Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Journal Pcap C
Transféré par
Kit Lara0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
539 vues3 pagesThis journal article summarizes a study on the etiology and factors associated with pneumonia in children under 5 years old in Mali. The study was conducted at a pediatric hospital and involved collecting samples and data from 118 pneumonia patients and analyzing causes and risk factors. It found that the most common causes were viruses like human metapneumovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and influenza. Additional factors included prior antibiotic use, underlying conditions, and lack of vaccinations. The study highlights the need for expanded vaccination programs to prevent pneumonia in young children.
Description originale:
Titre original
Journal Pcap c
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis journal article summarizes a study on the etiology and factors associated with pneumonia in children under 5 years old in Mali. The study was conducted at a pediatric hospital and involved collecting samples and data from 118 pneumonia patients and analyzing causes and risk factors. It found that the most common causes were viruses like human metapneumovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and influenza. Additional factors included prior antibiotic use, underlying conditions, and lack of vaccinations. The study highlights the need for expanded vaccination programs to prevent pneumonia in young children.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
539 vues3 pagesJournal Pcap C
Transféré par
Kit LaraThis journal article summarizes a study on the etiology and factors associated with pneumonia in children under 5 years old in Mali. The study was conducted at a pediatric hospital and involved collecting samples and data from 118 pneumonia patients and analyzing causes and risk factors. It found that the most common causes were viruses like human metapneumovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and influenza. Additional factors included prior antibiotic use, underlying conditions, and lack of vaccinations. The study highlights the need for expanded vaccination programs to prevent pneumonia in young children.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
School of Nursing
BAGUIO CITY, PHILIPPINES
RESEARCH TITLE:
Etiology and Factors Associated
with Pneumonia in Children under
5 Years of Age in Mali: A
Prospective Case-Control Study
- Bnet, T., Sylla, M., Messaoudi, M., Snchez Picot, V., Telles,
J., Diakite, A., & ... Vanhems, P. (2015)
Submitted by:
LARA, Kit B.
BSN II-A5
Submitted to:
Sir Paul Anthony G. Lorica, RN
(Clinical Instructor
04-28-16
SUMMARY OF THE JOURNAL
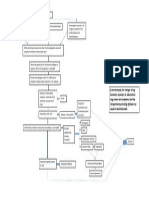
This research journal studies were all about the Etiology and Factors Associated with
Pneumonia in Children under 5 Years. The aim of this was to to assess the etiology and factors
associated with community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children and it was conducted at
Pediatric department of Gabriel Tour University Hospital at Bamako,Mali.
Pneumonia is the leading cause of child mortality from infectious diseases worldwide.
The main known causative pathogens reported are Streptococcus pneumoniae,Haemophilus
influenzae type B, and respiratory syncytial virus. The study was conducted at Pediatric
department of Gabriel Tour University Hospital at Bamako,Mali. Pneumonia cases were
hospitalized children who fulfilled the following criteria: cough, dyspnea, tachypnea and absence
of wheezing at auscultation. Nasal swabs, antibiotic usage history, urine sampled, whole blood
and pleural effusions was collected and analyze in terms of Demographic characteristics,
underlying diseases, medical history, clinical examination at enrollment, radiological findings,
vaccinations, and outcome were recorded prospectively for each patient on a standardized
form.
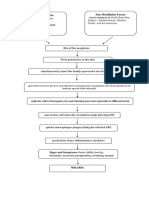
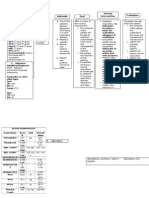
They found out that among the 118 patients with pneumonia, (13.6%) were referred from
another health center due to cases presented a ventricular septal defect. Among cases with
pulmonary crackles. Other signs or medical history of pneumonia cases included sickle-cell
anemia, dehydration, epilepsy, goiter, edema, pallor), and trisomy. The patient who took
antibiotics before hospitalization, received amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, amoxicillin, clavulanic acid,
cotrimoxazole. The 4 microbial agents associated with pneumonia, 3 were viruses: human
metapneumovirus, RSV, and influenza. Vaccine development, particularly against RSV, is
warranted to prevent pneumonia in children. The importance of the study were its prospective
design with the inclusion of controls that permitted to assess pneumonia etiologies while taking
into account the prevalence of pathogen detection in non-infected patients.
RELEVANCE TO AREA OF ROTATION:
Pediatric community-acquired pneumonia was very common disease in the area. The
relevance of this study is to provide an updated review on the etiology and factors of pneumonia
that may help in assessing or diagnosing patient with pneumonia and as a guide using the
factors associated, in rendering nursing management .
RELEVANCE TO NURSING EDUCATION:
This journal study is relevance to nursing practice because as a nurse we should know
the etiology and associated factors of pneumonia so that we know how to interpret and treat the
underlying cause of problem and prevent the infection.
LEARNING INSIGHTS ON THE JOURNAL:
I learned in this journal the management and how to treat pneumonia though the use of
vaccination and prevent the spreading of microorganism. Increased pneumococcal conjugate
vaccine coverage in children would significantly reduce the burden of pneumonia in this country.
eferences:
Bnet, T., Sylla, M., Messaoudi, M., Snchez Picot, V., Telles,
J., Diakite, A., & ... Vanhems, P. (2015). Etiology and Factors
Associated with Pneumonia in Children under 5 Years of Age in Mali: A
Prospective Case-Control Study. Plos ONE, 10(12), 1-15.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145447 Retrieved from:
http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?
direct=true&db=a9h&AN=111899386&site=eds-live
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- RH BLOOD GROUPDocument23 pagesRH BLOOD GROUPWho KnowsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyZandra Lyn AlundayPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Case Study PCAPDocument71 pagesFinal Case Study PCAPGabriel Lorenz S. ParongPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyDocument26 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyMenggay SanDiego57% (7)
- Bipolar Affective Disorder, Current Manic Episode With Symptoms of Psychotic and Care in NursingDocument4 pagesBipolar Affective Disorder, Current Manic Episode With Symptoms of Psychotic and Care in NursingKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- PA Tool Sample - JIJIDocument35 pagesPA Tool Sample - JIJIJirah RuedasPas encore d'évaluation
- Course in The WardDocument2 pagesCourse in The WardluedPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccination Certificate: Pet's Name Specie Breed Date of Birth Color/Marking Owner Address Contact NoDocument8 pagesVaccination Certificate: Pet's Name Specie Breed Date of Birth Color/Marking Owner Address Contact NoMaria GraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Case Study PCAPDocument72 pagesFinal Case Study PCAPKelly Tayag100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case Study: Zion FerrerDocument40 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Zion FerrerAllysa MacalinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument14 pagesCase Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaRachelPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdDocument330 pagesHandbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdPedro Jose Ramos Cabrera100% (2)
- Blood Administration and Transfusion Reactions QuizDocument5 pagesBlood Administration and Transfusion Reactions Quizremooheshmat100% (1)
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (Pecap) : Case StudyDocument32 pagesPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (Pecap) : Case StudyR Hornilla ArcegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resource Unit OliveDocument14 pagesResource Unit OliveCaryl AlivioPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning FeedbackDocument2 pagesLearning FeedbackDeejay L. RaramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Acquired Infections PDFDocument4 pagesHospital Acquired Infections PDFMuhammad Mohsin Ali DynamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study PCAPDocument32 pagesCase Study PCAPJohn Paul Andrade100% (1)
- Dengue Fever Case StudyDocument45 pagesDengue Fever Case StudyHazel Franz Nilo-HugoPas encore d'évaluation
- Patient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Document5 pagesPatient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Melinda Cariño BallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (PCAP) : Case StudyDocument38 pagesPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (PCAP) : Case StudyAndrew Perez0% (1)
- Case Study PcapDocument3 pagesCase Study PcapClaire PalaciosPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesNCP - BronchopneumoniaMaria Ivy Mendoza100% (1)
- Pediatric Pneumonia Case StudyDocument44 pagesPediatric Pneumonia Case StudyPreiane PayladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Atony Case StudyDocument53 pagesUterine Atony Case Studymikesan_lovers75% (8)
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesPas encore d'évaluation
- D. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesD. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaBill Clinton Lamira BabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pcap CDocument32 pagesPcap CCess DunwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pcap CDocument3 pagesJournal Pcap CKit Lara50% (2)
- Nursing Informatics Timeline (CENIZA BSN 3E)Document1 pageNursing Informatics Timeline (CENIZA BSN 3E)FATIMA IVAN S. CENIZAPas encore d'évaluation
- ASD Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument1 pageASD Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentMSPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitPas encore d'évaluation
- Midyr Case Study NewDocument18 pagesMidyr Case Study NewAndres Ham Samson BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPediatric Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanLizaMariePas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument18 pagesA Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseJaimie La PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- PCAPDocument2 pagesPCAPMizpah DuculanPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 pagesICS Pedia Wardsweet061991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careDocument11 pagesEssential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careAngelina Janiya NicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre EclampsiaDocument13 pagesPre EclampsiaEniamrahs DnalonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Case Study FinalllDocument56 pagesPneumonia Case Study Finalllbethrice melegritoPas encore d'évaluation
- NBS BrochureDocument2 pagesNBS BrochureMichael Jordan De VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Ab ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCell Ab ActivitiesJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Neonatal Pneumonia Case StudyDocument2 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Case StudyAngel Villamor0% (1)
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care for a Woman in LaborDocument7 pagesNursing Care for a Woman in LaborNicole cuencosPas encore d'évaluation
- VIII. Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesVIII. Discharge PlanPia Therese CabaticPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP EsrdDocument2 pagesNCP EsrdAziil LiizaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 1Document6 pagesNCP 1Maedine Urbano-BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Course in The WardDocument4 pagesCourse in The Wardenzomarfal100% (1)
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Document13 pagesCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2NF - Grand Case Presentation Written OutputDocument99 pages2NF - Grand Case Presentation Written OutputKyra Bianca R. FamacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Distress SGDDocument24 pagesFetal Distress SGDLyca Mae AurelioPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Health ProfileDocument11 pagesFamily Health ProfileCharm RowePas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia GuideDocument24 pagesPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia GuideJames Lagamayo JavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDocument42 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Case StudyGelah DacanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Leptospirosis Case StudyDocument3 pagesLeptospirosis Case StudyMarie Jennifer ParilPas encore d'évaluation
- TB Case StudyDocument2 pagesTB Case StudyReisabelle LabianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilPas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreDocument5 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreteuuuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument35 pagesNursing Care Plan for Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaJose Bryan NacillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Study Regarding PCAP WashingtonDocument1 pageJournal Study Regarding PCAP WashingtonLuis WashingtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Neumonia Por InfluenzaDocument19 pagesNeumonia Por InfluenzaEdgar GavilanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Clo 20Document4 pagesClo 20Kit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Geron Term PaperDocument11 pagesGeron Term PaperKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Christmas Party: Church of God Annininipan, Flora, ApayaoDocument2 pagesChristmas Party: Church of God Annininipan, Flora, ApayaoKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity No 10Document1 pageActivity No 10Kit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Irst Description: ObliteransDocument10 pagesIrst Description: ObliteransKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN FNCPDocument6 pagesCHN FNCPKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ignment of Program Outcomes, Field of Study Outcomes, Course Outcomes, Course Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesIgnment of Program Outcomes, Field of Study Outcomes, Course Outcomes, Course Learning OutcomesKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Saint Louis University School of Nursing Summary of Cases Of: Flores, Charlie Magne SDocument1 pageSaint Louis University School of Nursing Summary of Cases Of: Flores, Charlie Magne SKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- To: Reynaldo Corpuz Lara 127, Zone 4, Anninipan, Flora, Apayao Philippines, 3810 +639298954826Document2 pagesTo: Reynaldo Corpuz Lara 127, Zone 4, Anninipan, Flora, Apayao Philippines, 3810 +639298954826Kit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection JournalDocument1 pageReflection JournalKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoryDocument4 pagesHistoryKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous CellDocument1 pageNervous CellKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ate Alice AppraiseDocument5 pagesAte Alice AppraiseKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoryDocument4 pagesHistoryKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Uson JournalobDocument2 pagesUson JournalobKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection Journal About SchizophreniaDocument1 pageReflection Journal About SchizophreniaKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- SLU College Entrance Exam NoticeDocument1 pageSLU College Entrance Exam NoticeKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) AdultsDocument1 pageComplete Blood Count (CBC) AdultsKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CritiqueDocument1 pageCritiqueKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Authorization LetterDocument1 pageAuthorization LetterKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital NI LecDocument2 pagesCase Study of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital NI LecKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Corel VideoStudioDocument1 pageCorel VideoStudioKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Paprint CooksieDocument1 pagePaprint CooksieKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- PPH 2nd Edn Chap-13Document7 pagesPPH 2nd Edn Chap-13Kit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- KC AssDocument3 pagesKC AssKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ndolence: Lara, Kit B. Balisalisa Mary Rose Santiago, JoelDocument1 pageNdolence: Lara, Kit B. Balisalisa Mary Rose Santiago, JoelKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Apol's ResearchDocument3 pagesApol's ResearchKit LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CBC LalpathDocument2 pagesCBC Lalpathmoyic39272Pas encore d'évaluation
- HHHDocument4 pagesHHHAsad PrincePas encore d'évaluation
- Bio LabbDocument3 pagesBio LabbAnyss Hasni Al-banjariPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology VirologyDocument11 pagesBacteriology VirologyFERNANDO JOSE NOVAESPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Crri PresentationDocument83 pagesAnemia Crri PresentationassumptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Autoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Document5 pagesAutoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Afsha AnishPas encore d'évaluation
- Case AnalysisDocument1 pageCase AnalysisKatrina Jude EllePas encore d'évaluation
- American Red CrossDocument13 pagesAmerican Red CrossKeerthana SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Group Test ProcedureDocument5 pagesBlood Group Test ProcedureNIRANJANA SHALINIPas encore d'évaluation
- Unknown Lab ReportDocument4 pagesUnknown Lab ReportAlexander PhamPas encore d'évaluation
- MR - Mohankumar ReportDocument3 pagesMR - Mohankumar ReportJayaprabhu Prabhu0% (1)
- Processing CSF SampleDocument6 pagesProcessing CSF SampleSyazmin KhairuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is NorovirusDocument1 pageWhat Is NorovirusHunter GeiselPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Science Unit 2Document2 pages8 Science Unit 2usmanvirkmultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Borne DiseasesDocument3 pagesVector Borne DiseasesGo PrepPas encore d'évaluation
- 40 Años de Microbiología ClínicaDocument6 pages40 Años de Microbiología ClínicaDennis Lorena Cárdenas LealPas encore d'évaluation
- Zika Virus PDFDocument2 pagesZika Virus PDFKrishna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.4 Microbiology PDFDocument31 pages3.4 Microbiology PDFQueena Yan Yie LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Geme 1Document9 pagesGeme 1นีล ไบรอันPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Biochemistry: Liver Function TestDocument1 pageDepartment of Biochemistry: Liver Function Testbinu k georgePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2BismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline On Dengue Fever - EDITEDDocument2 pagesOutline On Dengue Fever - EDITEDDavid Skeat0% (1)
- Basic Principles of Diagnostic of Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesBasic Principles of Diagnostic of Infectious DiseasesBombomPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation & Purification of Bacteriophage Particles From Soil SampleDocument6 pagesIsolation & Purification of Bacteriophage Particles From Soil SampleHarsh Purwar100% (2)
- Ha 2Document3 pagesHa 2Divyansh Singh ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation