Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Small: A Region Near The Nucleus in The Cell Cytoplasm, Containing Thecentrioles
Transféré par
Anjo Jimenez0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues2 pagesanatomy
Titre original
Anatomy 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentanatomy
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues2 pagesSmall: A Region Near The Nucleus in The Cell Cytoplasm, Containing Thecentrioles
Transféré par
Anjo Jimenezanatomy
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
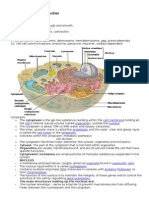
DESCRIPTION
The cell membrane is selectively permeable
to ions and organic molecules and controls
the movement of substances in and out of
cells.
Centrosomesa small region near the nucleus in the cell
cytoplasm, containing thecentrioles.
Cytoplasm- The cytoplasm comprises cytosol
(the gel-like substance enclosed within the
cell membrane) and the organelles the
cell's internal sub-structures. All of the
contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms
(such as bacteria, which lack a cell nucleus)
are contained within the cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus- an organelle, consisting of
layers of flattened sacs, that takes up and
processes secretory and synthetic products
from the endoplasmic reticulum and then
either releases the finished products into
various parts of the cell cytoplasm or
secretes them to the outside of the cell.
Lysosomes- One of the key organelles involved in
digestion and waste removal is
the lysosome.Lysosomes are organelles that
contain digestive enzymes. They digest excess or
worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed
viruses or bacteria. Lysosomesare like the
stomach of the cell.
Microvillitiny hairlike folds in the plasma membrane that extend fr
om the surface of many absorptive or secretory cells. Th
ey aremost clearly visible with an electron microscope b
ut may be seen as a "brush border" with a light microsco
pe.
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of
the cell. They are organelles that act like a
digestive system which takes in nutrients, breaks
them down, and creates energy rich molecules for
the cell. The biochemical processes of the cell are
known as cellular respiration.
-All eukaryotic cells (those found in animals, plants,
protists, and fungi) have a control center called the
nucleus. This is where genetic material, or DNA, is
stored. Surrounding every nucleus is a doubleFUNCTION
-The basic function of the cell membrane is
to protect the cell from its surroundings. It
consists of the phospholipid bilayer with
embedded proteins.
-is performed by other cell organelles. They help in
regulating the cell cycle and are an integral part of
cell division by mitosis. They are made of centrioles
and a surrounding pericentriolar material (PCM).
The PCM is made up of proteins like tubulin,
pericentrin and ninein. The two centrioles are
located orthogonal to each other.
-The jelly-like fluid that fills a cell is
called cytoplasm. It is made up of mostly water
and salt. Cytoplasm is present within the cell
membrane of all cell types and contains all
organelles and cell parts.
- The main function of the Golgi apparatus is to modify,
sort and package the macromolecules that are
synthesized by the cells for secretion purposes or for
use within the cell.
-The functions of lysosomes concern the different ways
in which the enzymes contained within the membrane
(that defines and encloses the lysosome) affect other
materials, which can originate from either outside or
inside the cell.
- Microvilli are attached to the collections of cells
known as villi that extend from the tissue of the
small intestine. They work to dramatically increase
the amount of surface area available for the
digestive process.
- mitochondria is to produce energy. The simpler
molecules of nutrition are sent to the mitochondria to be
processed and to produce charged molecules. These
charged molecules combine with oxygen and produce
ATP molecules. This process is known as oxidative
phosphorylation.
- nuclear membrane is to separate the nucleus of a
cell from the cytoplasm that surrounds it. The
nuclear membrane, also called the nuclear
envelope, is defined as a membrane that surrounds
the genetic material contained within the nucleus of
a cell. The nuclear membrane is made up of the
inner and outer membranes, the lamina and pore
complexes
layered membrane called the nuclear
membrane or nuclear envelope.
-any of numerous structures with complex
openings in a nuclear membrane which allow
passage of molecules between the nucleus
and surrounding cytoplasm; any of the
numerous perforations in a nuclear
membrane which allow materials to flow in
and out
- The nucleolus is a round body located inside the
nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is not surrounded by
a membrane but sits in the nucleus.
The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from
proteins and ribosomal RNA, also known as rRNA.
- Nuclear pores are protein-based channels
in the nuclear envelope. They regulate the
movement of molecules from the nucleus
to the cytoplasm, and vice versa. In most
eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is enclosed by
this nuclear membrane in order to
separate it from the cytoplasm.
- Its main function is to rewrite ribosomal
RNA (rRNA) and combine it with proteins.
This results in the formation of incomplete
ribosomes. There is an uninterrupted chain
between the nucleoplasm and the interior
parts of the nucleolus, whichoccurs
through a system of nucleolarpassages.
These passages allow macromolecules with
a molecular weight up to 2,000 kDato be
easily circulated throughout the nucleolus.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Cytoplasm in A CellDocument5 pagesThe Role of Cytoplasm in A CellRishikesh BhintadePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology ProjectBemnet TayePas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Last-Cell Organelles.Document3 pagesLecture Last-Cell Organelles.OnSolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument15 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesAndrew MahilumPas encore d'évaluation
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 The CellDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Document10 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamPas encore d'évaluation
- Module IDocument18 pagesModule IAdvith A JPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15Pas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydePas encore d'évaluation
- Function of Animal CellDocument2 pagesFunction of Animal CellLyn UmpadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell The smalle-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageCell The smalle-WPS OfficeGreatle Mae D. BasbañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument7 pagesCellPrashant PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewalePas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Week 2Document22 pagesCell Week 2maureganitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument43 pagesStructure and Function of The CellElvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Kiera Slideshare PDFDocument9 pagesKiera Slideshare PDFKiera SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayarePas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 001 6th LectureDocument37 pagesBIO 001 6th LectureManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsPas encore d'évaluation
- ImprimirDocument3 pagesImprimirmgg9st6k5jPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument46 pagesCell Structure and OrganizationLara Lyn PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Cell StructureDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell StructurePRINTDESK by DanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab #2Document8 pagesLab #2Regina RazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular BiologyDocument8 pagesCellular BiologyStellaPas encore d'évaluation
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDocument9 pagesPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell & Tissue StructureDocument19 pagesCell & Tissue StructureBrintha Kani KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology FSC Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology FSC Chapter 1Diana PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Animal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisNicole CatolicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusPas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument17 pagesCellsnguyenbohaePas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacy CPDProvider v2Document9 pagesPharmacy CPDProvider v2PRC BoardPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Document8 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Noor JanahiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Bacterial Cell - Structures and FunctionsDocument27 pagesThe Bacterial Cell - Structures and FunctionsFRANCIS PAOLO CUADRAPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Breeding 2Document67 pagesAnimal Breeding 2Charles Joseph MaldiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells ReviewerDocument3 pagesCells ReviewerIvy LumapacPas encore d'évaluation
- HHS Public Access: Down SyndromeDocument43 pagesHHS Public Access: Down SyndromeJonnahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction Test ReviewDocument5 pagesReproduction Test ReviewtssandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Arihant Ncert Exemplar Biology Solution Class 12Document290 pagesArihant Ncert Exemplar Biology Solution Class 12Md Kutubuddin Sardar50% (2)
- Sub Cloning Notebook EuroDocument72 pagesSub Cloning Notebook Eurod-fbuser-97323052Pas encore d'évaluation
- One Taq DNAPolDocument2 pagesOne Taq DNAPolMuni SwamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure (Take Home)Document5 pagesCell Structure (Take Home)Princy CaesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Planaria Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPlanaria Lab Reportapi-201420601Pas encore d'évaluation
- 60 IzovacDocument3 pages60 Izovacuzairch491Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2Document20 pagesLectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2desalegn abera100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal - Mucosal.repair - And.experimental - Therapeutics Ublog - TKDocument261 pagesGastrointestinal - Mucosal.repair - And.experimental - Therapeutics Ublog - TKpotaiskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter of MotivationDocument2 pagesLetter of MotivationSaharudin Bioscience88% (8)
- ESDA DNA From DocumentsDocument5 pagesESDA DNA From DocumentsNikolaos KalantzisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Revision SheetsDocument7 pagesBiology Revision Sheetsapi-272802868Pas encore d'évaluation
- Immunoassays: Fundamental Questions For An Analytical ChemistDocument25 pagesImmunoassays: Fundamental Questions For An Analytical ChemistDea Maylika SopiyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Biological MoleculeDocument3 pagesImportance of Biological MoleculeMary Antonette LucioPas encore d'évaluation
- ChEn 3701Document2 pagesChEn 3701ConePas encore d'évaluation
- Flashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument75 pagesFlashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSESabbath the sign of GodPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Pharmaceutical Classification SystemDocument7 pagesBio Pharmaceutical Classification SystemRafi Arif 7189Pas encore d'évaluation
- StefanelliDocument5 pagesStefanelliYuscha AnindyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Introduction GuideDocument1 pageBiology Introduction GuideAna Lucia Lozada NoePas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Cell Division BSC StudentsDocument64 pagesReview of Cell Division BSC StudentsKripa SusanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940, Rule 1945 by Dr. Izhar AhmadDocument49 pagesDrugs and Cosmetics Act 1940, Rule 1945 by Dr. Izhar AhmadijharPas encore d'évaluation
- 7-1 WorksheetDocument5 pages7-1 WorksheetPak RisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell StructureDocument37 pagesCell Structurechantellelim100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Regulation ModelDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Regulation ModelzafiharoPas encore d'évaluation