Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mahogany
Transféré par
liezl CmCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mahogany
Transféré par
liezl CmDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Botanicals Description of Mahogany
Mahogany (Swietenia mahogani) is a member of the family Meliaceae, which contains about
500 other species of trees and shrubs native to tropical forests in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
Other common names for this species are the Spanish or West Indies mahogany. Various other
species of trees have also been given the name mahogany, but the true mahogany is Swietenia
mahogani. Mahogany is one of the most valuable of the tropical hardwoods because of its
desirable qualities for the crafting of fine furniture.
Mahogany is a commercially important lumber prized for its beauty, durability, and color, and
used for paneling and to make furniture, boats, musical instruments and other items. Mahogany
has a straight, fine, and even grain, and is relatively free of voids and pockets. Its reddish-brown
color darkens over time, and displays a reddish sheen when polished. It has excellent
workability, and is very durable. Historically, the tree's girth allowed for wide boards from
traditional mahogany species. These properties make it a favorable wood for crafting cabinets
and furniture.
Much of the first-quality furniture made in the American colonies from the mid-18th century
was made of mahogany, when the wood first became available to American craftsmen.
Mahogany is still widely used for fine furniture; however, the rarity of Cuban mahogany and
over harvesting of Honduras and Brazilian mahogany has diminished their use.
Mahogany also resists wood rot, making it attractive in boat construction. It is a tone wood,
often used for musical instruments, particularly the backs, sides and necks of acoustic guitars,
electric guitar bodies, and drum shells because of its ability to produce a very deep, warm tone
compared to other commonly used woods such as maple or birch. Mahogany is native to humid
tropical forests of the West Indies, Mexico, and Central America. Until rather recently, mahogany
was especially abundant in forests in Honduras. However, the quantity of mahogany has been
greatly reduced throughout its range by extensive logging. Although much reduced in abundance,
mahogany is not yet considered an endangered species.
[
Mahogany is also indigenous to extreme southern Florida, where it occurs in some of the
hardwood "islands" in the saw grass wetlands of Everglades National Park, known locally as
hammocks. However, mahogany reaches the northern limits of its range in southern Florida, and
is rather sparse in that region. Because of its great value as lumber, mahogany has also been
planted in suitable tropical climates beyond its native range.
Botanicals Description of Mahogany
Mahogany are indigenous to extreme southern Florida, where it occurs in some of the
hardwood "islands" in the saw grass wetlands of Everglades National Park, known locally as
hammocks. However, mahogany reaches the northern limits of its range in southern Florida, and
is rather sparse in that region. Because of its great value as lumber, mahogany has also been
planted in suitable tropical climates beyond its native range. Much of the first-quality furniture
made in the American colonies from the mid-18th century was made of mahogany, when the
wood first became available to American craftsmen. Mahogany is still widely used for fine
furniture; however, the rarity of Cuban mahogany and over harvesting of Honduras and Brazilian
mahogany has diminished their use. Mahogany is one of the most valuable of the tropical
hardwoods because of its desirable qualities for the crafting of fine furniture. These properties
make it a favorable wood for crafting cabinets and furniture. Because mahogany is a
commercially important lumber prized for its beauty, durability, and color, and used
for paneling and to make furniture, boats, musical instruments and other items.
Mahogany has a straight, fine, and even grain, and is relatively free of voids and pockets. Its
reddish-brown color darkens over time, and displays a reddish sheen when polished. It has
excellent workability, and is very durable. Mahogany also resists wood rot, making it attractive
in boat construction. It is a tone wood,[ often used for musical instruments, particularly the backs,
sides and necks of acoustic guitars, electric guitar bodies, and drum shells because of its ability
to produce a very deep, warm tone compared to other commonly used woods such
as maple or birch.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Ticket To Ride SATBBDocument10 pagesTicket To Ride SATBBevelinesand100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Cineplex Magazine October 2002Document48 pagesCineplex Magazine October 2002Ronen Gaisiner0% (1)
- PlayscriptsDocument4 pagesPlayscriptsliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- No Cars Go PianoDocument4 pagesNo Cars Go PianoRubi Maihöfer100% (1)
- RRU5909s Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesRRU5909s Technical SpecificationsDmitry059Pas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application NoteDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application NoteInsan AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Root Causes of Poor Reading ComprehensionDocument1 pageRoot Causes of Poor Reading Comprehensionliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Intramurals Is The Perfect Time To Highlight Camaraderie, Sportsmanship and Vast TalentsDocument1 pageIntramurals Is The Perfect Time To Highlight Camaraderie, Sportsmanship and Vast Talentsliezl Cm100% (3)
- CSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets FormDocument4 pagesCSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets Formwyclef_chin100% (6)
- Teaching Techniques of Suzuki, Rolland, and ZweigDocument7 pagesTeaching Techniques of Suzuki, Rolland, and Zweigheidi cerna100% (2)
- Transcript - Ken Robinson Says Schools Kill CreativityDocument5 pagesTranscript - Ken Robinson Says Schools Kill Creativitysoniasedano0% (1)
- Candle Lighting MessageDocument3 pagesCandle Lighting Messageliezl Cm100% (8)
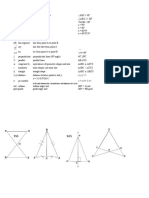
- Math SymbolsDocument2 pagesMath Symbolsliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL TemplateDocument2 pagesDLL Templateliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Presentation RubricDocument1 pageOral Presentation Rubricliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Damath PositionDocument1 pageDamath Positionliezl Cm100% (1)
- Final Examination in English 11 2018Document2 pagesFinal Examination in English 11 2018liezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- LIS Manual PDFDocument211 pagesLIS Manual PDFGapmil Noziuc NylevujPas encore d'évaluation
- LyricsDocument8 pagesLyricsliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- State Whether Each of The Following Is True or FalseDocument1 pageState Whether Each of The Following Is True or Falseliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Litera ADocument1 pageLitera AAna SanduPas encore d'évaluation
- Litera ADocument1 pageLitera AAna SanduPas encore d'évaluation
- Filipino Student RecordsDocument6 pagesFilipino Student Recordsliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7-10 MathematicsDocument63 pagesGrade 7-10 Mathematicsliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Praise and Worship SongDocument2 pagesPraise and Worship Songliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- ProgrammeDocument1 pageProgrammeliezl CmPas encore d'évaluation
- Audio Power Amplifier: Presented ByDocument12 pagesAudio Power Amplifier: Presented BySiddhartha SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Update & FACH Transfer: Security LevelDocument27 pagesCell Update & FACH Transfer: Security Levelsos987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Music Theory Worksheet 1 The StaffDocument1 pageMusic Theory Worksheet 1 The StaffMichelle KiernanPas encore d'évaluation
- RHCP Can't StopDocument4 pagesRHCP Can't StopRed Raphael SanzioPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical InterviewDocument3 pagesTechnical InterviewGerard Paul NaidasPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Unit 7 DVD Script: PHOTOCOPIABLE © Pearson Education Limited 2015Document2 pagesElementary Unit 7 DVD Script: PHOTOCOPIABLE © Pearson Education Limited 2015Turgut Enes AteşPas encore d'évaluation
- Sol EndDocument8 pagesSol EndBorn MaDPas encore d'évaluation
- (Naruto Shippuden) - Many Experience BattleDocument2 pages(Naruto Shippuden) - Many Experience BattleHarry Damian Ramirez ArrietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stolen GlancesDocument5 pagesStolen Glancesタンマリー・グロPas encore d'évaluation
- History and Evolution of GSM and 3G Mobile NetworksDocument220 pagesHistory and Evolution of GSM and 3G Mobile NetworksArif PashaPas encore d'évaluation
- MEDICAL POLICY ID Compressed PDFDocument130 pagesMEDICAL POLICY ID Compressed PDFnirikshith pPas encore d'évaluation
- CommblksDocument583 pagesCommblksgvirbila1298Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mesa Boogie Studio 22 ManualDocument7 pagesMesa Boogie Studio 22 ManualGeko7Pas encore d'évaluation
- T40140 With Man PlatformDocument61 pagesT40140 With Man Platformbenjamin100% (1)
- Experiment No. 2 AIM:: A) To Measure Phase Difference Between Two WaveformsDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 2 AIM:: A) To Measure Phase Difference Between Two Waveformsnishugoel0102Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aip EbciDocument50 pagesAip Ebcigiuseppe751Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sanoy, Angel L. 12-Humss A (10:15-11:15) Contemporary Arts From RegionDocument9 pagesSanoy, Angel L. 12-Humss A (10:15-11:15) Contemporary Arts From RegionJoey MalongPas encore d'évaluation
- GPS KLN 900Document210 pagesGPS KLN 900zeeshanshaPas encore d'évaluation
- MC 10-08-91Document3 pagesMC 10-08-91Sanji VinsmokePas encore d'évaluation
- OpenVox G410E On Elastix Guide ManualDocument18 pagesOpenVox G410E On Elastix Guide ManualMarco CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tupac ShakurDocument4 pagesTupac ShakurDamonta HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- WiFi Technology GuideDocument40 pagesWiFi Technology GuideSowjanya Sowji100% (1)
- Sony Xav A1 Xav c1 PDF Rus PDFDocument115 pagesSony Xav A1 Xav c1 PDF Rus PDFСергей ЗадылякPas encore d'évaluation