Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2 Forces in One Dimension Worksheet
Transféré par
Cris BaldozaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2 Forces in One Dimension Worksheet
Transféré par
Cris BaldozaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
September 8, 2016
Grade 10 PHYSICS (XS) -- SY 2016 2017
QUARTER 2
FORCES IN ONE DIMENSION
Force and Motion
- Force is a push or pull exerted on an object.
- Forces can cause objects to speed up, slow down, or change direction as they move.
Contact Forces and Field Forces
- A contact force exists when an object from the external world touches a system and thereby exerts a
force on it.
- Field forces are exerted without contact.
Free-body Diagram
- type of physical model, which represents the forces acting on a system
I. COMBINING FORCES (Determining NET FORCE)
The vector sum of all the forces on an object is the net force.
1. Two horizontal forces, 225 N and 165 N, are exerted on a canoe. If these forces are applied in the
same direction, find the net horizontal force on the canoe. (Glencoe)
2. If the same two forces as in the previous problem are exerted on the canoe in opposite directions,
what is the net horizontal force on the canoe? Be sure to indicate the direction of the net force.
(Glencoe)
3. Three confused sleigh dogs are trying to pull a sled across the Alaskan snow. Alutia pulls east with a
force of 35 N, Seward also pulls east but with a force of 42 N, and big Kodiak pulls west with a force of
53 N. What is the net force on the sled? (Glencoe)
4. What is the net force acting on a 1.0-kg ball in free-fall? (Glencoe)
Shared document\ Bhing\SY 2016-2017\Junior High School\XS Grade 10 Science\Quarter 2 Physics\II. Forces in One Dimension\2 Forces in One Dimension
September 8, 2016
II. NEWTONS FIRST LAW
An object that is at rest will remain at rest, and an object that is moving will continue to move in a
straight line with constant speed, if and only if the net force acting on that object is zero.
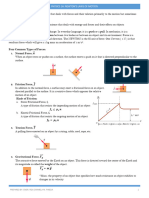
Force
Symbol
Friction
Ff
Normal
FN
Spring
F sp
Tension
FT
Thrust
Fthrust
Weight
Fg
Definition
The contact force that acts to
oppose sliding motion between
surfaces
The contact force exerted by a
surface on an object
A restoring force; that is, the
push or pull a spring exerts on an
object
The pull exerted by a string,
rope, or cable when attached to a
body and pulled taut
A general term for the forces that
move objects such as rockets,
planes, cars, and people
A field force due to gravitational
attraction between two objects,
generally Earth and an object
Direction
Parallel to the surface and opposite
the direction of sliding
Perpendicular to and away from the
surface
Opposite the displacement of the
object at the end of the spring
Away from the object and parallel
to the string, rope, or cable at the
point of attachment
In the same direction as the
acceleration of the object, barring
any resistive forces
Straight down toward the center of
Earth
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist change. If an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest.
According to Newtons first law, a net force is something that causes the velocity of an object to change.
If the net force on an object is zero, then the object is in equilibrium.
An object is in equilibrium if it is at rest or if it is moving at a constant velocity.
1. An object is moving at a constant velocity. All but one of the following statements could be true.
Which one cannot be true? (Cutnell)
(a) No forces act on the object.
(b) A single force acts on the object.
(c) Two forces act simultaneously on the object.
(d) Three forces act simultaneously on the object.
2. The net external force acting on an object is zero. Which one of the following statements is true?
(Cutnell)
(a) The object can only be stationary.
(b) The object can only be traveling with a constant velocity.
(c) The object can be either stationary or traveling with a constant velocity.
(d) The object can only be traveling with a velocity that is changing.
3. A cup of coffee is sitting on a table in a recreational vehicle (RV). The cup slides toward the rear of
the RV. According to Newtons first law, which one or more of the following statements could describe
the motion of the RV?
(A) The RV is at rest, and the driver suddenly accelerates.
(B) The RV is moving forward, and the driver suddenly accelerates.
(C) The RV is moving backward, and the driver suddenly hits the brakes.
(a) A
(d) A and B
Shared document\ Bhing\SY 2016-2017\Junior High School\XS Grade 10 Science\Quarter 2 Physics\II. Forces in One Dimension\2 Forces in One Dimension
September 8, 2016
(b) B
(c) C
III. NEWTONS SECOND
(e) A, B, and C
LAW
Newtons second law states that the acceleration of a system equals the net force acting on it,
divided by its mass.
1. Joyce and Efua are skating. Joyce pushes Efua, whose mass is 40.0-kg, with a force of 5.0 N. What is
Efuas resulting acceleration? (Glencoe)
2. A car of mass 2300 kg slows down at a rate of 3.0 m/s 2 when approaching a stop sign. What is the
magnitude of the net force causing it to slow down? (Glencoe)
3. After Thanksgiving, Kevin and Gamal use the turkeys wishbone to make a wish. If Kevin pulls on it
with a force 0.17 N larger than the force Gamal pulls with in the opposite direction, and the wishbone
has a mass of 13 g, what is the wishbones initial acceleration? (Glencoe)
4. Two people are pushing a stalled car, as Figure 4.5a indicates. The mass of the car is 1850 kg. One
person applies a force of 275 N to the car, while the other applies a force of 395 N. Both forces act in
the same direction. A third force of 560 N also acts on the car, but in a direction opposite to that in
which the people are pushing. This force arises because of friction and the extent to which the
pavement opposes the motion of the tires. Find the acceleration of the car. (Cutnell)
5. In Case A an object is moving straight downward with a constant speed of 9.80 m/s, while in Case B
an object is moving straight downward with a constant acceleration of magnitude 9.80 m/s 2. Which
one of the following is true? (Cutnell)
Shared document\ Bhing\SY 2016-2017\Junior High School\XS Grade 10 Science\Quarter 2 Physics\II. Forces in One Dimension\2 Forces in One Dimension
September 8, 2016
(a) A nonzero net external force acts on the object in both cases.
(b) A nonzero net external force acts on the object in neither case.
(c) A nonzero net external force acts on the object in Case A only.
(d) A nonzero net external force acts on the object in Case B only.
Shared document\ Bhing\SY 2016-2017\Junior High School\XS Grade 10 Science\Quarter 2 Physics\II. Forces in One Dimension\2 Forces in One Dimension
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument14 pagesNewtons Law of MotionJohn Irvin M. AbatayPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces and MotionDocument37 pagesForces and MotionpjpanisPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - DynamicsDocument2 pages3 - DynamicsStephen CamsolPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocument22 pages05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument54 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionjhegster saclutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen.-Physics-1 Ch-46 Plus Week 6 Complete 10 Pages.v.1.0Document10 pagesGen.-Physics-1 Ch-46 Plus Week 6 Complete 10 Pages.v.1.0John Bernard Abella GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE IGCSE ForcesDocument62 pagesCIE IGCSE ForcesRudi HartonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiPas encore d'évaluation
- ch3 - 1d DynamicsDocument17 pagesch3 - 1d Dynamicsapi-301275445Pas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument53 pagesPhysicsIwana Rademaekers100% (1)
- WTS Mechanics Crossnight PDFDocument31 pagesWTS Mechanics Crossnight PDFBontle PrincessPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Workno.1 ch4.1 Grade 12 4th Quater S.R 2023Document4 pagesClass Workno.1 ch4.1 Grade 12 4th Quater S.R 2023Rola TawfikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsDocument47 pagesLecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsThea MPas encore d'évaluation
- MotionDocument51 pagesMotionJohanna Marie SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch4newtonsslaws 101013161156 Phpapp02Document94 pagesCh4newtonsslaws 101013161156 Phpapp02Reynante Dap-ogPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionJhulia IlogonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Physics 1 - Newtons LawsDocument7 pagesAp Physics 1 - Newtons Lawsapi-293989776Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document74 pagesChapter 4Melody Mae O. Damole43% (7)
- Dynamics 2Document49 pagesDynamics 2Zubair FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch04 Homework SolutionsDocument88 pagesCh04 Homework SolutionsOsama Maher100% (1)
- 5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsDocument1 page5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsMuhamad AfdalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces NotesDocument13 pagesForces NotesAthena HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics Motion & Force DynamicsDocument12 pagesAP Physics Motion & Force DynamicspuvalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument5 pagesModule 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Document19 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Lesson 3Aimee Gallego AngoluanPas encore d'évaluation
- ForcesDocument68 pagesForcesJohn Mark MadrazoPas encore d'évaluation
- APPhys Newtons Laws 1Document9 pagesAPPhys Newtons Laws 1Waleska MejiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Convert MefsDocument3 pagesConvert MefssaghfadPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 5Document23 pagesGroup 5Gavin avPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonDocument6 pagesClass 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonGarvitPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 - Newton2&3Document2 pagesLesson 6 - Newton2&3AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Newtons Law 1Document34 pagesApplication of Newtons Law 1Mae Antoinette FabrePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Document77 pagesLesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Norman AcainPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Newton'sLawsofMotionDocument44 pagesPhysics Newton'sLawsofMotionCamela LacsamaPas encore d'évaluation
- V. Laws of Motion PDFDocument6 pagesV. Laws of Motion PDFMike Kenneth BlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Document36 pagesForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSI Physics: Table of Contents: DynamicsDocument30 pagesPSI Physics: Table of Contents: DynamicsibaadullahbaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceDocument5 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceCharl CuaPas encore d'évaluation
- LP Week 1 2 Science 8Document4 pagesLP Week 1 2 Science 8rommel mukayPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 2 3 Notes Teacher CH 12 2 and 12 3Document7 pages1 2 3 Notes Teacher CH 12 2 and 12 3api-369706779Pas encore d'évaluation
- ID Newtons 3 LawsDocument2 pagesID Newtons 3 LawsErik Setiawan0% (1)
- FORCEDocument41 pagesFORCEdivine grace mesiasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Document7 pages2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Jit AggPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Newtons LawsDocument54 pagesLesson 5 Newtons Lawss.pcobrado22Pas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 3 - PhysicsDocument42 pagesUNIT 3 - PhysicsPpx XdPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaDocument20 pagesFisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaMUHAMMAD SALAFYPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4 - Newtons Laws Lecture Notes PDFDocument12 pagesCH 4 - Newtons Laws Lecture Notes PDFLilyPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument47 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of Motionoman92870164Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - The Laws of MotionDocument26 pagesChapter 6 - The Laws of MotionAbu SyakireenPas encore d'évaluation
- Law of MotionDocument76 pagesLaw of MotionLove With Books 2470% (1)
- Projectile) 1Document11 pagesProjectile) 1Hamidah Ashrafi FatehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces in One Dimension Grade 9 Adv ?Document29 pagesForces in One Dimension Grade 9 Adv ?alyaziahalkaabi19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldD'EverandDynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldPas encore d'évaluation
- CET Chemical Nomenclature Set BDocument8 pagesCET Chemical Nomenclature Set BCris BaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Formulas (Mhika)Document1 pageBasic Formulas (Mhika)Cris BaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Energy and Power WorksheetDocument5 pagesElectrical Energy and Power WorksheetCris BaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of Motion Application - 1B (ICA Problems)Document1 pageLaws of Motion Application - 1B (ICA Problems)Cris BaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012EM8Document35 pages2012EM8Android EmailPas encore d'évaluation
- CSEC Physics P2 2016 JanuaryDocument19 pagesCSEC Physics P2 2016 JanuaryBill BobPas encore d'évaluation
- Minolta Special LensesDocument15 pagesMinolta Special LensesazamamaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 VOLT DC MOTOR ProjectDocument9 pages12 VOLT DC MOTOR ProjectrameshPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ultimate Guide To Learning How To Use Your RST DSLR: Elliot HookDocument38 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Learning How To Use Your RST DSLR: Elliot Hookonmyway133Pas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Book Modern PhysicsDocument64 pagesComplete Book Modern Physicssweta gupta100% (1)
- Lecture 23 Intro To Optical Amplifiers PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 23 Intro To Optical Amplifiers PDF0938089460Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Randy Giles, and Emmanuel DesurvireDocument13 pagesModeling Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Randy Giles, and Emmanuel DesurvireElbis Santos CardosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template 1 Newtons LawDocument3 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template 1 Newtons LawSamson Meim80% (5)
- 10 Science TP 13 1Document7 pages10 Science TP 13 1KSP Classes GondiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Xi CbseDocument234 pagesPhysics Xi CbseSakiAtScribdPas encore d'évaluation
- NLM 9Document4 pagesNLM 9Ramesh BadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam I - OPT201Document11 pagesExam I - OPT201rittaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Fiberoptic Communications: Dr. Ir. Erna Sri Sugesti, M.SCDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Fiberoptic Communications: Dr. Ir. Erna Sri Sugesti, M.SCAya MoustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- S2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.2 Refraction)Document15 pagesS2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.2 Refraction)Kyaw Sit Nyein MaungPas encore d'évaluation
- Spherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesDocument1 pageSpherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesRonit RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Are The Skies Blue and The Sunsets RedDocument5 pagesWhy Are The Skies Blue and The Sunsets RedKah Ching SimPas encore d'évaluation
- Practise Questions On CoulombDocument2 pagesPractise Questions On CoulombRajani NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Robert Caldwell - Dark Energy CosmologyDocument21 pagesRobert Caldwell - Dark Energy CosmologyLopmazPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Waves Definitions and ConceptsDocument3 pagesIB Waves Definitions and ConceptsVaspan PalkivalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Optical Fiber ConnectionDocument39 pagesChapter 4 - Optical Fiber ConnectionFaizal EngintechPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Lesson 1 and 2Document8 pagesFinal Lesson 1 and 2Busy Bee 60Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal VisionDocument10 pagesThermal VisionRejo georgePas encore d'évaluation
- Charged, Conducting, Rotating Sphere: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document2 pagesCharged, Conducting, Rotating Sphere: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544parveezPas encore d'évaluation
- Site Acceptance Test Procedures and Plan For Optial Fibre Cables - SatDocument19 pagesSite Acceptance Test Procedures and Plan For Optial Fibre Cables - SatMayank Porwal100% (2)
- Chapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesDocument12 pagesChapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesVV Cephei100% (1)
- OSA Handbook of Applied Photometry Photometric StandardsDocument51 pagesOSA Handbook of Applied Photometry Photometric StandardsCarlos Alejandro BriozzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Field Theory Fundamentals 2nd Edition by Bhag Singh Guru and Huseyin R Hiziroglu (1) Part1Document365 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory Fundamentals 2nd Edition by Bhag Singh Guru and Huseyin R Hiziroglu (1) Part1Basil A'abed50% (2)
- Free Travel Photography GuideDocument23 pagesFree Travel Photography GuideJangbu SherpaPas encore d'évaluation