Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Angle Modulation NOTES
Transféré par
Jay Amiel AjocCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Angle Modulation NOTES
Transféré par
Jay Amiel AjocDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electronics and Communications Engineering
Angle Modulation
1. FM and PM are both forms of Angle Modulation.
2. Angle modulation has several advantages over amplitude modulation such as noise
reduction, improved system fidelity and more efficient use of power.
3. The disadvantages of angle modulation over amplitude modulation are that it requires a
wider bandwidth, therefore it uses a greater spectrum space and it has a more complex
circuit.
4. Angle modulation was first introduced in 1931 as an alternative to amplitude modulation.
5. Major Edwin Howard Armstrong developed the first successful FM radio system in 1936. He
also developed the superheterodyne receiver.
6. He also developed the first successful radio system in June 17, 1936.
7. He played a jazz record over conventional AM radio then switched to an FM broadcast.
8. Armstrong spent the remainder of his life involved in lawsuits in an attempt to receive
royalties from his inventions, and finally, a broken man, he committed suicide in 1954.
9. FM is used extensively for radio broadcasting, for sound signal in television, for two-way
fixed and mobile radio systems, for satellite communications and for cellular telephone
systems.
10.PM is used in data communications.
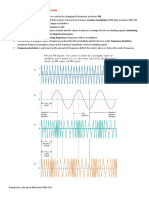
11.In frequency modulation, the amplitude of the carrier does not change.
12.The amplitude and power of an FM or PM signal do not change with modulation.
13.An FM receiver does not have to respond to amplitude variations, thus, it can ignore noise
to some extent.
14.FM transmitters use class C amplifiers.
15.Angle modulation results whenever the phase angle of a sinusoid wave is varied with
respect to time.
16.Whenever the frequency of a carrier is varied, the phase is also varied and vice versa.
17.FM and PM must both occur whenever either form of modulation is performed.
18.The magnitude and direction of the frequency shift is proportional to the amplitude and
polarity of the modulating signal.
19.Modulation will cause the signal frequency to deviate from its resting value.
20.Frequency is the rate of change of phase.
21.The relative displacement of the carrier frequency in hertz in respect to its unmodulated
value is called frequency deviation.
22.Whenever the period of a sinusoidal carrier changes, its frequency and phase also change.
23.Phase modulation is the first integral of the frequency modulation.
24.With FM, the maximum frequency deviation occurs during the maximum positive and
negative peaks of the modulating signal.
25.With PM, the maximum frequency deviation occurs during the zero crossings of the
modulating signal.
26.Peak phase deviation is called the modulation index.
27.Frequency deviation is the change in frequency that occurs in the carrier when it is acted
on by a modulating-signal frequency.
28.The peak-to-peak frequency deviation is sometimes called carrier swing.
29.A phase modulator is a circuit in which the carrier is varied in such a way that its
instantaneous phase is proportional to the modulating signal.
30.A frequency modulator, often called frequency deviator is a circuit in which the carrier is
varied in such a way that its instantaneous phase is proportional to the integral of the
modulating signal.
31.In a frequency or phase modulator, a single frequency modulating signal produces and
infinite number of pairs of side frequencies and, thus, has an infinite bandwidth.
1
Prepared by: Jay Amiel Ajoc
2015
MSU General Santos City
Electronics and Communications Engineering
Angle Modulation
32.A practical rule of thumb is to ignore sidebands with a Bessel coefficient whose absolute
value is less than 0.01.
33.A side frequency is not considered significant unless it has amplitude equal to or greater
than 1% of the unmodulated carrier amplitude.
34.Carsons rule approximates the bandwidth necessary to transmit an angle-modulated
wave twice the sum of the peak frequency deviation and the highest modulating-signal
frequency.
35.Carsons rule is an approximation and gives transmission bandwidths that are slightly
narrower than the bandwidths determined using the Bessel table.
36.Deviation ratio is also called the worst-case modulation index. It produces the widest
output frequency spectrum.
37.It is impossible to distinguish FM from PM by changing the modulating signal amplitude. To
see the difference between two forms of angle modulation, the modulating signal
frequency must be changed.
38.FCC has assigned the commercial FM broadcast service a 20-MHz band of frequencies that
extends from 88 MHz to 108 MHz.
39.Larger values for the deviation result in an increased signal-to-noise ratio, while also
resulting in greater bandwidth.
40.To provide high-quality, reliable music, the maximum frequency deviation allowed is 75
kHz with a maximum modulating signal frequency of 15 kHz.
41.Adjacent channel interference occurs when the highest side frequencies form one channel
spills over into adjacent channels.
42.The total power in an angle-modulated wave is equal to the power of the unmodulated
carrier.
43.The noise voltage at the output of a PM demodulator is constant with frequency, whereas
the noise voltage at the output of an FM demodulator increases linearly with frequency.
44.The frequency of the noise interference is the difference between the carrier frequency
and the frequency of the single-frequency interfering signal.
45.The original reason for developing FM was to give improved performance in the presence
of noise.
46.The effect of noise can be reduced by making the signal voltage large as possible relative
to the noise voltage.
47.In phase modulation the angle is varied linearly with the message signal.
48.In frequency modulation the instantaneous frequency is varied linearly with message
signal.
49.A frequency modulated signal can be generated using a phase modulator by first
integrating m(t) and using it as an input to a phase modulator.
50.
Prepared by: Jay Amiel Ajoc
2015
MSU General Santos City
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Deadlands - Dime Novel 02 - Independence Day PDFDocument35 pagesDeadlands - Dime Novel 02 - Independence Day PDFDavid CastelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed) Declaration of Factual Innocence Under Penal Code Section 851.8 and OrderDocument4 pagesProposed) Declaration of Factual Innocence Under Penal Code Section 851.8 and OrderBobby Dearfield100% (1)
- A Beautiful Mind - Psychology AnalysisDocument15 pagesA Beautiful Mind - Psychology AnalysisFitto Priestaza91% (34)
- Borer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFDocument272 pagesBorer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFNicolás Bastarrica100% (1)
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument107 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationvivekanandaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceD'EverandThe Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpacePas encore d'évaluation
- Claim &: Change ProposalDocument45 pagesClaim &: Change ProposalInaam Ullah MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation TheoryD'EverandOptimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation TheoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypnosis ScriptDocument3 pagesHypnosis ScriptLuca BaroniPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle ModulationDocument26 pagesAngle Modulationajeesh r100% (1)
- 16 - CommunicationDocument89 pages16 - CommunicationKamran KhursheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Bit Error Rate and Signal To Noise Ratio Performance Evaluation of OFDM System With QPSK and QAM MDocument16 pagesBit Error Rate and Signal To Noise Ratio Performance Evaluation of OFDM System With QPSK and QAM MPhilip KpaePas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Filters for Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Design, and ApplicationsD'EverandMicrowave Filters for Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Design, and ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- (s5.h) American Bible Society Vs City of ManilaDocument2 pages(s5.h) American Bible Society Vs City of Manilamj lopez100% (1)
- FSKDocument10 pagesFSKJyotirmoy DekaPas encore d'évaluation
- FM DelieveredDocument46 pagesFM DelieveredFaizan Ashraf100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Digital Mod - Part 1Document47 pagesChapter 4 Digital Mod - Part 1posktovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Noise: Any Unwanted Signal That Interfere With Wanted Signal Impair Communication System Degrade The System PerformanceDocument45 pagesNoise: Any Unwanted Signal That Interfere With Wanted Signal Impair Communication System Degrade The System PerformanceMuhammad Salah ElgaboPas encore d'évaluation
- 50999219SZA7 - Antenna & Wave Propagation - Solution Manual PDFDocument52 pages50999219SZA7 - Antenna & Wave Propagation - Solution Manual PDFmboillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplitude ModulationDocument12 pagesAmplitude ModulationamrilsiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Passive Microwave Components: DefinitionsDocument13 pages6 Passive Microwave Components: DefinitionsYohannes NakachewPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problem in Microwave Engineering Part 2Document15 pagesSolved Problem in Microwave Engineering Part 2Tunde EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Digital Modulation - Part 1Document47 pagesChapter 4 Digital Modulation - Part 1Jazmi MukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3rohankataria26100% (1)
- Problemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesDocument17 pagesProblemas Parte I Comunicaciones DigitalesNano GomeshPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFDocument45 pages5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFajayroy12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of Communications Angle Modulation: Intro To Frequency ModulationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Communications Angle Modulation: Intro To Frequency ModulationEunice Jane Bolgado-DoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle ModulationDocument8 pagesAngle ModulationEmmanuel MerinPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle Modulation Includes The Following Types of ModulationDocument7 pagesAngle Modulation Includes The Following Types of ModulationshankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Kennedy FM QuestionDocument4 pagesKennedy FM Questionjeanne pauline cruzPas encore d'évaluation
- CellularDocument52 pagesCellularRidwan CrraPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. (5) : Frequency Modulation & Demodulation: - ObjectDocument5 pagesExperiment No. (5) : Frequency Modulation & Demodulation: - ObjectFaez FawwazPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Waveguide PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Waveguide PDFHiroshi RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemsSolomon Tadesse AthlawPas encore d'évaluation
- Blake Ch01 Solution ManualDocument7 pagesBlake Ch01 Solution ManualLorenique Tan100% (4)
- Planar Transmission Lines PDFDocument12 pagesPlanar Transmission Lines PDFGECM85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Small Scale Fading Discussion-4Document36 pagesSmall Scale Fading Discussion-4Sang Dorjee TamangPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Demodulation PDFDocument13 pagesFM Demodulation PDFashwini100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Amplitude ModulationDocument22 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Amplitude ModulationDurga Bhavani AlankaPas encore d'évaluation
- ELEN443 Project II BPSK ModulationDocument18 pagesELEN443 Project II BPSK ModulationZiad El SamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Frenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Document22 pagesFrenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Patrick James De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase ModulationDocument2 pagesPhase ModulationAnjielo Magpantay100% (1)
- Amplitude Modulation MCQDocument20 pagesAmplitude Modulation MCQgunasekaran kPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle ModulationDocument52 pagesAngle ModulationkshitijPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample AM NumericalsDocument4 pagesSample AM NumericalsDisha GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimum Receiver DesignDocument76 pagesOptimum Receiver DesignbiruckPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter4 - Single Sideband CommunicationsDocument26 pagesChapter4 - Single Sideband CommunicationskhicomPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet #1 SolutionDocument5 pagesSheet #1 Solutionسام النعمانPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal KatariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Line Code DecoderDocument11 pagesLine Code DecoderMor DepRzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument19 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationShubhangBaghelPas encore d'évaluation
- Am Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesAm Solved Problemssukhi_digra100% (2)
- Iecep EsatDocument29 pagesIecep EsatIvy Cee100% (1)
- IIT - Project Report On Modulation (New-Main)Document32 pagesIIT - Project Report On Modulation (New-Main)Pranil Ingole0% (1)
- Parabolic Antenna Efficiency and Power Gain: Eduardo Punto JRDocument30 pagesParabolic Antenna Efficiency and Power Gain: Eduardo Punto JRXyPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Division Multiplexing (Transmitter, Receiver, Commutator)Document27 pagesTime Division Multiplexing (Transmitter, Receiver, Commutator)Jowi VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Angle Modulation FinalDocument51 pagesChapter 3 Angle Modulation Finalshiwangizaw tikaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On Principle of CommunicationsDocument2 pagesProblems On Principle of Communicationsnicdocu100% (1)
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocument59 pagesAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramPas encore d'évaluation
- Low and High Transmitter Block DiagramDocument6 pagesLow and High Transmitter Block DiagramRainier RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp - No.1-Amplitude Modulation (DSB-LC)Document11 pagesExp - No.1-Amplitude Modulation (DSB-LC)موسى سعد لعيبيPas encore d'évaluation
- Modulation 1Document6 pagesModulation 1Tamiranashe Tammie NyunguPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Communication System, Chapter 7 AnsDocument16 pagesElectronic Communication System, Chapter 7 AnsRonald ArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Between AM, PM and FM: Term Paper OnDocument20 pagesComparison Between AM, PM and FM: Term Paper OnAshish VaniyaPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Radio FrequencyDocument7 pagesFM Radio FrequencySushant RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Coco Syrup SAEADocument8 pagesCoco Syrup SAEAJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming ATmega328Document4 pagesProgramming ATmega328Jay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 191 3rd QuizDocument7 pagesECE 191 3rd QuizJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE Laws and EthicsDocument2 pagesECE Laws and EthicsJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency ModulationDocument7 pagesFrequency ModulationJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Wings of Love Chords by Jeffrey Osborne at Ultimate-GuitarDocument1 pageOn The Wings of Love Chords by Jeffrey Osborne at Ultimate-GuitarJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- PortmainxmlDocument1 pagePortmainxmlJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Pan and Tilt Code InoDocument1 pagePan and Tilt Code InoJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- R A 9292 PDFDocument18 pagesR A 9292 PDFDaryl Langamon Uy CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Mr. and Ms. Fitness ResoDocument1 pageMr. and Ms. Fitness ResoJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultimate RC INODocument2 pagesUltimate RC INOJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational AmplifiersDocument1 pageOperational AmplifiersJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis ScriptDocument2 pagesThesis ScriptJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece 122Document1 pageEce 122Jay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- TelevisionDocument2 pagesTelevisionJay Amiel AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncDocument2 pages23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncPamelaPas encore d'évaluation
- EMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Document34 pagesEMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Eucarlos MartinsPas encore d'évaluation
- KalamDocument8 pagesKalamRohitKumarSahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Thermodynamics - DraughtDocument22 pagesApplied Thermodynamics - Draughtpiyush palPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesPsychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (9)
- TEsis Doctoral en SuecoDocument312 pagesTEsis Doctoral en SuecoPruebaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous WorkshopDocument5 pagesPresent Continuous WorkshopPaula Camila Castelblanco (Jenni y Paula)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Espn NFL 2k5Document41 pagesEspn NFL 2k5jojojojo231Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1634313583!Document24 pages1634313583!Joseph Sanchez TalusigPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics NotesDocument7 pagesStatistics NotesAhmed hassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final ReflectionDocument4 pagesFinal Reflectionapi-314231777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer Pricing 8Document34 pagesTransfer Pricing 8nigam_miniPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Document37 pagesNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonPas encore d'évaluation
- PCI Bank V CA, G.R. No. 121413, January 29, 2001Document10 pagesPCI Bank V CA, G.R. No. 121413, January 29, 2001ademarPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL LayoutDocument4 pagesDLL LayoutMarife GuadalupePas encore d'évaluation
- Undertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Document3 pagesUndertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Anuj ManglaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maule M7 ChecklistDocument2 pagesMaule M7 ChecklistRameez33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Student Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDANIELA SIMONELLIPas encore d'évaluation
- TestDocument56 pagesTestFajri Love PeacePas encore d'évaluation
- Roman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3Document81 pagesRoman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3The Glamorgan-Gwent Archaeological Trust LtdPas encore d'évaluation
- Water and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceDocument18 pagesWater and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceJoyce Marian BelonguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Wetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsDocument3 pagesWetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsManish thapaPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Document9 pagesCAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Christina FrancisPas encore d'évaluation