MicroscopeDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of MicroscopeRitesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesJhon Carlo Bataller Monleon100% (1)
- Document 1Document2 pagesDocument 1nathanmaingi86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection and SamplingDocument13 pagesInspection and SamplingBryan Paul50% (2)
- Endocrin E Glands Location Hormone Chemical Group Target Tissue Action Clinical Condition Hyposecretion Hypersecretion PituitaryDocument6 pagesEndocrin E Glands Location Hormone Chemical Group Target Tissue Action Clinical Condition Hyposecretion Hypersecretion PituitaryBryan PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- The Other Side of The Coin: Chelsea Audrey Paqueo Masuhay October 10 11:17 PMDocument2 pagesThe Other Side of The Coin: Chelsea Audrey Paqueo Masuhay October 10 11:17 PMBryan PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Uy Discussionboard3 L Pha 2Document1 pageUy Discussionboard3 L Pha 2Bryan PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Kollicoat Smartseal 30 D ShortDocument39 pagesKollicoat Smartseal 30 D ShortniknenadPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics of Natural Systems-137-140Document4 pagesThermodynamics of Natural Systems-137-140Asep IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry - Concepts and Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChemistry - Concepts and Multiple ChoiceGeorge Isaac McQuiles100% (1)
- Prepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurDocument26 pagesPrepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurKarna Satish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Wastewater - Types, Characteristics & RegulationDocument50 pagesWastewater - Types, Characteristics & Regulationsam samPas encore d'évaluation
- January 2006 QP M1 EdexcelDocument13 pagesJanuary 2006 QP M1 EdexcelOmar HashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Colour Compound (Mega) 215Document2 pagesAssignment Colour Compound (Mega) 215Anant JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Lab Oxidation ReductionDocument3 pagesChem Lab Oxidation ReductionMayara Halper100% (2)
- Hydro Cyclone: Centripetal Force Fluid ResistanceDocument10 pagesHydro Cyclone: Centripetal Force Fluid ResistanceMaxwell ToffahPas encore d'évaluation
- Act 3 ConclusionDocument13 pagesAct 3 ConclusionVon A. DamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- PCM Moineau MR MVDocument6 pagesPCM Moineau MR MVendi suhendi awansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Ontario Curriculum SyllabusDocument46 pagesChemistry Ontario Curriculum SyllabusNorlailatulakma BolhassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Relief Load For Liquids Near Critical TemperatureDocument3 pagesCalculating Relief Load For Liquids Near Critical TemperatureMoca PhoenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Woodward's RuleDocument48 pagesWoodward's RuleDeshan Wolfey100% (1)
- Iso 9073 3 1989Document8 pagesIso 9073 3 1989Cong Dech Thong100% (1)
- Design and Validation of Bellows As Per EJMA-FEA (White Paper) PDFDocument5 pagesDesign and Validation of Bellows As Per EJMA-FEA (White Paper) PDFJaveed A. KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyacetal (POM) : Polyplastics Co., LTDDocument19 pagesPolyacetal (POM) : Polyplastics Co., LTDPhuoc Thinh TruongPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 1 HypersonicsDocument76 pagesCHP 1 HypersonicsMatthew AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Many Worlds InterpretationDocument26 pagesMany Worlds InterpretationahsbonPas encore d'évaluation
- fourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFDocument7 pagesfourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFfdcarazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat and Thermodynamics - 2 PDFDocument126 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics - 2 PDFPurvi Binani100% (1)
- Hydrologic Processes:: Evaporation and InfiltrationDocument25 pagesHydrologic Processes:: Evaporation and InfiltrationEmmanuel LazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 9th CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPhy 9th CH 1 To 4Hameedashiq7 AshiqhameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave-Assisted Synthesis and Photochemical Reactions of Some Novel Organosulfur Compounds Relevant To Green ChemistryDocument15 pagesMicrowave-Assisted Synthesis and Photochemical Reactions of Some Novel Organosulfur Compounds Relevant To Green ChemistryDr. K.P.SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- 121 Ultrasonic Testing of Copper WeldsDocument10 pages121 Ultrasonic Testing of Copper WeldsVikas DighePas encore d'évaluation
- The Islamic University of Gaza-Environmental Engineering Department Water Treatment (EENV - 4331) Course OutlineDocument1 pageThe Islamic University of Gaza-Environmental Engineering Department Water Treatment (EENV - 4331) Course OutlineAbo-Khaled MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- DTR Rampa Amtrv-Pro 2022 - enDocument19 pagesDTR Rampa Amtrv-Pro 2022 - enEglė STPas encore d'évaluation
- BattleTech Touring The Stars BobDocument19 pagesBattleTech Touring The Stars BobGarret Craig100% (1)
- Industrial Battery: MaintenanceDocument26 pagesIndustrial Battery: MaintenanceJonathan CDNPas encore d'évaluation
- String Theory I (ICTS Reading Course) : Basic InfoDocument10 pagesString Theory I (ICTS Reading Course) : Basic Infodave chaudhuryPas encore d'évaluation