Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stock Price Valuation Method
Transféré par
Anika MafizCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stock Price Valuation Method
Transféré par
Anika MafizDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Chapter-1
Page
Introduction
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
This course Financial Market and Institution ( F-304) shows the importance of importance
of financial markets and institution in the present era. The stock market activities and
procedure is thoroughly discussed in this course .To understand the stock pricing valuations
from practical viewpoint, we discussed in this report about various ways of valuation
methods for stock of Singer BD and factors that affect the Singer , BDs stock prices
1.1 Origin of the report
This report is prepared for Dr. M. Farid Ahmed , Professor, Course teacher of Financial
Markets and Institutions, Course # F-304, Faculty of Business Studies at University of
Dhaka as a partial requirement of the course. Our course instructor has assigned us, to make
report on Stock Valuation Methods and Factors Affecting Stock Prices And for this
purpose we implement our theoretical knowledge of stock valuation methods and factors
affecting stock prices over Singer Bangladesh. This report is prepared during the 1st
semester, 3rd Year and would be submitted in the same semester. The standard procedure for
the long, formal report is followed here as part of the instruction of the course instructor.
1.2 Objective of this report
The primary objective of the report is to fulfill the partial requirement of the course.
The secondary objectives of this report are to:
owledge about stock valuation methods.
1.3 Methodology
The type of methods used in this report is mainly of a descriptive nature. Mainly secondary
Page
Secondary Data Collection:
data analysis was selected as the basic research method.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Certain data for this report has been extracted from secondary sources, since the descriptive
nature of the study to prepare this report calls for existing facts and information compilation.
1.4 Limitations
Although we have tried our level best to prepare a fault free report by valuing stock for
previous several years. But because of our lack of professional knowledge we may make
some unintentional mistakes in case of interpreting the ratios. We are also unable to some
extent to understand the firms management policy in case of internal important executive
Page
decisions which may affect the interpretation
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Chapter-2
Page
Theoretical overview
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
2.1 Stock Valuation Method:
Investors conduct valuations of stocks when they make their investment decisions. They
consider investing in undervalued stock and selling their holdings of stock that are considered
to be overvalued. There are many different methods of valuing stocks. They are:
Price-Earnings (PE) method:
A relatively simple method of valuing a stock is to apply the mean price earnings
ratio of all publicly traded competitors in the respective industry to the firms
expected earnings for the next year.
Valuation per share= (Expected earnings per share Mean industry PE ratio)
The logic behind this method is that future earnings are an important determinant of a
firms value. Although earnings beyond the next year are also relevant, this method
implicitly assumes that the growth in earnings in future years will be similar to that of
industry.
Limitation of PE method: The PE method may result in an inaccurate valuation for a
firm if errors are made in forecasting the firms future earnings or in choosing the
industry composite used to derive the PE ratio.
Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
It was developed by John B. Williams in 1931. He stated that the price of a stock
should reflect the present value(PV) of the stocks future dividends, or
Price =
Dn
(1+r)n
Where, n = period
Dn = Dividend in t period
r = Discount rate
Limitation of Dividend Discount Model: The DDM may result in an inaccurate
valuation for a firm if errors are made in determining the dividend to be paid over the
next year or in the growth rate or the required rate of return. The limitations of this model
are more pronounced when valuing firms that retain most of their earnings, rather than
Page
the growth rate.
distributing them as dividend, because the model relies on the dividend base for applying
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Adjusted Dividend Discount Model: The dividend discount model can b adapted to
assess of any firm, even those that retain most or all of their earnings. From the
investors perspective , the value of the stock is
(1) The PV of the future dividends to be received over the investment horizon,
(2) The PV of the forecasted price at which the stock will be sold at the end of
the investment horizon
Limitation of Adjusted Dividend Discount Model: The Adjusted Dividend
Discount Model may result in an inaccurate valuation for a firm if errors are made in
deriving the PV of dividends over the investment horizon or the PV of the forecasted
price at which the stock can be sold at the end of the investment horizon. The required
rate of return may also lead to error.
Free Cash Flow:
For firms that do not pay dividends, a more suitable valuation may be the free cash
flow model, which is based on the PV of future cash flows.
Step-1: estimate the free cash flow that will result from operations;
Step-2: subtract existing liabilities to determine the value of the firm
Step-3: divide the value of the firm by the number of shares to derive a value
per share
Limitations of Free Cash Flow: The limitation of this model is the difficulty of
obtaining an accurate estimate of free cash flow per period. One possibility is to start
with the forecasted earnings and then add a forecast of the firms noncash expenses
and capita; investment and working capital investment required to support the growth
in the forecasted earnings. Obtaining accurate earnings forecast can be difficult .The
flexibility of the accounting rules can major errors in estimating free cash flow based
on earnings.
2.2 Determining Required Rate of Return to Value Stocks:
When investors attempt to value a firm based on discounted cash flows, they must determine
the required rate of return. Investors require a rate of return that reflects the risk free rate plus
a premium. Two most commonly used model to determine the required rate of return are
Page
given below:
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM):
It is used to estimate the rate of return for any firm with publicly traded stock. It only
considers systematic risk. It suggest that the return of an asset is influenced by the risk
free rate, the market return and the covariance between the risk free rate and the
market return.
Rj = Rf + (Rm-Rf)
Where, Rj = Required rate of return
Rf = Risk free rate
Rm = Market return
= Beta, reflects the sensitivity of the stocks return to the markets
overall return
Limitation of CAPM: Beta is the main driver of the CAPM method. Generally, the
high beta firms outperformed low-beta firms during market upswings. Again the low
beta firms perform better than the high-beta firms during market downswings. So, the
rate of return highly depends on the beta.
Arbitrage Pricing Model (APT):
It suggests that a stocks price can be influenced by a set of factors in addition to the
market. These factors can be economic growth, inflation, and other variables that
could systematically affect the stock prices.
E(R) = B0 +
=
Where, E(R) = expected return of asset
B0 = a constant
Fi.Fm = values of factors 1 to m
Bi = sensitivity of the asset return to particular force
The main disadvantage of APT is that it is not as well defined as CAPM. These
characteristics could be perceived as an advantage, however, since it allows investors
particular firm.
to include factors which are relevant in deriving the required rate of return for a
Page
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
2.3 Factors that affect stock prices:
Many factors can cause the price of a stock to rise or fall from specific news about a
companys earnings to a change in how investors feel about the stock market in general.
Stock prices are driven by three types of factors:
1. Economic Factors,
2. Market-related Factors and
3. Firm-specific factors.
All the major three factors are described below:
2.3.1. Economic Factors:
A firms value should reflect the present value of its future cash flows. Investors consider
various economic factors that affect a firms cash flows when valuing a firm to determine
whether its stock is over or undervalued. Basically economic growth, interest rates and
exchange rate value are major economic factors.
i.
Impact of economic growth:
An increase in economic growth is expected to increase the demand for products and
services produced by firms and therefore increase a firms cash flows and valuation.
Participants in the stock market monitor economic indicators such as employment, gross
domestic products, retail sales, and personal income because this indicators may signal
information about economic growth and therefore affect cash flows. In general,
unexpected favorable information about the economy tends to cause a favorable revision
of a firms expected cash flows and therefore places upward pressure on the firms value.
Because the government fiscal and monetary policies affect economic growth, they are
also continually monitored by investors. If it looks like the economy is going to expand,
stock prices may rise. Investors may buy more stocks thinking they will see future profits
and higher stock prices. If the economic outlook is uncertain, investors may reduce their
Page
buying or start selling.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
ii.
Impact of Interest rates:
The Bangladesh bank can raise or lower interest rates to stabilize or stimulate the
Bangladesh economy. This is known as monetary policy. If a company borrows money
to expand and improve its business, higher interest rates will affect the cost of its debt.
This can reduce company profits and the dividends it pays shareholders. As a result, its
share price may drop. And, in times of higher interest rates, investments that pay interest
tend to be more attractive to investors than stocks.
iii.
The value of the Bangladeshi Taka:
Many Bangladeshi companies sell products to buyers in other countries. If the
Bangladeshi taka rises, their customers will have to spend more to buy Bangladeshi
goods. This can drive down sales, which in turn can lead to lower stock prices. When the
price of the Bangladeshi taka falls, it makes it cheaper for others to buy our products. This
can make stock prices raise.
2.3.2. Market related factors:
Market related factor also drive stock prices these factors include stock include investors
sentiment and January effect.
i.
Investors sentiment:
Investor sentiment or confidence can cause the market to go up or down, which can cause
stock prices to rise or fall. Since the stock valuations reflect expectations in some periods
the stock market performance is not highly correlated with existing economic conditions.
For example, even though the economy is weak stock prices may rise if most investors
expect that the economy will improve in the near future. That is there is a positive
sentiment because of optimistic expectations. The general direction that the stock price
takes can affect the value of a stock:
Bull market a strong stock market where stock prices are rising and investor
well as investor optimism
confidence is growing. It's often tied to economic recovery or an economic boom, as
Page
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Bear market a weak market where stock prices are falling and investor confidence
is fading. It often happens when an economy is in recession and unemployment is
high, with rising prices.
ii.
January effect:
The January effect is a hypothesis that there is a seasonal anomaly in the financial market
where securities' prices increase in the month of January more than in any other month.
Because many portfolio managers are evaluated over the calendar year, they tend to
invest in riskier small stocks at the beginning of the year and shift to larger companies
near the end of the year to lock in their gains. This tendency places upward pressure on
small stocks in January of every year, causing the so called January effect. Some studies
have found that most of the annual stock market gains occur in January. Once investors
discover the January effect they attempted to take more positions in the prior month. This
has placed upward pressure on stocks in mid- December, causing the January effect to
begin in December.
2.3.3. Firm-Specific Factors:
A firms industry sales forecasts, entry into the industry by new competitors, and price
movements of the industrys products etc. factors also affect stock price. Stock market
participants focus on these specific factors of a firm which may cause a revision in the
expected cash flows to be generated by that firm. Some firm-specific factors arei.
Dividend Policy changes:
An increase in dividends may reflect the firms expectation that it can more easily afford
to pay dividends. A decrease in dividends may reflect that it will not have sufficient cash
flows.
ii.
Earnings Surprises:
Earnings are used to forecast a firms future cash flows. When a firms announced
earnings are higher than expected, some investors raise their estimates of the firms future
iii.
Acquisitions and Divestitures:
Page
they revalue its stock downward.
10
cash flows and revalue its stock upward. If announced expected earnings are lower than
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
The expected acquisition of a firm increases its demand for targets stock and therefore
raises the stock price. But this effect is less clear, as it depends on the perceived synergies
that could result from acquisition. On the other hand, divestitures tend to be regarded as a
favorable signal about a firm if the divested assets are unrelated to the firms core
business. This indicates that firm intends to focus on its core business.
Expectations:
Investors attempt to anticipate new policies so that they can make their move in the
market before other investors. These help them to pay a lower price for a specific stock or
sell the stock at a higher price. But investors may not properly anticipate the firms
11
policies based on incomplete information.
Page
iv.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Chapter-3
Page
12
Practical overview
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
3.1. Price Earnings ratio:
Earnings per share in 2014= 219
Earnings per share in 2013= 186.8
Growth rate, g= 17.24%
Expected earnings per share= 256.75
Mean industry PE ratio= 30.12
Valuation per share= (Expected earnings per share Mean industry PE ratio)
= (256.75 30.12)
= BDT 7733.33
3.2. Capital Asset pricing model (CAPM):
CAPM suggests that the rate of return is influenced by the prevailing risk free rate (Rf), the
market return (RM) and beta ().
Rf =0.04
= .87
RM = (Market return- Risk free rate)
= (.0.215 - .04)
= 0.175
Rate of return= Rf + (RM-Rf)
= 0.19225
= 19.23%
3.3. Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
Dividend per share in 2013= 21
Page
Price=Expected dividend/ (Discount rate- growth rate)
13
In this case, the price of the stock depends on the expected dividend, growth rate and discount
rate.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Dividend per share in 2014, D0= 22
Growth rate, g= (22-21)/21 = 4.761%
Expected dividend in 2015, D1= 23.05
Discount rate, r = 9.04%
Price= D1/(r-g)
= 23.05/ (.094-.04761)
=BDT 538.19
3.4. Adjusted Dividend Discount Model:
To forecast the price at which the stock can be sold, investors estimate the companys
earnings per share in the year they plan to sell the stock. This estimate is derived by applying
an annual growth rate to the prevailing annual earnings of the share. Then, the estimate can
be used to derive the expected price per share at which the stock can be sold.
Now, lets assume an investor wants to sell his stock at the end of third year.
Earnings per share in 2014= 219
Earnings per share in 2013= 186.8
Growth rate, g= 17.24%
Earnings per share in three years=EPS (1+g) ^3
=219 (1+.1724)
= 352.90
Stock price in three years= EPS in three years PE ratio of industry
= 352.90 30.12
= 10629.21
Year-1
22
0.090
1.090
1.090
20.175
Year-2
22
0.090
1.090
1.189
18.502
Year-3
22
0.090
1.090
1.297
16.967
Page
Accounts
Dividend
R
1+r
(1+r)^n
Dividend/(1+r)^n
14
PV of stock:
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
PV of Stock= 20.175 + 18.502 + 16.967 + (10629.21/1.297)
= BDT 8253.31
3.5. Factors that affect stock prices of Singer Bangladesh:
Many factors cause the price of a stock of singer BD to rise or fall from specific news about
a companys earnings to a change in how investors feel about the stock market in general.
Stock prices of Singer BD are driven by given factors:
3.5.1. Economic Factors:
A firms value should reflect the present value of its future cash flows. Investors consider
various economic factors that affect a firms cash flows when valuing a firm to determine
whether its stock is over or undervalued.
Impact of economic growth:
If it looks like the economy is going to expand, stock prices of singer BD rise. Investors buy
more stocks of Singer BD thinking they will see future profits and higher stock prices. If the
economic outlook is uncertain, investors reduce their buying or start selling the stocks of
singer BD.
Impact of Interest rates:
The Bangladesh bank can raise or lower interest rates to stabilize or stimulate the Bangladesh
economy. This is known as monetary policy. If a company borrows money to expand and
improve its business, higher interest rates will affect the cost of its debt. This can reduce
company profits and the dividends it pays shareholders. As a result, its share price may drop.
And, in times of higher interest rates, investments that pay interest tend to be more attractive
to investors than stocks.
prices will also often lead to higher interest rates. For example, the Bangladesh Bank may
Page
Inflation means higher consumer prices. This often slows sales and reduces profits. Higher
15
Impact of Inflation:
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
raise interest rates to slow down inflation. These changes will tend to bring down stock
prices. Commodities however, may do better with inflation, so their prices may rise.
Impact of Deflation:
Falling prices tend to mean lower profits for companies and decreased economic activity.
Stock prices may go down, and investors may start selling their shares and move to fixedincome investments like bonds. Interest rates may be lowered to encourage people to borrow
more. The goal is increased spending and economic activity. The Great Depression (19291939) was one of the worst periods of deflation ever.
Impact of Economic and political shocks:
Changes around the world can affect both the economy and stock prices. For example, a rise
in energy costs can lead to lower sales, lower profits and lower stock prices. An act of
terrorism can also lead to a downturn in economic activity and a fall in stock prices.
Impact of Changes in economic policy:
If a new government comes into power, it may decide to make new policies. Sometimes these
changes can be seen as good for business, and sometimes not. They may lead to changes in
inflation and interest rates, which in turn may affect stock prices.
The value of the Bangladeshi Taka:
Many Bangladeshi companies sell products to buyers in other countries. If the Bangladeshi
taka rises, their customers will have to spend more to buy Bangladeshi goods. This can drive
down sales, which in turn can lead to lower stock prices. When the price of the Bangladeshi
taka falls, it makes it cheaper for others to buy our products. This can make stock prices raise.
3.5.2. Market related factors:
Market related factor also drive stock prices these factors include stock include investors
Page
Investor sentiment:
16
sentiment and January effect.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Investor sentiment or confidence can cause the market to go up or down, which can cause
stock prices to rise or fall. Since the stock valuations reflect expectations in some periods the
stock market performance is not highly correlated with existing economic conditions. Even
though the economy is weak stock prices of Singer BD rise sometimes if most investors
expect that the economy will improve in the near future. That is there is a positive sentiment
because of optimistic expectations
January effect:
The January effect is a hypothesis that there is a seasonal anomaly in the financial market
where securities' prices increase in the month of January more than in any other month the
prior month. This has placed upward pressure on stocks in mid- December, causing the
January effect to begin in December. But its impact is not so much severe in case of Singer
BD in Bangladesh
3.5.3. Firm-Specific Factors:
There are some conditions within the companys own industry than to general economic
conditions, these are known as firm-specific factors.
Dividend:
After the announcement of a dividend the stock price may increase by an amount close to the
dividend per share value. However, the stock price may drop on the ex-dividend date by the
dividend per share amount. Investors are looking forward to the AGM (Annual General
Meeting) to get lucrative dividend declaration.
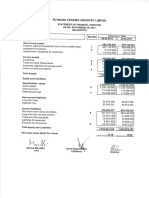
Dividend per share
2014
219.00
22.00
2013
186.80
21.00
2012
164.00
15.00
2011
287.40
3.00
2010
716.90
67.50
17
Market value per share
Page
Year
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
The company declares 195% cash dividend and 25% stock dividend constantly. Here we can
see that the stock price is reflected by the change in dividend payment. As of 2013 data, the
dividend per share increases to 21.00 from 15.00 and the market value per share increases
from 164.00 to 186.80. In 2014 the dividend per share is 22.00 and market value per share is
219.00. So, we can say that the market value per share data is consistent with the dividend
per share data.
Earnings surprises:
Expectation about earnings and future earnings affect Singer BDs stock price. Investors
monitor closely the P/E ratio, EPS, ROI, and R/E to accurately value the company. These
ratios provide the investors with the future expected cash flow of the company. Base on their
expectation, investors value the Singer BDs stock price.
The higher P/E ratio is the greater investors confidence. If the price of the share is too much
lower than the earning of the company, the stock is undervalued and it has the potential to
rise in the near future and vice versa. EPS helps decide the health of the company and
influence the buying tendency in the market. And Net income is the reason of high dividend
and important determinant, because expected dividend depends on it.
Takeover or Merger or change in Management:
Company being taken-over or company taking over another is anticipated to get a stock price
boost or drop in its share price. And any change in the management of Singer BD cause the
Page
18
stock price to fluctuate.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Conclusion
Finally we can say that valuation is very important for a company. The stock price of a
company represent it current market condition. Here we follow several methods for valuating
Singer BDs stock. We basically use CAPM, PE ratio and Dividend Discount Model for its
stock valuation. Each of the methods are important for valuation. And there are some macro
and micro economic factors that affect the price of a stock. The stock price of Singer BD is
also affected by such factors like economic factors, market related factors and firm specific
factors. We have learnt that how much each of the factors affect the market price of Singer
Page
19
BD stock. Inflation, deflation, exchange rate also influence the stock prices.
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Reference:
20
Financial Markets and Institutions
Jeff Madhra, 8th edition
www.investopedia.com
www.singerbd.com
Page
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Page
21
Appendix
Page
22
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Page
23
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Page
24
Stock Price Valuation Method and Factors Affecting Stock Prices
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Fuwangcer Q12018Document4 pagesFuwangcer Q12018Anika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- UGSFL-Annual Report-2014-15Document62 pagesUGSFL-Annual Report-2014-15Anika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Dividedn PolicyDocument36 pagesDividedn PolicyAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking Main ReportDocument21 pagesBanking Main ReportAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Detereminants of International TradeDocument46 pagesDetereminants of International TradeAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking Main ReportDocument21 pagesBanking Main ReportAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking Main ReportDocument21 pagesBanking Main ReportAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio of Singer BDDocument2 pagesRatio of Singer BDAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To Our PresentationDocument34 pagesWelcome To Our PresentationAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio of Singer BDDocument2 pagesRatio of Singer BDAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting ReportDocument34 pagesAccounting ReportAnika MafizPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Accenture FinalDocument7 pagesAccenture FinalFlori May Casakit100% (1)
- MSTC Final Exam 2017Document13 pagesMSTC Final Exam 2017Elis KomariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Port Pricing PDFDocument86 pagesPort Pricing PDFMw. MustolihPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Berkshire Hathaway Dividend Policy ParadigmDocument9 pagesCase Berkshire Hathaway Dividend Policy ParadigmHugoPas encore d'évaluation
- p2 - Guerrero Ch13 PDF Cost of Goods Sold IDocument4 pagesp2 - Guerrero Ch13 PDF Cost of Goods Sold IAl BertPas encore d'évaluation
- ME Ebay Case Study Notes by Renu & AvaniDocument4 pagesME Ebay Case Study Notes by Renu & AvaniNawazish KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Jakarta Post - April 5, 2017Document24 pagesThe Jakarta Post - April 5, 2017kesia78Pas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL GRP 7Document26 pagesFINAL GRP 7Louise AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Eway Bill 92Document19 pagesEway Bill 92Pranav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRM-CLASSWORK - 11th JuneDocument2 pagesDRM-CLASSWORK - 11th JuneSaransh MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dqs389-Interim PaymentDocument31 pagesDqs389-Interim Paymentillya amyraPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Strategy Starbucks IndiaDocument5 pagesMarketing Strategy Starbucks IndiaMohammad Imad Shahid Khan100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document8 pagesAssignment 3Syeda Umyma FaizPas encore d'évaluation
- Emerging Concepts in CostDocument66 pagesEmerging Concepts in CostShravan Kumar DevulapallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Plan Presentation on Jaul Green Coconut WaterDocument18 pagesMarketing Plan Presentation on Jaul Green Coconut WaterShelveyElmoDias100% (2)
- Sec 17.0 MC OligopolyDocument4 pagesSec 17.0 MC OligopolyVi Khuu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- ICICIdirect Model Portfolio ProductDocument54 pagesICICIdirect Model Portfolio ProductPrerna GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Shawarma 1Document25 pagesShawarma 1Leonel VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tybms - International MarketingDocument22 pagesTybms - International MarketingRithik ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- FeasibDocument5 pagesFeasibEnna Jane VillarinaPas encore d'évaluation
- AR AR FinancingDocument34 pagesAR AR FinancingDannis Anne RegajalPas encore d'évaluation
- MTP 8 32 Questions 1684842817Document17 pagesMTP 8 32 Questions 1684842817Sudeep kPas encore d'évaluation
- Belvilla en - Rent Out Your Holiday Home SuccessfullyDocument4 pagesBelvilla en - Rent Out Your Holiday Home SuccessfullyMartijn VerhoevenPas encore d'évaluation
- Foreign currency futures and options explainedDocument27 pagesForeign currency futures and options explainedBunyamin JosoephPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of China's Primary Wood Products Market (Minli Wan) PDFDocument129 pagesAnalysis of China's Primary Wood Products Market (Minli Wan) PDFthaonguyen1993Pas encore d'évaluation
- History of Tawara Mining: Report Produced By: Cristian Andres Salamanca ArevaloDocument2 pagesHistory of Tawara Mining: Report Produced By: Cristian Andres Salamanca ArevaloCristian Andres Salamanca ArevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Law On Supply and Demand ExamDocument6 pagesLaw On Supply and Demand ExamSharah Del T. TudePas encore d'évaluation
- "Micro-Finance Management & Critical Analysis in India": A Project Report OnDocument61 pages"Micro-Finance Management & Critical Analysis in India": A Project Report OnAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Commodity Money: Money Derived from CommoditiesDocument5 pagesCommodity Money: Money Derived from Commoditieshasan jamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Value Added TaxDocument6 pagesValue Added Taxarjohnyabut80% (10)