Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Joseph Demo
Transféré par
SKSU KalamansigCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Joseph Demo
Transféré par
SKSU KalamansigDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lesson Plan
BFT-1
Physiology of Fishes
February 22, 2013
I.
II.
III.
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
a. Recognized the internal anatomy of the bony fish
b. Value the internal anatomy of fish
c. Discuss and ask questions regarding the topic
SUBJECT MATTER
Topic: internal anatomy of the fish
Reference: internet, Fishes
Materials: charts, visual aids, overhead projector- power point presentation
Time frame: 2:00-3:00
LEARNING PROCEDURES
a. Greetings
Good afternoon class
Have a seat
b. Checking of attendance
c. Review
External parts of fish
d. Motivation
Have you ever tried to open a fish? Beyond your curiosity, have you tried to ask
yourselves that why would fish contain those internal parts?
e. Lesson Proper
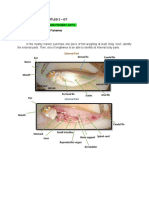
Internal anatomy of a bony fish: finned aquatic vertebrates animal with skin covered with
scales. It lives in water and is usually oviparous.
Brain: seat of the mental faculties of a fish.
Esophagus: part of the digestive tract connecting the mouth to the stomach.
Dorsal aorta: vessel in the back that carries blood from the heart to the organs.
Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine.
Air bladder: pocket in which urine collects.
Spinal cord: part of the nervous system that connects the brain to all other parts of a fish.
Kidney: blood-purifying organ.
Urinary orifice: opening for eliminating urine.
Genital Orifice: opening related to the genital organs.
Anus: end of the digestive tract.
Gonad: hormone-secreting sexual gland of a fish.
Intestine: last part of the digestive tract.
Pyloric cecum: cul-de-sac related to the intestine.
Gall bladder: small sac containing the bile.
Liver: bile-producing digestive gland.
Heart: blood-pumping organ.
Gills: respiratory organ of a fish.
Tooth: hard organ of a fish used to shred food.
Eye: sight organ of a fish.
Olfactory bulb: bulging part of the smell organ of smell of a fish.
f. Activity
h.
g.
i.
a. Student activity
g. Teachers activity
b.
h.
c. *listening to the lesson
d. *listing of the internal
i. *presenting the topic
j. *discussing the topic
k. *dissecting the fish
parts of fish
e. *observing on
dissecting fish
f.
j.
l.
m.
IV.
V.
VI.
k.
l.
m.
n.
o.
p. Values Integration
q.
Humans contain different organs that functions to in their lifestyle habit.
Fishes have theirs too. Even the smallest organ, completes the routine of
different systems of the fish.
GENERALIZATION
r. Fish have their different internal organs such as brain, esophagus, dorsal aorta,
stomach, air bladder, spinal cord, kidney, urinary orifice, genital orifice, anus, gonad,
intestine, pyloric cecum, gall bladder, liver, heart, gills, tooth, eyes, and olfactory
bulb.
EVALUATION
s. Direction: answer the following questions
1. Tooth: hard organ of a fish used to shred food
2. Gall bladder: small sac containing the bile
3. Brain: seat of the mental faculties of a fish
4. Gonad: hormone-secreting sexual gland of a fish
5. Anus: end of the digestive tract
6. Heart: blood-pumping organ.
7. Eye: sight organ of a fish
8. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine.
9. Kidney: blood-purifying organ.
10. Liver: bile-producing digestive gland.
ASSIGNMENT
t. Advance study about the muscular and locomotion
u.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- LESSON II: External Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsDocument32 pagesLESSON II: External Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsLourdicel De la RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bony Fish AnatomyDocument9 pagesBony Fish AnatomyDbalt100% (1)
- Fishery Arts Fishery Arts: Mrs. Sally C. SaldeDocument28 pagesFishery Arts Fishery Arts: Mrs. Sally C. SaldeJered Morato100% (1)
- Fish Biology Student Activity WorkbookDocument21 pagesFish Biology Student Activity WorkbookGURPREET SINGH TIWANA100% (1)
- TLE15 Fishery Part 1Document21 pagesTLE15 Fishery Part 1Joanna April100% (5)
- 4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairDocument5 pages4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairEvi SintaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Meco ChicaPas encore d'évaluation
- External and Internal Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsDocument18 pagesExternal and Internal Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsHazel Leah KhaePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 2 SheetDocument9 pagesPractical 2 SheetNur IzzatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 231 - Lab #4Document4 pagesBio 231 - Lab #4Shayden LesliePas encore d'évaluation
- mod 5.1Document19 pagesmod 5.1Jhoana Paula EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE 4 Introduction to Fish Morphology, Culture, Capture & PreservationDocument9 pagesTLE 4 Introduction to Fish Morphology, Culture, Capture & PreservationAlondra JanePas encore d'évaluation
- English For Student's Fish PDFDocument73 pagesEnglish For Student's Fish PDFEchy Dwi HermawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Crayfish Dissection LabDocument2 pagesCrayfish Dissection LabKate FairleyPas encore d'évaluation
- What is a Fish? Its Parts and Branches of FisheryDocument5 pagesWhat is a Fish? Its Parts and Branches of FisheryGian ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Laprak IkanDocument13 pagesLaprak IkanRezky AmaliahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fish 1Document30 pagesFish 1Adnan mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 OsteichthyesDocument32 pages3 OsteichthyeshilyaalawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of The FishDocument2 pagesParts of The Fishjosephstayhappy.29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of GillsDocument55 pagesFish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of Gillsbongsky1Pas encore d'évaluation
- External Fish AnatomyDocument4 pagesExternal Fish AnatomyKissha Jane100% (1)
- Comprehension Check Science 5thDocument2 pagesComprehension Check Science 5thJohana HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Snout Are Called Nostrils, or Nares.:: Have No FearDocument22 pagesSnout Are Called Nostrils, or Nares.:: Have No FearKristine Joy Eyao BalayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chordata: Salient Features and ExamplesDocument20 pagesChordata: Salient Features and Examplesasmita100% (1)
- Squid DissectionDocument3 pagesSquid Dissectionapi-297841438100% (1)
- Michael Pallon Biology II - Honors Skate DissectionDocument1 pageMichael Pallon Biology II - Honors Skate Dissectionmichael_pallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Praktikum Struktur Hewan Unit IkanDocument40 pagesPraktikum Struktur Hewan Unit IkanSt. Asyah Alya Faradiba.pPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Trial Test Unit 4Document21 pagesScience Trial Test Unit 4fm5z2cbxkhPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 26 - Mollusks lp5Document12 pagesCHP 26 - Mollusks lp5api-259321090Pas encore d'évaluation
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDocument5 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 3 Intro To Agri-Fishery Art Labawan Joel JRDocument4 pagesMODULE 3 Intro To Agri-Fishery Art Labawan Joel JRJoel LabawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dla Quarter 3 Week 1 Act 1Document2 pagesDla Quarter 3 Week 1 Act 1Joyce Dela Rama JulianoPas encore d'évaluation
- ) Fusiform: A) Torpedo-Shaped B) Allows Minimal Drag While Swimming C) Best Shape For A Pelagic CruiseDocument63 pages) Fusiform: A) Torpedo-Shaped B) Allows Minimal Drag While Swimming C) Best Shape For A Pelagic CruiseUit CatPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Nilem Fish and CatfishDocument18 pagesAnatomy of Nilem Fish and CatfishDion Satrio PambudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tle PT Grade 8 Q1Document7 pagesTle PT Grade 8 Q1Israel Marquez100% (2)
- Frog DissectionDocument2 pagesFrog DissectionKylle CalipesPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCEDocument5 pagesSCIENCEJj MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- FishesDocument23 pagesFishesevelin.szaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Animals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratesDocument9 pagesAnimals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratessmedificationPas encore d'évaluation
- External Anatomy of FishDocument2 pagesExternal Anatomy of FishZeb Cabalfin100% (1)
- 12DIGESTIVEDocument5 pages12DIGESTIVEDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaDocument9 pagesLab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaEricka ElloPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1 - Anatomy of A FishDocument1 pageActivity 1 - Anatomy of A FishMarie Flor BongatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - AquacultureDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - AquacultureEvangeline GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Squid DissectionDocument3 pagesSquid Dissectionapi-296981910100% (1)
- CDU ZOOLOGY Anatomical Terminologies in Chordates and Vertebrates WorksheetDocument4 pagesCDU ZOOLOGY Anatomical Terminologies in Chordates and Vertebrates WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Planes and Body CavitiesDocument14 pagesBody Planes and Body CavitiesUzma KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- StemchartDocument8 pagesStemchartapi-297052087Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyDocument7 pagesFisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyEezem Rachid AushoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fish Intro Part 2Document87 pagesFish Intro Part 2Jesusa villarozaPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP in Science 4 q2Document4 pagesDLP in Science 4 q2Ela F M PulligPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepare and Cook Seafood Dishes: Perform Mise en Place: CookeryDocument11 pagesPrepare and Cook Seafood Dishes: Perform Mise en Place: CookeryLoli Gonzales Artiaga100% (1)
- BIOL330 Lab 2 - Lab ManualDocument7 pagesBIOL330 Lab 2 - Lab ManualOliverPas encore d'évaluation
- 5E Learning Plan Identifies Parts and Functions of AnimalsDocument4 pages5E Learning Plan Identifies Parts and Functions of AnimalsMLG F100% (3)
- RPP HeniDocument25 pagesRPP HeniHeru Wide WirdhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Intreoduction and ClassificationDocument9 pages1 - Intreoduction and Classificationahmed 312Pas encore d'évaluation
- FishesDocument2 pagesFishesObiora Ekene HilaryPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Digestion in Teleost Fishes - 2Document23 pages1 Digestion in Teleost Fishes - 2Evi Nurul IhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Digestive System FunctionsDocument6 pagesGrade 9 Digestive System FunctionsRamyRamia ElzantPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE - Organisation and The Digestive SystemDocument20 pagesScience Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE - Organisation and The Digestive Systemda_reaper_dasPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyDocument20 pagesEndocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyD AngelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Body SystemsDocument4 pagesBody SystemsKathryn Schultz29% (14)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: S8LT-Iva-13Document12 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: S8LT-Iva-13Kiesha Dame Eclipse Saliwan100% (2)
- Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Digestive System Exam Reviewhugomiso100% (3)
- Human Digestive System Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesHuman Digestive System Lesson PlanMarichu Cayabyab100% (2)
- Journey Through the Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesJourney Through the Digestive SystemAsif KPas encore d'évaluation
- PeppermintDocument5 pagesPeppermintDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (1)
- Tibetan MedicineDocument0 pageTibetan MedicineHun Lye100% (2)
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemchinchuPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionDocument68 pagesCASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionMaria Paula Bungay91% (22)
- The College Study: Nutrition NotesDocument11 pagesThe College Study: Nutrition NotesAbbas HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Biological ScienceDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Biological Sciencejanelle belanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument22 pagesDigestive SystemRancesh FamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahasa Inggris WDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggris WAnnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- From Tasting To DigestingDocument7 pagesFrom Tasting To DigestingSanket Sinai PaussoPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive and Respiratory Organs DefinitionDocument4 pagesDigestive and Respiratory Organs DefinitionSidne E. AgorPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Terminology CH 8Document139 pagesMedical Terminology CH 8ياسين المسطوPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Cleanse INSTRUCTIONSDocument6 pagesMaster Cleanse INSTRUCTIONSAlexander Rosental100% (2)
- Questions To AnswerDocument3 pagesQuestions To AnswerjanePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation GastroenteritisDocument58 pagesCase Presentation GastroenteritisShereen Manabilang100% (3)
- Rat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyDocument10 pagesRat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyValar Mathei PadmanadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition by AllanDocument62 pagesTest Bank For Medical Language For Modern Health Care 4th Edition by Allansophiacarrdabemqozri100% (22)
- Bio RevisionDocument58 pagesBio RevisionKesithan AnandarashPas encore d'évaluation
- Young Living For Detoxification and Weight Management Class NotesDocument16 pagesYoung Living For Detoxification and Weight Management Class Notesnurifauziyah100% (1)
- Biology Diagram McqsDocument23 pagesBiology Diagram McqsFatima Obaid0% (1)
- Strategic Intervention for the Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesStrategic Intervention for the Digestive SystemKarla Javier PadinPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSIOLOGYDocument10 pagesPHYSIOLOGYapi-1986354875% (4)
- Human Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesHuman Digestive Systemfatimah17Pas encore d'évaluation