Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Belt Analysis - Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt
Transféré par
Suchi Suchi SuchiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Belt Analysis - Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt
Transféré par
Suchi Suchi SuchiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
[Pg 1 / 4]
Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt.xmcd
V-Belt
The Units used as standard:
(Q 17-17)
m, kg, N, Pa, sec, watts
N, kg, m, Pa, sec/min, watts/kW
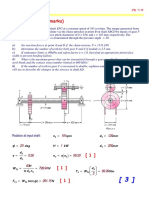
A V-belt system is to be selected to deliver engine power to the wheel-drive transmission of a riding
tractor. A 5 kW engine is used. At most, 60% of this power is transmitted to the belt. The driving
sheave has a diameter of 155-mm, the driven, 300-mm. The belt selected should be as close to a
2300-mm pitch length as possible. The engine speed is governor-controlled to a maximum of 3100
rpm. Select a suitable belt and the belt life in hours.
In this analysis, the design engineer decide the type of belt used based on the
recommended pitch length (Lp) specified. However he should take consideration of the
constraints of selecting V-belts which have exact Lp based on two tables (Table 17-10 and
17-11). Power = 60% of 5kW = 3kW
Specs given:
Recommended Lp : closest to 2300-mm as possible
Other constraints: d = 155mm, D = 300mm, H = 3.0kW
Possible choice: A2250, B2250, C2250 (see Table 17-10)
Check for constraints and limitations stipulated in Table 17-9:
Belt type A is OK
Belt type B is OK
Belt type C cannot be not selected because minimum sheave size limitation [ d 230mm]
See Table 17-11:
Target Lp (closest to 2300mm)
A2250: Lp = 2250 + 32 = 2282
B2250: Lp = 2250 + 45 = 2295
A2400: Lp = 2400 + 32 = 2432
A2400: Lp = 2400 + 45 = 2445
We shall select B2250 as pitch length closest to 2300mm.
Hence the result:
Lp = 2295mm
driving sheave:
d = 155mm
driven sheave:
D = 300mm
engine speed:
n1 = 3100rpm
The corrected center to center distance,
2
C = 0.25 Lp
( D + d ) + Lp
( D + d ) 2 ( D d ) = 786.804 mm
2
2
[Pg 2 / 4]
Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt.xmcd
D d
= 2.957
2C
Eq 17-1
d = 2 asin
Power from motor: Hnom = 60% 5.0kW = 3 kW
Ks = 1.3( see Table 17-15 )
Service factor,
nd = 1.0
Design factor,
Hd = Hnom Ks nd = 3.9 kW
Designed power capacity,
The designed power above is the capacity to be transferred through the belt. The next
step is to calculate the number of belts required to transfer such load by calculating
the capacity per belt.
n1 = 3100 rpm
V =
d n1
= 25.159
60
m
sec
See Table 17-12 for tabulated power per belt using V = 25.2 m/s
For larger sheave, D = 300mm:
Htab = 3.66kW
For smaller sheave, D = 155mm:
Htab = 2.98kW
Conclusion: Always select the value for smaller sheave !
Htab = 2.98kW
To find K1
x =
Dd
C
= 0.184
Use Table 17-13 to find K1 (interpolate if necessary)
x 0.2
0.1 0.2
K1 0.97
0.99 0.97
Interpolated value : K1 = 0.973
[Pg 3 / 4]
Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt.xmcd
From Table 17-14, for belt type B2250, L = 2.250m,
the length correction factor, K2 = 1.00
The allowable power capacity per belt, Ha = K1 K2 Htab = 2.9 kW
Number of belts,
Nb =
Hd
Ha
( )
= 1.345
Nb = ceil Nb = 2
Actual number of belts required:
Nb = 2
If the designed power is smaller than allowable power per belt (ie using 1 belt only), the
following calculation is based on "designed power, Hd ".
If the designed power is larger than allowable power per belt (ie several belts are
needed) then the calculation is based on per belt analysis => used " average designed
power per belt, Hd/Nb "
From Table 17-16,
Kc = 0.965
2
V
Fc = Kc = 106.045 N
2.4
To find F1, F2, Fi
From Eq 17-22
d = 2.957
F =
F1 Fc
From Eq 17-19
F2 Fc
60
Hd
n1 d Nb
= 77.507 N
= exp 0.5123 d
From Eq 17-24
F2 = F1 F
Initial tension,
F1 + F2
Fi =
Fc = 60.593 N
2
Torque,
Hence ,
T =
30Hd
n1
= 12.014 N m
F1 = 205.392 N F2 = 127.884 N Fi = 60.593 N
Fc = 106.045 N
[Pg 4 / 4]
Belt Q17-17 v4 V-Belt.xmcd
From Table 17-16,
Kb = 65.0
From pg 883, belt tension induced flexural stress, Fb
At small sheave,
At larger sheave,
Equivalent belt tensions,
Fb1 =
Fb2 =
Kb
= 419.355
d
Kb
= 216.667
T1 = F1 + Fb1 = 624.746 N
T2 = F1 + Fb2 = 422.058 N
From pg 884, Table 17-17, find K and b:
From Eq 17-27
Np =
K = 5309
1
K
T
1
K
+
T2
9
Np = 14.05 10
9
If Np > 10
t =
b = 10.926
N p Lp
3600V
number of passes.
9
then Np = 10 number of passes
= 25338.924
(hrs)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Lecture Note - Refrigeration CycleDocument35 pagesLecture Note - Refrigeration CycleSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution BoltDocument5 pagesSolution BoltSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial - ICEDocument4 pagesTutorial - ICESuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial - Gas Turbine CyclesDocument3 pagesTutorial - Gas Turbine CyclesSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- UTM SME3523 Components Design Test 2 QuestionsDocument2 pagesUTM SME3523 Components Design Test 2 QuestionsSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 2 - Solution - Q1 - Angular Contact Ball BearingDocument3 pagesTest 2 - Solution - Q1 - Angular Contact Ball BearingSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- skmm3023 Test2 20140520 v1Document1 pageskmm3023 Test2 20140520 v1Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note - Steam CycleDocument37 pagesLecture Note - Steam CycleSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument66 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1 q1 StaticDocument4 pagesTest 1 q1 StaticSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Outlining Method of Ps OrganizationDocument9 pagesOutlining Method of Ps OrganizationSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Test 2 20122013 1 BearingDocument1 pageSoalan Test 2 20122013 1 BearingSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Sampling: by Using Robot (Drone)Document10 pagesWater Sampling: by Using Robot (Drone)Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Speaking Outline ExampleDocument3 pagesPublic Speaking Outline ExampleSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution VBeltDocument3 pagesSolution VBeltSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution GearDocument4 pagesSolution GearSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 10 BeltsDocument24 pagesSlide 10 BeltsSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Test 1 20122013 2Document3 pagesSoalan Test 1 20122013 2Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 8 GearsDocument15 pagesSlide 8 GearsSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Analysis - Sample 2 v5Document4 pagesGear Analysis - Sample 2 v5Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution BearingDocument3 pagesSolution BearingSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Test 1 20122013 1 StaticDocument2 pagesSoalan Test 1 20122013 1 StaticSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- BearingProblem 11 31Document3 pagesBearingProblem 11 31Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing Selection - Bearing Sample 2A V2Document3 pagesBearing Selection - Bearing Sample 2A V2Suchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Perdanahandbook 20132014 NewDocument133 pagesPerdanahandbook 20132014 NewSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration System Performance TestDocument2 pagesRefrigeration System Performance TestSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Perdanahandbook 20132014 NewDocument133 pagesPerdanahandbook 20132014 NewSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis ListDocument7 pagesThesis ListSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Perdanahandbook 20132014 NewDocument133 pagesPerdanahandbook 20132014 NewSuchi Suchi SuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Pile Cap For 1 PilesDocument5 pagesPile Cap For 1 Pileshemantkle2u80% (5)
- Algorithms For Data Science: CSOR W4246Document58 pagesAlgorithms For Data Science: CSOR W4246EarthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course 1 Anchor Instalation inDocument39 pagesCourse 1 Anchor Instalation inViktorMarkuletsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tackling The Universal Journal (ACDOCA) Data Challenge: White Paper (RUN Phase)Document22 pagesTackling The Universal Journal (ACDOCA) Data Challenge: White Paper (RUN Phase)Ramesh MariyappaPas encore d'évaluation
- MC74HC589A 8-Bit Serial or Parallel-Input/Serial-Output Shift Register With 3-State OutputDocument12 pagesMC74HC589A 8-Bit Serial or Parallel-Input/Serial-Output Shift Register With 3-State OutputViviana AlbornozPas encore d'évaluation
- BPJ Lesson 18Document4 pagesBPJ Lesson 18api-308024418Pas encore d'évaluation
- PMU-Based Fast Sub-synchronous Oscillation DetectionDocument7 pagesPMU-Based Fast Sub-synchronous Oscillation DetectionDaniel Germán RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- DS2100 Standard EU ENDocument31 pagesDS2100 Standard EU ENsundaygboroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit ToolsDocument4 pagesLab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit ToolsAlvaro Avila QuirosPas encore d'évaluation
- JmeterDocument21 pagesJmetervenkatd24Pas encore d'évaluation
- AEP StudyGuide MediaPlanning PDF Inline DownloadDocument68 pagesAEP StudyGuide MediaPlanning PDF Inline DownloadRayan Mirza100% (1)
- CBSE Board Problems: A Concise Guide to Electronics and Logic CircuitsDocument4 pagesCBSE Board Problems: A Concise Guide to Electronics and Logic CircuitsBee PPas encore d'évaluation
- New Concept Note SEA Creative Camp For SE As (Update 240919)Document11 pagesNew Concept Note SEA Creative Camp For SE As (Update 240919)Winda Putri Dea lestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Name:-Sastik Kumar Das: Pps Lab - 5Document17 pagesName:-Sastik Kumar Das: Pps Lab - 5Aparannha RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithm Design and Analysis (CS60007) Assignment 1: 1 Interval SchedulingDocument6 pagesAlgorithm Design and Analysis (CS60007) Assignment 1: 1 Interval SchedulingBraj SehraPas encore d'évaluation
- KC30403 Lecture 3: Mathematical Modeling Laplace TransformDocument10 pagesKC30403 Lecture 3: Mathematical Modeling Laplace TransformDebrah DebbiePas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Grading System For Teachers and StudentsDocument2 pagesAutomated Grading System For Teachers and StudentsAnone Anone0% (1)
- BIS-EM-580-315 - EN (Biskra, Jijel H2 Plant Manual) )Document149 pagesBIS-EM-580-315 - EN (Biskra, Jijel H2 Plant Manual) )zakarianoui35Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chat GPT FileDocument5 pagesChat GPT Filejagan venkatPas encore d'évaluation
- CFC 09Document30 pagesCFC 09jesuz_mtz26Pas encore d'évaluation
- SS - 25!30!20 - 25 External Doorset System - Alumil S67 Hinged SystemDocument2 pagesSS - 25!30!20 - 25 External Doorset System - Alumil S67 Hinged SystemAhmad ManasraPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Gas Metering SystemsDocument16 pagesNatural Gas Metering Systemssina giahkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Genelec Catálogo de SoportesDocument24 pagesGenelec Catálogo de SoportesGurvan LandreinPas encore d'évaluation
- YG1ENMXMILLDocument2 pagesYG1ENMXMILLKING Rooster PlayPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital - Drilling - IntlSOS - Welcome - Handout - Mar2020 (2) V2Document2 pagesCapital - Drilling - IntlSOS - Welcome - Handout - Mar2020 (2) V2Nelson RichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet 6ES7331-7KF02-0AB0: Supply VoltageDocument5 pagesData Sheet 6ES7331-7KF02-0AB0: Supply VoltageCatalin OnofrencoPas encore d'évaluation
- Living in The IT Era ModuleDocument97 pagesLiving in The IT Era ModuleChai-chai Cortez CalunodPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - AssignmentDocument4 pagesEee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - AssignmentchaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 64148069036e353d2c4d1930 - Weekly Timesheet Template - My HoursDocument9 pages64148069036e353d2c4d1930 - Weekly Timesheet Template - My Hoursoces1551Pas encore d'évaluation
- iOS Forensics For InvestigatorsDocument317 pagesiOS Forensics For Investigatorsb-elhadjhotmail.fr100% (1)