Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HW 1
Transféré par
Susheel SrinivasTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HW 1
Transféré par
Susheel SrinivasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
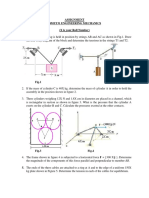
Dynamics (ME20001): Kinetics of Particles
Home Work 1
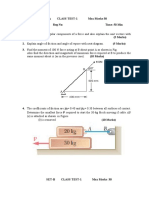
The 50-kg crate is projected down an incline as shown in Fig. 1 with an initial speed of 7 m/s at
x = 0. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40. Investigate the time t required for the crate to come
to rest and the corresponding distance x traveled if (a) = 15o and (b) = 30o .
Fig. 1: Problem 1
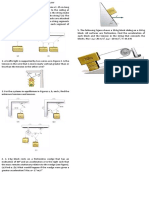
What fraction n of the weight of the jet airplane is the net thrust (nozzle thrust T minus air
resistance R) required for the airplane to climb at an angle with the horizontal with an acceleration
a in the direction of flight?
Fig. 2: Problem 2
3 Calculate the vertical acceleration a of the 100-lb cylinder for each of the two cases illustrated in
Fig. 3. Neglect friction and the mass of the pulleys.
Fig. 3: Problem 3
The 10-kg steel sphere is suspended from the 15-kg frame which slides down the 20o incline. If
the coefficient of kinetic friction between the frame and incline is 0.15, compute the tension in each
of the supporting wires A and B.
1
Fig. 4: Problem 4
If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the 20-kg block A and the 100-kg cart B
are both essentially the same value of 0.50, determine the acceleration of each part for (a) P = 60 N
and (b) P = 40 N.
Fig. 5: Problem 5
The system is released from rest with the cable taut. For the friction coefficients s = 0.25 and
k = 0.20, calculate the acceleration of each body and the tension T in the cable. Neglect the small
mass and friction of the pulleys.
Fig. 6: Problem 6
The nonlinear spring has a tensile force-deflection relationship given by Fs = 150x + 400x2 , where
x is in meters and Fs is in newtons. Determine the acceleration of the 6-kg block if it is released from
rest at (a) x = 50 mm and (b) x = 100 mm.
Fig. 7: Problem 7
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Test1Review 1Document2 pagesTest1Review 1Cathy NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 8 9e1bcf17Document3 pages2011 8 9e1bcf17Noor Farrah Wahida MuradPas encore d'évaluation
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersDocument4 pagesPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersBuddhisagar BastolaPas encore d'évaluation
- HW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationDocument8 pagesHW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationBradley NartowtPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Muhammed IfkazPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4 Friction - Solutions PDFDocument9 pagesTutorial 4 Friction - Solutions PDFBharat SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- HW09 - StaticsDocument6 pagesHW09 - StaticsBradley NartowtPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 - Chapter 13Document2 pagesTutorial 3 - Chapter 13MohdFirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice # 8Document9 pagesPractice # 8AfifaFarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Lab3a-Briefing SheetDocument9 pagesDynamic Lab3a-Briefing SheetchaugulePas encore d'évaluation
- 325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Document7 pages325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Bradley NartowtPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. TechDocument7 pagesSecond Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. Techlatendra kumar srivastavPas encore d'évaluation
- Final MEEM 4150 Dec. 15th, 2004: Table 1: PropertiesDocument2 pagesFinal MEEM 4150 Dec. 15th, 2004: Table 1: PropertiesRayleight SilversPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Problems Chapter 4Document13 pagesReview Problems Chapter 4Alberto RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech304 MT1Document3 pagesMech304 MT1Muhammed AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework3 Confined Column AnalysisDocument8 pagesHomework3 Confined Column AnalysisQingzhi LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- A915814272 16021 25 2017 CAtest1Document2 pagesA915814272 16021 25 2017 CAtest1arpit atriwalPas encore d'évaluation
- 5826Document6 pages5826zubbbuPas encore d'évaluation
- EMech Prob Set IV FrictionDocument3 pagesEMech Prob Set IV FrictionSamrat SadhukhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MN116 - Whole-Course TutorialDocument11 pagesMN116 - Whole-Course Tutorialjordangeorge.66jPas encore d'évaluation
- Btes103 203 em QBDocument10 pagesBtes103 203 em QBSurajPas encore d'évaluation
- EM ModelDocument4 pagesEM ModelArunGopal PonnusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.Document3 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.EUGENE ABULOC100% (1)
- PHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001 - Unit1st - Assisgnment1st - 2022 2harshitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 Fall Spring 2004 PDFDocument164 pages22 Fall Spring 2004 PDFcombatps1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applied MechanicsDocument3 pagesApplied MechanicssushilPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Soal RC PDFDocument23 pagesContoh Soal RC PDFIrfan Yahya IkhsanudinPas encore d'évaluation
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Document19 pagesNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargPas encore d'évaluation
- HW03 - ForcesDocument6 pagesHW03 - ForcesBradley NartowtPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective GATE QuestionsDocument24 pagesObjective GATE QuestionsAshwani GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Categories of Equilibrium: Problem 1.1Document33 pagesCategories of Equilibrium: Problem 1.1Suresh NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied MechanicsDocument13 pagesApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- Design of Diagonal Cross Bracings - Part 1 Theoretical Study PDFDocument5 pagesDesign of Diagonal Cross Bracings - Part 1 Theoretical Study PDFaapennsylvaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomDocument6 pagesMechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomIoana BoilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech 2 Lecture 4Document42 pagesMech 2 Lecture 4BADR ESLAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of NewtonDocument1 pageApplications of NewtonAlejandra Carvajal DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 8Document2 pagesTutorial 8fawwazfauzi2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics HW 5Document2 pagesPhysics HW 5Maya HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Em AssignmentDocument3 pagesEm AssignmentAnonymous 3VNugn100% (1)
- HW05 - Energy ConservationDocument7 pagesHW05 - Energy ConservationBradley Nartowt0% (1)
- BITMESRAIMPORTANTTutorial Sheets-Applied MechanDocument34 pagesBITMESRAIMPORTANTTutorial Sheets-Applied MechanmonumunduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Problems: Assignment No. 3 Problem SolvingDocument3 pagesFundamental Problems: Assignment No. 3 Problem SolvingYsrael0% (1)
- TUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Document6 pagesTUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Hareez FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Engineering and InformaticsDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Informaticszahid_polyPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 2151 e MechDocument22 pagesMe 2151 e Mechkalirajgurusamy33% (3)
- 2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDocument3 pages2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareFatih TokgözPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-10Document1 pageEngineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-10atulkumargaur26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bree DiagramDocument22 pagesBree DiagrampajadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Tan Jan Lloyd C. Chapter 2 Newtons Laws 12 14 PDFDocument9 pagesTan Jan Lloyd C. Chapter 2 Newtons Laws 12 14 PDFNorjana BarabatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument4 pagesMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument7 pagesSemester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringBong Kuek KongPas encore d'évaluation
- Part A (5 X 2 10) (Answer All The Questions)Document2 pagesPart A (5 X 2 10) (Answer All The Questions)RajueswarPas encore d'évaluation
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 4 Deformation and Strengthening MechanismsDocument90 pages4 Deformation and Strengthening MechanismsSusheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Mass LinMomentumDocument5 pagesAssignment Mass LinMomentumSusheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics Tutorial 2Document4 pagesBasic Electronics Tutorial 2Susheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- MUN ExperienceDocument1 pageMUN ExperienceSusheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Cysteine: Number of Chiral Center 1 Number of Chiral Center 0Document2 pagesB. Cysteine: Number of Chiral Center 1 Number of Chiral Center 0Susheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation