Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Análisis de velocidad y aceleración de un mecanismo de 5 eslabones
Transféré par
Alejandro RangelTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Análisis de velocidad y aceleración de un mecanismo de 5 eslabones
Transféré par
Alejandro RangelDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
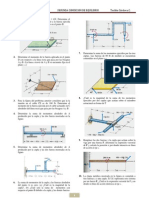
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
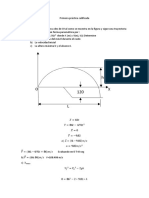
MECANISMO DE 5 ESLABONES
ANLISIS DE VELOCIDAD
DATOS DE ENTRADA:
2 = 2 = 152
3 = = 178
3 = = 127
3 = = 102
4 = = 203
2 = 2 / (, )
= 254 / ()
POLGONO DE VELOCIDAD
CALCULANDO LA VELOCIDAD DEL PUNTO A:
=
2 2
= 2 2 = (2 /)(152 ) = 304 /
= 365.9459 / ( )
= 394.1630 / ( )
/ = 202.2572 / ( )
/ = 115.9002 / ( )
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
/ = 144.3071 / ( )
/ = 530.3116 / ( )
/ =
3 3
/ = 3 3
3 =
/ 202.2572 /
=
= 1.1362 /
3
178
/ =
3 3
/ = 3 3
3 =
/ 115.9002 /
=
= 1.1362 /
3
102
/ =
3 3
/ = 3 3
3 =
/ 144.3071 /
=
= 1.1362 /
3
127
/ =
4 4
/ = 4 4
4 =
/ 530.3116 /
=
= 2.6123 /
4
203
=
+
/
=
+
/
=
+
/
=
+
/
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
CENTROS DE ROTACIN
= 5 ( )
# =
( 1) 5(5 1)
=
= 10
2
2
ESLABN
CENTROS
DE
ROTACIN
CENTROS
PRIMARIOS
1
2
3
4
5
O21
O31
O41
O51
O32
O42
O52
O43
O53
O54
O21
CENTROS
SECUNDARIOS
CENTROS
ABSOLUTOS
O31
O41
O21
O31
O41
O51
O51
O32
O42
O52
O43
O53
O54
CENTROS
RELATIVOS
CENTROS
PERMANENTES
CENTROS
INSTANTNEOS
O21
O31
O41
O51
O32
O42
O52
O43
O53
O54
O32
O42
O52
O43
O53
O54
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
LOS CENTROS DE ROTACIN SECUNDARIOS, SON LO QUE SE OBTENDRN POR MEDIO DEL TEOREMA DE
ARONHOLD-KENNEDY
2 = 2 / (, )
= 254 / ()
1
2
3
O31
O21
CONOCIDO
O32
CONOCIDO
O31
POR CONOCER
3
4
5
O41
O21
CONOCIDO
O41
POR CONOCER
O51
CONOCIDO
1
4
5
O53
O43
CONOCIDO
O54
CONOCIDO
O53
POR CONOCER
2
3
4
1
2
5
O52
O21
CONOCIDO
O52
POR CONOCER
O51
CONOCIDO
O42
O32
CONOCIDO
O43
CONOCIDO
O42
POR CONOCER
EL PUNTO A PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 2
=
2 /21
= 2 /21 = (2 /)(152 ) = 304 /
EL PUNTO A PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 3
=
3 /31
3 = 1.1362 /
/31 =
304 /
=
= 267.5585
3 1.1362 /
EL PUNTO B PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 3
=
3 /31
= 3 /31 = (1.1362 /)(320.6442 ) = 364.3159 /
EL PUNTO B PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 4
=
4 /41
EL PUNTO D PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 4
=
4 /41
= 4 /41
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
EL PUNTO D PERTENECIENTE AL ESLABN 5
=
5 /51
5 =
/51
254 /
= 0 /
ANLISIS DE ACELERACIN
= +
2 , , , :
= 0
=
=
2 (
2 2 )
= (22 )(2 ) = (2
2
) (152 ) = 608 / 2
= +
= +
= +
La velocidad lineal del punto D es constante, por lo tanto: = 0
No hay cambio en la direccin del punto D, debido a que es una corredera y la direccin de la velocidad
, por lo tanto:
siempre ser sobre la horizontal: = 0
= 0
/ = / + /
/ =
3 (
3 3 )
/ = (32 )(3 ) = (1.1362
2
) (178 ) = 229.7891 / 2
/ = / + /
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
/ =
3 (
3 3 )
/ =
(32 )(3 )
2
= (1.1362
) (102 ) = 131.6769 / 2
/ = / + /
/ =
3 (
3 3 )
/ =
(32 )(3 )
2
= (1.1362
) (127 ) = 163.9507 / 2
/ = / + /
/ =
4 (
4 4 )
/ = (42 )(4 ) = (2.6123
2
) (203 ) = 1385.2945 / 2
= + /
, por lo tanto: = /
= + / donde: = 0
= + /
= + /
GDLS
Prctica Mecanismos y Mquinas
Mtodos grficos anlisis de posicin, velocidad y aceleracin
UPB
Ingeniera Robtica
GDLS
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ejerc - Resueltos Analisis Dimensional Sem 3Document18 pagesEjerc - Resueltos Analisis Dimensional Sem 3Carlos MonsalvePas encore d'évaluation
- SuperficiesDocument2 pagesSuperficiesRamiro lazaro bonillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cuestionario Análisis Instrumental PDFDocument23 pagesCuestionario Análisis Instrumental PDFPABLO CONTRERAS GUERREROPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratorio Numero 4 Metodos NumericosDocument3 pagesLaboratorio Numero 4 Metodos NumericosEfrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Lanzamiento en CatapultaDocument5 pagesLanzamiento en CatapultaIvette GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Análisis Cinemático de Mecanismos TridimensionalesDocument5 pagesAnálisis Cinemático de Mecanismos TridimensionalesSergio MoysenPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase de Auxiliatura Mec 2251 A Nro. 18Document7 pagesClase de Auxiliatura Mec 2251 A Nro. 18horvicPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratorio N°2 Velocidad Del Sonido y Numero de Mach Aire Gas IdealDocument11 pagesLaboratorio N°2 Velocidad Del Sonido y Numero de Mach Aire Gas IdealJameson Big Gonzalez OrozcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Matematica 4Document4 pagesMatematica 4cesar eduardoPas encore d'évaluation
- RECOBRODocument8 pagesRECOBROCristian Paredes100% (1)
- GuiadeDerivacionEjercicios042 2osem.2012Document9 pagesGuiadeDerivacionEjercicios042 2osem.2012Sergio Andres UribePas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Parte ADocument10 pagesTaller Parte AKAREN VALERIA PEREZ JIMENEZPas encore d'évaluation
- M5 1948233 PiaDocument12 pagesM5 1948233 PiaEfren SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Ciclos múltiples de compresión mecánica R-22Document6 pagesCiclos múltiples de compresión mecánica R-22Marco Antonio Gutierrez TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Naca 2415Document5 pagesNaca 2415Valeria Marisol Cuevas AcevesPas encore d'évaluation
- Termofluidos Lab 2Document16 pagesTermofluidos Lab 2Nicolas Adolfo Quijon MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Demostración experimental del teorema de Torricelli mediante la medición de la velocidad y alcance de un chorro de aguaDocument7 pagesDemostración experimental del teorema de Torricelli mediante la medición de la velocidad y alcance de un chorro de aguasantosa107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 3 - Mov 2 DimensionesDocument2 pagesTaller 3 - Mov 2 DimensionesJose D. CabanillasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecuaciones diferenciales de Cauchy-EulerDocument9 pagesEcuaciones diferenciales de Cauchy-EulerPedro AlanocaPas encore d'évaluation
- MatricesDocument14 pagesMatricesJose David Garcia Moguel0% (3)
- Problemas2dacondiciondeequilibrio 1Document14 pagesProblemas2dacondiciondeequilibrio 1Javier Pulido Villanueva0% (1)
- Entropía y la SEGUNDA LEY DE LA TermodinámicaDocument48 pagesEntropía y la SEGUNDA LEY DE LA TermodinámicaRENZO RENATO VELASQUEZ LOLIPas encore d'évaluation
- Esferas HuecasDocument8 pagesEsferas HuecasRicardo Palma chuquePas encore d'évaluation
- 2 ProblemaDocument1 page2 ProblemaVanna VerarutPas encore d'évaluation
- Movimiento curvilíneo - Coordenadas normal y tangencialDocument21 pagesMovimiento curvilíneo - Coordenadas normal y tangencialPaul Santos IsidroPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometría de masas problemas y solucionesDocument5 pagesGeometría de masas problemas y solucionesJesús Bermúdez GambínPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Sesión 10Document6 pagesProblemas Sesión 10REVENGEPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 8 - Velocidades Relativas PDFDocument3 pagesTaller 8 - Velocidades Relativas PDFdaniel gomez gomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratorio #1 Laboratorio de ControlDocument11 pagesLaboratorio #1 Laboratorio de ControlEdgardoEnriqueContePas encore d'évaluation
- Distribucion de Probabilidad ConjuntaDocument32 pagesDistribucion de Probabilidad Conjuntamandalore_fettPas encore d'évaluation
- Deber 1 PDFDocument2 pagesDeber 1 PDFAguekePas encore d'évaluation
- Análisis Gráfico de Método DinámicoDocument2 pagesAnálisis Gráfico de Método DinámicoJose Carlos Blas HuarotoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 TERMICA Fisica 2Document8 pages4 TERMICA Fisica 2Luis Angel Bautista RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller de Error Númerico-Grupo de Trabajo 5Document17 pagesTaller de Error Númerico-Grupo de Trabajo 5mariafacostanPas encore d'évaluation
- Presión hidrostática y elevación de piezómetros en curso de Mecánica de Fluidos IDocument7 pagesPresión hidrostática y elevación de piezómetros en curso de Mecánica de Fluidos IjanilPas encore d'évaluation
- Resolución de un problema de estática por Gauss-SeidelDocument11 pagesResolución de un problema de estática por Gauss-SeidelGabriel Ac MPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulacion Hele ShawDocument3 pagesSimulacion Hele ShawNelson Fabian Sáenz LeguizamónPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia de LaboratorioDocument25 pagesGuia de LaboratorioNoelithaa Melendez AranibarPas encore d'évaluation
- Limadora-Laboratorio de MaterialesDocument10 pagesLimadora-Laboratorio de Materialesleidy mendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Un Primer Curso en Ecuaciones Diferenciales Ordinarias - Carmona PDFDocument226 pagesUn Primer Curso en Ecuaciones Diferenciales Ordinarias - Carmona PDFCristian RochaPas encore d'évaluation
- Auxiliar No 4Document5 pagesAuxiliar No 4Manuel Fuenzalida OrellanaPas encore d'évaluation
- MN Guia2Document6 pagesMN Guia2battosai7100% (1)
- Adquisición de MaquinariaDocument25 pagesAdquisición de MaquinariaVanesa DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Informe 5Document8 pagesInforme 5Alex AndrangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Semana 04 Fuerzas Concurrentes y Momento de Una Fuerza LabDocument4 pagesSemana 04 Fuerzas Concurrentes y Momento de Una Fuerza LabRODOLFO MENDOZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 1 PLM y Su Relación Con CAD CAM CAPP CIMDocument1 pageTarea 1 PLM y Su Relación Con CAD CAM CAPP CIMJuan Carlos Puente Saldivar0% (2)
- Ejercicios Propuestos 1er Parcial Tema Sustancias Puras, Gases Ideales, Factor de CompresibilidadDocument3 pagesEjercicios Propuestos 1er Parcial Tema Sustancias Puras, Gases Ideales, Factor de Compresibilidaddomingo osorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 1 - Centros de Masa y Cinematica RotacionalDocument4 pagesTaller 1 - Centros de Masa y Cinematica RotacionalMonica PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calor Especifico de SolidosDocument6 pagesCalor Especifico de SolidosJoséPas encore d'évaluation
- PRACTICA N°3 (2DA y 3RA LEY DE LA TERMODINÁMICA)Document4 pagesPRACTICA N°3 (2DA y 3RA LEY DE LA TERMODINÁMICA)Natalia DuranPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicio 1Document3 pagesEjercicio 1Hector Gonzalez del Valle0% (2)
- Movimiento parabólico proyectil y aceleración punto BDocument4 pagesMovimiento parabólico proyectil y aceleración punto BDiego PrincipePas encore d'évaluation
- Transferencia de calor unidimensionalDocument6 pagesTransferencia de calor unidimensionalvleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Guias 2 202050 PDFDocument6 pagesGuias 2 202050 PDFJose AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexion en Seccion AsimetricaDocument47 pagesFlexion en Seccion AsimetricaJordy Robinson Caichihua VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Proc Ii Examen Final - 2020 I Marzo 16 2021Document4 pagesProc Ii Examen Final - 2020 I Marzo 16 2021Eduardo Enrique Garcia NieblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Análisis Numérico 2015 S1 EDOs Numéricas Guía 01 MGC Ing. Civil. Mec. Marcelo Gallardo Maluenda BetaDocument8 pagesAnálisis Numérico 2015 S1 EDOs Numéricas Guía 01 MGC Ing. Civil. Mec. Marcelo Gallardo Maluenda BetaJosé Marambio RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Velocidad promedioDocument20 pagesVelocidad promediojorge mendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designD'EverandGeometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designPas encore d'évaluation
- UF1253 - Diagnóstico de deformaciones estructuralesD'EverandUF1253 - Diagnóstico de deformaciones estructuralesPas encore d'évaluation
- El CristianismoDocument2 pagesEl CristianismoAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Relevador Bimetálico (Informacion)Document4 pagesRelevador Bimetálico (Informacion)Alejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayuda Cinematica InversaDocument2 pagesAyuda Cinematica InversaAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- CiclosBarrenadoRoscadoDocument24 pagesCiclosBarrenadoRoscadoГомер МагазинPas encore d'évaluation
- Introducción Control DigitalDocument1 pageIntroducción Control DigitalAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Práctica SAM Torno CNCDocument6 pagesPráctica SAM Torno CNCAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- ExamenDocument14 pagesExamenAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Resolucion de Ejercicios de Electroneumatica, Paso A Paso y CascadaDocument39 pagesResolucion de Ejercicios de Electroneumatica, Paso A Paso y CascadadavarherPas encore d'évaluation
- Solución ExamenDocument13 pagesSolución ExamenAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- LedesmaDocument1 pageLedesmaAlejandro RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Historia de La Democracia en El EcuadorDocument2 pagesHistoria de La Democracia en El EcuadorEdu AdivPas encore d'évaluation
- Método de Cardano y FerrariDocument5 pagesMétodo de Cardano y Ferrarielbola_2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Listas Lenguaje CDocument49 pagesListas Lenguaje CAimee ZuñigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grafos PlanosDocument5 pagesGrafos PlanosJuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistemas Operativos y Optimización de Recursos (Unidad 2)Document20 pagesSistemas Operativos y Optimización de Recursos (Unidad 2)Florencia Baez Camacho100% (1)
- Aplicaciones de Circuitos DigitalesDocument19 pagesAplicaciones de Circuitos DigitalesHernanValencia0% (1)
- Itriplee Formato Informes PDFDocument7 pagesItriplee Formato Informes PDFRicardo Rodriguez VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Temario Mtro. Ricardo Adán Madrid TrejoDocument4 pagesTemario Mtro. Ricardo Adán Madrid TrejoEg AbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Casos de Factorizacion InfografiaDocument1 pageCasos de Factorizacion InfografiaHernan100% (1)
- Proyecto de Remodelacion 1 PDFDocument18 pagesProyecto de Remodelacion 1 PDFWilliam Espinoza OrellanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Check-in hotelero: requisitos, documentos e información para el proceso de entrada al hospedajeDocument1 pageCheck-in hotelero: requisitos, documentos e información para el proceso de entrada al hospedajeIsai ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Internet Sano en FormatoDocument22 pagesTaller Internet Sano en FormatoAnonymous 7shS14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mapa Conceptual Proceso de Control Interno y Sus ComponentesDocument1 pageMapa Conceptual Proceso de Control Interno y Sus Componentesfabiola burgos50% (2)
- Programa Investigación Geográfica IDocument4 pagesPrograma Investigación Geográfica IDiana Durán100% (1)
- PROYECTO Mantenimiento CorrectivoDocument93 pagesPROYECTO Mantenimiento CorrectivoJoseLuisSarangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reconstrucción 3D Mediante Nube de Puntos en C++Document14 pagesReconstrucción 3D Mediante Nube de Puntos en C++sistecelPas encore d'évaluation
- AlgoritmicoDocument3 pagesAlgoritmicoJonathan DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Práctica Pantalla Tactil Siemens 1819 - 2Document14 pagesPráctica Pantalla Tactil Siemens 1819 - 2Roberto Pedrón DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestion ProyectosDocument5 pagesGestion ProyectosyvanscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- BB 2012 Manual EsDocument573 pagesBB 2012 Manual EsjjhonkcarPas encore d'évaluation
- Matemática básica: Productos y cocientes notablesDocument2 pagesMatemática básica: Productos y cocientes notablesLisseth Mahecha Diaz SantamariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ensayo CiberseguridadDocument14 pagesEnsayo CiberseguridadSharon LozadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ND 1200 Quadra-Chek 682 - 110-50Document145 pagesND 1200 Quadra-Chek 682 - 110-50hugo_cortes5275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Informe 3 Control DigitalDocument6 pagesInforme 3 Control DigitalNico PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrucciones y licencias ESETDocument8 pagesInstrucciones y licencias ESETrunatechPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucero RivasDocument4 pagesLucero RivaszalathielPas encore d'évaluation
- CECATI 173 Programación 2017 2018Document8 pagesCECATI 173 Programación 2017 2018joserra33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ensayo Jennifer BlancoDocument4 pagesEnsayo Jennifer BlancolrjansenPas encore d'évaluation
- El Archivo de Historias Clínicas. Cuestión de EspacioDocument4 pagesEl Archivo de Historias Clínicas. Cuestión de EspacioabresesamoPas encore d'évaluation