Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
P2 Process Model v3
Transféré par
matteozamoloCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
P2 Process Model v3
Transféré par
matteozamoloDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
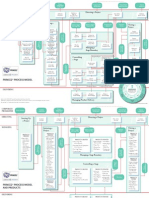
Corp/Program
Corporate or Program Management
Project
Mandate
Initiation Stage
Pre-Project
Direction
Starting Up a
Project (SU)
Project Brief
Initiation Stage Plan
Appoint Exec &
PM
Capture Previous
Lessons
Design & appoint
PMT
Management
Prepare outline
Business Case
Select the Project
Select& Pr.
approach
approach,
assemble
the Project
Brief
Plan Initiation
Stage
Authorize
Initiation
Notification
Notification
Authorize
The Project
Authorize A
Stage or
Exception Plan
Project Initiation
Document
& Benefit Review
Plan
Initiating a
Project (IP)
Prepare Risk
Man. Strat.
Prepare
Quality
Man.Strat
Prepare
Configuration
Man.Strat.
Prepare
Communication Man.Strat
Set-up Project
Controls
Create project
plan
Delivery Stage I
Delivery Stage II
Directing a Project (DP)
Authorization
Premature
Authorize A Authorization
Give Ad-Hoc Stage End
Stage or
Direction
Exception Plan
Highlight Report or
Exception Report
Escalated Issues
Next Stage or
ExceptionPlan
Controlling
a Stage (CS)
Manage a
Stage
Boundary
(MSB)
Authorize
Work
Packages
Receive
completed
Work
packages
Plan the next
Stage
Or, Produce
an exception
plan
Capture and
examine
issues & risks
Update the
Business Case
Review Stage
Status
Report Stage
End
Take
Corrective
action
Refine the
Business Case
Manage a
Stage
Boundary
(MSB)
Or, Produce
an exception
plan
Update the
Project Plan
Update the
Business Case
Report Stage
End
Highlight Report
Work Package
End Stage Report
Exception Report
Issue Report
Update Issue Register
Update Lessons Log
Lessons Report
Product Status account
Report
Highlights
Assemble The
PID
Next Stage or
ExceptionPlan
Plan the next
Stage
Review work
package status
Update the
Project Plan
Notification
Escalate
issues and
risks
Notification
Premature
Authorize
Project
Closure
Give Ad-Hoc Stage End
Direction
Highlight Report or
Exception Report
Controlling
a Stage (CS)
Close
Project (CP)
Authorize
Work
Packages
Receive
completed
Work
packages
Prepare
planned
closure
Or, Prepare
premature
closure
Hand over
products
Review work
package status
Capture and
examine
issues & risks
Review Stage
Status
Evaluate the
project
Recommend
project closure
Take
Corrective
action
Report
Highlights
Escalate
issues and
risks
Four Management levels ->
Delivery
pankajsh10@yahoo.com
Project Mandate
Project Brief
Project Definition
Outline Business Case
Proj. Product. Description
Proj. Approach
PMT Structure
Role descriptions
References
Initiation Stage Plan
Daily Log
Lessons Log
Business Case
Exec Summary
Reasons
Expected Benefits
Expected dis-benefits
Timescale
Costs
Investment appraisal
Major Risks
Plan (Stage, Project, Team)
Plan description
Prerequisites
Dependencies
Assumptions
Lessons
Monitoring & control
Budgets
Tolerances
Prod. Descriptions
Schedule
Project Initiation Document
Extracts from P.Brief
Risk Man. Strategy
Quality Man. Strategy
Config Man. Strategy
Communication
Man.Strategy
Proj Man Team structure
Role descriptions
Detailed Business Case
Project Plan
Project Controls
Next Stage Plan
Benefits Review Plan
Configuration Item Records
Issue Register
Quality Register
Risk Register
Manage Product Delivery (MP)
Manage Product Delivery (MP)
Accept Work
Package
Accept Work
Package
Execute Work
Package
Highlight Report
Date
Reporting Period
Status Summary
Products & work packages
This reporting period
Next reporting period
Project & Stage tolerances
Requests for Change
Key issues & risks
Lessons Report
PRINCE2 is a Registered Trademark of AXELOS LTD
Deliver Work
Package
Execute Work
Package
Additional work estimates
Checkpoint Report
Date, period
Follow-ups
This/next reporting period
Work Package tolerance
status
Issues & risks
Acceptance Records
(See Project Product
Description)
End Project Report
Follow-on actions recs
Lessons report
Deliver Work
Package
Update / close
Project Plan
Configuration item records
Benefits review plan
Registers:
Issue Register,
Quality Register,
Risk Register,
Daily Log
The four integrated elements of PRINCE2
(Why?)
(Who?)
(What?)
(How? How Much? When?)
(What if? )
(Whats the impact?)
(On Target? Tolerance?)
Tailoring PRINCE2 to
create fit with project
environment and
context of the project.
PRINCE2 can be
tailored to any type or
size of project.
Quality
Purpose is to judge if project is/remains desirable,
viable, achievable. Projects products enable business
to acheive benefits:
Output: projects specialist products
Outcome: derived from using projects outputs
Benefit: measurable improvement perceived by
stakeholders.
Project
Outputs
consequences
Create
Desired
Outcomes
Measured in
Realize
further
BC lifecycle:
Develop: get information to make
decisions (SU & IP)
Result in
Verify: assess if project is (still)
worthwhile (CS)
Disbenefits
Maintain: Update costs, benefits and
forecasts (MSB)
Confirm: if benefits are/will be
Realized, mostly post-project. (MSB,
CP, post project)
Acceptance
Criteria
Project Product
Description
Quality Managem.
Strategy
Product
Descriptions
PRINCE2
Product Based
Planning
Technique
Benefits
Quality Register
PRINCE2 quality
review
technique
Helps acheive
one or more
Strategic
Objectives
Business Executive: looks after business interests; products to meet
business needs, value for money.
Senior User: represents users requirements on projects outputs; who:
- Will use the project outputs to realize benefits after the project
- Will operate, maintain or support the projects outputs
- Will be impacted by project outputs
Senior User specifies outputs and ensures delivery.
Supplier represents those who will provide skills and produce project
product.
Change Authority: Board
Corporate or program management
can delegate authority for
Project
RFCs or off-specs.
Project Board
ManageSeverity ratings in
Senior
Business
Senior
ment
Configuration Man.
User
Executive Supplier
Team
Strategy list who handles
(PMT)
requests :
Corporate/programme
Change
Project
management
Project
Authority
Manager
Assurance
Project Board
Change Authority
Project
Project Manager.
Team
Support
Manager
Delegated authorities are
written into role
descriptions.
Team Members
Project Assurance: Project Board Checks all aspects of the projects
performance independent of Project Manager. PB members are responsible
for aspects of Project Assurance from their respective areas: business, user
or supplier. If they have no time or skills they appoint separate individuals
Project Manager: responsible for day-to-day management of project within
constraints set by Project Board. Project Manager ensures that project
produces required products within set tolerances.
Project Support: Responsibility of Project Manager. He can delegate work
to Project Support: administrative services, they advice on project
management tools, configuration management, provide specialists for
planning or risk management.
Team Manager: ensures cration of products in workpackage. Role may be
combined with PM
Product
Quality Approval
Records
Acceptance
Records
Plans
Corporate or
programme plan
Project Plan
(Initiation)
Stage Plan
(Delivery)
Stage Plans
Team Plans
(Optional, free structure)
Design the plan
(during Plan the Project)
Define & analyse
products
Proj.prod.descr. (proj plan)
Prod. Breakdown
Prod. Descriptions
Prod. Fow Diagr.
Identify Activities and
dependencies
Prepare Estimates
Prepare the schedule
Document the plan
Tolerance Area/Management Prod.:
Quality
Business Case (B)
Risk
Project Plan (T,C,S) Risk.strat.(R)
Scope
Stage Plan (T,C.S.R)
Work Package (T,C,S,R)
(Project) Product Description (Q)
(Scope tol.of plans defined by products)
Quality planning: to control quality, there must be a plan
defining the products required of the project, with their
respective quality criteria, quality methods (including effort
required for quality control and product acceptance) and the
quality responsibilities of those involved.
Quality Expectations in broad terms (Robust, fast, etc.).
Acceptance Criteria are Measurable; Rated: MoSCoW
Expectations & Criteria are in Project Product Description
expectations
Quality Planning
Enable
Business
Changes
Objectives depend on project type:
Feasibility study
Compulsory project
Also Cause
Not-for-profit project
Evolving project
Customer/supplier project
Side effects
Multi-organization project.
and
The Quality Audit Trail
From Customer
Project
Response
Customers Quality
Repeated for
Project Plan
Stage Plan
Team Plan (optional)
Business Case
Organization
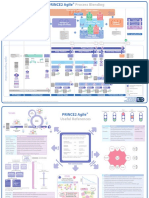
Seven Processes
1. Starting Up A Project (SU)
2. Directing A Project (DP)
3. Initiating a Project (IP)
4. Controlling A Stage (CS)
5. Managing Product Delivery (MP)
6. Managing Stage Boundaries (MSB)
7. Closing a Project (CP)
Tolerances on the 6 project objectives
Time
help delegate authority - Management
by Exception.
Cost
Benefit
Quality assurance :
Quality
Establishes and maintains a
Components
quality management system
Reviews a projects
Quality Criteria
organization, processes,
and Tolerances
products to assess if quality
will be met.
Quality assurance is independent
Quality Methods
of the Project Management
Team,it is a corporate
responsibility, but quality
Quality
planning and control are done by
Responsibilities
the project. The project is
responsible that quality
assurance is arranged.
Quality control focuses on the
operational techniques and activities
used by those involved in the project to:
Fulfil the requirements for quality
Quality
(for example, by quality
Control
inspections or testing)
Identify ways of eliminating causes
of unsatisfactory performance (for
example, by introducing process
improvements as a result of
lessons learned).
The purpose of Plans is to facilitate communication
and control by defining means of delivering products;
the where and how, by whom, and estimating the
when and how much).
Exception Plans
(As nescessary)
Three levels of plan for three different levels of
management; Project, Stage and Team. The Initiation
Stage Plan is created (with the Project Brief) by
Starting up a Project (influenced by corporate or
programme plans). The Project Plan is created during
Initiation (in the PID). Following Stage Plans created
by Managing a Stage Boundary. Team Plans created
by Managing Product Delivery(Accept Workpackage).
Benefits Review Plan covers activities during and after
the project that check if Business Case benefits have
been acheived. It may be part of a corporate or
programme plan. The Benefits Review Plan covers
corporate, project and stage levels. Created during
Initiation, updated during Managing a Stage
Boundary
An Exception Plan is a plan prepared for the
appropriate management level to show the actions
required to recover from the effect of a tolerance
deviation. If approved, the Exception Plan will replace
the plan that is in exception(Stage or project).
Project assurance is responsibility of
project board; Checking on all aspects of
project performance
Quality assurance is responsibility of
Corporate or Programme management
(Quality policies outside the project). It
provides stakeholders with confidence
that quality requirements can be fulfilled
Quality assurance should not be confused
with Project Assurance. Project assurance
refers to the Project Boards accountability pankajsh10@yahoo.com
Risk
Purpose of Risk theme is to identify, assess and
control uncertainty and, as a result, improve the
ability of the project to succeed. In the context of a
project, it is the projects objectives that are at risk.
These will include completing the project to a
number of targets, covering time, cost, quality,
scope, benefits and risk.
Risk Appetite: an organisations attitude to risk
taking. Risk tolerance: amount of risk that is
acceptable
Threat
Responses
Opportunity
Responses
Avoid
Exploit
Reduce
(probability and/or
impact)
Enhance
Fallback
(reduces impact only)
Transfer
(reduces impact only,
and often only the
financial impact
Risk Management procedure:
Identify context; obtain information on
Share
project to understand specific
objectives at risk and formulate Risk
Reject
Accept
Management Strategy.
Risk Owner: responsible for management,
Identify risks; recognize the threats and
monitoring, control of all aspects of a risk,
opportunities that may affect the
including implementation of responses.
projects objectives.
Risk Actionee: caries out actions
Assess threats and opportunities to the
Summary risk profile
project in terms of probability and
1 3
impact. Risk proximity describes how
Very high
Num
be
quickly risk can materialize .
4
2
Risk rs from
High
Regis
ter
Plan; prepare management responses to Medium
8
6
threats and opportunities;remove/
10
Low
7
reduce threats, maximize opportunities.
9
5
Very Low
Implement; action risk responses,
Very
Very
Prob
monitor effectiveness, take corrective
Low Medium High
Impact Low
high
action
Communicate
Seven Themes
1. Business Case
2. Organization
3. Quality
4. Plans
5. Risk
6. Change
7. Progress
Analyse Risks
Seven Principles
1. Continued business justification
2. Learn from experience
3. Defined roles and responsibilities
4. Manage by stages
5. Manage by exception
6. Focus on products
7. Tailor to suit the project
environment.
Tolerances:
Progress
Progress describes mechanisms to: monitor and compare
achievements against plans, forecast projects objectives and
viability, control deviations within tolerances, escalate
deviations outside tolerances.
Corporate or programme
management
Project
tolerances
Project Progress/
exceptions
It contributes to the principles Managing by stages,
Project Board
Continued business justification, Manage by exception. It
can be monitored at Work Package, Stage and Project level.
Each level of the PMT can check the next level:
Stage
Stage progress/
Monitor progress
Tolerances
exceptions
Compare level of achievement with plan
Review plans and options against future situations
Project Manager
Detect problems and identify risks
Initiate corrective action
Work Package
Authorize further work.
Work Package
progress/
Tolerances
Tolerances are permissible deviations above and below a
Issues
plans target for time and cost without escalating to the next
level. There may also be tolerance for quality, scope, benefit
Team Manager
and risk. Exception is when it can be forecast that there will be
a deviation beyond the agreed tolerance levels.
Specialist work aligned to management stages
Management Stage 1 Management Stage 2 Management Stage 3 Management Stage 4
Specification
Peripheral
design
Over all
Detailed Design
Commissioned
Facility
design
Built
facility
Training
Syllabus
Trained Staff
Change
To identify, assess and control any potential changes to the baseline and get
them approved or dis-approved. Issue and change control is the continual
activity throughout the project that identifies possible changes. Without
ongoing effective issue and change control, a project will become
unresponsive to stakeholders or drift out of control. Issues cover all relevant
events; Concern, Request for Change, or Off-Specifications
PRINCE2 is a Registered Trademark of AXELOS LTD
Configuration management is the administrative activity concerned
with maintaining a controlled configuration throughout the life of a product.
Baselines are management products, once approved they are subject to
Change control (Benefits review plan, Business Case, All Strategies in the
PID, plans, (Project) product description, Brief, PID and Workpackage)
Procedure: Planning, Identification, Control, Status acc., Verification & Audit
Steps: Establish Controls, Set-up a
Configuration Management procedure and setup a Change Control procedure, ( Also see
Change Authority in the PMT descriptions).
A change budget prevents that Projects or
Stage tolerances are eaten by changes.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 100 Nebosh Revision QuestionsDocument21 pages100 Nebosh Revision QuestionsMarius Alexandru50% (4)
- PRINCE2 Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Quick Reference Guidezigmoid100% (4)
- 2021 Philippine Quality Award: Sultan Kudarat State University Application ReportDocument71 pages2021 Philippine Quality Award: Sultan Kudarat State University Application ReportSultan Kudarat State University100% (4)
- Spa Psslai and AfpslaiDocument1 pageSpa Psslai and Afpslaijci028Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Foundation User Guide v1.6Document76 pagesPrince2 Foundation User Guide v1.6Marissa YaxleyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionD'EverandThe Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management: Prince2Document13 pagesProject Management: Prince2Shreyo Chakraborty100% (3)
- PRINCE2-Practitioner Dumps PRINCE2 Practitioner ExamDocument49 pagesPRINCE2-Practitioner Dumps PRINCE2 Practitioner ExamDing Ding Dang100% (1)
- Prince2® Process Model: Directing A ProjectDocument2 pagesPrince2® Process Model: Directing A ProjectSam DesuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Courant Lecture Notes) Louis Nirenberg-Topics in Nonlinear Functional Analysis - Unknown (2001)Document153 pages(Courant Lecture Notes) Louis Nirenberg-Topics in Nonlinear Functional Analysis - Unknown (2001)Fis MatPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Agile Slides2Document132 pagesPRINCE2 Agile Slides2Seboka Matsoso100% (1)
- PRINCE2 in One Thousand WordsDocument7 pagesPRINCE2 in One Thousand WordsSolomon Joseph100% (1)
- 11 Point Plan Passing Your Prince2 Exam PDFDocument2 pages11 Point Plan Passing Your Prince2 Exam PDFbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Practitioner: DurationDocument1 pagePrince2 Practitioner: DurationhomsomPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 ProcessesDocument2 pagesPrince2 Processesnitind_k100% (3)
- Your PRINCE2 Processes and Products Roadmap - Projex AcademyDocument16 pagesYour PRINCE2 Processes and Products Roadmap - Projex AcademyEric DesportesPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince 2Document35 pagesPrince 2Zipel SnakhPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Agile®: Process BlendingDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Agile®: Process BlendingStephen NibaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Official PRINCE2 Agile Accreditor Sample Examination Papers Terms of UseDocument24 pagesThe Official PRINCE2 Agile Accreditor Sample Examination Papers Terms of UseVishnu RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2-PractitionerV7 1Document359 pagesPrince2-PractitionerV7 1Ding Ding Dang100% (1)
- Prince2 for Beginners - Introduction to Prince2 Project Management ConceptsD'EverandPrince2 for Beginners - Introduction to Prince2 Project Management ConceptsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Learn PRINCE2 ThruQuestionsDocument82 pagesLearn PRINCE2 ThruQuestionsEdson Garcia de Freitas100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2Document7 pagesPRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2spm9062100% (1)
- 2000 A4 Questions 1 Prince2 PracDocument28 pages2000 A4 Questions 1 Prince2 Pracupadhyayprakash67% (3)
- Prince2 Foundation Study Notes-Session 4-ThemesDocument36 pagesPrince2 Foundation Study Notes-Session 4-ThemesskiseretsePas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Implementation Case StudyDocument43 pagesPRINCE2 Implementation Case StudypvpramodPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Process ModelDocument1 pagePrince2 Process Modelian mckinleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Master The PRINCE2 Processes With PicturesDocument12 pagesMaster The PRINCE2 Processes With PicturesKnowledge Train100% (2)
- Agile Prince 2Document5 pagesAgile Prince 2Andrei BadeaPas encore d'évaluation
- GB - EX03 PRINCE2 Sample Practitioner Paper - V2.13 - July 12 ReleaseDocument64 pagesGB - EX03 PRINCE2 Sample Practitioner Paper - V2.13 - July 12 ReleasematteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Agile Exam 2022Document12 pagesPrince2 Agile Exam 2022WizzardPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Agile Exam PreparationDocument4 pagesPRINCE2 Agile Exam Preparationsanja34Pas encore d'évaluation
- To Download Prince2 Slides (PDFDrive)Document156 pagesTo Download Prince2 Slides (PDFDrive)MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince 2Document33 pagesPrince 2Korede AkinseyePas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Step by Step GuideDocument58 pagesPRINCE2 Step by Step GuideBukola Bukky100% (2)
- PRINCE2 OverviewDocument8 pagesPRINCE2 OverviewprojectingIT100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Process MapDocument3 pagesPRINCE2 Process MapSreedhar Madur50% (2)
- Introduction To PRINCE2Document58 pagesIntroduction To PRINCE2YoEmprendo100% (1)
- Analisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaiDocument142 pagesAnalisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaibustamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Meraki Juniper Mist BCDocument28 pagesMeraki Juniper Mist BCvicPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.5Document237 pagesPrince2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.5Luis Alberto Lamas LavinPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Candidate GuidanceDocument8 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Candidate GuidanceJohn N. Constance100% (1)
- 169 - 171 - G.R. No. 195641 Case DigestDocument2 pages169 - 171 - G.R. No. 195641 Case DigestRennette AlfaroPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pen Project A Fully Documented Sampl PDFDocument101 pagesThe Pen Project A Fully Documented Sampl PDFNikolaos Alifragis50% (2)
- Master The PRINCE2 Themes With PicturesDocument11 pagesMaster The PRINCE2 Themes With PicturesKnowledge Train100% (1)
- The Importance of The Project Board in Managing and Directing Projects With Prince2®Document20 pagesThe Importance of The Project Board in Managing and Directing Projects With Prince2®K T-KPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Sample PaperDocument43 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Sample PaperAndre Kaiser67% (3)
- Project Lifecycles and PRINCE2 20190403Document31 pagesProject Lifecycles and PRINCE2 20190403csharpplusPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 PractitionerDocument115 pagesPrince2 PractitionerRicha TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 PMBOK ISO Paper PDFDocument10 pagesPRINCE2 PMBOK ISO Paper PDFm.dominiqPas encore d'évaluation
- AFA PRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsDocument5 pagesAFA PRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsmailmendPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Agile Process Map PDFDocument2 pagesPrince2 Agile Process Map PDFSantiago Manuel Rios Lara100% (2)
- To Download Prince2 Slides (PDFDrive)Document156 pagesTo Download Prince2 Slides (PDFDrive)Mohamed100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Foundation Theme NotesDocument28 pagesPRINCE2 Foundation Theme Notescong lePas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Practitionerdemo PDFDocument61 pagesPRINCE2 Practitionerdemo PDFfaraonxxxPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Methodology DiagramDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Methodology Diagramshaunbuk100% (2)
- Prince2 Process ModelDocument2 pagesPrince2 Process ModelSiddharth Pareek100% (1)
- Prince2 User GuideDocument85 pagesPrince2 User GuideSamba-Diom BaPas encore d'évaluation
- MindMap For PRINCE2Document1 pageMindMap For PRINCE2muralidurai100% (3)
- Prince 2 PresentationDocument164 pagesPrince 2 PresentationLaiq ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Management Product MapDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Management Product MapSushil GoswamiPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.7Document237 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.7pkdor2008100% (7)
- Prince2 in 60 Minutes Flat v7.2Document59 pagesPrince2 in 60 Minutes Flat v7.2Reni Dimitrova100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsDocument3 pagesPRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsBasil AlsahrawyePas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Guide - by Ashish Dhoke (ProjectingIT)Document16 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Guide - by Ashish Dhoke (ProjectingIT)projectingIT100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Resource Book v3 7 181Document1 pagePRINCE2 Practitioner Resource Book v3 7 181anuarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortigate 600f SeriesDocument10 pagesFortigate 600f SeriesmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortigate 1800f SeriesDocument11 pagesFortigate 1800f SeriesmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- FortiGate_6000F_Series (2)Document13 pagesFortiGate_6000F_Series (2)matteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortigate 3000f SeriesDocument11 pagesFortigate 3000f SeriesmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- fortigate-2600f-seriesDocument11 pagesfortigate-2600f-seriesmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- ITSPMO ProjectRiskPlan v3Document2 pagesITSPMO ProjectRiskPlan v3matteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Register: Risk Identification Quali Ative RatingDocument3 pagesRisk Register: Risk Identification Quali Ative RatingmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- fortigate-400f-series (1)Document10 pagesfortigate-400f-series (1)matteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- PMP Ppts Pmbok 5th EditionDocument476 pagesPMP Ppts Pmbok 5th EditionmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- PMP Ppts Pmbok 5th EditionDocument476 pagesPMP Ppts Pmbok 5th EditionmatteozamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- QM ZG528 - L1Document26 pagesQM ZG528 - L1RamPrasathPas encore d'évaluation
- Talent Acquisition Excellence July 2023Document66 pagesTalent Acquisition Excellence July 2023Anish SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia Surepay® Real-Time, Convergent Charging SolutionDocument6 pagesNokia Surepay® Real-Time, Convergent Charging SolutionAnil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- JKUAT 1.2 Lecture 5 Levels and Skills of ManagementDocument14 pagesJKUAT 1.2 Lecture 5 Levels and Skills of ManagementPrashansa JaahnwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Optonic - Winter of 2015Document13 pagesOptonic - Winter of 2015arijit nayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Factsheet GB en Gb00byvxbg82Document9 pagesFactsheet GB en Gb00byvxbg82RocketPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 28Document3 pagesForm 28naresh singlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guante Anticorte Grado 5 G-Tek 16-560Document1 pageGuante Anticorte Grado 5 G-Tek 16-560andromora08 PsnPas encore d'évaluation
- Petitioner vs. vs. Respondent: First DivisionDocument10 pagesPetitioner vs. vs. Respondent: First DivisionSabPas encore d'évaluation
- Amended: The United Republic of Tanzania Business Registrations and Licensing AgencyDocument5 pagesAmended: The United Republic of Tanzania Business Registrations and Licensing AgencyMselem KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Management AnalysisDocument23 pagesManagement AnalysisMiracle Vertera100% (1)
- Maxlein Addai-Minkah PDFDocument84 pagesMaxlein Addai-Minkah PDFpooja phadkePas encore d'évaluation
- Product Category LifecyclesDocument13 pagesProduct Category LifecyclesAdam Andrew OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Via Email & U.S. Mail: Steven - Mnuchin@treasury - GovDocument5 pagesVia Email & U.S. Mail: Steven - Mnuchin@treasury - GovJason PuhrPas encore d'évaluation
- CPDD-ACC-01-A Application Form As Local CPD Provider 2020Document2 pagesCPDD-ACC-01-A Application Form As Local CPD Provider 2020Elie DGPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-3 Political-Legal EnvironmentDocument22 pagesUnit-3 Political-Legal EnvironmentCHANDANI YADAVPas encore d'évaluation
- Market AppraisalDocument14 pagesMarket AppraisalnandishPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Development of Competitive IntelligenceDocument27 pagesModule 2 - Development of Competitive IntelligenceMoksh rathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Admission Guideline Hanyang Uni 2020Document9 pagesAdmission Guideline Hanyang Uni 2020Kavi YaPas encore d'évaluation
- MLDC Degree College SubjectsDocument3 pagesMLDC Degree College Subjectssomani josephPas encore d'évaluation
- Attach-15 Work Procedure For Welding Consumables ControlDocument12 pagesAttach-15 Work Procedure For Welding Consumables ControlSukalyan BasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study2 Shabu HachiDocument11 pagesCase Study2 Shabu Hachimcahya82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacies 2Document38 pagesPharmacies 2Fadi AyoubPas encore d'évaluation