Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
D 55 e 982 B 5 C 2 Attachmentshmdps 6 MB 2
Transféré par
Manjunath Mohite0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
19 vues2 pagesDescribe the construction and working of calomel electrode and its half cell reactions and mention its advantages and disadvantages. Describe the cell formed by coupling of two zinc electrodes immersed in zinc sulphate solutions. Calculate the cell potential of the following cell at 298K Ag / Ag +(0.001M) / / Ag+(0.50M)/ Ag. What will be the potential, when the concentration of silver ions in the above cell is changed from 0.001M to
Description originale:
Titre original
98197374556d55e982b5c2attachmentshmdps6mb2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDescribe the construction and working of calomel electrode and its half cell reactions and mention its advantages and disadvantages. Describe the cell formed by coupling of two zinc electrodes immersed in zinc sulphate solutions. Calculate the cell potential of the following cell at 298K Ag / Ag +(0.001M) / / Ag+(0.50M)/ Ag. What will be the potential, when the concentration of silver ions in the above cell is changed from 0.001M to
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
19 vues2 pagesD 55 e 982 B 5 C 2 Attachmentshmdps 6 MB 2
Transféré par
Manjunath MohiteDescribe the construction and working of calomel electrode and its half cell reactions and mention its advantages and disadvantages. Describe the cell formed by coupling of two zinc electrodes immersed in zinc sulphate solutions. Calculate the cell potential of the following cell at 298K Ag / Ag +(0.001M) / / Ag+(0.50M)/ Ag. What will be the potential, when the concentration of silver ions in the above cell is changed from 0.001M to
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Question Bank Module I- Electrochemistry and Battery
Technology
1. Define single electrode potential and standard electrode potential.
2. Define emf.
3. Define cell potential.
4. Derive an expression for single electrode potential (OR) Derive Nernst
equation.
5. With examples mention different types of electrode.
6. What is metal metal salt ion electrode? Give example.
7. Define metal-metal ion electrode with example.
8. What are ion selective electrodes? Give example.
9. Distinguish between galvanic cell and electrolytic cell.
10.What are reference electrodes? Mention the limitations of primary reference
electrodes and advantages of secondary reference electrodes.
11.How do you construct a calomel electrode? Write its half cell reactions and
mention its advantages ( OR) Describe the construction and working of
calomel electrode.
12.Write a note on Ag/AgCl electrode (OR) Explain the construction and working
of Ag/AgCl electrode and mention its uses.
13.How is electrode potential experimentally determined? OR Explain the
measurement of standard electrode potential using saturated calomel
electrode or reference electrode illustrate with an example.
14.Discuss the construction and working of glass electrode and mention its
advantages and disadvantages.
15.What is glass electrode? Give the principle involved in the determination of
pH using glass electrode and explain the method of determining pH using
glass electrode.
16.Explain the construction and working of electrolyte concentration cell.
17.Explain the construction and working of metal electrode concentration cell.
18.Distinguish a galvanic cell from a concentration cell.
19.Define concentration cell.
20.Construct a concentration cell by taking same electrolyte and explain its
working.
21.Represent the cell formed by coupling of two zinc electrodes immersed in zinc
sulphate solutions. Concentration of zinc ions in one electrode system is 100
times more concentrated than the other. Write the cell reaction and calculate
the potential at 305K.
22.Calculate the cell potential of the following cell at 298K Ag/Ag +(0.001M)//
Ag+(0.50M)/Ag. What will be the potential, when the concentration of silver
ions in the above cell is changed from 0.001M to 0.005M at the same
temperature?
23.A concentration cell was constructed by immersing two copper electrodes in
0.02M and 0.002M CuSO4 solution. Write the cell representation, cell reaction
and calculate the emf of the concentration cell.
24.Emf o f the cell Ag/AgNO3(0.02M)// AgNO3(C2M) is 1.2V. Calculate C2 of the
cell.
25. Distinguish between a cell and a battery.
Question Bank Module I- Electrochemistry and Battery
Technology
26.Give the classification of batteries with example.
27.Distinguish between primary, secondary and reserve batteries with example.
28.Explain the characteristics of battery.
29.Explain the following characteristics of battery
a) Cell potential or voltage b) Capacity c) Shelf life d) Cycle life
30.Describe the construction and working of Zinc Air battery. Mention its
applications.
31.Why secondary batteries are considered as storage batteries? Explain the
construction and working of Ni-MH battery. Give the reactions involved during
charging and discharging modes.
32.Why Lithium is used as anodic active material, support your answer.
33. Explain the construction and working of Li MnO 2 cell. Mention its uses.
34.Describe the construction and working of Li-ion battery. Mention its uses.
35.What are reserve batteries?
36.Give the classification of fuel cell on the basis of temperature, fuel and
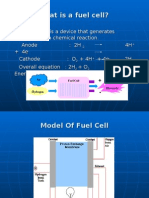
electrolyte.
37.How does a fuel cell differ from a battery? Explain the construction and
working of Methanol-oxygen fuel cell with H 2SO4 as electrolyte. Indicate the
advantages of H2SO4 as electrolyte over alkali electrolyte.
38. Differentiate conventional cell and fuel cell.
39.List the limitations and advantages of Fuel cell.
40.What are fuel cells?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- List of Venues For Phase I Preliminary Examination PDFDocument3 pagesList of Venues For Phase I Preliminary Examination PDFManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 3rd Semester Vacation Assignment SolutionsDocument3 pagesECE 3rd Semester Vacation Assignment SolutionsManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Kas PDFDocument3 pagesKas PDFManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- List of Venues For Phase I Preliminary Examination PDFDocument3 pagesList of Venues For Phase I Preliminary Examination PDFManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4: Vestigial Side Band ModulationDocument9 pagesUnit 4: Vestigial Side Band ModulationSeela Balaji KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communications Lab MannualDocument74 pagesDigital Communications Lab MannualwizardvenkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Economic Growth & DevelopmentDocument1 pageDifference Between Economic Growth & DevelopmentManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Haryana SSC Recruitment 2018 18218 Vacancies Part I PDFDocument18 pagesHaryana SSC Recruitment 2018 18218 Vacancies Part I PDFManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles of Governing & AuditDocument1 pageBasic Principles of Governing & AuditManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- MN Lab ManualDocument58 pagesMN Lab ManualManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- 5134 Fast Algorithams For Gaussian Noise Invariant Independent Component AnalysisDocument9 pages5134 Fast Algorithams For Gaussian Noise Invariant Independent Component AnalysisManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Digital PaymentsDocument31 pagesDigital PaymentsKarthikeyanShanmugasundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- D 3 F 5 e 061396 Attachmentsuaz 7 UqllhDocument1 pageD 3 F 5 e 061396 Attachmentsuaz 7 UqllhManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Measurements NotesDocument15 pagesPressure Measurements NotesManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Factsheet3 Mobile Phone ManufacturingDocument2 pagesFactsheet3 Mobile Phone ManufacturingManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To Apple : by Pramod. SDocument25 pagesWelcome To Apple : by Pramod. SManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Second-Order Blind Source Separation BasedDocument8 pagesSecond-Order Blind Source Separation BasedManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Design ProcessDocument77 pagesCircuit Design ProcessManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Blackberry Technology: Unnikrishnan.P.KDocument31 pagesBlackberry Technology: Unnikrishnan.P.Karka_ganguly140% (1)
- Analog Communication UNIT-1: RANDOM PROCESS: Random Variables: Several RandomDocument8 pagesAnalog Communication UNIT-1: RANDOM PROCESS: Random Variables: Several RandomManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- SC2Document1 pageSC2Manjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- RadarDocument24 pagesRadarManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless FudelityDocument1 pageWireless FudelityManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Article On Designing of Printed Circuit BoardDocument5 pagesArticle On Designing of Printed Circuit BoardManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Valores Comerciales de RESISTENCIAS & CONDENSADORESDocument1 pageValores Comerciales de RESISTENCIAS & CONDENSADORESOmarbin BrachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Resistor ValuesDocument2 pagesStandard Resistor ValuesManjunath MohitePas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Constitution Politics QBDocument21 pagesIndian Constitution Politics QBrakshaPas encore d'évaluation
- A51 Assembler A251 Assembler: Macro Assemblers For The 8051 and MCS 251 MicrocontrollersDocument245 pagesA51 Assembler A251 Assembler: Macro Assemblers For The 8051 and MCS 251 Microcontrollersbinhnhi0007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- NP12-100 (12V100AH) : Gel Lead-Acid BatteryDocument1 pageNP12-100 (12V100AH) : Gel Lead-Acid BatteryRaphael JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- HD 1224 Desulfation Test Conducted by CPS 9 18 15 FINALDocument6 pagesHD 1224 Desulfation Test Conducted by CPS 9 18 15 FINALAnselmo Aguado cortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ripmax Sigma Eq PDFDocument20 pagesRipmax Sigma Eq PDFSonny VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- 48V 100Ah lithium-ion battery system for telecom, off-grid and household energy storageDocument2 pages48V 100Ah lithium-ion battery system for telecom, off-grid and household energy storageSandra Paola Pulido PeñuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- JustRadios CAPACITOR & RESISTOR Price ListDocument8 pagesJustRadios CAPACITOR & RESISTOR Price ListwilfredoinimPas encore d'évaluation
- 12V 20ah Vrla Gel Battery 6-DZM-20: Features & BenefitsDocument2 pages12V 20ah Vrla Gel Battery 6-DZM-20: Features & BenefitsRafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Specifications Data Sheet For CCR Batteries: BattteryDocument4 pagesTechnical Specifications Data Sheet For CCR Batteries: BattterySubstationPas encore d'évaluation
- VRLA Batteries ChargingMethodsDocument8 pagesVRLA Batteries ChargingMethodsbinodePas encore d'évaluation
- 0.1. Batería 6.5 Ah, 12 Voltios Modelo 12v6a5 Ficha Técnica enDocument2 pages0.1. Batería 6.5 Ah, 12 Voltios Modelo 12v6a5 Ficha Técnica enG Abigail MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Storage SystemDocument204 pagesEnergy Storage SystemBISWANATH MURMU100% (1)
- Fuel Cell in Space ApplicationsDocument21 pagesFuel Cell in Space ApplicationsArjunSahooPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Hydropower Status Report Double Pages PDFDocument39 pages2015 Hydropower Status Report Double Pages PDFermanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014-01 Considerations For Polymer Capacitors in Extreme Environments PDFDocument2 pages2014-01 Considerations For Polymer Capacitors in Extreme Environments PDFCristian BandilaPas encore d'évaluation
- T105 Trojan Data SheetsDocument2 pagesT105 Trojan Data SheetsImadPas encore d'évaluation
- BatteryActivationInstructions EnglishDocument2 pagesBatteryActivationInstructions EnglishDaniel Trujillo RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen Power With Siemens Gas TurbinesDocument22 pagesHydrogen Power With Siemens Gas TurbinesMal KukuraPas encore d'évaluation
- CSB HR1221 - Hoja de DatosDocument1 pageCSB HR1221 - Hoja de DatosGermanYPPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Management Strategy To Enhance Drive Range of Electric BicycleDocument7 pagesPower Management Strategy To Enhance Drive Range of Electric BicycleAnonymous DbmKEDxPas encore d'évaluation
- Narada 190 PDFDocument2 pagesNarada 190 PDFMartinKampffPas encore d'évaluation
- New CO2 Battery Will Make Wind and Solar Dispatchable 'At An Unprecedented Low Price' - RechargeDocument4 pagesNew CO2 Battery Will Make Wind and Solar Dispatchable 'At An Unprecedented Low Price' - RechargeTest TestPas encore d'évaluation
- Li-MnO2 Batteries (Varta)Document4 pagesLi-MnO2 Batteries (Varta)MedSparkPas encore d'évaluation
- Bat SunStone OPG2-600Document2 pagesBat SunStone OPG2-600Eman EdlesPas encore d'évaluation
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesAluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: Specificationsnanodocl5099Pas encore d'évaluation
- Battery-Assisted Low-Cost H2 Production From Solar Energy - Cost AnalysisDocument15 pagesBattery-Assisted Low-Cost H2 Production From Solar Energy - Cost Analysisfrancisco NeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- SES Users Manual V41Document620 pagesSES Users Manual V41Ivi LatoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Gwf-Int 01 2011 ArtikelDocument12 pagesGwf-Int 01 2011 ArtikelPetra Margot PedrazaPas encore d'évaluation
- 499 Topics For Seminars Electrical and Electronics Engineering - Electrical Engineering PDFDocument11 pages499 Topics For Seminars Electrical and Electronics Engineering - Electrical Engineering PDFBaneeIshaqueKPas encore d'évaluation
- Pierlite-Baci 2 Led Exit LightDocument1 pagePierlite-Baci 2 Led Exit LightErvin SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation and Analysis of Highspeed Modular Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Using MATLAB SimulinkDocument6 pagesSimulation and Analysis of Highspeed Modular Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Using MATLAB Simulinkgunasekaran sPas encore d'évaluation
- PCM Products GeneralDocument6 pagesPCM Products Generalvenugopalan srinivasanPas encore d'évaluation