Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
MBA FMGT Exam Formula Sheet 7th and 6th Edn Users - With Cover Sheet
Transféré par
tobyTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MBA FMGT Exam Formula Sheet 7th and 6th Edn Users - With Cover Sheet
Transféré par
tobyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MBA FMGT Formula Sheet
APPROVED READING
Titman, S, Martin, T, Keown, AJ & Martin, JD 2016, Financial management:
principles and applications, 7th edn, Pearson Australia, Victoria.
Petty, JW, Titman, S, Keown, AJ, Martin, T, & Martin, JD 2012, Financial
management: principles and applications, 6th edn, Pearson Australia, New
South Wales.
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA
Copyright Regulations 1969
WARNING
This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Australian Institute of Business pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act).
The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any
further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of
copyright protection under the Act.
Do not remove this notice.
MBA FINANCIAL MANAGMENT
Exam Formula Sheet
Please note: This sheet contains formulas for users of the 7th edition textbook.
Operating profit = Total revenue (Total variable cost-Total fixed cost) = 0
F
Accounting Break-even Point: = PV
Accounting Break-even Sales:
FD
Cash Break-even Point: = PV
Net Working Capital = Current assets- Current liabilities
Operating Cycle = Inventory conversion period + Average collection period
Accounts Payable Deferral Period =
365
Cash Conversion Cycle = Operating cycle Accounts payable deferral period
Inventory Conversion Period =
Inventory Turnover Ratio =
365
Average Collection Period =
/365
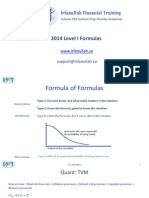
Future Value:
FVn = PV(1 + i)n or using PV tables FVn = PV(FVIFi,n)
Present Value:
PV = FVn / (1 + i)n or using PV tables PV = FVn(PVIFi,n)
Future Value of an ordinary annuity:
or using PV tables FVn = PMT (FVIFA i,n)
Present Value of an ordinary annuity:
or using PV tables PV = PMT (PVIFA i,n)
th
Formulas for the 7 edition textbook are continued on the next page.
Australian Institute of Business. 18MAR16
th
Formulas for the 7 edition textbook continued.
Present Value of a perpetuity: PV = PMT/i
Bond Value:
or
or using PV tables
Valuation of ordinary shares Constant dividend growth rate model:
VE = D1/ (RE-g) or VE = D0 (1 + g) / (RE -g)
Preference share valuation:
VP =
Annual Dividend (D)
Required rate of return (R)
Expected Rate of Return:
E(r) = Pr(r1) x r1 + Pr(r2) x r2 + + Pr(rn) x rn
Standard Deviation:
Portfolio Expected Rate of Return:
E(rportfolio) = (W1 E(r1)) + (W2 E(r2)) + + (Wn E(rn))
Portfolio Standard Deviation:
CAPM equation:
Expected return on risky asset j = E(rasset j) = rf + asset j ( E(rm) rf )
Net Present Value:
1
2
NPV = CF0 + (1+)
1 + (1+)2 + . + (1+)
Profitability Index:
PI =
1
(1+)1
2
+(1+)
2 + .+(1+)
Internal Rate of Return:
CF0 + (+)
+ (+) + . + (+) =0
Weighted Average Cost of Capital:
WACC = (kD (1-t) WD) + ( kP Wp ) + ( kE WE)
Australian Institute of Business. 18MAR16
MBA FINANCIAL MANAGMENT
Exam Formula Sheet
Please note: This sheet contains formulas for users of the 6th edition textbook.
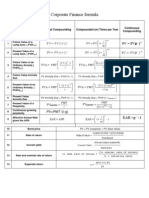
Break-even point:
Break-even point sales revenue:
The EOQ model:
Total Inventory Costs: CQ / 2 + SO / Q
Future Value: FVn = PV(1 + i)n or using appendix FVn = PV(FVIFi,n)
Present Value: PV = FVn / (1 + i)n or using appendix PV = FVn(PVIFi,n)
Future Value of an ordinary annuity:
or using appendix FVn = PMT (FVIFA i,n)
Present Value of an ordinary annuity:
or using appendix PV = PMT (PVIFA i,n)
Perpetuity: PV = PMT/i
Bond Value:
or
or using appendix
Annual Dividend (D)
Preference share valuation: VP = Required rate of return (R)
Valuation of ordinary shares Single Holding Period: VE = D1/(1+RE) + P1 /(1+RE)
Valuation of ordinary shares Multiple Holding Period:
VE = D1/ (RE-g) or VE = D0 (1 + g) / (RE -g)
The Fisher Effect: 1 + i = (1 + R) (1 + r);
i = R + r + rR
Holding Period Return or Historical Return: Rt = (Pt / Pt-1) 1
Expected Return: R* = P(R1) x R1 + P(R2) x R2 + + P(Rn) x Rn
Average Return:
=1
= (R1+R2+ +Rn)/n
th
Formulas for the 6 edition textbook are continued on the next page.
Australian Institute of Business. 18MAR16
th
Formulas for the 6 edition textbook continued.
Standard Deviation:
Security Beta: j = jm x j/m
Portfolio Beta: portfolio = =1(percentage invested in stock j) x ( of stock j)
CAPM: Rj = Rf + j ( Rm Rf )
n
Net Present Value: NPV ACF t IO
t
(1 k )
t 1
n
Profitability Index:
ACF t
(1 k )
PI
t 1
IO
n
Internal Rate of Return: IO
t 1
ACFt
(1 IRR ) t
n
( AP )
Accounting Rate of Return:
t 1
ARR
n
( IO ESV )
2
Market price of debt: P0 I t ( PVIFARd ,n ) $M ( PVIFRd ,n )
n
t
Before-tax cost of debt: NP0 (1 K
t 1
d , BT
M
(1 K d , BT ) n
After-tax cost of debt: K d , AT K d , BT (1 T )
Before-tax cost of preference shares:
K d , BT
D /(1 T )
NP0
D
After-tax cost of preference shares: K d , AT NP
0
Cost of ordinary equity dividend growth model: RE
Before-tax cost of retained earnings: RE , BT
D (1 g )
D1
g 0
g
P0
P0
D0 (1 g ) /(1 T )
g
VE
Cost of retained earnings by CAPM approach: RE R f ( Rm R f )
Before-tax cost of ordinary equity new share issue: K E , BT
D0 (1 g ) /(1 T )
g
NP0
After-tax cost of ordinary equity new share issue K E , AT D0 (1 g ) g
NP0
Australian Institute of Business. 18MAR16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- EM302 Formula Sheet 2013Document4 pagesEM302 Formula Sheet 2013Jeff JabePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 - Leverage - Text and End of Chapter Questions - 1Document39 pagesChapter 12 - Leverage - Text and End of Chapter Questions - 1naimenimPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceDocument6 pagesFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemPas encore d'évaluation
- MGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Document13 pagesMGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Farhan UL HaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Management FormulasDocument9 pagesFinancial Management FormulasTannao100% (1)
- CFA Level I Formula SheetDocument27 pagesCFA Level I Formula SheetAnonymous P1xUTHstHT100% (4)
- Chapter 2 Part 1 of 2 PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Part 1 of 2 PDFASAD ULLAHPas encore d'évaluation
- E V: A A P: Perceived MispricingDocument19 pagesE V: A A P: Perceived MispricingHeidi HCPas encore d'évaluation
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocument12 pagesPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i ISyed Abdul Mussaver ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Finance NoteDocument19 pagesFinance NoteHui YiPas encore d'évaluation
- FormulasDocument7 pagesFormulaskasimgenelPas encore d'évaluation
- t1 2020 Tfin202 Sample Final ExamDocument4 pagest1 2020 Tfin202 Sample Final ExamSravya MagantiPas encore d'évaluation
- FINVEST Free Cash Flow Valuation SlidesDocument5 pagesFINVEST Free Cash Flow Valuation SlidesOliverCheongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Time Value of MoneyDocument12 pagesChapter 5 - Time Value of MoneyDenise LabordoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Investment EfficiencyDocument70 pagesChapter 4 Investment Efficiency10-12A1- Nguyễn Chí HiếuPas encore d'évaluation
- Determinants of Interest RatesDocument51 pagesDeterminants of Interest RatesBrithney ButalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document29 pagesChapter 2ebrahimnejad64Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument37 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionLIAW ANN YIPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN 401 - Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFIN 401 - Cheat SheetStephanie NaamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Profitability (بلانت)Document32 pagesProfitability (بلانت)Naser SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Công TH C TCDNDocument10 pagesCông TH C TCDNlâm lêPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 - Financial Management - Seminar 2 - QADocument4 pagesWeek 3 - Financial Management - Seminar 2 - QAvatsalt11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Factors: How Time and Interest Affect MoneyDocument48 pagesFactors: How Time and Interest Affect Moneymichelleromac100% (1)
- f9 FormulasDocument16 pagesf9 FormulasLesh GaleonnePas encore d'évaluation
- MGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Document11 pagesMGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Ali IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Penman 5ed AppendixDocument32 pagesPenman 5ed AppendixHirastikanah HKPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Valuation Models: Two Methods: 1. Discounted Cash Flow 2. Relative ValuesDocument24 pagesBusiness Valuation Models: Two Methods: 1. Discounted Cash Flow 2. Relative ValuesIndra S ChaidrataPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of CapitalDocument13 pagesCost of Capitalஇலக்கியச்செல்வி உமாபதிPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Value of Money PDFDocument52 pagesTime Value of Money PDFStar CelestinePas encore d'évaluation
- ACFI5084 Jan 2022 Exam - V1Document10 pagesACFI5084 Jan 2022 Exam - V1purushotham reddy vanipallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocument15 pagesPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i INadir AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetDocument5 pagesCorporate Finance Formula SheetChan Jun LiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEngineering Economics Formula Sheetmani123975% (4)
- Financial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesFinancial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial ManagementAakash TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering EconnmicsDocument40 pagesEngineering EconnmicsboknoypokongPas encore d'évaluation
- List of FormulaeDocument4 pagesList of FormulaeSumeet DekatePas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- Lyceum of The Philippines University-Cavite Engineering Economy April 15, 2020 WedDocument5 pagesLyceum of The Philippines University-Cavite Engineering Economy April 15, 2020 WedKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetEdithPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet-2nd QuizDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet-2nd QuizEge MelihPas encore d'évaluation
- Gitman Ch09 01 StudentDocument42 pagesGitman Ch09 01 StudentFatima AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- 615515556Document31 pages615515556Jay SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems in Engineering Economics: CLSU-AE Board Exam Review Materials 1Document49 pagesSolved Problems in Engineering Economics: CLSU-AE Board Exam Review Materials 1Abas Acmad50% (2)
- L7 SP 08 Value Common Stock 2Document23 pagesL7 SP 08 Value Common Stock 2Imad RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- EconomyDocument12 pagesEconomyRayZa Y MiralPas encore d'évaluation
- (IE) Chapter 4 - Investment EfficiencyDocument88 pages(IE) Chapter 4 - Investment EfficiencyJane VickyPas encore d'évaluation
- New Lecture 10 SPR 09Document11 pagesNew Lecture 10 SPR 09bat0oPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Value of MoneyDocument54 pagesTime Value of MoneyBibhudatta SinghSamantPas encore d'évaluation
- TABLE 3.4: Summary of Discrete Compounding Formulas With Discrete PaymentsDocument4 pagesTABLE 3.4: Summary of Discrete Compounding Formulas With Discrete PaymentsaycapltPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Annual Worth AnalysisDocument27 pagesModule 5 Annual Worth AnalysisMeifrinaldiGamaBizenPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate Finance FormulasDocument3 pagesCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- DCF Method of ValuationDocument45 pagesDCF Method of Valuationnotes 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- A212 - Topic 3 - Annuity Perpetuity - Part Ii (Narration)Document34 pagesA212 - Topic 3 - Annuity Perpetuity - Part Ii (Narration)Teo ShengPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Review - Key ConceptsDocument10 pagesMidterm Review - Key ConceptsGurpreetPas encore d'évaluation
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)D'EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Évaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (17)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)D'EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 2, Financial Decision Making (1-year access)D'EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 2, Financial Decision Making (1-year access)Pas encore d'évaluation
- MTPDocument52 pagesMTPtobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Oilhead Hall Sensors PDFDocument15 pagesOilhead Hall Sensors PDFtoby100% (1)
- 713ent Overview 26jul16Document16 pages713ent Overview 26jul16tobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Governance PolicyDocument2 pagesBoard Governance PolicytobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Elliott Wave TheoryDocument3 pagesComplete Elliott Wave TheorySachin2210100% (2)
- Navigating The Digital Age AU 6Document68 pagesNavigating The Digital Age AU 6tobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Recruitment and Selection Project PDFDocument2 pagesRecruitment and Selection Project PDFtoby100% (1)
- MTPDocument52 pagesMTPtobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bryce Gilmore's XABCD Tables PDFDocument34 pagesBryce Gilmore's XABCD Tables PDFtoby100% (1)
- Project Report On Selection and Recruitment PDFDocument2 pagesProject Report On Selection and Recruitment PDFtobyPas encore d'évaluation
- AlphOmega Elliott Waves 5.7Document114 pagesAlphOmega Elliott Waves 5.7api-19624416100% (1)
- How To Write HD Exam Answers SHRM May 2016Document2 pagesHow To Write HD Exam Answers SHRM May 2016tobyPas encore d'évaluation
- 360 Degree QuestionnaireDocument3 pages360 Degree QuestionnaireAlapati AparnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Snowman Project Proposal FeedbackDocument2 pagesSnowman Project Proposal FeedbacktobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Adobe Performance ManagementDocument25 pagesAdobe Performance ManagementtobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Questionnaire 136Document3 pagesPa Questionnaire 136Stephen SelvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- When The Performance Management Bubble BurstDocument4 pagesWhen The Performance Management Bubble Bursttoby100% (1)
- Different Relationships Between Perceptions of Developmental Performance Appraisal and Work PerformanceDocument21 pagesDifferent Relationships Between Perceptions of Developmental Performance Appraisal and Work PerformancetobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Estate InvestarDocument7 pagesReal Estate InvestartobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing The Business Idea: True-False QuestionsDocument12 pagesDeveloping The Business Idea: True-False QuestionsjenovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Snehal Project FinalDocument63 pagesSnehal Project Finalravi kangnePas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Tests Partnership FormationDocument10 pagesPractice Tests Partnership FormationClaire RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- BBS 4th Year Financial SpecializationDocument13 pagesBBS 4th Year Financial Specializationrajendrakumar44% (9)
- Financial Markets - Chapter 5 - Overview of Risk and ReturnDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 5 - Overview of Risk and ReturnCharrise BechaydaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Test QuestionsDocument24 pagesReview Test QuestionsKent Mathew BacusPas encore d'évaluation
- SPICEJET ISSUES AND Solution TechniqueDocument2 pagesSPICEJET ISSUES AND Solution TechniquenikeeetPas encore d'évaluation
- 1915314-Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument14 pages1915314-Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementArun ArunPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Management Final ExamDocument5 pagesInvestment Management Final ExamArleen NateraPas encore d'évaluation
- Carne Aifmd Guide V2.04.19 PDFDocument52 pagesCarne Aifmd Guide V2.04.19 PDFdemetraPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN 370 Final Exam 30 Questions With AnswersDocument11 pagesFIN 370 Final Exam 30 Questions With Answersassignmentsehelp0% (1)
- Chapter 18 - Evaluating Investment PerformanceDocument62 pagesChapter 18 - Evaluating Investment PerformanceRavi PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Putri Prihatin Ningsih, IIN Indarti (2012)Document23 pagesPutri Prihatin Ningsih, IIN Indarti (2012)Nanda Julyantie RatmanaPas encore d'évaluation
- ICICI Pru Smart Kid Premier BrochureDocument14 pagesICICI Pru Smart Kid Premier Brochuredencybk123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Reliance Mutual FundDocument13 pagesProject On Reliance Mutual FundNancy AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Aurelio Gurrea Martínez & Nydia Remolina - The Law and Finance of Initial Coin Offerings (2019)Document45 pagesAurelio Gurrea Martínez & Nydia Remolina - The Law and Finance of Initial Coin Offerings (2019)Alberto Fernández MatíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 1st Quarter 2nd Quarter 3rd Quarter 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesQuarter 1st Quarter 2nd Quarter 3rd Quarter 4th QuarterKelvin Jay Sebastian SaplaPas encore d'évaluation
- Invest in Tech Startups - Cebron GroupDocument3 pagesInvest in Tech Startups - Cebron Groupcebron groupPas encore d'évaluation
- Vault Finance Interviews Practice GuideDocument120 pagesVault Finance Interviews Practice GuideHaohan XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Literacy and Investor AwarenessDocument3 pagesFinancial Literacy and Investor AwarenessRishabh KhichiPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges Facing Zimbabwean Pension Funds: July 2019Document5 pagesChallenges Facing Zimbabwean Pension Funds: July 2019madzibaba munengwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini Project 2 (A)Document8 pagesMini Project 2 (A)Himanshu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BL.2802 Drill 1 - Corporation MAY 2020: Business Law Atty. Ong/LopezDocument2 pagesBL.2802 Drill 1 - Corporation MAY 2020: Business Law Atty. Ong/LopezMaePas encore d'évaluation
- CTDocument55 pagesCTAnitha GirigoudruPas encore d'évaluation
- MBFS - 3Document30 pagesMBFS - 3Kaviya KaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Exam Valuation Concepts and Methodologies PDF FreeDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Valuation Concepts and Methodologies PDF FreeMarynissa CatibogPas encore d'évaluation
- Competitors Analysis With 4 Others Bank: Total AssetDocument3 pagesCompetitors Analysis With 4 Others Bank: Total AssetMd. Muhinur Islam AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Investments Bodie Chapter 25 SolutionsDocument8 pagesInvestments Bodie Chapter 25 SolutionstaysisongPas encore d'évaluation
- BTEC HNDs Managing Financial ResourcesDocument3 pagesBTEC HNDs Managing Financial Resourceskillu87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why Companies Fail - and HowTheir Founders Can BounceBackDocument2 pagesWhy Companies Fail - and HowTheir Founders Can BounceBackJunaid MunirPas encore d'évaluation