Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fisika
Transféré par
shabrinaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fisika
Transféré par
shabrinaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
STEAM POWER PLANT ( PLTU) BOSOWA
ABSTRACT
PLTU Jeneponto 2x125 MW is a Coal-Fired Steam Power Plant belongs to PT. Bosowa
Energi. Located in Desa Punagaya, Kecamatan Bengkala, Kabupaten Jeneponto, South
Sulawesi Province, PLTU Jeneponto is currently the biggest capacity Coal-Fired Steam
Power Plant located in the eastern part of Indonesia.
In order to support PT. Bosowa Energi as the Owner to reach the required Commercial
Operation Date of PLTU Jeneponto 2x125MW, PT. D&C through its subcontractor, PT.
Human Karya (Persero) started the work of excavation of Circulating Water Pump House,
concrete Power Block area and initialed the Steel Structure. Power plant built on an area
of 230 hectares (ha) it requires an investment of about US $ 200 million.
1. PRELIMINARY (Pendahuluan)
1.1.
Background
For centuries, humans have observed
about the process tejadinya electricity.
They have made several experiments in
order to get the puzzle solving of the onset
of electricity. Many figures were uncovered
and made a discovery that's close relation
with them is Michael Faraday electricity
with one result kegiatanya is about
electromagnetic rotation. Penemuanya
result is an important basis of the
development of the next electricity. The
invention being developed in various
electromagnetic tools such as
transformers and generators.
Electromagnetic generator that uses a
rotation system was first discovered by
HM Pexii of Paris in 1832. The first
generator uses a horseshoe-shaped
permanent magnet, is rotated around an
iron core berlilitan connected with a
commutator and when rotated will produce
sparks. In addition to Michael Faraday still
many other figures who was instrumental
in the advancement of the field of
electrical technology. History of the first
commercial electric operation in 1882,
namely in January in London, followed in
New York in September of the same year.
This commercial electricity using direct
current with a low voltage. In Indonesian
history electricity supply was first initiated
by a powerhouse in Gambir, Jakarta, in
May 1897, followed by other cities in
Indonesia, namely: Medan in 1899,
Surakarta in 1908, Bandung on
tahun1906, Surabaya on 1912 and
Banjarmasin in 1922. At first the centers of
electric power using thermal energy but
continue to be developed so that the use
of hydropower is more economical and
efficient. Of the several types of plants that
exist today, in this paper the author
discusses only power generation systems
using steam.
1.2 Purpose
The purpose of the research to be
conducted that includes:
1. To know about the means of the
steam
power
plant
(PLTU)
BOSOWA
2. describes the functions and
working principle of the power plant
3. know the mechanism of steam
power plant BOSOWA
4. understand the result of PLTU
BOSOWA distributed
1.3 Problem Formula
In this final project will be
discussed several issues, among
others:
1. What is the means of the
steam power plant (PLTU)
BOSOWA
2. How is the mechanism of
steam power plant (PLTU)
BOSOWA
3. Where is the result of PLTU
BOSOWA distributed?
1.4 Research Methods
Research methods that will be used in
the implementation of this final project
is:
1. Formulate and limit problems
2. The study of literature
The literature in this regard include
books, research, handouts, journals
and other sources from the internet.
3. Perform observations and collect
data
4. Planning Phase
5. Discussion
Discussions related to the thesis
with friends, teachers and other
interested parties about the data,
troubleshooting, and suggestions.
1.5 Sistematika Writing
Systematics of writing that will be
used in this thesis are:
BAB I : Preliminary
Contains background of the
problem, objectives, formulation of the
problem, problem definition, research
methods, systematic writing on the
report
BAB II : Discussion
BAB III : Finality
Containing the conclusions of the
analysis that has been done, as well
as recommendations or suggestions
for
improvement
development.
and
further
2. DISCUSSION
2.1 Functions and working principle of
the power plant
Steam power plant is A power generation
system that converts chemical energy
electricity by using steam as the working
fluid, by harnessing the kinetic energy of
steam to drive the blade shaft - blade
turbine.
Turbine blade work the turbine shaft,
turbine shaft to further work the generator.
Of the generator is then generated
electrical energy.
Power plant is a type of thermal power
plant that is widely used, because of its
fuel efficiency is good and easily obtained
thus producing electrical energy
economically.
Energy conversion in plant
Mechanical energy provided by steam to a
steam turbine generator will cause the
rotor to spin. Generator rotor is spinning
inside a large magnet coil to produce
electrical energy. Energy conversion
process in the plant progresses through
three stages, namely:
Chemical energy in the fuel is
converted into heat energy in the
form of vapor pressure and high
temperature.
Thermal energy (steam) converted
into mechanical energy in the form
of a round.
Mechanical energy is converted
into electrical energy.
How it Works plant
Air into the compressor through the air
inlet
(Inlet),The compressor serves to suck and
raise the air pressure, so that the air
temperature is also increased. Then this
pressurized air into the combustion
chamber. In the combustion chamber of
the combustion process is carried out by
mixing compressed air and fuel. The
combustion process takes place in a state
of constant pressure so that it can be said
combustor only to raise the temperature.
The combustion gas supplied to the gas
turbine through a nozzle which serves to
direct the flow to the turbine blades. The
power generated by the gas turbine is
used to turn the compressor itself and
turning the other loads such as electric
generators, etc. After passing through this
turbine the gas will be expelled through
the exhaust duct
(Exhaust).
In general, the process that occurs in a
gas turbine system are as follows:
Compression (compression) in the suction
and compressed air
Burning (combustion) of fuel mixed into
the combustion chamber with air and then
burned.
Expansion (expansion) of combustion gas
expands and flows out through the
nozzles (nozzle)
,
Exhaust (exhaust) gases of combustion
are removed through drains.
In fact, there is no process that is always
ideal, persists kerugiankerugian that can
cause a decline in the power generated by
gas turbines and result in decreased
performance of the gas turbine itself. Such
losses can occur on all three components
of the gas turbine system. Causes of loss
include:
Fluid friction that causes pressure loss
(Pressure losses)
in the combustion chamber.
The existence of excessive working time
compression process which causes
friction between the wind turbine bearings.
Changing the value Cp of the working fluid
due to temperature changes and changes
in the chemical composition of the working
fluid.
Their mechanical loss, etc.
2.2 Parts of power plant
Main Part
The main part contained in a plant that
is:
Boiler
Boilers used to convert water (feed
water) into hot steam up (superheated
steam) which will be used to turn
turbines.
steam turbine
The steam turbine is used to convert
the heat energy contained by the steam
into rotary energy (mechanical energy).
Turbine shaft is coupled to the
generator shaft so that when the
turbine rotates the generator also
rotates.
Condenser
The condenser serves to condense the
vapor trail of the turbine (steam which
has been used to turn turbines).
Generator
Function generator to convert rotary
energy of the turbine into electrical
energy.
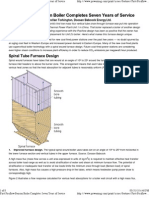
2.3 The working principle Boiler
Boiler or boiler is a machine tool that
serves to convert water into steam.
The process of changing water into
steam occurs by heating water that is
inside the pipes by utilizing the heat
from the burning fuel. Combustion is
performed
continuously
in
the
combustion chamber with fuel and air
flow from the outside.
The steam generated by the boiler is a
superheat steam temperature and high
pressure. The amount of steam
production depends on the heat
transfer surface area, the rate of flow,
and the heat of combustion is given.
Boiler construction consists of pipes
filled with water is called the water
tube boiler.
In generating units, boilers also
commonly referred to as steam
generators (steam generator) to
remember the meaning of the word
boiler boiler only, while in fact
generated from the boiler high
pressure steam superheat.
Judging from the fuel is used, then the
plant can be divided into:
-Coal power plant
-Oil plant
-gas power plant
-Nuclear power plants or nuclear
power plants
Types of coal power plant can still be
distinguished by the combustion
process, ie plant with pulverized coal
combustion (Pulverized Coal / PC
Boiler) and coal-burning power plant
with the bulk (Circulating Fluidized
Bed).
The difference between coal power
plant with oil or gas power plant
equipment and systems is the
handling and combustion of fuel and
waste handling ashes. Coal power
plant auxiliary equipment has more
and more complex than oil or gas
power plant. Gas power plant is the
simplest plant equipment accessories.
Judging from the boiler combustion
chamber pressure, the power plant
can be divided into:
Pressurised steam power plant with
Boiler
Plant with Balanced Draft Boiler
Plant with Vacuum Boiler
Combustion
chamber
pressure
regulation system (furnace pressure)
is usually called a draft or static
pressure in the combustion chamber
where fuel combustion process takes
place. Power plants with pressurized
boiler (positive combustion chamber
pressure) is used for the combustion
of fuel oil or gas. Positive pressure
combustion chamber caused by the
airflow from the fan forced press
(Forced Draft Fan, FDF). Exhaust
gases out of the combustion chamber
to the atmosphere due to the pressure
difference.
Plant with Balanced Draft Boiler
(balanced pressure) is used for fuel
combustion
of
coal.
Pressure
combustion chamber is made slightly
below atmospheric pressure, usually
around -10 mmH2O. The pressure
generated from two fan settings, which
forced suction fan (Induced Draft Fan,
IDF) and fan forced press (Forced
Draft Fan, FDF). FDF serves to supply
combustion air to the combustion
chamber (furnace) in the boiler, while
the IDF serves to suck gas from the
combustion chamber and throw into
the atmosphere through the chimney.
While the vacuum boiler plant is not
developed yet, so at this time there is
no longer the plant by applying
negative pressure boilers.
Boiler Water Cycle
The water cycle is a series of chain
cycle working fluid. Boilers got a
working fluid supply water and
generate steam to flow into the turbine.
Water as the working fluid filled into the
boiler using a water pump filler with
through
economiser
and
accommodated in the steam drum.
Economiser is a tool which is the last
water heater before entering into the
drum. In the economiser water absorbs
heat from the exhaust gases exit the
superheater before being discharged
into the atmosphere through the
chimney.
Equipment which passed in the water
cycle is a drum boiler, down comer,
under the header (header bottom), and
the riser. Water cycle in the steam drum
is, the water from the drum down
through the pipes down comer to the
bottom header (header bottom). From
the bottom of the water distributed to
the header pipes heating (riser) are
arranged to form the walls of the boiler
combustion chamber. In riser water is
warming and rising to the drum back
due to the temperature difference.
Heat transfer from the flame (flue
gas) into the water in the boiler pipes
occurring radiation, convection and
conduction. As a result of heating in
addition to the temperature rose to
boiling water circulation also occurs
naturally, ie from the drum down
through the down comer to the header
down and climbed back into the drum
through the riser pipes. This circulation
is necessary for the case of cooling to
heating pipes and accelerate the
process of heat transfer. Velocity of
circulation will affect the production of
steam and pressure and temperature
rise.
In addition to the natural
circulation, also known as forced
circulation (forced circulation). For the
circulation of this type used a
circulation pump (circulation pump).
Generally has a circulation pump
circulation rate of about 1.7, meaning
that the amount of water that is
circulated 1.7 times the capacity of
evaporation. Some of the advantages
of forced circulation systems, among
others:
Start time (heating) faster
Have a better response in maintaining
the flow of water into the heating pipes
at the start and full load.
Prevents the possibility of stagnation in
the evaporation
2.4 Supporting Equipment
Supporting equipment contained in a
hydropower in general are:
Desalination Plant (Unit Desal)
This equipment is used to convert sea
water (brine) into fresh water (fresh water)
with a distillation method (combination of
evaporation and condensation). This is
due to the corrosive nature of sea water,
so if the sea water is allowed directly into
the main unit, it can cause damage to
plant equipment.
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Has the same functions as the
desalination plant but used different
methods. This equipment is used semipermeable membrane that can filter out
salts contained in sea water, so it can
produce fresh water as the desalination
plant.
Pretreatment on cooling units that use
groundwater / river
For a power plant that uses ground water /
river water, pre-treatment is used to
remove sediment, dirt and minerals
contained in the water.
Demineralizer Plant (Unit Demin)
Serves to remove mineral content (ion)
contained in fresh water. Water as the
working fluid must be free of mineral plant,
because if water still contains minerals
means the conductivity is high so as to
cause induction GGL when the water
passes through the piping in the plant.
This may cause corrosion on plant
equipment.
Hydrogen Plant (Unit Hydrogen)
At the power plant to use hydrogen (H2)
as a cooling Generator.
Chlorination Plant (Unit Chlorine)
Serves to produce a compound of sodium
hypochlorite (NaOCl) is used to
intoxicate / weaken marine microorganisms in the water intake area. This is
intended to avoid pengerakkan (scaling)
the condenser pipes and unit Desal due to
the proliferation of micro-organisms of the
sea.
Auxiliary Boilers (Boiler Auxiliary)
In general, an oil-fired boiler (fuel oil),
which serves to produce vapor (steam)
which is used when the main boiler startup as well as auxiliary steam (auxiliary
steam).
Coal Handling (Coal Services Unit)
A processing unit that serves coal is the
process of loading and unloading of ships
(ship unloading) in the dock, the
distribution of stock to the area until
delivery to the bunker units.
Ash Handling (Abu Service Unit)
A processing unit that serves both the ash
falling ash (bottom ash) and fly ash (fly
ash) from the hopper and SDCC
Electrostatic Precipitator (Submerged
Drag Chain Conveyor) on the main unit to
the shelter ash (ash valley)
Each of the major components and
support equipment is equipped with
systems and tools that support the work of
the component. Disruption or malfunction
of one of the main component parts could
cause a disruption of the entire system of
the plant.
2.5 Duty cycle power plant
Cycle working fluid is a closed-cycle
power plant, which uses the same fluid
repeatedly. Working fluid cycle power
plant is described in the following
explanation. First the water filled into
the boiler to fill the entire surface area
of heat transfer. Water in the boiler is
heated with hot gases of combustion
of fuel with air that turns into steam.
Steam production is still in the form of
saturated steam boiler, then heated
again using dry steam superheater so
be that then the temperature and
pressure are directed to do work in a
turbine to produce mechanical power
in the form of a round.
Former steam turbines out into the
water-cooled condenser for cooling in
the form of sea water in the pump
using the pump CWP (Circulation
Water Pump) in order to turn into water
through
condensation
process.
Condensate water is then heated
again gradually using the heater /
heating using steam extraction through
LPH1, LPH2, Daerator, HPH4 and
HPH5. Demin water is reused as boiler
water filler. Thus the cycle continues
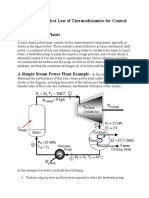
and repetitive. Figure 1 shows a
diagram of a closed cycle power plant
working fluid.
Round turbine is used to turn a
generator which is coupled directly to
the turbine so that when rotating
turbine generated electricity from the
generator output terminals. Before
turning full / 3000rpm, 8 hours before
using the rotary generator in gear
turning at a speed of 3 rpm for 8
hours. useful to keep the shaft in order
to avoid slack.
Although his fluid cycle is a closed
cycle, but the amount of water in the
cycle would decrease. Water reduction
is caused by leakage whether
intentional or unintentional. To replace
the lost water, it is necessary to add
water into the cycle. Criteria water
enhancer should be the same as the
existing water in the cycle.
Duty cycle power plant that converts
water into steam to superheat steam
expansion in the turbine and then
converted again into water
2.6 Coal Power Plant Fuel System
Coal fuel in coal power plant is as a
primary
fuel.
Coal
supplies
accommodated in the open field (coal
stock area) and to serve the needs of
combustion in boilers, coal bunkers
accommodated at (silos) in each
boiler. The supply of coal from the
bunker to the burner combustion
chamber is done through coal feeder,
mill / pulveriser (PC Boiler), and coal
pipe. Setting and recording the
number of coal flow is done with coal
feeder.
Mill (pulverizer) serves to grind coal to
a powder ( 200 mesh). As for bringing
coal powder into the burner, the
primary air is blown into the mill.
Primary air generated by the Primary
Air Fan (PAF) and before entering the
mill preheated primary air heater
(Primary Air Heater) which is sufficient
to dry the coal powder.
3. FINALITY
3.1 Conclusion
Steam power plant (power plant) is a
plant that rely on the kinetic energy of
the steam to generate electricity.The
main form of this type of power plant is
connected to a turbine generator which
is driven by the kinetic energy of steam /
dry. Steam power plants use a variety of
fuels, especially coal and fuel oil
The process of energy conversion in the
plant progresses through three stages,
namely:
First, the chemical energy in the fuel is
converted into heat energy in the form
of vapor pressure and high temperature.
Second, the thermal energy (steam) is
converted into mechanical energy in the
form of a round.
Third, the mechanical energy is
converted into electrical energy.
Plant uses water working fluid
circulating in a closed steam. Closed
cycle means using the same fluid
repeatedly. The sequence of circulation
in brief is as follows:
1) water filled into the boiler. to fill the
entire surface area of heat transfer.
Water in the boiler is heated with
hot gases of combustion of fuel with
air that turns into steam.
2) the steam boiler output with
production pressure and
temperature are directed to turn a
turbine to generate mechanical
power in the form of a round.
3) generator which is coupled directly
with rotating turbine produces
electricity as a result of the rotating
magnetic field in the coil, so that
when the rotating turbine generated
electricity from the generator output
terminals.
4) Former steam exits the turbine into
the condenser
to be cooled with cooling water in
order to turn back into water called
condensate water. Condensate
water vapor condensation is then
used again as a filler water boiler.
-Thus the cycle continues and
repeated
3.2 Suggestion
Based on the analysis of the
observations made, it can be a few
suggestions for the development of
further research:
We need for additional computer
equipment in its application with the
operating system running so that work
very fast and precise and One way to
improve the professionalism of
teachers is to make simple props that
provide broad success in a learning
BIOGRAPHY (Daftar Pustaka)
1.http://constrengineering.blogspot.co
m/2013/04/pltu-site-paiton.
2.http://farizpembangkitlistrik.blogspot.
com
3.http://Pln-research.blogspot.com
4.http://raka-bsd.blogspot.com
5.http://sideofardeliani.wordpress.com
6.http://candycoffin.blogspot.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Posiflow Benson BoilerDocument8 pagesPosiflow Benson BoilerKarthick VelayuthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Report G.H.T.P, Lehra MohabbatDocument47 pagesTraining Report G.H.T.P, Lehra Mohabbatgoyalz100% (2)
- Energy Audit Book, Module-1Document17 pagesEnergy Audit Book, Module-1vpzfarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocean EnergyDocument7 pagesOcean EnergyhasanPas encore d'évaluation
- TE II Unit1Document31 pagesTE II Unit1Phani TejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summer Training Course: FTR 231 North Cairo Power StationDocument46 pagesSummer Training Course: FTR 231 North Cairo Power Stationkarim gamil100% (1)
- Gvu We' Yr K ' I Cwimsl VB: Solar Gas Hfo HSD Hydro Coal ImportDocument13 pagesGvu We' Yr K ' I Cwimsl VB: Solar Gas Hfo HSD Hydro Coal ImportWahed ImtiazPas encore d'évaluation
- PFD PDFDocument1 pagePFD PDFFajar AgumPas encore d'évaluation
- BioMass Conversion TechnologiesDocument5 pagesBioMass Conversion Technologiessanthoshi durgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrohelp 1 An Excel Program Dection For Hydroelectric Sites 1Document1 pageHydrohelp 1 An Excel Program Dection For Hydroelectric Sites 1amoghimi100% (1)
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 4 PDFMuhammed Bn JihadPas encore d'évaluation
- QB. PPDocument15 pagesQB. PPRajib MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pltu Process OverviewDocument1 pagePltu Process OverviewDimasQiPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Slide - RonyDocument14 pagesFinal Slide - RonyOMar FaruqPas encore d'évaluation
- Mingyung Solar Power System DatasheetDocument19 pagesMingyung Solar Power System DatasheetPieter FouriePas encore d'évaluation
- GSA Report Al Ahsa GovernorateDocument4 pagesGSA Report Al Ahsa GovernorateMohits952Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFDocument1 page1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFsuby100% (1)
- Certificate of Electrical Safety: Prescribed Electrical Installation WorkDocument1 pageCertificate of Electrical Safety: Prescribed Electrical Installation WorkAlamdar HassnainPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler MaintenanceDocument144 pagesBoiler Maintenanceaziz100% (2)
- Chapter 4: The First Law of Thermodynamics For Control Volumes B) Steam Power PlantsDocument8 pagesChapter 4: The First Law of Thermodynamics For Control Volumes B) Steam Power PlantsTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Rec Solar ReferencesDocument22 pagesModule Rec Solar Referenceseltrance81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wuxi Boiler Qualifications 031111Document22 pagesWuxi Boiler Qualifications 031111jokanovPas encore d'évaluation
- 92200-2024 - R0 - Boiler Startup Procedure Without BCPDocument7 pages92200-2024 - R0 - Boiler Startup Procedure Without BCPharry2586Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Rooftop DIY - The Homeowner's Guide To Installing Your Own Photovoltaic Energy SystemDocument281 pagesSolar Rooftop DIY - The Homeowner's Guide To Installing Your Own Photovoltaic Energy SystemMuhammad Naveed100% (1)
- Me6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument1 pageMe6404 Thermal EngineeringKani SelvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternative Sources of EnergyDocument6 pagesAlternative Sources of EnergykagePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2Jehana NaolPas encore d'évaluation
- DS ACPowerBlock A4Document2 pagesDS ACPowerBlock A4edsonleviPas encore d'évaluation
- Net Metering Application Form 1Document3 pagesNet Metering Application Form 1anon-288596100% (2)