Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
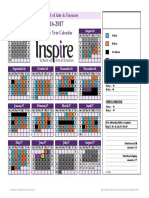
Is Unit 1 Schedule - Scientific Practices 2016
Transféré par
api-260189186Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Is Unit 1 Schedule - Scientific Practices 2016
Transféré par
api-260189186Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Practices - What is Life pp.
1-29
Day &
Date
Learning Objectives
Due Today
DAY 3
8/24
W
DAY 4
8/31
W
Disciplinary Core Idea
Screencast 1.1 &
Outline 1.1 What is
science?
Screencast 1.2 Outline 1.2 Science
literacy is essential in
the modern world
Signed syllabus
Signed safety contract
Inquiry Cube
The rules of science
[science practices]
Science vs. Superstition
Outline 1.3 Scientific
thinking is a powerful
approach to
understanding the world
Thought experimentDrive-Up ATMs
Experimental Design
Screencast 1.4 - Outline
1.4 Thinking like a scientist:
how do you use the
scientific method?
Screencast 1.4 Outline 1.4 Thinking
like a scientist: how do
you use the scientific
method?
Wht mks a grup scxxul
Lab - Bounty Claim
Experimental design
and test
Finish lab
Science Practice
Planning and carrying out
a lab investigation
Bounty paper towel lab
rough draft
Errrrt. A little research
goes a long way
Introducing the NIH,
CDC and FDA
Video - Vaccine Wars
Credibility - Lancet
Article - Autism and
MMR Vaccine
1.17 Pseudoscience
Lab revision (question)
Screencast 1.5 & Outline
1.5 Make observations.
Screencast 1.6 - Outline
1.6 Formulate a hypothesis
Screencast 1.7 - Outline
1.7 Devising a testable
prediction
Science Practice
I can obtain, evaluate and
communicate information
I can formulate a
hypothesis related to a
question
I can generate a testable
prediction for my
hypothesis
1.
Quiz - Hypotheses and
Predictions
Formulating Hypotheses
practice
The Null" Hypothesis
Generating predictions
Bounty Lab revisions
(hypothesis / variables)
Screencast 1.8 & Outline
1.8 Conduct a critical
experiment
Screencast 1.11 & Oultine
1.11 Controlling variables
makes experiments more
powerful
Science Practice
Formulate a hypothesis
related to their question
Generate a testable
prediction for their
hypothesis
1.
8/29
M
DAY 5
Practice And Cross Cutting
Concept
Screencast 1.1 & Outline
1.1 What is science?
Screencast 1.2 - Outline
1.2 Science literacy is
essential in the modern
world
Signed syllabus
Signed safety contract
8/18
Th
8/22
M
Homework Assigned
Syllabus
Safety contract
Outline & Schedule
Website
Scientific literacy/
Science Ethics
DAY 1
DAY 2
In Class
Screencast 1.5 &
Outline 1.5 Make
observations.
Screencast 1.6 Outline 1.6 Formulate a
hypothesis
Screencast 1.7 Outline 1.7 Devising a
testable prediction
Cross Cutting Concept
I can identify patterns
1.
2.
I can define science.
I can define scientific literacy.
1.
I can define what an observation is and can write/
verbalize examples
I can define what a question is and can write/verbalize
examples
I can describe the importance of recognizing patterns
to solve problems in science
I can define empirical and can explain the importance
of data driven
2.
Science Practice
I can ask questions about
my observations
I can obtain, evaluate and
communicate information
3.
4.
2.
2.
I can identify the National Institute of Health, Center
for Disease Control, & Food and Drug
Administration as three important sources for biology
research.
I can list and describe characteristics of credible
resources and non-credible resources.
I can define what a hypothesis is and can write/
verbalize examples
I can define what a testable prediction is and can
write/verbalize examples
Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Practices - What is Life pp. 1-29
Day &
Date
DAY 6
9/2
F
DAY 7
9/7
W
DAY 8
Learning Objectives
Due Today
9/14
W
Homework Assigned
Practice And Cross Cutting
Concept
Disciplinary Core Idea
Screencast 1.8 &
Outline 1.8 Conduct a
critical experiment
Screencast 1.11 &
Oultine 1.11 Controlling
variables makes
experiments more
powerful
Class read - 1.12
Arthroscopic surgery An example of good
design
Features of a data table
Bounty Experimental
design (procedure)
Screencast 1.9 & Outline
1.9 Draw conclusions,
make revisions
Screencast 1.10 & Outline
1.10 When do hypotheses
become theories, and what
are theories?
Watch screencast 2 analyzing and interpreting
data
Answer outline questions
analyzing and interpreting
data
Science Practice
Planning and carrying out
a lab investigation
Screencast 1.9 &
Outline 1.9 Draw
conclusions, make
revisions
Screencast 1.10 &
Outline 1.10 When do
hypotheses become
theories, and what are
theories?
Quiz 1.1 - 1.12
Bounty Experiment Take 2
Watch screencast on
analyzing and interpreting
data
Answer outline questions
analyzing and interpreting
data
Science Practice
I can analyze and
interpret data
I can use mathematics
and computational
thinking
1.
2.
Outline questions
analyzing and
interpreting data
Quiz - Biozone
Variables Catalase
Types of data
Data analysis
(transformation) and
interpretation on rattle
snakes
Bounty - Data analysis
and interpretation
Screencast 1.15 & Outline
1.15 Visual Displays of
data can help us
understand and explain
phenomena
Science Practice
I can analyze and
interpret data
I can use mathematics
and computational
thinking
1.
2.
Drawing line graphs, bar
graphs, pie charts and
histograms Quiz - Types
of graphs
Video - Causation and
correlation
Bounty causation and
correlation
Descriptive Statistics
Science Practice
I can analyze and
interpret data
I can use mathematics
and computational
thinking
1.
2.
9/12
M
DAY 9
In Class
Screencast 1.15 &
Outline 1.15 Visual
Displays of data can
help us understand and
explain phenomena
1.
2.
3.
4.
3.
3.
3.
4.
I can define treatment and identify it in my own and
example experiments
I can define experimental group and identify the it in
my own and example experiments
I can define control group and identify it in my own
and example experiments
I can define variables (independent, dependent and
standardizing) and identify them in my own and
example experiments
I know data can be qualitative, quantitative, or ranked
I know quantitative data can be continuous or
discontinuous.
I can transform raw data to identify important features
I know data can be qualitative, quantitative, or ranked
I know quantitative data can be continuous or
discontinuous.
I can transform raw data to identify important features
I can use graphs to visualize data and identify trends.
I can use a graph type appropriate to the type of data
you have collected.
I can summarize data and describe its basic features
using statistics (e.g. mean, median and mode).
I can use a statistic appropriate to the type of data and
its distribution
Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Practices - What is Life pp. 1-29
Learning Objectives
Day &
Date
Due Today
DAY 10
Descriptive Statistics
In Class
Dont argue with me
Spider GoatsA closer
look at argumentation
Write termite argument
Review for exam
9/16
F
DAY 11
9/19
M
Unit Outline
Bounty Lab
Bounty Argument
Exam - Science practices
Homework Assigned
Practice And Cross Cutting
Concept
Disciplinary Core Idea
Write bounty argument
Science Practice
I can engage in an
argument from evidence
(written or verbal)
1.
Rest and relaxation
All Practices and Cross Cutting
Concepts
All Disciplinary Core Ideas
I know and can describe the 3 parts to an argument
(claim, evidence, justification).
Unit 1 Vocabulary
Control
Data
Controlled variable
Descriptive statistics
Dependent variable
Graph
Hypothesis
Independent variable
Mean
Median
Mode
Model
Observation
Research
Prediction
Qualitative data
Quantitative data
Raw data
Histogram
Bar graph
Table
Variable
Percent
Hypothesis
Argue
Analyze
Interpret
Scatter plot
Line graph
Graph
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Deadly Alcohol Needs Global Regulation Health Expert Says - Scientific AmericanDocument7 pagesDeadly Alcohol Needs Global Regulation Health Expert Says - Scientific Americanapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- 21: Science's Limit When It Comes To The Drinking Age: by Jen Christensen, CNNDocument3 pages21: Science's Limit When It Comes To The Drinking Age: by Jen Christensen, CNNapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elementsapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 11 Activity - Atomic Pudding Models of An AtomDocument5 pagesLesson 11 Activity - Atomic Pudding Models of An Atomapi-26018918640% (5)
- Lesson 12 Classwork - Atoms by Numbers Atomic Number and Atomic MassDocument5 pagesLesson 12 Classwork - Atoms by Numbers Atomic Number and Atomic Massapi-260189186100% (1)
- Lesson 26 Activity - Electron Glue Bonding 1Document7 pagesLesson 26 Activity - Electron Glue Bonding 1api-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 9 Activity - Create A Table Properties of ElementsDocument8 pagesLesson 9 Activity - Create A Table Properties of Elementsapi-26018918650% (2)
- 16-17 Ab Calendar - Final PublicDocument1 page16-17 Ab Calendar - Final Publicapi-260189186100% (1)
- Lesson 6 Activity - A New Language Chemical Names and SymbolsDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Activity - A New Language Chemical Names and Symbolsapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Schedule - Mental HealthDocument1 pageUnit 2 Schedule - Mental Healthapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ocean CurrentsDocument2 pagesOcean Currentsapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Lab - All That Glitters DensityDocument4 pagesLesson 5 Lab - All That Glitters Densityapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Haspi Evidence of Evolution ArticlesDocument3 pagesHaspi Evidence of Evolution Articlesapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Schedule Unit 7 - EvolutionDocument1 pageSchedule Unit 7 - Evolutionapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- U S Chambers Fracking S Midwest Energy NewsDocument5 pagesU S Chambers Fracking S Midwest Energy Newsapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Huffington Post - California Shuts Down Injection of Fracking Waste To Protect Scarce WaterDocument3 pagesHuffington Post - California Shuts Down Injection of Fracking Waste To Protect Scarce Waterapi-260189186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Fast Hardware Computation of X Mod Z: J. T. Butler T. SasaoDocument5 pagesFast Hardware Computation of X Mod Z: J. T. Butler T. Sasaoshashank guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - RecursionDocument55 pagesChapter 6 - RecursionBandar AbdallatPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization With R - Tips and TricksDocument17 pagesOptimization With R - Tips and TricksRMolina65Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Percaya Diri 1Document13 pagesJurnal Percaya Diri 1Baihaqi HatakePas encore d'évaluation
- Lahore University of Management Sciences: Midterm Exam Schedule Fall 2012Document13 pagesLahore University of Management Sciences: Midterm Exam Schedule Fall 2012Ahmad_Bilal_As_3566Pas encore d'évaluation
- Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesLiterature Reviewfayyazmodi50% (2)
- Short-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting With MARS, SVR and ARIMADocument16 pagesShort-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting With MARS, SVR and ARIMAharri8026Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Modeling of Synthetic CurvesDocument13 pagesMathematical Modeling of Synthetic Curvesakshat_aghaPas encore d'évaluation
- F HG I KJ F HG I KJ: Differentiation CPP (Basics)Document3 pagesF HG I KJ F HG I KJ: Differentiation CPP (Basics)Pratham SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2001 P2 PDFDocument15 pages2001 P2 PDFErwin CahanapPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Experiment 3Document6 pagesLaboratory Experiment 3ernestPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 29 (Markov Chains) PDFDocument23 pagesChapter 29 (Markov Chains) PDFWesam WesamPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Compass ErrorDocument36 pagesMagnetic Compass ErrorNimesh Perera67% (3)
- SMDM ProjectDocument19 pagesSMDM Projectnishant100% (1)
- Carlos Nunes Proj5 Me412 BackupDocument29 pagesCarlos Nunes Proj5 Me412 BackupCarlos AlbertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-8, Math-5 Lecture Note Summer 20-21Document15 pagesCh-8, Math-5 Lecture Note Summer 20-21আসিফ রেজাPas encore d'évaluation
- Emgt5220 c9 TLDocument28 pagesEmgt5220 c9 TLmike jPas encore d'évaluation
- DicaDocument26 pagesDicaganga_ch1Pas encore d'évaluation
- RSA (Cryptosystem) : 1 HistoryDocument9 pagesRSA (Cryptosystem) : 1 HistoryTanmay RajPas encore d'évaluation
- ECCV06 Tutorial PartI YuriDocument64 pagesECCV06 Tutorial PartI YuriNavdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics in The Modern World Problem Set Preliminary PeriodDocument2 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Problem Set Preliminary PeriodMikay.Pas encore d'évaluation
- GO Math Guidance Grade 5 - FINALv3Document26 pagesGO Math Guidance Grade 5 - FINALv3aamario128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Summative-TEst Q1 4th m91011Document1 pageSummative-TEst Q1 4th m91011Sharmaine MedianeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Dumas 1998Document48 pagesDumas 1998Yuming MaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethan Berman at Riskmetrics Group PDFDocument2 pagesEthan Berman at Riskmetrics Group PDFConnie0% (1)
- Vol Prism 1Document2 pagesVol Prism 1Moneyball7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IDocument21 pagesBored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IVardhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Tumor MriDocument23 pagesBrain Tumor MrisekharraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsAndrew BullPas encore d'évaluation