Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes - Laws of Motion
Transféré par
mailme4121Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes - Laws of Motion
Transféré par
mailme4121Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
HOME
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
CLASSES
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
ENTRANCE EXAMS
RESOURCES
HC VERMA SOLUTIONS
GOT A QUESTION? ASK US HERE!
Adsby Google
PhysicsNotes
PhysicsClass11
PhysicsFormulas
Experiment
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes : Laws of
Motion
September 2, 2014 by Neepur Garg Leave a Comment
Inertia
The property of an object by virtue of which it cannot change its state of rest or of uniform motion along a
straight line its own, is called inertia.
StartDownload
ConvertAnyFiletoaPDF.GettheFreeFromDoctoPdfApp!
Inertia is a measure of mass of a body. Greater the mass of a body greater will be its inertia or vice-versa.
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
1/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
Inertia is of three types:
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
(i) Inertia of Rest When a bus or train starts to move suddenly, the passengers sitting in it falls backward
dueSTUDY
to inertia
of rest.
MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
(ii) Inertia of Motion When a moving bus or train stops suddenly, the passengers sitting in it jerks in forward
direction due to inertia of motion.
(iii) Inertia of Direction We can protect yourself from rain by an umbrella because rain drops can not change
its direction its own due to inertia of direction.
Force
Force is a push or pull which changes or tries to change the state of rest, the state of uniform motion, size
or shape of a body.
Its SI unit is newton (N) and its dimensional formula is [MLT-2].
Forces can be categorized into two types:
(i) Contact Forces Frictional force, tensional force, spring force, normal force, etc are the contact forces.
(ii) Action at a Distance Forces Electrostatic force, gravitational force, magnetic force, etc are action at a
distance forces.
Impulsive Force
A force which acts on body for a short interval of time, and produces a large change in momentum is called
an impulsive force.
Linear Momentum
The total amount of motion present in a body is called its momentum. Linear momentum of a body is equal
to the product of its mass and velocity. It is denoted by p.
Linear momentum p = mu.
Its S1 unit is kg-m/s and dimensional formula is [MLT-1].
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
2/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
It is a vector quantity and its direction is in the direction of velocity of the body.
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
Impulse
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
The product of impulsive force and time for which it acts is called impulse.
Impulse = Force * Time = Change in momentum
Its S1 unit is newton-second or kg-m/s and its dimension is [MLT-1].
It is a vector quantity and its direction is in the direction of force.
Newtons Laws of Motion
1. Newtons First Law of Motion
A body continues to be in its state of rest or in uniform motion along a straight line unless an external force
is applied on it.
This law is also called law of inertia.
Examples
(i) When a carpet or a blanket is beaten with a stick then the dust particles separate out from it.
(ii) If a moving vehicle suddenly stops then the passengers inside the vehicle bend outward.
2. Newtons Second Law of Motion
The rate of change of linear momentum is proportional to the applied force and change in momentum
takes place in the direction of applied force.
Mathematically F &in1; dp / dt
F = k (d / dt) (mv)
where, k is a constant of proportionality and its value is one in SI and CGS system.
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
3/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
F= mdv / dt = ma
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
Examples
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
(i) It is easier for a strong adult to push a full shopping cart than it is for a baby to push the same cart. (This
is depending on the net force acting on the object).
(ii) It is easier for a person to push an empty shopping cart than a full one (This is depending on the mass of
the object).
3. Newtons Third Law of Motion
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction and both acts on two different bodies
Mathematically F12 = F21
Examples
(i) Swimming becomes possible because of third law of motion.
(ii) Jumping of a man from a boat onto the bank of a river.
(iii) Jerk is produced in a gun when bullet is 1red from it.
(iv) Pulling of cart by a horse.
Note Newtons second law of motion is called real law of motion because 1rst and third laws of motion can
be obtained by it.
The modern version of these laws is
(i) A body continues in its initial state of rest or motion with uniform velocity unless acted on by an
unbalanced external force.
(ii) Forces always occur in pairs. If body A exerts a force on body B, an equal but opposite force is exerted
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
4/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
by body B on body A.
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
If no external force acts on a system, then its total linear momentum remains conserved.
Linear momentum depends on frame of reference but law of conservation of linear momentum is
independent of frame of reference.
Newtons laws of motion are valid only in inertial frame of reference.
Weight (w)
It is a 1eld force, the force with which a body is pulled towards the centre of the earth due to gravity. It has
the magnitude mg, where m is the mass of the body and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
w = mg
Apparent Weight in a Lift
(i) When a lift is at rest or moving with a constant speed, then
R = mg
The weighing machine will read the actual weight.
(ii) When a lift is accelerating upward, then apparent weight
R1 = m(g + a)
The weighing machine will read the apparent weight, which is more than the actual weight.
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
5/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
(iii) When a lift is accelerating downward, then apparent weight
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
R2 = m (g a)
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
The weighing machine will read the apparent weight, which is less than the actual weight.
(iv) When lift is falling freely under gravity, then
R2 = m(g g)= 0
The apparent weight of the body becomes zero.
(v) If lift is accelerating downward with an acceleration greater than g, then body will lift from oor to the
ceiling of the lift.
Rocket
Rocket is an example of variable mass following law of conservation of momentum.
Thrust on the rocket at any instant F = u (dM / dt)
where u = exhaust speed of the burnt and dM / dt = rate 0f gases combustion of fuel.
Velocity of rocket at any instant is given by u = vo + u loge (Mo / M )
where, vo = initial velocity of the rocket,
Mo = initial mass of the rocket and
M = present mass of the rocket.
If effect of gravity is taken into account then speed of rocket
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
6/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
u = vo + u loge (Mo / M) gt
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
Friction
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
A force acting on the point of contact of the objects, which opposes the relative motion is called friction.
It acts parallel to the contact surfaces.
Frictional forces are produced due to intermolecular interactions acting between the molecules of the
bodies in contact.
Friction is of three types:
1. Static Friction
It is an opposing force which comes into play when one body tends to move over the surface of the other
body but actual motion is not taking place.
Static friction is a self adjusting force which increases as the applied force is increased,
2. Limiting Friction
It is the maximum value of static friction when body is at the verge of starting motion.
Limiting friction (fs) = sR
where s, = coef1cient of limiting friction and R = normal reaction.
Limiting friction do not depend on area of contact surfaces but depends on their nature, i.e., smoothness or
roughness.
If angle of friction is , then coef1cient of limiting friction
s = tan
3. Kinetic Friction
If the body begins to slide on the surface, the magnitude of the frictional force rapidly decreases to a
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
7/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
constant value fk kinetic friction.
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
Kinetic friction, fk = k N
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
where k = coef1cient of kinetic friction and N = normal force.
Kinetic friction is of two types:
(a) Sliding friction
(b) Rolling friction
As, rolling friction < sliding friction, therefore it is easier to roll a body than to slide.
Kinetic friction (fk) = k R
where k = coef1cient of kinetic friction and R = normal reaction.
Angle of repose or angle of sliding It is the minimum angle of inclination of a plane with the horizontal,
such that a body placed on it, just begins to slide down.
If angle of repose is a. and coef1cient of limiting friction is , then
s = tan
Motion on an Inclined Plane
When an object moves along an inclined plane then: different forces act on it like normal reaction of plane,
friction force acting in opposite direction of motion etc. Different relations for the motion are given below.
Normal reaction of plane
R = mg cos
and net force acting downward on the block.
F = mg sin f
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
8/18
7/1/2016
HOME
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
Acceleration on inclined plane a = g (sin cos )
When angle of inclination of the plane from horizontal is less than the angle of repose (), then
(i) minimum force required to move the body up the inclined plane
f1 = mg (sin + cos )
(ii) minimum force required to push the body down the inclined plane
f2 = mg ( cos sin ) J
Tension
Tension force always pulls a body.
Tension is a reactive force. It is not an active force.
Tension across a massless pulley or frictionless pulley remain constant.
Rope becomes slack when tension force becomes zero.
Motion of Bodies in Contact
(i) Two Bodies in Contact If F force is a applied on object of mass m1 then acceleration of the bodies
a = F / (m1 + m2)
Contact force on m1 = m1a = m1F / (m1 + m2)
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
9/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
Contact force on m2 = m2a = m2F / (m1 + m2)
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
(ii) Three Bodies in Contact If F force is applied an object of mass m1, then acceleration of the bodies = F /
(m1STUDY
+ m2 +MATERIAL
m3)
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
Contact force between m1 and m2
F1 = (m2 + m3) F / (m1 + m2 + m3)
Contact force between m2 and m3
F2 = m3 F / (m1 + m2 + m3)
(iii) Motion of Two Bodies, One Resting on the Other
(a) The coef1cient of friction between surface of A and B be . If a force F is applied on the lower body A.
then common acceleration of two bodies
a = F / (M + m)
Pseudo force acting on block B due to the accelerated motion
f= ma
The pseudo force tends to produce a relative motion between bodies A and B and consequently a frictional
force
f = N = mg is developed. For equilibrium
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
10/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
ma mg or a g
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
(b) Let friction is also present between the ground surface and body A Let the coef1cient of friction between
theSTUDY
given surface
and bodyTALENT
A is 1 SEARCH
and the EXAMS
coef1cient
of friction between the surfaces of bodies A and B is
MATERIAL
& OLYMPIADS
2 If a force F is applied on the lower body A
Net accelerating force = F fA = F 1(M + m)g
Net acceleration
a = F 1(M + m)g / (M + m) = F / (M + m) g
Pseudo force acting on the block B
f = ma
The pseudo force tends to produce a relative motion between the bodies A and B are consequently a
frictional force fB = mg is developed. For equilibrium
ma le; 2 mg or a 2 g
If acceleration produced under the the effect of force F is more than 2g, then two bodies will not move
together.
(iv) Motion of Bodies Connected by Strings
Acceleration of the system a = F / (m1 + m2 + m3)
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
11/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
Tension in string T1 = F
HOME
CBSE
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
T2 = ( m2 + m3 ) a = (m2 + m3) F / (m1 + m2 + m3)
STUDY MATERIAL
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
T3 = m3a = m3F / (m1 + m2 + m3)
Pulley Mass System
(i) When unequal masses m1 and m2 are suspended from a pulley
(m1 > m2)
m1g T = m1a, and T m2g = m2a
On solving equations, we get
a = ((m1 m2) / (m1 + m2)) * g
T = 2m1m2 / (m1 + m2) * g
(ii) When a body of mass m2 is placed frictionless horizontal surface, then
Acceleration a = m1g / (m1 + m2)
Tension in string T = m1m2g / (m1 + m2)
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
12/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
(iii) When a body of mass m2 is placed on a rough horizontal surface, then
HOME
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
Acceleration a = ((m1 m2) / (m1 + m2)) * g
Tension in string T = (m1m2(1 + ) / (m1 + m2)) * g
(iv) When two masses m1 and m2 are connected to a single mass M as shown in 1gure, then
m1g T1 = m1a ..(i)
T2 m2g = m2a (ii)
T1 T2 = Ma .(iii)
Acceleration a = ((m1 m2 / (m1 + m2 + M)) * g
Tension T1 = (2m2 + M / (m1 + m2 + M) * m1g
T2 = (2ma + M / (m1 + m2 + M) * m2g
(v) Motion on a smooth inclined plane, then
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
13/18
7/1/2016
HOME
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
m1g T = m1a ..(i)
T m2g sin = m2a (ii)
Acceleration a = ((m1 m2 sin / (m1 + m2)) * g
Tension T = m1m2(1 + sin ) g / (m1 + m2)
(vi) Motion of two bodies placed on two inclined planes having different angle of inclination, then
Acceleration a = (m1 sin 1 m2 sin 2) g / m1 + m2
Tension T = (m1m2 / m1 + m2) * (sin 1 sin 2) g
All CBSE Notes for Class 11 Physics
Maths Notes
Chemistry Notes
Biology Notes
If you have any query regarding this topic please post your queries HERE
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
14/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
0
HOME
CBSE0
Google+
ICSE1/ ISC
STUDY MATERIAL
Filed Under: CBSE
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
Tagged With: CBSE 11 Notes, CBSE Class Notes, CBSE Notes, Class 11 Notes, Class 11th Notes, Free CBSE Notes, Free
Notes
YOURREACTION?
Happy
Excited
Amused
Angry
Indifferent
16
2
PoweredbyVICOMI
Adsby Google
CbseNotes
ActingSchools
PhysicsScience
Newton
STAY UPDATED!
Get all updates and information in your Inbox. Enter your email below:
E-Mail Address
GO
comments
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
15/18
7/1/2016
HOME
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
the site ...
STATE BOARDS Search
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
STAY UPDATED!
Get all updates and information in your
Inbox. Enter your email below:
E-Mail Address
GO
MOCK TESTS
IMO Mock Test | IEO Mock Test | NSO Mock Test
PSA Online Mock Test
KVPY Online Mock Test
NTSE Online Mock Test
RELATED POSTS
DownloadAFreeAudiobook
Ad mobile.audible.com
CBSEClass11Physics
Notes:Oscillations
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
16/18
7/1/2016
HOME
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
schools.aglasem.com
CBSEClass612Online
Ad learnnext.com
CBSEClass11Physics
Notes:Gravitation
schools.aglasem.com
CBSEClass11Physics
Notes:SurfaceTension
schools.aglasem.com
CBSEClass11Physics
Notes:KineticTheoryof...
schools.aglasem.com
NCERTSolutionsforClass
11thPhysics:Chapter...
schools.aglasem.com
Class11Important
QuestionsforPhysics
Laws...
schools.aglasem.com
Class11Important
QuestionsforPhysics
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
17/18
7/1/2016
CBSEClass11PhysicsNotes:LawsofMotion
Adsby Google
HOME
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
NewtonsLawsofMotion
CbseNotes
Friction
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
The materials and information provided on this website are for reference purposes only. Click Here for complete
Disclaimer.
http://schools.aglasem.com/46484
18/18
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics Notes Class 11 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionAshwin100% (1)
- Abhay Kumar Singh I E Irodov Solutions To I.E. Irodov S Problems in General Physics. Volume 2 Waves Optics Modern Physics 1998Document408 pagesAbhay Kumar Singh I E Irodov Solutions To I.E. Irodov S Problems in General Physics. Volume 2 Waves Optics Modern Physics 1998Boris UrrutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- XI Physics DSM 2020 - 1Document24 pagesXI Physics DSM 2020 - 1MeersPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Class 11 Part 2Document162 pagesChemistry Class 11 Part 2Aniket Sharma100% (2)
- NEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Document4 pagesNEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Sankar KumarasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Energy and Energy ConservationDocument62 pagesWork Energy and Energy ConservationMichole Godwin Regala100% (1)
- Problems and Numericals On Electrostatics Gauss Law and PotentialDocument17 pagesProblems and Numericals On Electrostatics Gauss Law and Potentialp_k_soni_iit_physics100% (2)
- 4 Work and Energy OswDocument95 pages4 Work and Energy OswOoi Soo WeiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.electric Potential and CapacitancetheoryDocument33 pages4.electric Potential and CapacitancetheoryGomes RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Rotational Dynamics PDF PrintDocument22 pages1 Rotational Dynamics PDF PrintHarshal MankarPas encore d'évaluation
- DifferencesDocument3 pagesDifferenceschhabra navdeep100% (1)
- IIT JEE Physics Preparation BooksDocument3 pagesIIT JEE Physics Preparation Booksgaurav2011999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Notes Class 11 Chapter 7 System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument12 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 Chapter 7 System of Particles and Rotational MotionAbhishek UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulae For Class 12 MathsDocument19 pagesFormulae For Class 12 Mathspsingh_286392100% (3)
- Electrostatics1 PDFDocument92 pagesElectrostatics1 PDFPriyanshu Raj100% (1)
- Fluids Properties NotesDocument4 pagesFluids Properties NotesVirendra GaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete A Level Physics Definitions PDFDocument5 pagesComplete A Level Physics Definitions PDFnaziya begumPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure VMC Study MaterialDocument52 pagesAtomic Structure VMC Study MaterialMamePas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Document18 pagesIGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Izatul NadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTES of PHYSICS Class 11 Units and DimensionDocument6 pagesNOTES of PHYSICS Class 11 Units and DimensionYash MahantPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Conventional Energy SourcesDocument28 pagesNon Conventional Energy Sourcesgodhani_lalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Floatation Notes.Document7 pagesFloatation Notes.Mandeep Singh PlahaPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Periodic Classification of Elements CBSE Class 10 NCERT SolutionDocument9 pagesCBSE Periodic Classification of Elements CBSE Class 10 NCERT Solutionlovely umaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Energy and PowerDocument21 pagesWork Energy and PowerMohammed Aftab AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument18 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesMitanshu BagulPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Chemistry Shiv Das First TermDocument29 pages12 Chemistry Shiv Das First TermRaj AgamPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsadvaithPas encore d'évaluation
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsDocument17 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves ChapterDocument3 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion and Waves ChapterIrteza khan100% (1)
- 1 Electricity - Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solutions For Class 10 Physics CBSE - TopperLearningDocument74 pages1 Electricity - Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solutions For Class 10 Physics CBSE - TopperLearningPalanshAgarwal100% (2)
- System of Particles & Rotational Motion: Chapter - 00Document32 pagesSystem of Particles & Rotational Motion: Chapter - 00Raichal P BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Introduction To Mechanics PDFDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Mechanics PDFsubyPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT-JEE Study Material Sample PDFDocument14 pagesIIT-JEE Study Material Sample PDFShiv BeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics IIDocument88 pagesMechanics IIHema AnilkumarPas encore d'évaluation
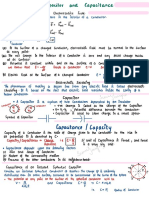
- Capacitors & CapacitanceDocument4 pagesCapacitors & CapacitancePearl TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Title/ Chemistry Lab Manual 12thDocument10 pagesTitle/ Chemistry Lab Manual 12thAyush K. Sharma50% (2)
- Thermodynamics of Heat Engine: Dr. Prasant KumarDocument25 pagesThermodynamics of Heat Engine: Dr. Prasant Kumaromer faruqePas encore d'évaluation
- CrashUp 11PH07 Rotational Motion PDFDocument39 pagesCrashUp 11PH07 Rotational Motion PDFAnuwak Mathur100% (1)
- AP Physics NotesDocument18 pagesAP Physics Notesfhsphysics100% (1)
- NSO Level 2 Class 9 Paper 2017 18 Part 1Document3 pagesNSO Level 2 Class 9 Paper 2017 18 Part 1chirayu2888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample PDF of STD 11th Precise Physics Notes Book Science Maharashtra BoardDocument34 pagesSample PDF of STD 11th Precise Physics Notes Book Science Maharashtra Boardssmv135Pas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of MotionDocument31 pagesLaws of MotionManas ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Mechanicsapi-248483124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerDocument29 pagesClass 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerPriyanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Brilliants KinematicsDocument89 pagesBrilliants KinematicsAbhishekkumar92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Potential and Capacitance PDFDocument110 pagesElectric Potential and Capacitance PDFAkshit JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper 2019Document25 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper 2019Vivek YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Space Study NotesDocument46 pagesSpace Study NotesMadeleine ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Vectors and Their PropertiesDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Vectors and Their PropertiesSesha Sai Kumar100% (1)
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsABHISHEKPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Notes DeterminantsDocument8 pagesClass 12 Notes DeterminantsAasthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion Electrostatics Theory PDFDocument52 pagesMotion Electrostatics Theory PDFGaurav AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateDocument7 pagesDPP - Daily Practice Problems: Name: DateAnonymous 9uu04elPas encore d'évaluation
- The Particulate Nature of Matter - MindmapDocument1 pageThe Particulate Nature of Matter - MindmapEllen Koh100% (1)
- Physics I: Mechanics and LabDocument3 pagesPhysics I: Mechanics and LabGarlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - LearnCBSE - inDocument29 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - LearnCBSE - inpartham yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational Motion PDFDocument50 pagesRotational Motion PDFSuvathielanchezhianPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 CH - 14Document12 pagesClass 12 CH - 14Kumaran100% (1)
- Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesLaws of MotionsumitchintuPas encore d'évaluation
- State Space StabilityDocument4 pagesState Space Stabilitymailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Root LocusDocument27 pagesRoot LocusAzmi Bin A MataliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial SheetDocument11 pagesTutorial Sheetmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Project On 111Document15 pagesA Project On 111mailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eec451-Ec Lab IIDocument37 pagesEec451-Ec Lab IImailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6Document53 pagesCH 6mailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Sizing V2.0Document32 pagesChapter Sizing V2.0mailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- A2 PDFDocument1 pageA2 PDFmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design FIR and IIR Filters in MatlabDocument12 pagesDesign FIR and IIR Filters in Matlabmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eec452-De Lab IIDocument26 pagesEec452-De Lab IImailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Overview 08Document8 pagesGSM Overview 08Remon Adel AsaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch70 Message SwichingDocument13 pagesCh70 Message SwichingMithilesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel Formulas A Quick List PDFDocument6 pagesExcel Formulas A Quick List PDFIrfan Abbasi100% (1)
- TEC-301 Solid State Devices CircuitsDocument2 pagesTEC-301 Solid State Devices Circuitsmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Switching SystemsDocument174 pagesDigital Switching SystemsOmar Hellel100% (1)
- Vlsi Unit1 NotesDocument34 pagesVlsi Unit1 Notesmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- DSP Book Ch20Document10 pagesDSP Book Ch20Jatin AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Logic Circuits: A. MarzukiDocument25 pagesDynamic Logic Circuits: A. Marzukisreekanthreddy peramPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor Question BankDocument67 pagesMicroprocessor Question BankArpit SPas encore d'évaluation
- ENSC380 Objectives: Summary of Different Fourier Transform Methods Learn The Relationship Between Different DT MethodsDocument11 pagesENSC380 Objectives: Summary of Different Fourier Transform Methods Learn The Relationship Between Different DT Methodsmailme4121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ideal GasDocument60 pagesIdeal Gas68zrvtr9bfPas encore d'évaluation
- Drill Pipe Eng PDFDocument8 pagesDrill Pipe Eng PDFTariq ChagouriPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Ejector Selection PDFDocument9 pagesAir Ejector Selection PDFmyungkwan haPas encore d'évaluation
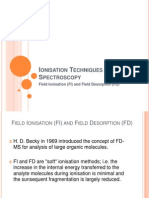
- Field Desorption, Field IonisationDocument13 pagesField Desorption, Field Ionisationhey80milionPas encore d'évaluation
- NBS - 001-Services (Mechanical) Sample Specification-2019-07-29Document13 pagesNBS - 001-Services (Mechanical) Sample Specification-2019-07-29Nay Win MaungPas encore d'évaluation
- SIMONE (Equations and Methods)Document65 pagesSIMONE (Equations and Methods)Amine DoumiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Adiabatic InvariantsDocument6 pages5 Adiabatic InvariantsStephen NatanaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Asme Material SpecsDocument4 pagesAsme Material SpecsRajwinder Singh100% (1)
- Pages From EPRI EL-6800Document6 pagesPages From EPRI EL-6800981002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skiladaemi 3Document8 pagesSkiladaemi 3Esra MollaPas encore d'évaluation
- AISC Seismic Design Steel Structures EssentialDocument10 pagesAISC Seismic Design Steel Structures EssentialSaman A AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Tinrhert Field Development Project - Epc 1: Inlet Separation and Boosting Facility in OhanetDocument35 pagesTinrhert Field Development Project - Epc 1: Inlet Separation and Boosting Facility in OhanetsathishPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Process Related DefectsDocument1 pageWelding Process Related DefectskapsarcPas encore d'évaluation
- Geohazards: Madhavi Latha Gali P. Raghuveer Rao EditorsDocument753 pagesGeohazards: Madhavi Latha Gali P. Raghuveer Rao EditorsHeni Susiati0% (2)
- Stage-8-Science-Paper-2 JJKBBDocument6 pagesStage-8-Science-Paper-2 JJKBBTarek FaramawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev11 en Manual Piclassic CutDocument12 pagesRev11 en Manual Piclassic Cutmausanchezmej.ingenieriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Chapter 2 Dynamic Systems Modeling Simulation and Control KlueverDocument33 pagesSolution Chapter 2 Dynamic Systems Modeling Simulation and Control KlueverWillians Fernando de OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Torsion 91Document1 pageTorsion 91bagmass0% (1)
- RRL 4Document6 pagesRRL 4Pzynae FlorentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Purwanchal Vidyamandir Session: 2020 - 2021 Class: IX Subject: Geography Study Material - 3 Chapter - 8 EarthquakesDocument4 pagesPurwanchal Vidyamandir Session: 2020 - 2021 Class: IX Subject: Geography Study Material - 3 Chapter - 8 EarthquakesKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9APas encore d'évaluation
- 711-Copes Vulcan Vo II DesuperheaterDocument8 pages711-Copes Vulcan Vo II DesuperheaterWADEPas encore d'évaluation
- Wire Rs For LNG ElseDocument2 pagesWire Rs For LNG ElserajabalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical N Chemical ChangesDocument16 pagesPhysical N Chemical Changessarahudi100% (4)
- List of Courses PHY 2022-2023-I New-06-04-23Document1 pageList of Courses PHY 2022-2023-I New-06-04-23Sushi KeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Tile Testing Standards GuideDocument4 pagesTile Testing Standards GuideLucky KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Duct Design ChartDocument7 pagesDuct Design ChartMohsen HassanPas encore d'évaluation
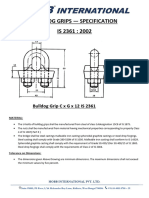
- Bull Dog Clamp - SpecificationDocument2 pagesBull Dog Clamp - SpecificationsanjoyPas encore d'évaluation
- MSC 337Document36 pagesMSC 337Alfred Esquillio MontealtoPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Doubly Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Doubly Reinforced Concrete BeamAnton_Young_1962Pas encore d'évaluation
- ADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1Document23 pagesADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1EDGAR RIVERAPas encore d'évaluation