Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Point Contact Transistor
Transféré par
Gilberto ManhattanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Point Contact Transistor
Transféré par
Gilberto ManhattanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Point-contact transistor
A point-contact transistor was the rst type of solidstate electronic transistor ever constructed. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter
Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December, 1947.[1] They
worked in a group led by physicist William Shockley. The
group had been working together on experiments and theories of electric eld eects in solid state materials, with
the aim of replacing vacuum tubes with a smaller, less
power-consuming device.
in 1951 that operates as transistors still do, with the low
current input terminal as the base and the two high current output terminals are the emitter and collector.
The critical experiment, carried out on December 16,
1947, consisted of a block of germanium, a semiconductor, with two very closely spaced gold contacts held
against it by a spring. Brattain attached a small strip of
gold foil over the point of a plastic triangle a conguration which is essentially a point-contact diode. He then
carefully sliced through the gold at the tip of the triangle.
This produced two electrically isolated gold contacts very
close to each other.
The point-contact transistor was commercialized and sold
by Western Electric and others but was soon superseded
by the bipolar junction transistor, which was easier to
manufacture and more rugged. Germanium was employed extensively for two decades in the manufacture
of transistors, but was then almost totally replaced by
silicon and other alloyed materials. As of 2012 germanium point-contact diodes continued to be available for
use as radio-frequency detectors.[3] Point-contact diodes
are made of other materials, including silicon, and have
good microwave properties.[4] Research continued as of
2012.[5]
Unlike later semiconductor devices, it was possible for an
amateur to make a point-contact transistor, starting with
a germanium point-contact diode as a source of material (even a burnt-out diode could be used; and the transistor could be re-formed if damaged, several times if
necessary).[2]
1 Forming
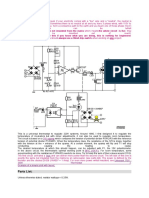
An early model of a transistor
The piece of germanium used had a surface layer with an
excess of electrons. When an electric signal traveled in
through the gold foil, it injected holes (points which lack
electrons). This created a thin layer which had a scarcity A model of the rst commercially available point-contact tranof electrons.
sistor
A small positive current applied to one of the two contacts
had an inuence on the current which owed between
the other contact and the base upon which the block of
germanium was mounted. In fact, a small change in the
rst contact current caused a greater change in the second
contact current, thus it was an amplier. The rst contact is the emitter and the second contact is the collector. The low-current input terminal into the pointcontact transistor is the emitter, while the output high
current terminals are the base and collector. This diers
from the later type of bipolar junction transistor invented
To make a point-contact transistor work, a brief highcurrent pulse was used to fuse the wires to the germanium
and create the P-type material around the point of contact, a technique called 'electrical forming'. Usually this
was done by charging a capacitor of a specied value to a
specied voltage then discharging it between the emitter
and the base electrodes. Forming had a signicant failure
rate, so many commercial encapsulated transistors had to
be discarded; an uncased device as could be made by amateurs could be re-formed if damaged.[2]
1
Characteristics
Some characteristics of point-contact transistors dier
from the later junction transistor:
The common base current gain (or ) of a pointcontact transistor is around 2 to 3, whereas of
bipolar junction transistor (BJT) cannot exceed 1
and the common emitter current gain (or ) of a BJT
is typically between 20 and 200.
Dierential negative resistance.
When used in the saturated mode in digital logic,
they latch in the on-state, making it necessary to remove power for a short time in each machine cycle
to return them to the o-state.
See also
Crystal radio
References
[1] Levine, Alaina G. John Bardeen, William Shockley,
Walter BrattainInvention of the Transistor, 2008,
American Physical Society Retrieved on October 6, 2010
[2] HOME-MADE TRANSISTORS: P B Helsdon, Wirless
World, January 1954. Article starts It is quite practicable
to make point-contact transistors at home which compare
quite well with those advertised by professional manufacturers.
[3] NTE manufacture point-contact germanium diodes 1N34
and NTE110MP (matched pair)
[4] MBT Microwave/RF Semiconductors product Guide, listing several silicon microwave point-contact diodes. Accessed 23 April 2012
[5] Voltage sensitivity of a point-contact GaAs/AlGaAs heterojunction microwave detector, A Suziedelis, S Asmontas, J Kundrotas, V Nargeliene and J Gradauskas,
Phys. Scr.85(2012) 035702 (5pp). Example of ongoing
research into point-contact devices.
External links
The Point-contact Transistor
Picture of the rst transistor ever assembled
(2092x2086)
PBS article
EXTERNAL LINKS
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
6.1
Text
Point-contact transistor Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Point-contact_transistor?oldid=701264436 Contributors: Topory, RTC,
Glenn, Haukurth, Greglocock, Blainster, Murtasa, Wtshymanski, Pol098, DonSiano, Lionelbrits, Ewlyahoocom, Shaddack, Kooky, Tonywalton, Raistolo, Nkendrick, Vicarious, SmackBot, Barney Stratford, Jeomatic, Bdiscoe, Moquist, Rogerbrent, Pinbucket, Anthony22,
Verdy p, WillMak050389, Sskennel, Allstarecho, Transisto, Andy Dingley, Into The Fray, 718 Bot, K2W, Addbot, Magus732, Lightbot,
OlEnglish, Yobot, AnomieBOT, OgreBot, Dalba, EmausBot, K6ka, Wbm1058 and Anonymous: 22
6.2
Images
File:Fcspct.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/a2/Fcspct.jpg License: Cc-by-sa-3.0 Contributors: ? Original artist:
?
File:Question_book-new.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/9/99/Question_book-new.svg License: Cc-by-sa-3.0
Contributors:
Created from scratch in Adobe Illustrator. Based on Image:Question book.png created by User:Equazcion Original artist:
Tkgd2007
File:_.png Source:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7b/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%
D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%B2%D8%B3%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%B1_%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%86%D9%82%D8%B7%
D9%8A.png License: CC-BY-SA-3.0 Contributors: Transferred from en.wikipedia Original artist: Jeomatic at en.wikipedia
6.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- For Other UsesDocument11 pagesFor Other Usesashishsharma_1432Pas encore d'évaluation
- DiodeDocument16 pagesDiodeGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Semiconductor DeviceDocument6 pagesSemiconductor DeviceGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reg. # 2014-ch-215Document20 pagesReg. # 2014-ch-215Atif MehfoozPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory Class 12 Full Exclusive Project CbseDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Class 12 Full Exclusive Project CbseAyu Harshal44% (16)
- Evolution of Microelectronics: (From Discrete Devices To Modern Integrated Circuits - A Brief Review)Document50 pagesEvolution of Microelectronics: (From Discrete Devices To Modern Integrated Circuits - A Brief Review)ARUOS SouraPas encore d'évaluation
- How transistors amplify and switch signalsDocument29 pagesHow transistors amplify and switch signalsS.r.Siddharth45% (20)
- Diode: Navigation SearchDocument15 pagesDiode: Navigation SearchElwin Sam CorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistor PDFDocument14 pagesTransistor PDFMuhammad JameelPas encore d'évaluation
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorferdinando16Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICS Project File Class 12: Categories Top Downloads Login Register UploadDocument17 pagesPHYSICS Project File Class 12: Categories Top Downloads Login Register UploadSaptarshi RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument245 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentb2_coolguy123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics Chapter 1 2Document29 pagesBasic Electronics Chapter 1 2victor kimutaiPas encore d'évaluation
- DiodeDocument21 pagesDiodemcmusbixPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDiode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesTransistor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlwyzz Happie RaamzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode: For Data Diodes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument52 pagesDiode: For Data Diodes, See - For Other Uses, SeenafeesPas encore d'évaluation
- Semiconductor Types and Applications in 40 CharactersDocument16 pagesSemiconductor Types and Applications in 40 Charactersk lightPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode: Tube Diode (Now Rarely Used Except in Some High-Power Technologies) IsDocument16 pagesDiode: Tube Diode (Now Rarely Used Except in Some High-Power Technologies) IsGorishsharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Semiconductor Assignment: Name-Ishant ROLL NO. - 2K18/B12/1588 Submitted To - MR - Deshraj Meena SirDocument12 pagesSemiconductor Assignment: Name-Ishant ROLL NO. - 2K18/B12/1588 Submitted To - MR - Deshraj Meena Sirarnav preetPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of ADocument14 pagesReverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of AVaron MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 - TransistorDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - TransistorPavan G MPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode - WikipediaDocument3 pagesDiode - WikipediaGowtham SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesDiode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamountfestusPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistor MakeDocument6 pagesTransistor Makedwarika2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diode - WikipediaDocument101 pagesDiode - WikipediaMarcinPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics: Evolution and ComponentsDocument33 pagesBasic Electronics: Evolution and ComponentsVarun YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Contents ListDocument27 pagesContents ListBandaru Lakshmi RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode Basics: A Guide to Diode Components and OperationDocument108 pagesDiode Basics: A Guide to Diode Components and OperationSushanta Kumar SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Determine Bestfit TopologyDocument3 pagesDetermine Bestfit TopologyAbraha GebrekidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistor As A Switch: Ali Habeb Aseeri, Fouzeyah Rajab AliDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor As A Switch: Ali Habeb Aseeri, Fouzeyah Rajab AlishahzaibPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanPas encore d'évaluation
- L 1 - Mse628a - 31 7 19Document44 pagesL 1 - Mse628a - 31 7 19Dhanishtha SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Semiconductors: MaterialsDocument5 pagesHistory of Semiconductors: MaterialsGarrette EncomiendaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1materials Laboratory II (MScE 3202)Document42 pages1materials Laboratory II (MScE 3202)XO MusicPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Semiconductor, Its Uses and ApplicationDocument3 pagesTypes of Semiconductor, Its Uses and ApplicationIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- Semiconductor Doping Techniques Surface EngineeringDocument21 pagesSemiconductor Doping Techniques Surface EngineeringRatandeep PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigate (3D) TransistorsDocument19 pagesTrigate (3D) TransistorsPankaj Kumar100% (4)
- History: Vacuum Tube DiodesDocument3 pagesHistory: Vacuum Tube DiodesAsr ARPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Passive ComponentsDocument7 pagesI. Passive Componentsdare beastPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Semiconductor Diodes, Ic, TransistorDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Semiconductor Diodes, Ic, TransistorBlessious Joseph LandoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode: Thermionic Diode Is A Vacuum Tube With Two Electrodes, ADocument24 pagesDiode: Thermionic Diode Is A Vacuum Tube With Two Electrodes, AMarie MythosPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT PresentationDocument24 pagesBJT PresentationzakirecePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics DIODEDocument16 pagesPhysics DIODEr97756598Pas encore d'évaluation
- BXE Practical Journal (Experiment No. 1 To 8) - 1Document55 pagesBXE Practical Journal (Experiment No. 1 To 8) - 1kakashi hatakePas encore d'évaluation
- For Initial ExperimentsDocument2 pagesFor Initial ExperimentsKimberly LeysonPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding InductorsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding InductorsSamreen ChowlkarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify or Switch Electronic Signals and Electrical PowerDocument2 pagesA Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify or Switch Electronic Signals and Electrical PowerGeorge NeagoePas encore d'évaluation
- Point Contact DiodeDocument6 pagesPoint Contact Diodekprk414Pas encore d'évaluation
- Main Functions: Vacuum Tube DiodesDocument2 pagesMain Functions: Vacuum Tube Diodesdwarika2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Active Devices GuideDocument44 pagesMicrowave Active Devices GuideKobid Karkee100% (2)
- Introduction To Vacuum TubesDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Vacuum TubesChrisTPas encore d'évaluation
- Divais MikroelektronikaDocument6 pagesDivais MikroelektronikaFaiza Abu RizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Test Eee 2023Document4 pagesSample Test Eee 2023Nguyễn Ngọc TùngPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Electromagnetic: W. L. BarrowDocument31 pagesTransmission Electromagnetic: W. L. BarrowMurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- TransistorDocument22 pagesTransistorRahul DevPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsD'EverandTransistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 22Document1 pageRadical 22Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 21Document1 pageRadical 21Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 21Document1 pageRadical 21Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 15Document1 pageRadical 15Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 12Document1 pageRadical 12Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 20Document1 pageRadical 20Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 19Document1 pageRadical 19Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 16Document1 pageRadical 16Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 19Document1 pageRadical 19Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 18Document1 pageRadical 18Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 17Document1 pageRadical 17Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 14Document1 pageRadical 14Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 6Document1 pageRadical 6Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 10Document1 pageRadical 10Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 13Document1 pageRadical 13Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- RectifierDocument14 pagesRectifierGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 11Document1 pageRadical 11Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 9Document1 pageRadical 9Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- SnubberDocument3 pagesSnubberGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 7Document1 pageRadical 7Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 4Document1 pageRadical 4Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 8Document1 pageRadical 8Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical 3Document1 pageRadical 3Gilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument4 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifierGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- DimmerDocument7 pagesDimmerGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Barrier TransistorDocument6 pagesSurface Barrier TransistorGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Saturable ReactorDocument2 pagesSaturable ReactorGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amorphous Solids ExplainedDocument3 pagesAmorphous Solids ExplainedGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyristor: AnodeDocument7 pagesThyristor: AnodeGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Photo CathodeDocument3 pagesPhoto CathodeGilberto ManhattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Airpro Fan Drawing ApprovalDocument1 pageAirpro Fan Drawing ApprovalPatricio AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- JBL - Ctrl14C - T v1 PDFDocument2 pagesJBL - Ctrl14C - T v1 PDFashielaniePas encore d'évaluation
- Distortion - Based On The JHS® Andy Timmons™Document4 pagesDistortion - Based On The JHS® Andy Timmons™ZalPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.protection Components RelaysDocument66 pages6.protection Components RelaysRian KamekPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Parts List ForDocument154 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Parts List ForFred WestlingPas encore d'évaluation
- 1485-In001 - En-P KwikLink General Purpose DeviceNet Media Installation InstructionsDocument4 pages1485-In001 - En-P KwikLink General Purpose DeviceNet Media Installation InstructionsjosePas encore d'évaluation
- ACr63-r315L-TUV IT 14 ATEX-050X Eng - Rev.7Document19 pagesACr63-r315L-TUV IT 14 ATEX-050X Eng - Rev.7ratheesh vidyadharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Catálogo EZ-LightDocument4 pagesCatálogo EZ-Lightbrunonunes2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cigre 812Document108 pagesCigre 812NamLe100% (4)
- NYT ZJ40DBST Drilling Rig Communication System Operation ManualDocument28 pagesNYT ZJ40DBST Drilling Rig Communication System Operation ManualJohn SimancaPas encore d'évaluation
- SRP (540 555) BMA BG - Frame - 182 - ENDocument2 pagesSRP (540 555) BMA BG - Frame - 182 - ENYilin TeoPas encore d'évaluation
- GE Quartzline Lamps Brochure 1960Document8 pagesGE Quartzline Lamps Brochure 1960Alan MastersPas encore d'évaluation
- CsirkekeltetőDocument2 pagesCsirkekeltetőklauszpeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Shutdown SystemDocument101 pagesEmergency Shutdown SystemAmiruddin Abdul RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- 1993 MR2 Wiring Diagram GuideDocument189 pages1993 MR2 Wiring Diagram GuideHamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machine - Mechatronics - EPEG 2013Document3 pagesElectrical Machine - Mechatronics - EPEG 2013Pra GoPas encore d'évaluation
- S280-43-1 150 2015-12-06Document24 pagesS280-43-1 150 2015-12-06Ratana Kem100% (1)
- L&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection ChartsDocument48 pagesL&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection Chartsrdeepak99100% (7)
- Main Generator MaintenanceDocument9 pagesMain Generator MaintenanceAkli Djebbari100% (1)
- Requirements:: Sudo Nano Led - PyDocument5 pagesRequirements:: Sudo Nano Led - PyNivedan LiyePas encore d'évaluation
- Easy UPS 3M For External Batteries Battery RuntimesDocument2 pagesEasy UPS 3M For External Batteries Battery RuntimesJesus Enrique Anaya100% (1)
- Harley Benton PowerPlant ISO-2 Pro User ManualDocument1 pageHarley Benton PowerPlant ISO-2 Pro User ManualPredrag IvanovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Aqualis2 CARTA ELECTRONICA TRIFASICA MCI25CH-IDocument7 pagesAqualis2 CARTA ELECTRONICA TRIFASICA MCI25CH-IJOSESAMBORAPas encore d'évaluation
- B01-TB16I-003 - TB16IN Basic Installation Instructions - ENG - V1.2Document2 pagesB01-TB16I-003 - TB16IN Basic Installation Instructions - ENG - V1.2Kien Nguyen TrungPas encore d'évaluation
- Eet 3454 Electrical Machine Drives CompleteDocument138 pagesEet 3454 Electrical Machine Drives Completeblessedgeraldie78Pas encore d'évaluation
- C3153Document4 pagesC3153luisoasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Clean Agent (Fm-200) Fire Suppression System Checklist: Project Location System: DateDocument7 pagesClean Agent (Fm-200) Fire Suppression System Checklist: Project Location System: DateCenon Cyrus JustaleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Transformers: Support TypeDocument5 pagesCurrent Transformers: Support Type『ɠl』 ༒հedocᛝPas encore d'évaluation
- ReneSola Micro Replus Inverters Improve PV HarvestingDocument2 pagesReneSola Micro Replus Inverters Improve PV HarvestingDario del AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Features Description: Toy Motor Driver Series MX214Document8 pagesFeatures Description: Toy Motor Driver Series MX214jaluadiPas encore d'évaluation