Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fiq Eo 1
Transféré par
SamTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fiq Eo 1
Transféré par
SamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
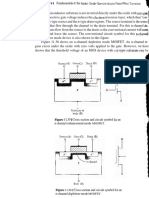
EOC chapter 1
1. Describe the categories of silicon and germanium as semiconductor devices.
Both this material can become conductor and insulator
Has 4 electron valence
Can allow or suppress electrical current flow
2. Draw the atomic structure of germanium containing 32 electrons. Show the
calculations.
2
2
2
2
3.
x
x
x
x
1^2
2^2
3^2
4^2
=
=
=
=
2
8
18
32
(32)
(30)
(22)
(4)
A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing
of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs,
and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share
electrons, is known as covalent bonding.[1][better source needed] For many molecules, the
sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding
to a stable electronic configuration.
There are four method to allow electron freed by covalent bond which is:
Heat
Potential Difference
Temperature rise
Doping Process
4. a) Adding impurities to the intrinsic semiconductor we can change the
conductivity of
the material,this is called doping.
N-type doping
-N-type : pentavalent (atom with 5 valence electrons) impurityatoms are
added
-[Sb(Antimony)+Si].Arsenic phosphorus
-Negative charges (electrons) are generated
-N-type has lots of free electrons
P-type doping
-P-type : trivalent (atom with 3 valence electrons) impurity atoms are
added
-[B(bond)+ Si] . Gallium, Indium
-Positive charges (holes) are generated
-P-type has lots of holes
5. a) Forward biased :
Depletion region become thinner as the holes in the P-type region and
the electrons in
the N-ype region are pushed toward the junction.
With increasing forward-bias voltage (Bias voltage V bias >barrier
voltage V bar)the depletion zone eventually becomes thin enough and
reducing electrical resistance.
b) Reverse biased ;
P-type material connected to the negative terminal while N-type region
is connected to the positive terminal.
The holes in the P-type metarial are pulled away from the junction and
the electrons in the N-type region will also be pulled away from the
junction causing the width of the depletion zone to increase.
Resistance becomes higher and a current cannot paas through.
The increase in resistance of the p-n junction results in the junction as
an insulator
6. Difference between Intrinsic and Extrinsic
INTRINSIC
-Material is chemically very pure
(pure semiconductor)
EXTRINSIC
-An improved intrinsic semiconductor with a small
amount of impurities added by a process known as
doping
-Possesses poor conductivity
-Alters the electrical properties of the
semiconductors and improves its conductivity
7. 2 effect high reverse bias in P-N junction
If the P-N junction are supplied with a very high reverse bias voltage,it will
disturb the stability of covalent bond,the electrons will attracted to positive
potential and become free as a current carrier
When the electric fields increases (with voltage),more and more electrons
are freed from its covalent bonds,these will result a high value reverse
current flow (breakdown occur)
The voltage where the breakdown occurs is called breakdown voltage.
Then,the P-N junction will burn
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Case Study: PN Norakmar Binti JamalDocument13 pagesCase Study: PN Norakmar Binti JamalSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Pneumatic 2aDocument4 pagesLab Pneumatic 2aSam100% (1)
- Lab Pneumatic 2bDocument4 pagesLab Pneumatic 2bSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 AmplifierDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 AmplifierSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 2 - DC Power SupplyDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - DC Power SupplySam67% (3)
- EXPERIMENT 1 - Diode As RectifierDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 1 - Diode As RectifierSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Eoc 1 e System AnsweredDocument4 pagesEoc 1 e System AnsweredSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding ReportDocument15 pagesWelding ReportSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Eoc 2 - Linear DC Power Supply - Q - Jun 2016Document2 pagesEoc 2 - Linear DC Power Supply - Q - Jun 2016SamPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Chapter ForDocument17 pagesChapter Forbelacheweshetu222Pas encore d'évaluation
- EE-ESE'2015-Objective Paper II (Set-A) - New3 PDFDocument28 pagesEE-ESE'2015-Objective Paper II (Set-A) - New3 PDFsherlinPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT FabricationDocument26 pagesBJT Fabricationabhinavbhatnagar0% (1)
- Electronics and Micrprocessor NotesDocument95 pagesElectronics and Micrprocessor NotesSam SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument92 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsjoePas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Devices: Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University Guyeon@eecs - Harvard.eduDocument27 pagesMOSFET Devices: Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University Guyeon@eecs - Harvard.eduDr-Ahmed ElkoranyPas encore d'évaluation
- Opto Electronic DevicesDocument7 pagesOpto Electronic DeviceslvsaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1Document52 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1My WritingsPas encore d'évaluation
- EX - NO.: Characteristics of PN Junction Diode and Zener Diode DateDocument8 pagesEX - NO.: Characteristics of PN Junction Diode and Zener Diode Datepinky whitePas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Semiconductor TheoryDocument32 pages01 Semiconductor TheoryAnmay MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- LEDsDocument61 pagesLEDsGeethakshayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Semiconductor Science and Light Emitting DiodesDocument218 pagesSemiconductor Science and Light Emitting DiodesBalaji Raja RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems and SolutionsDocument14 pagesProblems and Solutionsdivakaran sundarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-8 Analog MCQ and MSQDocument43 pagesCh-8 Analog MCQ and MSQRintu MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- PN Dioed 3265 Ch1 IntrDocument18 pagesPN Dioed 3265 Ch1 Intrbobca117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cmos IssuesDocument180 pagesCmos IssuesArun Dev Dhar DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- ELECTRONICS@alinaimanarif PDFDocument41 pagesELECTRONICS@alinaimanarif PDFMazni Hanisah100% (1)
- Basics of MOSFET - QuestionsDocument6 pagesBasics of MOSFET - QuestionsAyush MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument44 pagesLecture 4 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaShameer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 15 16 Lecture Slides EEE ZG571 L8 1631939916541Document88 pagesSession 15 16 Lecture Slides EEE ZG571 L8 1631939916541Amal VPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Handout NotesDocument121 pagesPhysical Handout NotesJimmy MachariaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2896 C-V Char Mos CA#26c8b1Document10 pages2896 C-V Char Mos CA#26c8b1azizdostumPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1Document69 pagesModule 1Nicholas AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE XII Physics Notes SemiconductorDocument20 pagesCBSE XII Physics Notes Semiconductorkaushik2470% (1)
- Chapter 11 - MOSFETDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - MOSFETChandima Ishan DharmarathnePas encore d'évaluation
- Ele Lab ReportDocument42 pagesEle Lab ReportDik Man RyPas encore d'évaluation
- Module III IV Lasers Optical Fibers-1Document13 pagesModule III IV Lasers Optical Fibers-1OpenaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 9 Semiconductor 2023Document6 pagesUnit 9 Semiconductor 2023spcodrPas encore d'évaluation
- Electroluminescence PDFDocument217 pagesElectroluminescence PDFLibro De Oro De Los Experimentos QuimicosPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc MCQDocument5 pagesEdc MCQRajesh PathakPas encore d'évaluation