Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Upsc Ese Syllapus
Transféré par
logicvirus0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues7 pagesUPSC optional subject syllabus of Mechanical engineering
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentUPSC optional subject syllabus of Mechanical engineering
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues7 pagesUpsc Ese Syllapus
Transféré par
logicvirusUPSC optional subject syllabus of Mechanical engineering
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
UNION PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION, NEW DELHI
CSE Mechanical Engineering Syllabus
Paper - I
1. Mechanics:
Mechanics of rigid bodies: Equations of equilibrium in
space and its application; first and second moments of
area; simple problems on friction; kinematics of particles
for plane motion; elementary particle dynamics.
Mechanics of deformable bodies: Generalized Hookes law
and its application; design problems on axial stress, shear
stress and bearing stress; material properties for dynamic
loading; bending shear and stresses in beams;.
determination of principle stresses and strains - analytical
and graphical; compound and combined stresses; bi-axial
stresses - thin walled pressure vessel; material behaviour
and design factors for dynamic load; design of circular
shafts for bending and torsional load only; deflection of
beam for statically determinate problems; theories of
failure.
2. Engineering Materials: Basic concepts on structure of
solids; common ferrous and non-ferrous materials and their
applications; heat-treatment of steels; non-metals- plastics,
ceramics, composite materials and nano-materials.
3. Theory of Machines: Kinematic and dynamic analysis of
plane mechanisms. Cams, Gears and epicyclic gear trains,
flywheels, governors, balancing of rigid rotors, balancing of
single and multicylinder engines, linear vibration analysis of
mechanical systems (single degree of freedom), Critical speeds
and whirling of shafts.
4. Manufacturing Science:
Manufacturing Process: Machine tool engineering
Merchants force analysis; Taylors tool life equation;
conventional machining; NC and CNC machining process;
jigs and fixtures. Non-conventional machining EDM, ECM,
ultrasonic, water jet machining etc; application of lasers
and plasmas; energy rate calculations. Forming and
welding processes- standard processes. Metrology concept of fits and tolerances; tools and gauges;
comparators; inspection of length; position; profile and
surface finish.
Manufacturing Management: System design: factory
location- simple OR models; plant layout - methods based;
applications of engineering economic analysis and breakeven analysis for product selection, process selection and
capacity planning; predetermined time standards. System
planning; forecasting methods based on regression and
decomposition, design and balancing of multi model and
stochastic assembly lines; inventory management
probabilistic inventory models for order time and order
quantity determination; JIT systems; strategic sourcing;
managing inter plant logistics. System operations and
control: Scheduling algorithms for job shops; applications
of statistical methods for product and process quality
control - applications of control charts for mean, range,
percent defective, number of defectives and defects per
unit; quality cost systems; management of resources,
organizations and risks in projects. System improvement:
Implementation of systems, such as total quality
management, developing and managing flexible, lean and
agile organizations.
Paper - II
1. Thermodynamics, Gas Dynamics and Turbine:
Basic concept of First law and second law of
Thermodynamics; concept of entropy and reversibility;
availability and unavailability and irreversibility.
Classification and properties of fluids; incompressible and
compressible fluids flows; effect of Mach number and
compressibility; continuity momentum and
energy
equations; normal and oblique shocks; one dimensional
isentropic flow; flow or fluids in duct with frictions that
transfer.
Flow through fans, blowers and compressors; axial and
centrifugal flow configuration; design of fans and
compressors; single problems compresses and turbine
cascade; open and closed cycle gas turbines; work done in
the gas turbine; reheat and regenerators.
2. Heat Transfer:
Conduction heat transfer- general conduction equation Laplace, Poisson and Fourier equations; Fourier law of
conduction; one dimensional steady state heat conduction
applied to simple wall, solid and hollow cylinder & spheres.
Convection heat transfer- Newtons law of convection; free
and forces convection; heat transfer during laminar and
turbulent flow of an incompressible fluid over a flat plate;
concepts of Nusselt number, hydrodynamic and thermal
boundary layer their thickness; Prandtl number; analogy
between heat and momentum transfer- Reynolds, Colbum,
Prandtl analogies; heat transfer during laminar and
turbulent flow through horizontal tubes; free convection
from horizontal and vertical plates.
Black body radiation - basic radiation laws such as StefanBoltzman, Planck distribution, Weins displacement etc.
Basic heat exchanger analysis; classification of heat
exchangers.
3. I .C. Engines:
Classification, thermodynamic cycles of operation;
determination of break power, indicated power,
mechanical efficiency, heat balance sheet, interpretation
of performance characteristics, petrol, gas and diesel
engines.
Combustion in SI and CI engines, normal and abnormal
combustion; effect of working parameters on knocking,
reduction of knocking; Forms of combustion chamber for
SI and CI engines; rating of fuels; additives; emission.
Different systems of IC engines- fuels; lubricating; cooling
and transmission systems. Alternate fuels in IC engines.
4. Steam Engineering:
Steam generation- modified Rankine cycle analysis;
Modern steam boilers; steam at critical and supercritical
pressures; draught equipment; natural and artificial
draught; boiler fuels solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Steam
turbines - principle; types; compounding; impulse and
reaction turbines; axial thrust.
Steam nozzles- flow of steam in convergent and divergent
nozzle; pressure at throat for maximum discharge with
different initial steam conditions such as wet,
saturated and superheated, effect of variation of back
pressure; supersaturated flow of steam in nozzles, Wilson
line.
Rankine cycle with internal and external irreversibility;
reheat factor; reheating and regeneration, methods of
governing; back pressure and pass out turbines.
Steam power plants - combined cycle power generation;
heat recovery steam generators (HRSG) fired and unfired,
cogeneration plants.
5. Refrigeration and air-conditioning:
Vapour compression refrigeration cycle - cycle on p-H & T-s
diagrams; eco-friendly refrigerants - R134a,123; Systems
like evaporators, condensers, compressor, expansion
devices. Simple vapour absorption systems.
Psychrometry - properties; processes; charts; sensible
heating and cooling; humidification and dehumidification
effective temperature; air-conditioning load calculation;
simple duct design.
UNION PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION, NEW DELHI
ENGINEERING SERVICES EXAMINATION (ESE) SYLLABI
Branch/Discipline: Mechanical Engineering
Contents for syllabi of both the Papers together for
Stage-I objective type
PaperII and separately for Stage-II Conventional type
Paper-I and Paper II
PAPER I
1. Fluid Mechanics:
Basic Concepts and Properties of Fluids, Manometry, Fluid
Statics, Buoyancy, Equations of Motion, Bernoullis equation
and applications, Viscous flow of incompressible fluids, Laminar
and Turbulent flows, Flow
through pipes and head losses in pipes.
2. Thermodynamics and Heat transfer:
Thermodynamic systems and processes; properties of pure
substance; Zeroth, First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics;
Entropy,
Irreversibility
and
availability;
analysis
of
thermodynamic cycles related to energy conversion: Rankine,
Otto, Diesel and Dual Cycles; ideal
compressibility factor; Gas mixtures.
and
real
gases;
Modes of heat transfer, Steady and unsteady heat conduction,
Thermal resistance, Fins, Free and forced convection,
Correlations for convective heat transfer, Radiative heat
transfer Radiation heat transfer coefficient; boiling and
condensation, Heat exchanger performance analysis
3. IC Engines, Refrigeration and Air conditioning:
SI and CI Engines, Engine Systems and Components,
Performance characteristics and testing of IC Engines; Fuels;
Emissions and Emission Control.
Vapour compression refrigeration, Refrigerants and Working
cycles, Compressors, Condensers, Evaporators and Expansion
devices, Other types of refrigeration systems like Vapour
Absorption, Vapour jet, thermo electric and Vortex tube
refrigeration. Psychometric properties and processes, Comfort
chart, Comfort and industrial air conditioning, Load calculations
and Heat pumps.
4. Turbo Machinery:
Reciprocating and Rotary pumps, Pelton wheel, Kaplan and
Francis Turbines, velocity diagrams, Impulse and Reaction
principles, Steam and Gas Turbines, Theory of Jet Propulsion
Pulse jet and Ram Jet Engines, Reciprocating and Rotary
Compressors Theory and Applications
5. Power Plant Engineering:
Rankine and Brayton cycles with regeneration and reheat, Fuels
and their properties, Flue gas analysis, Boilers, steam turbines
and other power plant components like condensers, air
ejectors, electrostatic precipitators and cooling towers their
theory and design, types and applications;
6. Renewable Sources of Energy:
Solar Radiation, Solar Thermal Energy collection - Flat Plate and
focusing collectors their materials and performance. Solar
Thermal Energy Storage, Applications heating, cooling and
Power Generation; Solar Photovoltaic Conversion; Harnessing of
Wind Energy, Bio-mass and Tidal Energy Methods and
Applications, Working principles of Fuel Cells.
PAPER II
7. Engineering Mechanics:
Analysis of System of Forces, Friction, Centroid and Centre of
Gravity, Dynamics; Stresses and Strains-Compound Stresses
and Strains, Bending Moment and Shear Force Diagrams,
Theory of Bending Stresses-Slope and deflection-Torsion, Thin
and thick Cylinders, Spheres.
8. Engineering Materials:
Basic Crystallography, Alloys and Phase diagrams, Heat
Treatment, Ferrous and Non Ferrous Metals, Non metallic
materials, Basics of Nano-materials, Mechanical Properties and
Testing, Corrosion prevention and control
9. echanisms and Machines:
Types of Kinematics Pair, Mobility, Inversions, Kinematic
Analysis, Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Planar
Mechanisms, CAMs with uniform acceleration and retardation,
cycloidal motion, oscillating followers; Vibrations Free and
forced vibration of undamped and damped SDOF systems,
Transmissibility Ratio, Vibration Isolation, Critical Speed of
Shafts. Gears Geometry of tooth profiles, Law of gearing,
Involute profile, Interference, Helical, Spiral and Worm Gears,
Gear Trains- Simple, compound and Epicyclic; Dynamic Analysis
Slider crank mechanisms, turning moment computations,
balancing of Revolving & Reciprocating masses, Gyroscopes
Effect of Gyroscopic couple on automobiles, ships and aircrafts,
Governors.
10. Design of Machine Elements:
Design for static and dynamic loading; failure theories; fatigue
strength and the S-N diagram; principles of the design of
machine elements such as riveted, welded and bolted joints.
Shafts, Spur gears, rolling and sliding contact bearings, Brakes
and clutches, flywheels.
11. Manufacturing
Engineering:
,Industrial
and
Maintenance
Metal casting-Metal forming, Metal Joining, Machining and
machine tool operations, Limits, fits and tolerances, Metrology
and inspection, computer Integrated manufacturing, FMS,
Production planning and Control, Inventory control and
operations research - CPM-PERT. Failure concepts and
characteristics-Reliability, Failure analysis, Machine Vibration,
Data acquisition, Fault Detection, Vibration Monitoring, Field
Balancing of Rotors, Noise Monitoring, Wear and Debris
Analysis, Signature Analysis,
DT Techniques in Condition
Monitoring.
12. Mechatronics and Robotics:
Microprocessors
and
Microcontrollers:
Architecture,
programming, I/O, Computer interfacing, Programmable logic
controller. Sensors and actuators, Piezoelectric accelerometer,
Hall effect sensor, Optical Encoder, Resolver, Inductosyn,
Pneumatic and Hydraulic actuators, stepper motor, Control
Systems- Mathematical modeling of Physical systems, control
signals, controllability and observability. Robotics, Robot
Classification, Robot Specification, notation; Direct and Inverse
Kinematics; Homogeneous Coordinates and Arm Equation of
four Axis SCARA Robot
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Extrusion of PlasticsDocument49 pagesExtrusion of PlasticsDenys MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Test 1 - Grade 8Document2 pagesLong Test 1 - Grade 8katherine corvera100% (2)
- Wind Turbine DesignDocument58 pagesWind Turbine Designlogicvirus100% (1)
- Piping Interview QuestionDocument5 pagesPiping Interview Questionmithunjobs100% (3)
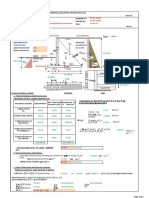
- ACI 318-08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort - Rev1.0 - 08-Apr-2014Document4 pagesACI 318-08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort - Rev1.0 - 08-Apr-2014Janmesh Nivrutti KhedkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing Multiple Choice QuestionDocument7 pagesEngineering Drawing Multiple Choice Questionlogicvirus59% (27)
- Basic Autopilot SystemsDocument4 pagesBasic Autopilot SystemsSonali Srivastava100% (1)
- Calculations For FADDocument5 pagesCalculations For FADEngr. Umer Farooq100% (1)
- Unit I - Introduction of Fatigue FailureDocument32 pagesUnit I - Introduction of Fatigue Failurelogicvirus100% (1)
- 15 2018 Ccs-Ii QP 230219 PDFDocument78 pages15 2018 Ccs-Ii QP 230219 PDFvidhya88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tiruvallur District - Tiruvallur Taluk - Revenue VillagesDocument7 pagesTiruvallur District - Tiruvallur Taluk - Revenue VillageslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- TN Police CUG PV299Document2 pagesTN Police CUG PV299logicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Unicorn Insurance2016Document1 pageUnicorn Insurance2016logicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar 3rd YearDocument2 pagesSeminar 3rd YearlogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid MechanicsDocument1 pageSolid MechanicslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Iqac Monthly ReportDocument2 pagesIqac Monthly ReportlogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Moc of Air and NitrogenDocument4 pagesMoc of Air and NitrogenlogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum & Syllabi of 3rd To 8th Sem For B.E.aero SNSCT AutonomousDocument18 pagesCurriculum & Syllabi of 3rd To 8th Sem For B.E.aero SNSCT AutonomouslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Monitoring Report TutorialDocument1 pageMonitoring Report TutoriallogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 DfsDocument16 pages1 DfslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012-16 AraDocument2 pages2012-16 AralogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2logicvirus0% (1)
- Me217strength of Materials L T P CDocument2 pagesMe217strength of Materials L T P ClogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Conternt Beyond SyllabusDocument3 pagesConternt Beyond SyllabuslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Mft-II Lab ManualDocument48 pagesMft-II Lab Manualதியாகராஜன் அரிதாஸ்Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conternt Beyond SyllabusDocument3 pagesConternt Beyond SyllabuslogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaPas encore d'évaluation
- FM QPDocument2 pagesFM QPlogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computer Science (I) : T. K. Yin, Nuk-CsieDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Computer Science (I) : T. K. Yin, Nuk-CsielogicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus R2013 PDFDocument105 pagesSyllabus R2013 PDFlogeshboy007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Timoshenko, S. P., 1921, On The Correction Factor For Shear of The Differential Equation For Transverse Vibrations of Bars of Uniform Cross-SectioDocument1 pageTimoshenko, S. P., 1921, On The Correction Factor For Shear of The Differential Equation For Transverse Vibrations of Bars of Uniform Cross-SectiologicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.1.88Document10 pages10.1.1.88logicvirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 1401 - Finite Element Analysis 2marks With AnswersDocument22 pagesMe 1401 - Finite Element Analysis 2marks With AnswersMak86% (14)
- Study Note Stress - Strain Analysis of Simple Structures RevBDocument20 pagesStudy Note Stress - Strain Analysis of Simple Structures RevBSboniso KhethukuthulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Properties and Anisotropy of Elastic BehaviorDocument44 pagesElastic Properties and Anisotropy of Elastic Behaviorkhers_zalPas encore d'évaluation
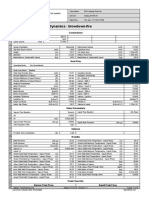
- Depressuring - Dynamics: Blowdown-Fire: ConnectionsDocument4 pagesDepressuring - Dynamics: Blowdown-Fire: ConnectionsNKPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To RefrigerationDocument79 pagesIntroduction To RefrigerationN S SenanayakePas encore d'évaluation
- Div ( ( (Rho NuEff) Dev2 (T (Grad (U) ) ) ) )Document17 pagesDiv ( ( (Rho NuEff) Dev2 (T (Grad (U) ) ) ) )bahakumatyPas encore d'évaluation
- FloorDocument4 pagesFloorNadir Khattak Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- EPS White Book Public 2004-04Document67 pagesEPS White Book Public 2004-04danaromalandPas encore d'évaluation
- Fracture Toughness and Brittle Failure: A Pressure Vessel Case StudyDocument6 pagesFracture Toughness and Brittle Failure: A Pressure Vessel Case StudyEnp JgcPas encore d'évaluation
- Whole GardnerMarkAlan2004 ThesisDocument380 pagesWhole GardnerMarkAlan2004 ThesisAnil kumar RPas encore d'évaluation
- EKT Mech 2014 2Document9 pagesEKT Mech 2014 2Ravinder ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fsi Due To Water SplashingDocument4 pagesFsi Due To Water Splashingsaugat pandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook TabsDocument1 pageHandbook TabsABPPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Thermodynamics Unit Iv Compressors, Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument28 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Unit Iv Compressors, Refrigeration and Air ConditioningMuthuvel MPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Work and Mechanical EnergyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 Work and Mechanical Energyehab maysaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 01-03Document15 pagesLecture 01-03Fayaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 09 07-PrePoMax-v1 1 0-Examples-ManualDocument29 pages2021 09 07-PrePoMax-v1 1 0-Examples-ManualMarcelo ResendePas encore d'évaluation
- PHY12 Thermal Physics Problem Set Thermal ExpansionDocument2 pagesPHY12 Thermal Physics Problem Set Thermal ExpansionReese VespertinePas encore d'évaluation
- INDIAN Steel TableDocument9 pagesINDIAN Steel Tablekeshav langerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document76 pagesChapter 5esra kadriye akgülPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic3 FluidMotionDocument35 pagesTopic3 FluidMotionSomnath SomadderPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation FullDocument57 pagesEvaporation FullMonty KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso Deformação 2285Document5 pagesIso Deformação 2285Eric FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- 17me3302 - Unit One TheoryDocument70 pages17me3302 - Unit One TheoryZayeem ZehekPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No - 4: University of Zakho College of Engineering Department of Petroleum Eng Laboratory of Drilling FluidDocument12 pagesExperiment No - 4: University of Zakho College of Engineering Department of Petroleum Eng Laboratory of Drilling FluidNasih AhmadPas encore d'évaluation