Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Motherboard
Transféré par
Anonymous 9QDHkm0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
125 vues3 pagesTitre original
What is a Motherboard.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
125 vues3 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard
Transféré par
Anonymous 9QDHkmDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
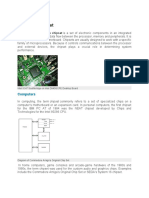
What is a Motherboard?
A motherboard is one of the most essential parts of a computer system. It holds
together many of the crucial components of a computer, including the central
processing unit (CPU), memory and connectors for input and output devices. The
base of a motherboard consists of a very firm sheet of non-conductive material,
typically some sort of rigid plastic. Thin layers of copper or aluminum foil,
referred to as traces, are printed onto this sheet. These traces are very narrow and
form the circuits between the various components. In addition to circuits, a
motherboard contains a number of sockets and slots to connect the other
components.
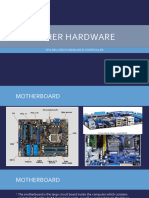
Parts of a Motherboard
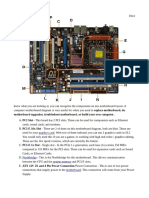
If you were to open up your computer and take out the motherboard, you would
probably get pretty confused about all the different parts. Depending on the make
and model of your computer, it might look something like the picture below.
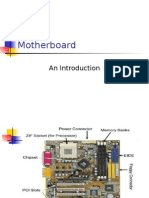
Photograph of a typical motherboard of a desktop computer
To understand how computers work you don't need to know every single part of
the motherboard. However, it is good to know some of the most important parts
and how the motherboard connects the various parts of a computer system together.
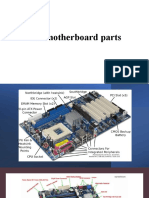
Some of the typical parts are described below - they are also labeled in the next
photograph:
A CPU socket - the actual CPU is directly soldered onto this
socket. Since high speed CPUs generate a lot of heat, there
are heat sinks and mounting points for fans right next to the
CPU socket.
A power connector to distribute power to the CPU and other
components.
Slots for the system's main memory, typically in the form of
DRAM chips.
A chip forms an interface between the CPU, the main
memory and other components. On many types of
motherboards this is referred to as the Northbridge. This
chip also contains a large heat sink.
A second chip controls the input and output (I/O) functions. It
is not connected directly to the CPU but to the Northbridge.
This I/O controller is referred to as the Southbridge. The
Northbridge and Southbridge combined are referred to as
the chipset.
Several connectors, which provide the physical interface
between input and output devices and the motherboard. The
Southbridge handles these connections.
Slots for one or more hard drives to store files. The most
common types of connections are Integrated Drive
Electronics (IDE) and Serial Advanced Technology
Attachment (SATA).
A Read-only memory (ROM) chip, which contains the
firmware, or startup instructions for the computer system.
This is also called the BIOS.
A slot for a video or graphics card. There are a number of
different types of slots, including Accelerated Graphics Port
(AGP) and Peripheral Component Interconnect Express
(PCIe).
Additional slots to connect hardware in the form of
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots.
Photograph of a typical motherboard with the most important
parts labeled
There are certainly a lot of acronyms to get used to! Don't worry too much about
trying to remember all the parts and their acronyms. The key is to remember that
the motherboard contains the central processing unit, the memory, and all the
connectors to the rest of the hardware of the computer system. The board is
the 'mother' of all components - that's where it gets its name.
Schematic Diagram
Another useful way to look at the motherboard is as a schematic diagram. This is
more of a logical organization of how the various parts are connected rather than
where they are physically located on the sheet of plastic. The connections between
these components are referred to as buses. So there is a CPU bus, a memory bus,
etc.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture 4 - CSS MotherboardDocument3 pagesLecture 4 - CSS MotherboardCharmis TubilPas encore d'évaluation
- How Motherboard WorksDocument12 pagesHow Motherboard Worksrez hablo100% (1)
- Parts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionDocument7 pagesParts of A Motherboard and Their FunctionLanie MagannonPas encore d'évaluation
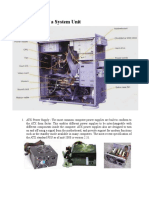
- The Computer System UnitDocument18 pagesThe Computer System UnitJohn Alfredo Koykoy VicioPas encore d'évaluation
- MotherboardDocument5 pagesMotherboardRichard Melvin GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- MotherboardDocument2 pagesMotherboardAimee Hernandez100% (1)
- Computer Motherboard Diagram Is Very Useful For When You Need To Replace Motherboard, DoDocument2 pagesComputer Motherboard Diagram Is Very Useful For When You Need To Replace Motherboard, Dohelen adoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN EXPDocument32 pagesCHN EXPAnanduPas encore d'évaluation
- MOTHERBOARDDocument13 pagesMOTHERBOARDUday HrudaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MotherboardDocument14 pagesMotherboardPalash Jain100% (1)
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru moses100% (1)
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)Document18 pagesPower Supply Unit (PSU)robeecalPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE2 Components of ComputerDocument59 pagesMODULE2 Components of ComputerJason EchevariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboards: The Main Board On A PCDocument85 pagesMotherboards: The Main Board On A PCUmar SheriffPas encore d'évaluation
- CHMA Unit - VDocument25 pagesCHMA Unit - VSayyan Shaikh100% (1)
- Final Project Introduction To Computer System UnitDocument19 pagesFinal Project Introduction To Computer System UnitMuhammad Usman AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Reading5 - ChipsetDocument3 pagesModule 2 - Reading5 - ChipsetChristopher AdvinculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Hard Disk BasicDocument27 pagesHard Disk BasicCharlesPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02Document42 pages23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02Kishore KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Storage Devices and Multimedia DevicesDocument25 pagesStorage Devices and Multimedia DevicesJoevertVillartaBentulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Block Diagram of MotherboardDocument9 pagesBlock Diagram of MotherboardJay Zala0% (1)
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Document54 pagesOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Form Factors (Motherboard)Document18 pagesComputer Form Factors (Motherboard)Akhila DakshinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 079 CMT pr-1Document8 pages079 CMT pr-1Aarunain PandavdraPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Repair and MaintenanceDocument2 pagesComputer Repair and Maintenanceclinton koechPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewing The Basics Chapter 1Document2 pagesReviewing The Basics Chapter 1zahed83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardJohnPaulLlenticPas encore d'évaluation
- Model - Day Wise Session Plan FOR FTCPDocument42 pagesModel - Day Wise Session Plan FOR FTCPJaveed AhamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarDocument23 pagesPresentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarSatyam JhawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhi PROJECT REPORTDocument89 pagesAbhi PROJECT REPORTDependra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Component of System UnitDocument52 pagesThe Component of System UnitgtPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 LabDocument5 pagesChapter 7 LabDuluth MarketsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardware BibleDocument123 pagesHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?Document13 pagesPractical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?funny videosPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesComputer HardwareEhnan J LamitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 LabDocument5 pagesChapter 6 LabDuluth Markets100% (1)
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4-Motherboard.18214342Document59 pagesModule 4-Motherboard.18214342Fercie Q. EngresoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 1Document8 pagesLect 1Ahmed SalihPas encore d'évaluation
- Seagate Command ReferenceDocument17 pagesSeagate Command ReferenceTrevor HallPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard and Other PartsDocument32 pagesMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- The MotherboardDocument39 pagesThe MotherboardGenevev Reyes100% (1)
- Motherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskDocument5 pagesMotherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskRoger EmbalsadoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHMA Unit - IIDocument14 pagesCHMA Unit - IISayyan ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Hardware Repairing Course - Computer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing Training Delhi Tilak NagarDocument4 pagesComputer Hardware Repairing Course - Computer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing Training Delhi Tilak NagarRakesh MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Computer & Their PartsDocument6 pagesTypes of Computer & Their PartsImtiaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Comptia A+ Lab ManualDocument4 pagesComptia A+ Lab ManualRon NecesitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer System Parts of MotherboardDocument28 pagesComputer System Parts of MotherboardJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Guide To Managing and Maintaining Your PC Chapter 4Document26 pagesGuide To Managing and Maintaining Your PC Chapter 4Frederick Leonard0% (1)
- The Cpu: Central Processing UnitDocument26 pagesThe Cpu: Central Processing Unitjim_finn_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument5 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemIssan VillaruelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9hbomber20Pas encore d'évaluation
- MB Level 2 - 1 Training MaterialsDocument24 pagesMB Level 2 - 1 Training MaterialsFernando Amaro HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard: DefinitionDocument3 pagesMotherboard: DefinitionJimmy RafadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tle ASSIGNMENTDocument3 pagesTle ASSIGNMENTmax magsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- PT14 Engine Monitor 1Document2 pagesPT14 Engine Monitor 1BJ DixPas encore d'évaluation
- Alien Vault Lab2Document28 pagesAlien Vault Lab2DukePas encore d'évaluation
- Zaroulas Mies Fullpaper 2020 05 21Document9 pagesZaroulas Mies Fullpaper 2020 05 21sidgonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Portland CementDocument46 pagesPortland Cementni putu diah untariningsihPas encore d'évaluation
- EN RotomaticDocument4 pagesEN RotomaticnajeerwPas encore d'évaluation
- E 7016 Product-SheetDocument1 pageE 7016 Product-SheetAlireza TakrimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Wire Anemometry HandoutDocument4 pagesHot Wire Anemometry HandoutZ-BPas encore d'évaluation
- CLS 747 200Document158 pagesCLS 747 200Rodrigo Adam100% (8)
- Idlers - Medium To Heavy Duty PDFDocument28 pagesIdlers - Medium To Heavy Duty PDFEd Ace100% (1)
- Tharmal Analysis BasicsDocument56 pagesTharmal Analysis BasicsNetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) OGIDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) OGIApram SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- U042en PDFDocument12 pagesU042en PDFTatiya TatiyasoponPas encore d'évaluation
- PBLauncherDocument50 pagesPBLauncherborreveroPas encore d'évaluation
- DT NotesDocument117 pagesDT NotestessPas encore d'évaluation
- zx350lc 3 InglesDocument6 pageszx350lc 3 InglesLuis Nahuelhuaique LemusPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Analysis Chap. 4 First Order Differential EquationDocument5 pagesNetwork Analysis Chap. 4 First Order Differential EquationSreeram Vijapurapu0% (1)
- Colchicine - British Pharmacopoeia 2016Document4 pagesColchicine - British Pharmacopoeia 2016Social Service (V)100% (1)
- 2 Coagulation FlocculationDocument26 pages2 Coagulation FlocculationNurSyuhada APas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction Into The Feynman Path Integral PDFDocument94 pagesAn Introduction Into The Feynman Path Integral PDFLivardy WufiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Module CellDocument4 pagesSolar Module CellVinod BabhalePas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of Circulation in A Free Vortex FlowDocument55 pagesConcept of Circulation in A Free Vortex FlowAnil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 05120 Structural Steel Part 1Document43 pagesSection 05120 Structural Steel Part 1jacksondcplPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock # Carbon Weight Burn Temp Puncture StrengthDocument8 pagesStock # Carbon Weight Burn Temp Puncture StrengthMintPas encore d'évaluation
- Cache MemoryDocument20 pagesCache MemoryKeshav Bharadwaj RPas encore d'évaluation
- Air-Bag: (1) Connector InformationDocument34 pagesAir-Bag: (1) Connector InformationbakriramziPas encore d'évaluation
- S09 Power TrainDocument90 pagesS09 Power TrainPLANEAMIENTO MDRILLPas encore d'évaluation
- Sec VlanaclsDocument10 pagesSec VlanaclsTry FajarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 03-1 Synchronous Machines 1 DNDocument25 pages03-1 Synchronous Machines 1 DNsaif thuraonPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Fluid Mechanics: Luigi Di Micco Email: Luigi - Dimicco@dicea - Unipd.itDocument16 pagesAdvanced Fluid Mechanics: Luigi Di Micco Email: Luigi - Dimicco@dicea - Unipd.itHubert MoforPas encore d'évaluation
- Method StatementDocument4 pagesMethod StatementtayitbatovPas encore d'évaluation