Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Theoretical Framework: Accountancy, Business, and Management Strand of K-12 IA1404/Group 3
Transféré par
Kamil Ubungen Delos ReyesDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Theoretical Framework: Accountancy, Business, and Management Strand of K-12 IA1404/Group 3
Transféré par
Kamil Ubungen Delos ReyesDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
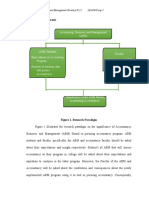
Accountancy, Business, and Management Strand of K-12
IA1404/Group 3
Theoretical Framework
The educational needs of the students change as fast as our technology evolves.
The ever dynamic economy of every nation has a direct impact on the changes in the
educational system of a country. Past approaches to teaching and the traditional
educational system have been effective so far but the present generation, with the help of
technology, is capable of learning more. The government together with educational
institutions should find ways on how to use the traditional education system while
integrating the new ones to form one innovative teaching method or system.
According to Charles H. Judd , the theory of generalization maintains that transfer
is a form of generalization which can be encouraged by training. It means that
experiences obtained in one situation are applicable to other situations. It puts emphasis
upon the value to understand, organize, and generalize specific experiences. There is a
need for the learner to interpret relationships and to be able to recognize and apply to
other situations the previously acquired facts or principles. (Jude,1946)
Additionally, Piagets theory of constructivism states that people produce
knowledge and form meaning based upon their experiences. Piagets theory covered
learning theories, teaching methods and education reform. Two of the key components
which create the construction of an individuals new knowledge are accommodation and
assimilation. Assimilating causes an individual to incorporate new experiences into the
old experiences. This causes the individual to develop new outlooks, rethink what were
once misunderstandings, and evaluate what is important, ultimately altering their
perceptions. Accommodation, on the other hand, is reframing the world and new
experiences into the mental capacity already present. Individuals conceive a particular
Accountancy, Business, and Management Strand of K-12
IA1404/Group 3
fashion in which the world operates. When things do not operate within that context, they
must accommodate and reframing the expectations with the outcomes.
On the other hand, according to the constructivism Theory of Jerome Bruner,
learning is an active process in which learners construct new ideas or concepts based
upon their current/past knowledge. The learner selects and transforms information,
construct hypotheses, and makes decisions, relying on a cognitive structure to do so.
Cognitive structure (i.e, schema, mental models) provides meaning and organization to
experiences and allows the individual to go beyond the information given.
Judds, Piagets, and Bruners theories are the most appropriate theories related to
this study. The theories suggests that past experiences as well as current knowledge of
something are tools that aid the change process. Also, one of the implications of these
theories is that the learner needs to gather all possible sources of knowledge and
experiences so mistakes in the past wont happen again. Just like the proponents, the
government, being the learner in this process, used its past understanding of the
educational system and developed a new one for its betterment, thus the birth of the K-12
Program.
Furthermore, Basic Education Sector Transformation (n.d) Theory of Change
(ToC) provides the desired outcomes of the Program, expected intermediate results for
learners, proposed strategies and the range of options for implementation. It shows how
change may occur in order to address problems, how interventions inter-relate and
contribute to achievement of end of program outcomes, given certain assumptions. It
builds on the problem analysis, the causal model and lessons learnt from past experience
of DepEd, DFAT and other development partners. It is based on a thorough and careful
Accountancy, Business, and Management Strand of K-12
IA1404/Group 3
analysis of how change can occur in the Philippines context, considering political
structures and processes, institutional culture and organizational capability, and evidence.
The Theory of Change underpinning this program is premised on four
considerations: 1. The principle of Inclusive Education which works to ensure that all
boys and girls have a right to basic education without regard for their sex, ethnicity, age
or physical or mental capacity. 2. The use of a systems perspective, to understand how
people, structures and processes work and influence one another as a whole. 3.
Consideration for DepEd levels of governance; i.e. the school level, Division, Region and
Central Office level with their corresponding focus on learners, schools, Divisions and
Policy and directions; for planning and implementing interventions.4. The establishment
of units of analysis and action based on specific grade level segments of Kindergarten to
Grade Three (primary level), Grade Four to Six (intermediate grades level), Grade 7 to 10
(secondary level) and Grade 11-12 (Senior High School). These segments represent
specific target groups distinct because of their age-range, psychosocial development and
differing educational objectives per group.
Learning competencies are distinct for each segment. At the Kindergarten to
Grade 3 level, it is the mastery of reading and numeracy; for Grade 10, it is measured by
readiness for Senior High School; and at Grade 12, it is indicated by competence in
selected academic or non-academic tracks. As an end point, more boys and girls will
complete their basic education when all boys and girls at the entry level age of each
segment are enrolled in school, when fewer boys and girls drop out of school, do not
repeat the grade and are retained in the next grade level. This proposition holds true for
all the four grade segments of K to Grade 12.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Power of Education: Education and LearningD'EverandThe Power of Education: Education and LearningPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Immersion Performance Chapter1Document17 pagesWork Immersion Performance Chapter1Gem Marie R. CletPas encore d'évaluation
- College Readiness Proposal - July 2019Document33 pagesCollege Readiness Proposal - July 2019Maria CrisalvePas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm-Examination Noriza B. BocaboDocument5 pagesMidterm-Examination Noriza B. BocaboTrisha Mae BocaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection 3Document17 pagesReflection 3MillababymafiaMyromeo'zjulietPas encore d'évaluation
- Compre. ExamDocument7 pagesCompre. ExamEden SumilayPas encore d'évaluation
- SSC Act Lesson 3 6Document8 pagesSSC Act Lesson 3 6Ana Marie NasolePas encore d'évaluation
- The Elusive Nature of Whole System Improvement in EducationDocument6 pagesThe Elusive Nature of Whole System Improvement in EducationCarola Fernanda Zañartu CanihuantePas encore d'évaluation
- SSC Act Lesson 3 6 1Document8 pagesSSC Act Lesson 3 6 1Ana Marie NasolePas encore d'évaluation
- Determinants of Curriculum DesignDocument30 pagesDeterminants of Curriculum DesignAaron MushunjePas encore d'évaluation
- School Counseling PsychologyDocument22 pagesSchool Counseling PsychologyNGOYA COURTNEYPas encore d'évaluation
- A Closer Look at K To 12: Awareness, Challenges, Difficulties, and Lived Experiences (Chapter 1 To 3)Document87 pagesA Closer Look at K To 12: Awareness, Challenges, Difficulties, and Lived Experiences (Chapter 1 To 3)Eiggy Yap100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Epsy5463Document7 pagesChapter 7 Epsy5463api-201648540Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment: Foundation of Education Educ 200 Block BDocument22 pagesAssignment: Foundation of Education Educ 200 Block BteachkhimPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilge Akar Bilge Akar 127679 474878547Document6 pagesBilge Akar Bilge Akar 127679 474878547api-707339091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample 3 CH 1-3Document57 pagesSample 3 CH 1-3api-300370017Pas encore d'évaluation
- CGS03025026 Take Home Examination CDDocument11 pagesCGS03025026 Take Home Examination CDAzizol YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- The Written Curriculum: What Do We Want To Learn?Document4 pagesThe Written Curriculum: What Do We Want To Learn?Melania AvramPas encore d'évaluation
- Master's Thesis (Jo Marie Garcia) - 015022Document113 pagesMaster's Thesis (Jo Marie Garcia) - 015022mariceldaan2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8609-1 Areej AmerDocument24 pages8609-1 Areej AmerZarlish KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Education Service Contracting (ESC) Scheme Questionnaire Edited..Document41 pagesEducation Service Contracting (ESC) Scheme Questionnaire Edited..Zicnarf Cajayon M100% (9)
- HSE4M Resource PDFDocument28 pagesHSE4M Resource PDFChris Corisco FreitasPas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy Refllection 4Document3 pagesPhilosophy Refllection 4kimbeerlyn doromasPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Strategies in Handling Unfavored Subject Across SHS StrandsDocument3 pagesAcademic Strategies in Handling Unfavored Subject Across SHS StrandsChals Luke Li UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 ThesisDocument8 pagesChapter 1 ThesisBryden Kyle Paringit BuhisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Educ302 Final Exam - HerminadoDocument4 pagesEduc302 Final Exam - HerminadoROD RYAN ETURMAPas encore d'évaluation
- QUANTIDocument6 pagesQUANTIdave niAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Thesis Merrylle AutosavedDocument27 pagesFinal Thesis Merrylle AutosavedJumaryse MarabutPas encore d'évaluation
- Misconception of Incoming Senior High School Students About The Implementation of Deped'S K-12 RequirementsDocument17 pagesMisconception of Incoming Senior High School Students About The Implementation of Deped'S K-12 RequirementsGabrielle BaltazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Better Learning Through Better Thinking Developing Students Metacognitive AbilitiesDocument13 pagesBetter Learning Through Better Thinking Developing Students Metacognitive AbilitiesMCHADPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper About Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument5 pagesResearch Paper About Learner Centered Psychological Principlesefe8zf19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy of EducationDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of EducationCharine DianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Research StudyDocument42 pagesFinal Research StudyJoshua T Conlu100% (1)
- Lesson 5Document6 pagesLesson 5Christine Joy FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Task ADocument17 pagesAssignment Task ANagarajan Pillai AboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformative LearningDocument7 pagesTransformative LearningIniobong IbokPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Studies Scope and SequenceDocument48 pagesSocial Studies Scope and Sequenceapi-169309159Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Manuscript On Educational Implications in Individual DifferencesDocument8 pagesA Manuscript On Educational Implications in Individual DifferencesJohn Paul JerusalemPas encore d'évaluation
- ChaptersDocument43 pagesChaptersMils Aled Zurc33% (6)
- Efficacy of Cooperative Learning Method To Increase Student Engagement and Academic Achievement 2Document7 pagesEfficacy of Cooperative Learning Method To Increase Student Engagement and Academic Achievement 2Aila Judea MoradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Tenacity: Mindsets and Skills That Promote Long-Term LearningDocument79 pagesAcademic Tenacity: Mindsets and Skills That Promote Long-Term LearningGatesFoundationPas encore d'évaluation
- FIRST S & R - Midterm - GS36 - EDAD203 - Maria Ceryll BalabagDocument5 pagesFIRST S & R - Midterm - GS36 - EDAD203 - Maria Ceryll BalabagMaria Ceryll BalabagPas encore d'évaluation
- ABSTRACT-José G. Vargas-Hernández PDFDocument13 pagesABSTRACT-José G. Vargas-Hernández PDFJoash Matthew S. CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrating HOTS Strategies in Students' Oral PresentationDocument7 pagesIntegrating HOTS Strategies in Students' Oral PresentationJoshua CasemPas encore d'évaluation
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument42 pagesThe Problem and Its Backgroundroneldayo62Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Gero SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Vismay Mona AttarPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Performances of Faculty and Students of College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences in Batangas State UniversityDocument26 pagesAcademic Performances of Faculty and Students of College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences in Batangas State UniversityKani Mahal KitahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction PaperDocument4 pagesReaction PaperAndrea D. MallariPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis About Teachers AttitudesDocument7 pagesThesis About Teachers Attitudesangielogantoledo100% (2)
- Cur Dev Group 3Document9 pagesCur Dev Group 3Nirvana Cherry YaphetsPas encore d'évaluation
- Misconception of Incoming Senior High School Students About The Implementation of Deped'S K-12 RequirementsDocument80 pagesMisconception of Incoming Senior High School Students About The Implementation of Deped'S K-12 RequirementsGabrielle BaltazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 EditedDocument28 pagesChapter 1 EditedJaypee Dela TorrePas encore d'évaluation
- ELC612Document24 pagesELC612YUVARANI SARAVANA SAMIPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles and Teaching Methods of Andragogy: Dr. Radhika KapurDocument14 pagesPrinciples and Teaching Methods of Andragogy: Dr. Radhika KapurAbhishek ShivappaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flipping ResearchDocument9 pagesFlipping ResearchMeriah Benett MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7Document5 pagesModule 7fahrid natPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Special Education AssignmentDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Special Education AssignmentDraft Night InvestingPas encore d'évaluation
- How Can Education Achieve A More Peaceful and Prosperous FutureDocument4 pagesHow Can Education Achieve A More Peaceful and Prosperous FutureJuenPas encore d'évaluation
- PR2 Research Chapter 2Document10 pagesPR2 Research Chapter 2Gabriel Jr. reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- General Banking ActDocument23 pagesGeneral Banking ActKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Negotiable Instruments Law Historical BackgroundDocument19 pagesThe Negotiable Instruments Law Historical BackgroundKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- New Central Bank ActDocument17 pagesNew Central Bank ActKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Planning and Strategic Management - NewDocument47 pages4 - Planning and Strategic Management - NewKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Managerial Decision MakingDocument34 pages3 - Managerial Decision MakingKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - HTML-lists and TablesDocument11 pages2 - HTML-lists and TablesKamil Ubungen Delos Reyes100% (1)
- 4 Audit SamplingDocument5 pages4 Audit SamplingKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting, Business, and Management (ABM) : Conceptual FrameworkDocument2 pagesAccounting, Business, and Management (ABM) : Conceptual FrameworkKamil Ubungen Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Defense Panel Report Sheet CRCDocument2 pagesDefense Panel Report Sheet CRCMyca DelimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Esl Lesson PlanningDocument5 pagesEsl Lesson PlanningAlireza MollaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Parent Handbook 20-21Document14 pagesStudent Parent Handbook 20-21api-169504372Pas encore d'évaluation
- Be A Frog, A Bird, or A TreeDocument45 pagesBe A Frog, A Bird, or A TreeHWelsh100% (2)
- Regan Walton ResumeDocument2 pagesRegan Walton Resumeapi-487845926Pas encore d'évaluation
- MUSIC 7 Q3 W1D1 MoroIslamic Vocal MusicDocument2 pagesMUSIC 7 Q3 W1D1 MoroIslamic Vocal MusicAires Ichon100% (1)
- Duxbury Clipper 2010 - 12 - 05Document48 pagesDuxbury Clipper 2010 - 12 - 05Duxbury ClipperPas encore d'évaluation
- Aurora Pioneers Memorial Ollege: (FORMERLY: Cebuano Barracks Institute)Document4 pagesAurora Pioneers Memorial Ollege: (FORMERLY: Cebuano Barracks Institute)Joan Mae Angot - VillegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Agriculture and Fishery ArtsDocument44 pagesAgriculture and Fishery ArtsJohn Ray EnajePas encore d'évaluation
- School Health ServicesDocument56 pagesSchool Health Servicessunielgowda80% (5)
- Eden, G. F., & Moats, L. (2002) - The Role of Neuroscience in The Remediation of Students With Dyslexia. Nature Neuroscience, 5, 1080-1084.Document5 pagesEden, G. F., & Moats, L. (2002) - The Role of Neuroscience in The Remediation of Students With Dyslexia. Nature Neuroscience, 5, 1080-1084.Jose LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Transactional and Transformational LeadershipDocument4 pagesTransactional and Transformational LeadershipAnonymous ZLSyoWhQ7100% (1)
- Field Study I A Guide For 21 Century Student TeachersDocument3 pagesField Study I A Guide For 21 Century Student TeachersSc JuanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fs JosephsonDocument393 pagesFs JosephsonZhanna Grechkosey100% (4)
- ĐỀ ĐẶC BIỆT KHÓA 2005Document5 pagesĐỀ ĐẶC BIỆT KHÓA 2005phuc07050705Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lac Sessions: General Tinio National High SchoolDocument1 pageLac Sessions: General Tinio National High SchoolFrancis JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Felipe Padilla de LeonDocument4 pagesFelipe Padilla de LeonJingky SallicopPas encore d'évaluation
- CVDocument5 pagesCVapi-267533162Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Rizal 1Document6 pagesLesson 1 Rizal 1Anne Maerick Jersey OteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Singapore Math Model Drawing EbookDocument19 pagesSingapore Math Model Drawing EbookAzwani Abdullah100% (3)
- Social Studies 10-1 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesSocial Studies 10-1 Course Outlineapi-189472135Pas encore d'évaluation
- hlth634 Brief Marketing Plan Outline Jewel BrooksDocument6 pageshlth634 Brief Marketing Plan Outline Jewel Brooksapi-299055548Pas encore d'évaluation
- Art TherapyDocument77 pagesArt TherapyMaria Tudosa100% (4)
- 6.MIL 5. Media and Information SourcesDocument32 pages6.MIL 5. Media and Information SourcesHeli Senn VentenillaPas encore d'évaluation
- CR 1993 Joyce ReynoldsDocument2 pagesCR 1993 Joyce ReynoldsFlosquisMongisPas encore d'évaluation
- Registration: Ramco Institute of TechnologyDocument2 pagesRegistration: Ramco Institute of TechnologySUNDARAMAHALINGAM APas encore d'évaluation
- Exam For Real Estate in CaliforniaDocument230 pagesExam For Real Estate in Californiaharpay100% (9)
- Aimless ScienceDocument19 pagesAimless Scienceaexb123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanSvg Frendz75% (4)
- Frontlearn 2021 Fee StructureDocument1 pageFrontlearn 2021 Fee StructureNjihiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)D'EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsD'EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.D'EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeD'EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeD'EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersD'EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryD'EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingD'EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldD'EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (80)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)D'EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Pas encore d'évaluation