Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Panchayati Raj: Amendment Act in 2011
Transféré par
Chandu ReddyDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Panchayati Raj: Amendment Act in 2011
Transféré par
Chandu ReddyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
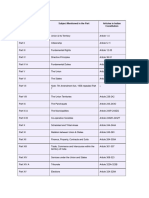
Part - I (Article 1 - 4)
Deals with territory of India formation of new states, alterations, names of
existing states.
Part - II (Art. 5 - 11)
Deals with various rights of Citizenship.
Part - III (Art. 12 - 35)
Deals with Fundamental Rights of Indian citizens.
(Art. 31 - dealing with the right to property was deleted by 44th
amendment).
Part - IV (Art. 36-51)
Deals with Directive Principles of State Policy.
Part - IV - A (Art. 51A)
Added by 42nd amendment in 1976.
Contains the FUNDAMENTAL DUTIES of the citizens.
Part - V (Art. 52 - 151)
Deals with govt. at the Union Level. (Duties & Function of PM, Ministers,
Presidents, Attorney General, Parliament - Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha,
supreme court, Comptroller & Auditor General).
Part - VI (Art. 152 - 237)
Deals with govt. at the State Level.
(Duties & functions of Chief Minister & his ministers, Governor, State
legislature, High Court, Advocate General of the State).
Part - VII (Art. 238)
Deals with States, was replaced in 1956 by the 7th amendment.
Part - VIII (Art.239 - 241)
Deals with Union Territories.
Part IX
Consists of 3 parts:
1. Added by 73rd amendment in 1992.
Contains a new schedule 'SCHEDULE ELEVEN'.
It contains 29 subjects related to Panchayati Raj.
(They have been given administrative powers).
2. (IX-A) Added by 74th amendment in 1992.
Contains a new schedule 'SCHEDULE TWELVE'.
It contains 18 subjects related to Municipalities.
(They have been given administrative powers).
3. (IX-B) Added by 97th amendment act in 2011.
Deals with the Cooperative societies.
Part - X (Art. 244, 244A)
Deals with Scheduled & Tribal Areas.
Part - XI (Art. 245 - 263)
Deals with relation between Union & States.
Part - XII (Art.264 - 300A)
Deals with distribution of revenue between Union & States, appointment of
Finance Commission (Article 280), contracts, liabilities etc.
Part - XIII (Art.301 - 307)
Relates to trade, commerce & intercourse within the Territory of India.
Part - XIV (Art.308 - 323)
Deals with UPSC and Public Service Commissions.
Part - XIV - A (Art.323A,
323B)
By 42nd amendment in 1976. Deals with administrative tribunals set up by
parliament to hear disputes & complaints regarding Union, States or local
govt.Employees.
Part - XV (Art.324 - 329)
Deals with elections (Also Election Commission)
Part - XVI (Art.330 - 342)
Deals with special provisions for Scheduled Castes & Scheduled Tribe &
Anglo - Indian Representation.
Part - XVII (Art. 343 - 351) Relates to official language.
Part, XVIII (Art.352 - 360) Deals with emergency provisions.
Part - XIX (Art.361 - 367)
Exemption of criminal proceedings for their official acts as President &
Governors.
Part - XX (Art. 368)
Deals with Amendment of Constitution.
Part - XXI (Art.369 - 392)
(Art-369 gives temporary powers to the Parliament to make laws for State
list).
(Art -370 contains temporary provisions of J & K - Restricts the parliament to
make laws for that State).
Part - XXII (Art.393 - 395)
Concerns the short title, commencement and repeal of the Constitution.
Schedules of the constitution
The original constitution had 8 schedules.
Today our constitution has 12 schedules.
9th schedule was added by the first constitution amendment act 1951.
10th schedule was added by the 35th constitution amendment act 1974.
This schedule laid down the terms and conditions of the associate status of sikkim.
However it was removed from sikkim as a full fledged state of india.
A new 10th schedule containing provisions on the ground of defection was added by the
52th constitution amendment act 1985.
11th schedule was added by the 73th constitution amendment act 1992.
12th schedule was added by the 74th constitution amendment act 1992.
There are twelve schedules to the consitution of india, which are given below:
First schedule:
This schedule is about the states and union territories of india.
Second schedule:
This schedule provisions made to the president and the governors of states, speaker
and the deputy speaker of the house of the people.
The chairman and the deputy chairman of the council of states.
The speaker and deputy chairman of the legislative council of a state.
The judges of the supreme court and of the high courts and the comptroller and
auditor-general of india.
Third schedule:
Forms of oaths or affirmations are mentioned in this schedule.
Fourth schedule:
This schedule specifies the allocation of seats in the council of states.[rajya sabha to the
states and the union territories(4 and 80)]
Fifth schedule:
provisions as to the administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes
are mentioned in this schedule.
The amendment of the schedule is also included in the part d of the scheduled. [Art 244]
Sixth schedule:
This schedule deals with the provisionsas to the administration of tribal areas in this
states of assam, meghalaya, tripura and mizoram. [art 244 & 275]
Seventh schedule:
The list I or the union list II or the states list and list III or the concurrent list are
included in this schedule.[246]
Art 246:- subject-matter of laws made by parliament and by the legislatures of
states.
Eight schedule:
The 22 languages selected as the official languages of india are mentioned in this
schedule.[344&351]
Under which amendment act, there additional languages such as nepali, konkini and
manipuri were added to 8th schedule of the constitution-71st amendment act-1992
Bodo, Dongri, Maithili and Santhili were added to 92nd amendment act 2003.
Sindhi was added by the 21st amendment act-1967.
Ninth schedule:
Validation of certain acts and regulations is dealt with in this schedule.
Acts and regulations (orginally 13 but presently 282) of the state legislatures
dealing with land reforms and abolition of the zamindari system and of the
parliament dealing with other matters.
This schedule was added by the 1st amendment act 1951 to protect the laws
included in it from judicial scrutiny on the ground of volation of fundamental rights.
However, in 2007 the suprme court ruled that the laws in this in this schedule after
april 24, 1973 are now open to judical review article (31-b)
Tenth schedule:
This schedule contains provisions regarding anti-defection act.(art 102-191)
Provisions relating to disqualification of legislators on ground of defection.
This schedule was added by the 52nd amendment act of 1985. It is also known as
anti-defection act.
Eleventh schedules:
This schedule talks about the powers, authority and responsibilites of
panchayats.[Art 243-g]
It has 29 matters.
This schedule was added by the 73rd Amendment act of 1992.
Twelveth schedule:
specifics the powers, authority and responsibilities of municipalities.[Art 243-w]
It has 18 matter
This schedule was added by the 74th amendment act of 1992.
Part I Union and Its Territory (1- 4)
1. Name and territory of the union
2. Admission or establishment of new states
2A. Sikkim to be associated with the Union (Repealed)
3. Formation of new states and alteration of areas, boundaries or names of existing
states
4. Laws made under Articles 2 and 3 to provide for the amendment of the First and the
Fourth Schedules and supplemental, incidental and consequential matters
Part II Citizenship (5 -11)
5. Citizenship at the commencement of the Constitution.
6. Rights of citizenship of certain persons who have migrated to India from Pakistan
7. Rights of citizenship of certain migrants to Pakistan
8. Rights of citizenship of certain persons of Indian origin residing outside India
9. Persons voluntarily acquiring citizenship of a foreign state not to be citizens
10. Continuance of the rights of citizenship
11. Parliament to regulate the right of citizenship by law
Citizenship Act -1955, which has been amended in 1986, 1992, 2003 and 2005.
Note 1: The provision for Commonwealth Citizenship was omitted by the Citizenship
(Amendment) Act, 2003.
Note 2: In 2011, the Government of India announced its decision to merge the PIO card
and OCI card schemes into a single scheme.
This new scheme is proposed to be called as the Overseas Indian Card Holders Scheme.
In this regard, the Citizenship (Amendment) Bill, 2011, is under consideration of the
Parliament.
Part III Fundamental Rights (12-35)
12. Definition of state
13. Laws inconsistent with or in derogation of the fundamental rights
14. Equality before law
15. Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth
16. Equality of opportunity in matters of public employment
17. Abolition of untouchability.
18. Abolition of titles
19. Protection of certain rights regarding freedom of speech, etc.
Freedom of Speech and Expression 19(1(a))
Freedom of Assembly 19(1(b))
Freedom of Association 19(1(c))
Freedom of Movement 19 (1(d))
Freedom of Residence 19(e))
Freedom of Profession, etc. 19(g))
20. Protection in respect of conviction for offences
21. Protection of life and personal liberty
21A. Right to elementary education (86th Constitutional Amendment Act 2002)
22. Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases.
23. Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
24. Prohibition of employment of children in factories, etc.
25. Freedom of conscience and free profession, practice and propagation of religion
26. Freedom to manage religious affairs
27. Freedom as to payment of taxes for promotion of any particular religion
28. Freedom as to attendance at religious instruction or religious worship in certain educational
institutions
29. Protection of interests of minorities
30. Right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions
31. Compulsory acquisition of property (Repealed)(44th Constitutional Amendment Act 1978)
31A. Saving of laws providing for acquisition of estates, etc.(1st Constitutional Amendment Act 1951)
31B. Validation of certain acts and regulations.(1st Constitutional Amendment Act 1951)
31C. Saving of laws giving effect to certain directive principles. (25th Constitutional Amendment
Act 1971)
31D. Saving of laws in respect of anti-national activities (42nd Constitutional Amendment Act 1976)
(Repealed) (43rd Constitutional Amendment Act 1977) (13 April, 1978) came in force.
32. Remedies for enforcement of fundamental rights including writs
33. Power of Parliament to modify the fundamental rights in their application to forces, etc.
34. Restriction on fundamental rights while martial law is in force in any area
35. Legislation to give effect to some of the provisions of fundamental rights.
Part IV-Directive Principles of State Policy (36-51)
36. Definition of State
37. Application of the directive principles
38. State to secure a social order for the promotion of welfare of the people
39. Certain principles of policy to be followed by the State
39A. Equal justice and free legal aid
40. Organisation of village panchayats
41. Right to work, to education, and to public assistance in certain cases
42. Provision for just and humane conditions of work and maternity relief
43. Living wage, etc. for workers
43A. Participation of workers in management of industries
43B. Promotion of co-operative societies
44. Uniform civil code for the citizens
45. Provision for early childhood care and education to children below the age of six years
46. Promotion of educational and economic interests of scheduled castes, scheduled tribes and
other weaker sections
47. Duty of the state to raise the level of nutrition and the standard of living and to improve
public health
48. Organisation of agriculture and animal husbandry
48A. Protection and improvement of environment and safeguarding of forests and wild life
49. Protection of monuments and places and objects of national importance
50. Separation of judiciary from executive
51. Promotion of international peace and security
Part IV-A Fundamental Duties (51A)
51A. Fundamental duties (42nd Amendment Act-1976)
51(a).To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals andinstitutions,the National Flag and the
National Anthem.
(b).To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom.
(c).To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
(d).To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
(e).To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood and preserve dignity of women.
(f).To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite cultures.
(g).To protect and improve natural environment.
(h).To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
(i).To safeguard public property and to abjure violence.
(j).To strive for excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity.
(k).To provide opportunities for educaton to his child or, as the case may be ward between the age of six
and fourteen years.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsD'EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsPas encore d'évaluation
- NTSE Sheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesNTSE Sheet 3 PDFVed bukhariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Architects of the Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesArchitects of the Indian ConstitutionABCPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesDocument5 pagesIndian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesShiva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian PolityDocument22 pagesIndian PolityPRABHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts and Important Articles of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesParts and Important Articles of The Constitutioncoolsumitan100% (1)
- Polity 2Document18 pagesPolity 2Swayam SwastikPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to India's ConstitutionDocument19 pagesIntroduction to India's ConstitutionvinodkumarjkPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of India Fundamental Rights GuideDocument44 pagesConstitution of India Fundamental Rights Guidesoumya612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of The Indian ConstituionDocument3 pagesStructure of The Indian ConstituionDolphinPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A VDocument10 pagesParts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A Vrakesh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Constituion of India ArticlesDocument4 pagesConstituion of India ArticlesRaghu RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance for SSC CGL Exam 2012Document6 pagesGuidance for SSC CGL Exam 2012Hariprasad Pampana100% (2)
- Constitution: Useful LinksDocument7 pagesConstitution: Useful LinkssatyajitPas encore d'évaluation
- The Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)Document2 pagesThe Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)ishk1989Pas encore d'évaluation
- Merged DocumentDocument68 pagesMerged DocumentPuneet JadaunPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution IDocument49 pagesConstitution Iajaybc2104Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important Amendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitutionkrishnasantana1988Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important AmendmentDocument30 pagesImportant Amendmentomkumar7349Pas encore d'évaluation
- Imp articles, Parts & Schedule (4)Document7 pagesImp articles, Parts & Schedule (4)Akash PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Amendments of the Indian ConstitutionDocument9 pagesImportant Amendments of the Indian ConstitutionParveen SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesMportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionNikunj VatsPas encore d'évaluation
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440Pas encore d'évaluation
- Union-State Legislative RelationsDocument34 pagesUnion-State Legislative RelationsGarvit ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Constitutional Amendments and SchedulesDocument3 pagesImportant Constitutional Amendments and SchedulesNavya AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- NnnppppaaaaDocument33 pagesNnnppppaaaayashuyash33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of IndiaDocument134 pagesConstitution of IndiarajdeeppawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of IndiaDocument19 pagesConstitution of Indiaanant_sahu_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important Amendments To The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesImportant Amendments To The ConstitutionprincePas encore d'évaluation
- List of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesList of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionpreetamdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Amendments Indian Constitution UPSCDocument8 pagesMajor Amendments Indian Constitution UPSCPrashant SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of ConstitutionDocument4 pagesParts of ConstitutionFake MailPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of India - List of All Articles (1-395) and Parts (1-22)Document21 pagesConstitution of India - List of All Articles (1-395) and Parts (1-22)ANSHUMANPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Schedules of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 35 PDFDocument6 pages12 Schedules of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 35 PDFRabiul HaquePas encore d'évaluation
- Artcles of India SocialDocument14 pagesArtcles of India Socialshreyas malvePas encore d'évaluation
- Indian PolityDocument53 pagesIndian PolityNagesh Reddy Katipelli100% (2)
- Case LawDocument6 pagesCase Lawrudrakshvijayvargiya4000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Major Constitutional Amendments: Part-2Document4 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendments: Part-2RAVI PRATAPPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Amendments of The Constitution of India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesList of Amendments of The Constitution of India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAmlandeep NandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Centre State Relations DR Mohd ImranDocument47 pagesCentre State Relations DR Mohd ImranVanshikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of India List of All Articles 1-395 and Parts 1-22Document20 pagesConstitution of India List of All Articles 1-395 and Parts 1-22BINDOSH TRADER'SPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjusDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjuskumarprincelkhPas encore d'évaluation
- Most Important Constitutional Amendments in Indian Constitution List of Amendments of The Constitution - General Knowledge in Indian PoliticsDocument2 pagesMost Important Constitutional Amendments in Indian Constitution List of Amendments of The Constitution - General Knowledge in Indian PoliticsAkbar KushanoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Forty-Second Amendment of The Constitution of IndiaDocument7 pagesForty-Second Amendment of The Constitution of IndiaPrasobh ShamohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Constitutional AmendmantsDocument4 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmantsShiva Shankar PandianPas encore d'évaluation
- 3Document2 pages3AMIR RAZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapDocument54 pagesImportant Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapANUBHAV SHUKLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Vishnu SharmaDocument15 pagesVishnu SharmaSauravMishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Preamble CitizenshipDocument22 pagesPreamble CitizenshipAbhayPas encore d'évaluation
- eBOOK 22091914205956Document42 pageseBOOK 22091914205956Kuwar NikhilPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of India - List of All Articles (1-395) and Parts (1-22)Document20 pagesConstitution of India - List of All Articles (1-395) and Parts (1-22)dipeshanairPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74Document8 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Polity and ConstitutionDocument10 pagesIndian Polity and ConstitutionRudra DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment ActDocument4 pages73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment ActMohan Kumar Singh0% (1)
- 1-34 Ias BabaDocument590 pages1-34 Ias BabaGagan KarwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Odisha Police Exam GuideDocument51 pagesOdisha Police Exam GuideAlokPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesParts of The Indian Constitutionserryserry362Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 ScheduleDocument6 pages12 ScheduleHackerzillaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Indian Constitution: Key Parts and SchedulesDocument9 pagesThe Indian Constitution: Key Parts and SchedulesRitwik PatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Corpo Digets 1Document11 pagesCorpo Digets 1AmberChan100% (1)
- Earthdawn Creature Summary N To ZDocument4 pagesEarthdawn Creature Summary N To ZWilliam YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Notice of Voluntary Dismissal Under Rule 41 in United States District CourtDocument4 pagesSample Notice of Voluntary Dismissal Under Rule 41 in United States District CourtStan BurmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Laganapan Vs Mayor AsedilloDocument1 pageLaganapan Vs Mayor Asedillomamp05Pas encore d'évaluation
- BDM Change Name Adult Application Form 4a GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBDM Change Name Adult Application Form 4a GuidelinesPelin üstünerPas encore d'évaluation
- Rough DraftDocument3 pagesRough DraftBharat JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- FBI Fingerprint Database (IAFISDocument3 pagesFBI Fingerprint Database (IAFISKarima Afandi QuiliumPas encore d'évaluation
- CitriculturaDocument40 pagesCitriculturaZamirCast100% (3)
- 1 Iloilo Jar Corp. v. Comglasco Corp Aguila GlassDocument7 pages1 Iloilo Jar Corp. v. Comglasco Corp Aguila GlassFrancis LeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Insular Life Assurance Co. vs Paulin sistersDocument2 pagesInsular Life Assurance Co. vs Paulin sistersLDPas encore d'évaluation
- Puno's Separate Opinion on the Applicability of Rights During the 1986 RevolutionDocument50 pagesPuno's Separate Opinion on the Applicability of Rights During the 1986 RevolutionElgieraydolph BuisonPas encore d'évaluation
- In Re Hilda Soltero Harrington, Debtor. Estancias La Ponderosa Development Corporation v. Hilda Soltero Harrington and Rafael Durand Manzanal, 992 F.2d 3, 1st Cir. (1993)Document4 pagesIn Re Hilda Soltero Harrington, Debtor. Estancias La Ponderosa Development Corporation v. Hilda Soltero Harrington and Rafael Durand Manzanal, 992 F.2d 3, 1st Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pribeagu v. Gwinnett County, No. A15A2026 (Ga. App. Apr. 13, 2016)Document13 pagesPribeagu v. Gwinnett County, No. A15A2026 (Ga. App. Apr. 13, 2016)RHTPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Form For EmploymentDocument2 pagesApplication Form For EmploymentvictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Javier vs. Court of Appeals 183 SCRA 171Document6 pagesJavier vs. Court of Appeals 183 SCRA 171Rimvan Le SufeorPas encore d'évaluation
- Edroso v. Sablan G.R. No. 6878, September 13, 1913 FactsDocument7 pagesEdroso v. Sablan G.R. No. 6878, September 13, 1913 FactsKarl Marxcuz ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Arnault Vs BalagtasDocument3 pagesArnault Vs BalagtasRoberts SamPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivo v. PAGCOR: Employee Dismissal Upheld for Lack of Due Process ViolationDocument2 pagesVivo v. PAGCOR: Employee Dismissal Upheld for Lack of Due Process ViolationloschudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Nominated Subcontractors On International ProjectsDocument9 pagesNominated Subcontractors On International ProjectsChikwason Sarcozy MwanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- September 4 2017 GR 225402Document2 pagesSeptember 4 2017 GR 225402lacbayen50% (2)
- ITL Mod 4Document22 pagesITL Mod 4Nicole CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Conditions Precedent to Recovery of Loss and Expense ClaimsDocument9 pagesConditions Precedent to Recovery of Loss and Expense Claimslengyianchua206Pas encore d'évaluation
- City of Iloilo vs. Legaspi: Requirements for Eminent Domain ComplianceDocument12 pagesCity of Iloilo vs. Legaspi: Requirements for Eminent Domain ComplianceApril SaligumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejectment Complaint with Mandatory InjunctionDocument8 pagesEjectment Complaint with Mandatory InjunctionImelda Arreglo-AgripaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comelec Ruling on 2004 Legaspi City Mayoralty Election ContestDocument14 pagesComelec Ruling on 2004 Legaspi City Mayoralty Election ContestChristellPas encore d'évaluation
- Valencia V CADocument10 pagesValencia V CApjPas encore d'évaluation
- York County Court Docket For Oct. 24Document15 pagesYork County Court Docket For Oct. 24York Daily Record/Sunday NewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacific Wide Realty and DevDocument2 pagesPacific Wide Realty and DevJohn Roel VillaruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Dibaratun V COMELECDocument2 pagesDibaratun V COMELECGenevieve Kristine ManalacPas encore d'évaluation
- Peer Review Report Phase 1 Legal and Regulatory Framework: Saint LuciaDocument86 pagesPeer Review Report Phase 1 Legal and Regulatory Framework: Saint LuciaOECD: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and DevelopmentPas encore d'évaluation