Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Julius Caesar Francia BS-N4A
Transféré par
pauchanmnlTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Julius Caesar Francia BS-N4A
Transféré par
pauchanmnlDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
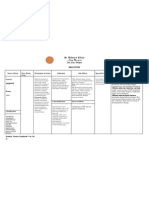
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Verapamil HCL
Verapamil inhibits
entry of calcium ions
into arterial smooth
muscle cells as well as
the myocytes and
conducting tissue.
These actions lead to
reversal and
preventions of
coronary artery spasm,
reduction in afterload
through peripheral
vasodilatation and
reduction in ventricular
rate in patients with
chronic atrial flutter or
fibrillation and
reduction in the
occurrence of
paroxysmal
supraventricular
tachycardia
Angina pectoris due to
coronary artery spasm
(Prinzmetals variant
angina)
Effort-associated angina
Chronic stable angina
Unstable, crescendo,
preinfarction angina
Essential hypertension
Parenteral: Treatment of
supraventricular
tachyarrhythmias
Parenteral: Temporary
control of rapid ventricular
rate in atrial flutter or
atrial fibrillation
Calcium channelblocker
Antianginal
Antiarrhythmic
Antihypertensive
Pregnancy
Category C
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
Cardiogenic shock,
severe bradycardia,
severe left ventricular
dysfunction,
uncompensatedheart
failure, hypotension
(systolic pressure
fast, slow, or
irregular
heartbeats;
shortness of
breath (even with
mild exertion),
swelling, rapid
weight gain;
a light-headed
feeling, like you
might pass out;
anxiety,
sweating, pale skin,
wheezing, gasping
for breath, cough
with foamy mucus,
chest pain;
flu symptoms
(fever, chills, body
aches, vomiting,
diarrhea); or
feeling like
you might pass out.
constipation;
headache;
dizziness; or
stuffy nose,
sinus pain, sore
throat.
Nursing
Responsibilities
Ensure that
patient swallows
SR tablets
whole; patient
should not cut,
crush, or chew
them.
Monitor BP very
carefully with
concurrent
doses of
antihypertensiv
es.
Monitor cardiac
rhythm regularly
during
stabilization of
dosage and
periodically
during longterm therapy.
Administer SR
form in the
morning with
food to
decrease GI
upset.
Protect IV
solution from
light.
Monitor patients
with renal or
hepatic
impairment.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Norepinephrine
Stimulates alphareceptors in arterial
Restoration of
BP in certain
Hypovolemic states,
except temporarily until
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
Nursing
Responsibilities
Hypotension;
Advise
patient to notify
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Vasopressor
Onset
Onset of IV
norepinephrine is
rapid.
Duration
Duration of
norepinephrine is
1 to 2 min
(discontinuation
of IV).
and venous beds and
beta1 receptors of
heart, resulting in
peripheral
vasoconstriction and
stimulation of heart
rate and contractility.
Coronary vasodilation
occurs secondary to
enhanced myocardial
contractility.
acute
hypotensive
states; adjunct
in treatment of
cardiac arrest
and profound
hypotension.
blood volume
replacement is
accomplished;
mesenteric or peripheral
vascular thrombosis,
unless essential;
generally contraindicated
during cyclopropane and
halothane anesthesia;
profound hypoxia or
hypercarbia.
increased peripheral
vascular resistance;
decreased carbon
monoxide; precordial
pain; ventricular
arrhythmias; reflex
bradycardia.
Headache;
dizziness; tremor;
insomnia; anxiety.
Metabolic acidosis;
hyperglycemia.
Respiratory
difficulties.
Gangrene (when
infused into small
vein); thyroid
enlargement;
irritation from
extravasation;
decreased urinary
output.
nurse if IV site
feels cool or
painful.
Instruct
patient to report
the following
symptoms to
health care
provider:
dizziness,
nausea, syncope,
abdominal pain,
chest pain or
confusion.
Caution
patient to avoid
sudden position
changes to
prevent
orthostatic
hypotension.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Isosorbide
Dinitrate
Isordil relaxes
vascular smooth
muscle with a
resultant
decrease in
venous return
and decrease in
arterial BP,
which reduces
left ventricular
workload and
decreases
myocardial
oxygen
consumption.
Antianginal
Nitrate
Vasodilator
Pregnancy
Category C
Indication
Dinitrate:
Treatment and
prevention of
angina pectoris
Mononitrate:
Prevention of
angina pectoris
Unlabeled use
(dinitrate):
Used
with hydralazine in
patients with
advanced CHF
Contraindication
Contraindicated
with allergy
to nitrates, severe
anemia, head
trauma, cerebral
hemorrhage,
hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy,
narrow-angle
glaucoma, postural
hypotension
Use cautiously
with pregnancy,
lactation, acute MI,
CHF.
Side Effects/ Adverse Effects
CNS: Headache,
apprehension,
restlessness,
weakness, vertigo,
dizziness, faintness
CV: Tachycardia,
retrosternal
discomfort,
palpitations,
hypotension,
syncope, collapse,
orthostatic
hypotension, angina,
rebound
hypertension, atrial
fibrillation, postural
hypertension
Dermatologic: Rash,
exfoliative dermatitis,
cutaneous
vasodilation with
flushing
GI: Nausea, vomiting,
incontinence of urine
and feces, abdominal
pain, diarrhea
GU: Dysuria,
impotence, urinary
frequency
Other: Muscle
twitching, pallor,
perspiration, cold
sweat, arthralgia,
bronchitis
Nursing
Responsibilities
Give sublingual
preparations
under the tongue
or in the buccal
pouch;
discourage the
patient from
swallowing.
Create a nitratefree period to
minimize
tolerance.
Give chewable
tablets slowly,
only 5 mg
initially, because
severe
hypotension can
occur; ensure
that patient does
not chew or
crush sustainedrelease
preparations.Giv
e oral
preparations on
an empty
stomach, 1 hr
before or 2 hr
after meals
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Citicholine
Citicoline
increases blood
flow and O2
consumption in
the brain. It is
also involved in
the biosynthesis
action.
Citicoline is indicated
in CVD in acute
recovery phase in
severe s/sx of
cerebrovascular
insufficiency and incranial traumatism and
their sequellae.
Citicoline in CVA,
stimulates brain
function.
Zynapse,
Somazina,
Cholinerv
CNS
Stimulant
Nootropics
Contraindication
Any allergy or
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
hypersensitivity to the
Fleeting and
Nursing Responsibilities
discrete
drug
hypotension
Hypertonia of the
effect, increased
parasympathetic nervous
parasympatheti
system
prescribed
blood pressure
Take Citicoline on
time
c effects, low
Use cautiously for
Take Citicoline as
Monitor patients
neurologic status
Note if there are
Itching or hives,
signs of slurring
Conscious use for patient
swelling in face
of speech
with renal and hepatic
or hands, chest
pregnancy and lactation
damage
tightness,
tingling in mouth
Note for adverse
reactions
and throat
Titer medication
when
discontinuing
Teach patient on
how to take the
drug
Arrange for
regular follow-ups
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Calcium
Gluconate
Calcium Gluconate
acts like digitalis on the
heart, increasing
cardiac muscle tone
and force of systolic
contractions(positive
inotropic effect)Rapidly
and effectively restores
serum calcium levels in
acute hypocalcemia
of various origins; also
effective as a cardiac
stabilizer under
conditions of
hyperkalemia or
resuscitation.
Negative calcium
balance (As in
neonatal tetany,
hypoparathyroidism,
vitamin D deficiency,
alkalosis). Also to
overcome cardiac
toxicity
of hyperkalemia,
for cardiopulmonary
resuscitation,
to prevent
hypocalcemia during
transfusion of
citrated blood. Also
as antidote for
magnesium sulfate,
for acute symptoms
of lead colic, to
decrease capillary
permeability in
sensitivity reactions,
and to relieve
muscle cramps from
insect bites or stings.
Oral calcium may be
used to maintain
normal calcium
balance during
pregnancy, lactation,
and childhood
growthand to prevent
Ventricular fibrillation,
metastatic bone disease,
injection into myocardium;
renal calculi,
hypercalcemia, predispositio
n to hypercalcemia
(hyperparathyroidism, certain
malignancies);digitalis
toxicity.
Calgonate
Electrolyte
and Water
Balance
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effetcs
Nursing
Responsibilities
Tingling sensation With
rapid IV, sensations of
heatwaves (peripheral
vasodilation),fainting.
Assess for
cutaneous burning
sensations
and peripheral
vasodilation with
moderate fall in BP,
during direct IV
injection.
Monitor ECG during
IV administration to
detect evidence
of hypercalcemia:
decreased QT
interval associated
with inverted T-wave.
Lab tests: determine
levels of calcium
and phosphorus and
magnesium
frequently, during
sustained therapy.
Deficiencies and
other ions, particularly
magnesium,
frequently coexist
with calcium ion
depletion
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
primary osteoporosis
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
Nursing
Responsibilities
Epinephrine
Naturally occurring
catecholamine obtained
from animal adrenal
glands; also prepared
synthetically. Acts
directly on both alpha
and beta receptors; the
most potent activator
of alpha receptors.
Strengthens myocardial
contraction; increasin
g systolic but may
decrease diastolic
blood pressure;
increases cardiac rate
and cardiac output.
Temporary relief of
bronchospasm, acute
asthmatic attack,
mucosal congestion,
hypersensitivity and
anaphylactic reactions,
syncope due to heart
block or carotid sinus
hypersensitivity, and to
restore cardiac rhythm
in cardiac arrest.
Ophthalmic preparatio
n is used in
management
of simple (open-angle)
glaucoma, generally
as an adjunct to
topical miotics and
oral carbonic
anhydrase inhibitors;
also used
asophthalmic
decongestant.
Relaxes myometrium
and inhibits
uterinecontractions
There are no absolute
contraindications to use
in a life-threatening
situation. Narrow-angle
glaucoma; shock
(nonanaphylactic);
during general
anesthesia with
halogenated
hydrocarbons or
cyclopropane;
individuals with organic
brain damage; local
anesthesia of certain
areas (eg, fingers,
toes); use during labor;
use in cardiac dilation
and coronary
insufficiency; situations
in which vasopressor
drugs may be
contraindicated (eg,
diabetes, hypertension
and other CV disorders,
obstetrics when
maternal BP is in
excess of 130/80, in
thyrotoxicosis);
hypersensitivity to
sympathomimetic
amines.
Nasal burning or stinging, dryness
of nasal mucosa, sneezing,
rebound congestion. Transient
stinging or burning of eyes,
lacrimation, browache,
headache, rebound conjunctival
hyperemia, allergy, iritis;
with prolonged use: melanin-like
deposits on lids, conjunctiva,
and cornea; corneal edema; loss
of lashes
(reversible);maculopathy with
central scotoma in aphakic
patients(reversible).
Monitor BP, pulse,
respirations, and urinary
output and observe patient
closely following IV
administration. Epinephrine
may widen pulse pressure.
If disturbances in cardiac
rhythm occur, with hold
epinephrine and notify
physician immediately.
Autonomic
nervoussystem
agent
alpha and beta
adrenergic
agonist
bronchodilator
Keep physician informed of
any changes in intake-output
ratio.
Use cardiac monitor with
patients receiving
epinephrine IV. Have full
crash cart immediately
available.
Check BP repeatedly when
epinephrine is administered
IV during first 5 min,
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
Nursing
Responsibilities
Heparin
Heparin increases the
inhibitory action of
antithrombin III (AT III)
on clotting factors XIIa,
XIa, IXa, Xa and
thrombin. This inhibits
the conversion of
prothrombin to
thrombin and
fibrinogen to fibrin. It
also inhibits platelet
function. It may reduce
the activity of ATIII at
very high doses.
Prevention and
treatment of venous
thrombosis and
pulmonary embolism
Treatment of atrial
fibrillation with
embolization
Diagnosis and
treatment of DIC
Prevention of
clotting in blood
samples and heparin
lock sets and during
dialysis procedures
Unlabeled
uses: Adjunct in
therapy of coronary
occlusion with acute
MI, prevention of left
ventricular thrombi
and CVA post-MI,
prevention of
cerebral thrombosis
in the evolving CVA
Patients predisposed to
active bleeding including
thrombocytopenia, peptic
ulcer disease,
cerebrovascular disorders,
haemorrhagic blood
disorders, bacterial
endocarditis, severe
hypertension, oesophageal
varices.
Slight fever, headache,
chills, nausea,
vomiting, constipation,
epistaxis, bruising,
slight haematuria, skin
necrosis (SC inj),
osteoporosis, alopecia.
Hypersensitivity
reactions include
urticaria, conjunctivitis,
rhinitis, asthma,
angioedema and
anaphylactic shock.
Priapism.
Potentially
Fatal: Heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia with
or without thrombosis;
bleeding
Adjust dose according to
coagulation
test
results
performed
just
before
injection (30 min before each
intermittent dose or q 46 hr
if continuous IV dose).
Therapeutic range aPTT:
1.52.5 times control.
Anticoagulant
Recent surgery at sites
where haemorrhage would
be an especial risk.
Severe renal and hepatic
impairment.
Cerebral or subarachnoid
haemorrhage, abdominal or
thoracic bleeding into
closed space, severe
traumatic bleed, hepatic,
renal, splenic or arterial
injury, severe haemostatic
defect, arterial thrombosis
with heparin-associated
thrombocytopenia.
IM admin.
Always check compatibilities
with other IV solutions.
Use heparin lock needle to
avoid repeated injections.
Give deep subcutaneous
injections; do not give
heparin by IM injection.
Do not give IM injections to
patients on heparin therapy
(heparin
predisposes to
hematoma formation).
Mix well when adding
heparin to IV infusion.
Do not add heparin to
infusion lines of other drugs,
and do not piggyback other
drugs into heparin line. If this
must be done, ensure drug
compatibility.
Provide for safety measures
(electric
razor,
soft
toothbrush) to prevent injury
from bleeding.
Check for signs of bleeding;
monitor blood tests.Alert all
health care providers of
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
heparin use.
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindic
ation
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effetcs
METFORMIN
(Insulin)
Decreases hepatic glucose
production, decreases
intestinal absorption
of glucose, and increases
peripheral uptake and utilization
of glucose.-
improve glycemic control
in clients with type
2diabetes- ExtendedRelease form used to
treat type2 diabetes as
initial therapy
Acute or
chronic
metabolic
acidosisAbnormal
hepatic
functionDehydration
and
lactationPregnancy
category B
Hypoglycemia,
diarrhea, N&V,
asthenia, flatulence,
headache, abdominal
pain/discomfort.
Fortamet,
Glucophage,
Glumetza, Riomet
Antidiabetic
Nursing
Responsibilities
Individualiz
e dosage
based on
tolerance
and
effectivenes
s.
Give with
meals
starting at a
low dose
with gradual
escalation
Inform
client that it
may cause
a metallic
taste;
should
subside.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Lidocaine
hydrochloride
Antiarrhythmic
agent
Local
anesthetic
injection
solution
Mechanism of
Action
Attenuates phase 4
diastolic
depolarization,
decreases
automaticity,
decreases action
potential duration,
and raises ventricular
fibrillation threshold;
inhibits conduction of
nerve impulses from
sensory nerves.
Indication
Acute management of
ventricular
arrhythmias; topical
anesthesia in local
skin disorders; local
anesthesia of
accessible mucous
membranes; topical
anesthesia prior to
venipuncture or
peripheral IV
cannulation; ocular
surface anesthesia
during ophthalmic
procedures.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to
amide local anesthetics;
Stokes-Adams
syndrome; WolffParkinson-White
syndrome; severe
degrees of sinoatrial,
AV, or intraventricular
block in absence of
pacemaker.
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Slow / shallow breathing,
slow/irregular
heartbeat, seizures.
New /worsening rash,
new or worsening
itching/swelling
(especially of the
face/tongue/throat),
severe dizziness, trouble
breathing.
Nursing
Responsibilities
Explain to patient that
adverse reactions related to
the CNS (eg, confusion,
convulsions, drowsiness,
paresthesias, respiratory
arrest) can occur and are a
result of CNS toxicity.
Emphasize
importance of not allowing
topical solution to come in
contact with eyes or broken
skin.
Advise patient not to
chew gum or eat food until
60 min after oral anesthetic
has been administered.
Advise patient that
drug may cause dizziness or
drowsiness and to avoid
getting out of bed or walking
without assistance.
For patients receiving
ophthalmic gel, advise them
to avoid rubbing or touching
the eye until the anesthesia
has worn off because
inadvertent damage may be
done to the anesthetized
cornea and conjunctiva.
Advise patients that
skin reactions, including
edema, erythema, and
petechiae, may occur with
the intradermal injection
system.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Sodium
Bicarbonate
Sodium
bicarbonate
raises blood
and urinary pH
by dissociation
to provide
bicarbonate
ions, which
neutralizes the
hydrogen ion
concentration. It
also neutralizes
gastric acid via
production of
carbon dioxide.
Urine
alkalinisation. To
prevent
development of
uric-acid renal
calculi in the
initial stages of
urico suric
therapy for
hyperuricaemia
in chronic gout.
(pulmonary
edema), congestive
heart failure, severe
kidney disease (e.g.,
inability to make urine),
severe liver disease
(e.g., ascites, cirrhosis),
high sodium
levels, swollen
ankles/legs/feet due to
retaining water
(peripheral edema).
low calcium levels, high
blood
pressure, heart problem
s (e.g., irregular
heartbeat), kidney
disease.
Electrolytes
Side Effects/ Adverse Effects
Metabolic alkalosis
mood changes
tiredness
shortness of breath
muscle weakness
irregular heartbeat
muscle hypertonicity
twitching,
tetany
hypernatremia
hyperosmolality
hypocalcaemia
hypokalemia
stomach cramps
flatulence
Tissue necrosis at injection
site.
Nursing
Responsibilities
Assess the
clients fluid
balance
throughout the
therapy. This
assessment
includes intake
and output, daily
weight, edema
and lung sounds.
Symptoms of
fluid overload
should be
reported such as
hypertension,
edema, difficulty
breathing or
dyspnea, rales or
crackles and
frothy sputum.
IV sites should
be observed
closely.
Extravasation
should be
avoided as tissue
irritation or
cellulitis may
occur when
taking sodium
bicarbonate.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Dopamine
(Intropin)
Stimulates beta-1
receptors in the
heart, causing more
complete and
forceful contractions
(inotropy). Also acts
on alpha receptors
(dose dependent)
and has
dopaminergic
effects.
Correction of
hemodynamic
imbalances present in
shock syndrome after
MI, trauma, endotoxic
septicemia, open heart
surgery, and renal
failure or chronic
cardiac
decompensation (eg,
CHF).
Pheochromocytoma;
uncorrected
tachyarrhythmias;
ventricular
fibrillation; allergy to
corn/corn products
(dextrose solutions).
Vasopressor
Half-life:
approximately 2
min.
Elimination:
Approximately
80% excreted in
the urine within 24
h as metabolites;
a very small
amount excreted
unchanged.
Onset:
Within 5 min.
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Duration:
Less than 10 min.
chest pain
fast, slow, or
pounding
heartbeats;
painful or
difficult
urination,
blood in your
urine;
weakness,
confusion,
swelling in
your feet or
ankles,
urinating less
than usual or
not at all;
weak or
shallow
breathing;
feeling like
you might
pass out, even
while lying
down;
burning, pain
Nursing Responsibilities
Monitor vital signs and ECG
closely throughout therapy.
Monitor I&O regularly; note
decreases in urine output.
Monitor CVP or pulmonary
wedge pressure if possible
during infusion. Note significant
changes in vital signs, ECG
changes, deterioration of
peripheral pulses, and/or cold,
mottled extremities. Closely
monitor urine flow, cardiac
output, and BP during
dopamine infusion. Acidosis,
hypercapnia, hypoxia, and
hypovolemia must be identified
and corrected prior to or
concurrent with dopamine
administration. Closely monitor
patients with a history of
occlusive vascular disease (eg,
atherosclerosis, arterial
embolism, Raynaud disease,
cold injury, diabetic endarteritis,
Buerger disease) for any
change in color or skin
temperature of the extremities.
Monitoring CVP or left
ventricular filling pressure may
be useful in detecting and
treating hypovolemia.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Amiodaron
e
Structurally related to
thyroxine. Class III
antiarrhythmic; also has
antianginal and
antiadrenergic
properties. Totally
unrelated to other
antiarrhythmics. Acts
directly on all cardiac
tissues. Prolongs
duration of action
potential and refractory
period without
significantly affecting
resting membrane
potential.
Indication
Prophylaxis and
treatment of lifethreatening
ventricular
arrhythmias and
supraventricular
arrhythmias,
particularly with
atrial fibrillation.
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
Hypersensitivity to
amiodarone, or benzyl
alcohol; cardiogenic shock,
severe sinus bradycardia,
advanced AV block unless
a pacemaker is available,
severe sinus-node
dysfunction or sick sinus
syndrome, bradycardia,
congenital or acquired QR
prolongation syndromes, or
history of torsade de
pointes; severe liver
disease, children. Safety
during pregnancy (category
D) or lactation is not
established.
G.I: Nausea,
vomiting,
constipation, loss of
appetite, anorexia
Monitor BP carefully
during infusion and slow
the infusion if significant
hypotension occurs;
bradycardia should be
treated by slowing the
infusion or discontinuing if
necessary. Monitor heart
rate and rhythm and BP
until drug response has
stabilized; report promptly
symptomatic bradycardia.
Sustained monitoring is
essential because drug
has an unusually long halflife.
CNS: loss of
coordination,
tingling/numbness of
the hands or feet,
uncontrolled
movements, vision
changes
INTEG: rash,
itching/swelling
CV: ventricular
arrhythmias,
bradycardia
Hepatic: Abnormal
liver-function tests.
RESP: Pulmonary
inflammation or
fibrosis
Monitor for S&S of:
Adverse effects,
particularly conduction
disturbances and
exacerbation of
arrhythmias, in patients
receiving concomitant
antiarrhythmic therapy
(reduce dosage of
previous agent by 3050%
several days after
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
amiodarone therapy is
started); drug-induced
hypothyroidism or
hyperthyroidism (see
Appendix F), especially
during early treatment
period; pulmonary toxicity
(progressive dyspnea,
fatigue, cough, pleuritic
pain, fever) throughout
therapy.
Lab tests: Baseline and
periodic assessments
should be made of liver,
lung, thyroid, neurologic,
and GI function. Drug may
cause thyroid function test
abnormalities in the
absence of thyroid
function impairment.
Monitor for elevations of
AST and ALT. If elevations
persist or if they are 23
times above normal
baseline readings, reduce
dosage or withdraw drug
promptly to prevent
hepatotoxicity and liver
damage.
Auscultate chest
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
periodically or when
patient complains of
respiratory symptoms.
Check for diminished
breath sounds, rales,
pleuritic friction rub;
observe breathing pattern.
Drug-induced pulmonary
function problems must be
distinguished from CHF or
pneumonia. Keep
physician informed.
Drug
Atropine
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Acts by selectively
blocking all
muscarinic
responses to
acetylcholine (ACh),
whether excitatory or
For sinus bradycardia
or asystole during CPR
or that is induced by
drugs or toxic
substances for
management of
Hypersensitivity to
belladonna alkaloids
synechial; angle-closure
glaucoma; parotitis;
obstructive uropathy, e.g.,
bladder neck obstruction
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
CV: tachycardia,
palpitation
G.I: Constipation
Nursing
Responsibilities
Monitor vital signs. HR is
a sensitive indicator of
patient's response to
atropine. Be alert to
changes in quality, rate,
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
inhibitory. Selective
depression of CNS
relieves rigidity and
tremor of
Parkinson's
syndrome.
Antisecretory action
(vagolytic effect)
suppresses
sweating,
lacrimation,
salivation, and
secretions from
nose, mouth,
pharynx, and
bronchi. Blocks
vagal impulses to
heart with resulting
decrease in AV
conduction time,
increase in heart
rate and cardiac
output, and
shortened PR
interval.
selected patients with
symptomatic sinus
bradycardia and
associated hypotension
and ventricular
irritability; for diagnosis
of sinus node
dysfunction and in
evaluation of coronary
artery disease during
atrial pacing; for
management of chronic
symptomatic sinus
node dysfunction.
caused by prostatic
hypertrophy; intestinal
atony, paralytic ileus,
obstructive diseases of GI
tract, severe ulcerative
colitis, toxic megacolon;
tachycardia secondary to
cardiac insufficiency or
thyrotoxicosis; acute
hemorrhage; myasthenia
gravis. Safety during
pregnancy (category C) or
lactation is not established.
CNS: blurred vision,
photophobia,
dizziness,
restlessness,tremor,
hallucinations,
delirium and coma
Renal: difficulty in
micturition
INTEG: skin rashes
RESP: respiratory
failure
and rhythm of HR and
respiration and to
changes in BP and
temperature.
Initial paradoxical
bradycardia following IV
atropine usually lasts
only 12 min; it most
likely occurs when IV is
administered slowly
(more than 1 min) or
when small doses (less
than 0.5 mg) are used.
Postural hypotension
occurs when patient
ambulates too soon after
parenteral administration.
Note: Frequent and
continued use of eye
preparations, as well as
overdosage, can have
systemic effects. Some
atropine deaths have
resulted from systemic
absorption following
ocular administration in
infants and children.
Monitor I&O, especially in
older adults and patients
who have had surgery
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
(drug may contribute to
urinary retention).
Palpate lower abdomen
for distension. Have
patient void before giving
atropine.
Monitor CNS status.
Older adults and
debilitated patients
sometimes manifest
drowsiness or CNS
stimulation (excitement,
agitation, confusion) with
usual doses of drug or
other belladonna
alkaloids. In addition to
dosage adjustment, side
rails and supervision of
ambulation may be
indicated.
Monitor infants, small
children, and older adults
for "atropine fever"
(hyperpyrexia due to
suppression of
perspiration and heat
loss), which increases
the risk of heatstroke.
Note: Intraocular tension
and depth of anterior
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
chamber should be
determined before and
during therapy with
ophthalmic preparations
to avoid glaucoma
attacks (ophthalmic
solutions and ointments
are available in various
strengths)
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Digitali
s
Widely used cardiac
glycoside of Digitalis
lanata. Acts by increasing
the force and velocity of
myocardial systolic
contraction (positive
inotropic effect). It also
decreases conduction
velocity through the
atrioventricular node.
Action is more prompt and
less prolonged than that
of digitalis and digitoxin.
Rapid
digitalization and
for maintenance
therapy in CHF,
atrial fibrillation,
atrial flutter,
paroxysmal
atrial
tachycardia.
Digitalis hypersensitivity,
ventricular fibrillation,
ventricular tachycardia
unless due to CHF. Full
digitalizing dose not given
if patient has received
digoxin during previous
week or if slowly excreted
cardiotonic glycoside has
been given during previous
2 wk.
CNS: visual
disturbances (blurred
or yellow vision),
headache, weakness,
dizziness, apathy,
confusion and mental
disturbances
G.I: anorexia, nausea,
vomiting and diarrhea
CV: ; atrial tachycardia
with block, AV
dissociation;
accelerated junctional
(nodal) rhythm;
Nursing Responsibilities
1. Take apical pulse for
1 full min, noting
rate, rhythm, and
quality before
administering drug.
2. Withold medication
and notify physician
if apical pulse falls
below ordered
parameters (e.g.,
<50 or 60/min in
adults and <60 or
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
unifocal or multiform
ventricular premature
contractions
(especially bigeminy or
trigeminy), ventricular
tachycardia; and
ventricular fibrillation.
70/min in children).
3. Be familiar with
patient's baseline
data (e.g., quality of
peripheral pulses,
blood pressure,
clinical symptoms,
serum electrolytes,
creatinine clearance)
as a foundation for
making
assessments.
4. Lab tests: Baseline
and periodic serum
digoxin, potassium,
magnesium, and
calcium. Draw blood
samples for
determining plasma
digoxin levels at
least 6 h after daily
dose and preferably
just before next
scheduled daily
dose.
5. Monitor for S&S of
drug toxicity: In
children, cardiac
arrhythmias are
usually reliable signs
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
of early toxicity. Early
indicators in adults
(anorexia, nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea,
visual disturbances)
are rarely initial signs
in children.
6. Monitor I&O ratio
during digitalization,
particularly in
patients with
impaired renal
function. Also
monitor for edema
daily and auscultate
chest for rales.
7. Monitor serum
digoxin levels closely
during concurrent
antibioticdigoxin
therapy, which can
precipitate toxicity
because of altered
intestinal flora.
8. Observe patients
closely when being
transferred from one
preparation (tablet,
elixir, or parenteral)
to another; when
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
tablet is replaced by
elixir potential for
toxicity increases
since 30% of drug
is absorbed
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Isupre
l
Synthetic
sympathomimetic
amine. Acts directly on
beta1-adrenergic
receptors with little or no
effect on alphaadrenoceptors. Drug
induced stimulation of
beta1-adrenergic
receptors results in
increased cardiac output
and cardiac work by
increasing strength of
contraction and, to a
slight degree, rate of
contraction of the heart.
Produces slight increase
in systolic BP and
decrease in diastolic
pressure.
Bronchodilator in
treatment of bronchial
asthma and reversible
bronchospasm
induced by anesthesia.
Also used as cardiac
stimulant in cardiac
arrest, carotid sinus
hypersensitivity,
cardiogenic and
bacteremic shock,
Adams-Stokes
syndrome, or
ventricular
arrhythmias. Used in
treatment of shock that
persists after
replacement of blood
volume.
Preexisting cardiac
arrhythmias associated
with tachycardia;
tachycardia caused by
digitalis intoxication,
central hyperexcitability,
cardiogenic shock
secondary to coronary
artery occlusion and MI;
simultaneous
administration with
epinephrine. Safe use
during pregnancy
(category C) or lactation
is not established.
CNS: Nervousness,
headache,
dizziness, nausea,
visual blurring.
CV: Tachycardia,
palpitations, angina,
Adams-Stokes
attacks,pulmonary
edema,
hypertension,
hypotension,
ventricular
arrhythmias,
tachyarrhythmias.
RESP:dyspnea.
Nursing Responsibilities
1. Check pulse before
and during IV
administration. Rate
>110 usually indicates
need to slow infusion
rate or discontinue
infusion. Consult
physician for
guidelines. Incidence
of arrhythmias is high,
particularly when drug
is administered IV to
patients with
cardiogenic shock or
ischemic heart
disease, digitalized
patients, or to those
with electrolyte
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
imbalance.
2. Note: Tolerance to
bronchodilating effect
and cardiac stimulant
effect may develop
with prolonged use.
3. Discontinue drug if
parotid swelling
occurs; has been
reported after
prolonged use.
4. Note: Once tolerance
has developed,
continued use can
result in serious
adverse effects
including rebound
bronchospasm.
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Niprid
e
Acts directly on
vascular smooth
muscle to produce
Short-term, rapid
reduction of BP in
hypertensive
Compensatory
hypertension, as in
atriovenous shunt or
CV: Bradycardia,
electrocardiographic
changes, tachycardia
Nursing Responsibilities
1. Monitor constantly to
titrate IV infusion rate to
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
peripheral vasodilation,
with consequent
marked lowering of
arterial BP, associated
with slight increase in
heart rate, mild
decrease in cardiac
output, and moderate
lowering of peripheral
vascular resistance.
crises and for
producing
controlled
hypotension
during anesthesia
to reduce
bleeding
coarctation of aorta, and
for control of hypotension
in patients with inadequate
cerebral circulation. Safety
during pregnancy
(category C) or lactation is
not established.
BP response.
INTEG: rash
ENDO:
Hypothyroidism
HEMA: Decreased
platelet aggregation
CNS: Increased
intracranial pressure.
2. Relieve adverse effects
by slowing IV rate or by
stopping drug; minimize
them by keeping patient
supine.
3. Notify physician
immediately if BP
begins to rise after drug
infusion rate is
decreased or infusion is
discontinued.
4. Monitor I&O.
5. Lab tests: Monitor blood
thiocyanate level in
patients receiving
prolonged treatment or
in patients with severe
kidney dysfunction
(levels usually are not
allowed to exceed 10
mg/dL). Determine
plasma cyanogen level
following 1 or 2 d of
therapy in patients with
impaired liver function.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
Nitroglyceri
n
Organic nitrate and
potent vasodilator that
relaxes vascular
smooth muscle by
unknown mechanism,
resulting in doserelated dilation of both
venous and arterial
blood vessels.
Promotes peripheral
pooling of blood,
reduction of peripheral
resistance, and
decreased venous
return to the heart.
Both left ventricular
preload and afterload
are reduced and
myocardial oxygen
consumption or
demand is decreased
Prophylaxis,
treatment, and
management of
angina pectoris. IV
nitroglycerin is used to
control BP in
perioperative
hypertension, CHF
associated with acute
MI; to produce
controlled hypotension
during surgical
procedures, and to
treat angina pectoris in
patients who have not
responded to nitrate or
beta-blocker therapy.
Hypersensitivity,
idiosyncrasy, or tolerance
to nitrates; severe
anemia; head trauma,
increased ICP; glaucoma
(sustained-release
forms). Also (IV
nitroglycerin):
hypotension, uncorrected
hypovolemia, constrictive
pericarditis, pericardial
tamponade; pregnancy
(category C), lactation.
CNS: Headache,
Transient
episodes of
lightheadedness,
syncope
Administer IV nitroglycerin
with extreme caution to
patients with hypotension
or hypovolemia since the IV
drug may precipitate a
severe hypotensive state.
CV: BP changes,
hypotension,
tachycardia
INTEG: contact
dermatitis
Monitor patient closely for
change in levels of
consciousness and for
dysrhythmias. IV
nitroglycerin solution
contains a substantial
amount of ethanol as
diluent. Ethanol intoxication
can develop with high
doses of IV nitroglycerin
(vomiting, lethargy, coma,
breath smells of alcohol). If
intoxication occurs, infusion
should be stopped
promptly; patient recovers
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
immediately with
discontinuation of drug
administration.
Be aware that moisture on
sublingual tissue is
required for dissolution of
sublingual tablet. However,
because chest pain
typically leads to dry
mouth, a patient may be
unresponsive to sublingual
nitroglycerin.
Assess for headaches.
Approximately 50% of all
patients experience mild to
severe headaches
following nitroglycerin.
Transient headache usually
lasts about 5 min after
sublingual administration
and seldom longer than 20
min. Assess degree of
severity and consult as
needed with physician
about analgesics and
dosage adjustment.
Supervise ambulation as
needed, especially with
older adult or debilitated
patients. Postural
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
hypotension may occur
even with small doses of
nitroglycerin. Patients may
complain of dizziness or
weakness due to postural
hypotension.
Take baseline BP and heart
rate with patient in sitting
position before initiation of
treatment with transdermal
preparations.
One hour after transdermal
(ointment or unit)
medication has been
applied, check BP and
pulse again with patient in
sitting position. Report
measurements to
physician.
Assess for and report
blurred vision or dry mouth.
Assess for and report the
following topical reactions.
Contact dermatitis from the
transdermal patch; pruritus
and erythema from the
ointment.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Procainamid
e
Amide analog of
procaine
hydrochloride with
cardiac actions
similar to those of
quinine. Class IA
antiarrhythmic agent.
Depresses
excitability of
myocardium to
electrical stimulation,
reduces conduction
velocity in atria,
ventricles, and HisPurkinje system.
Increases duration of
refractory period,
especially in the
atria.
Prophylactically to
maintain normal sinus
rhythm following
conversion of atrial
flutter or fibrillation by
other methods. Also to
prevent recurrence of
paroxysmal atrial
fibrillation and
tachycardia,
paroxysmal AV
junctional rhythm,
ventricular tachycardia,
ventricular and atrial
premature contractions.
Also cardiac
arrhythmias associated
with surgery and
anesthesia
Myasthenia gravis;
hypersensitivity to
procainamide or
procaine; blood
dyscrasias; complete
AV block, second
and third degree AV
block unassisted by
pacemaker.
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Hema:
Neutropenia,
thrombocytopenia,
or hemolytic
anemia
Integ: edema,
urticaria, pruritus,
flushing, and
maculopapular rash
G.I: Anorexia,
nausea, vomiting,
abdominal pain,
bitter taste, or
diarrhea
CNS: Dizziness or
giddiness,
weakness, mental
depression, and
psychosis with
hallucinations
Nursing Responsibilities
1. Check apical radial
pulses before each
dose during period of
adjustment to the oral
route.
2. Patients with severe
heart, liver, or kidney
disease and
hypotension are at
particular risk for
adverse effects.
3. Monitor the patient's
ECG and BP
continuously during IV
drug administration.
4. Discontinue IV drug
temporarily when (1)
arrhythmia is
interrupted, (2) severe
toxic effects are
present, (3) QRS
complex is
excessively widened
(greater than 50%),
(4) PR interval is
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
prolonged, or (5) BP
drops 15 mm Hg or
more. Obtain rhythm
strip and notify
physician.
5. Ventricular
dysrhythmias are
usually abolished
within a few minutes
after IV dose and
within an hour after
PO or IM
administration.
6. Report promptly
complaints of chest
pain, dyspnea, and
anxiety. Digitalization
may have preceded
procainamide in
patients with atrial
arrhythmias.
Cardiotonic glycosides
may induce sufficient
increase in atrial
contraction to dislodge
atrial mural emboli,
with subsequent
pulmonary embolism.
7. Therapeutic
procainamide blood
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
levels are reached in
approximately 24 h if
kidney function is
normal but are
delayed in presence
of renal impairment.
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Adverse Effects
Furosemid
e
Rapid-acting potent
sulfonamide "loop"
diuretic and
antihypertensive with
pharmacologic effects
Treatment of edema
associated with CHF,
cirrhosis of liver, and
kidney disease, including
nephrotic syndrome. May
History of
hypersensitivity to
furosemide or
sulfonamides;
increasing oliguria,
G.I:vomiting, nausea,
constipation,
diarrhea, cramping,
oral and gastric
irritation, anorexia,
Nursing
Responsibilities
Observe patients
receiving parenteral
drug carefully; closely
monitor BP and vital
signs. Sudden death
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
and uses almost
identical to those of
ethacrynic acid. Exact
mode of action not
clearly defined;
decreases renal
vascular resistance and
may increase renal
blood flow.
be used for management
of hypertension, alone or
in combination with other
antihypertensive agents,
and for treatment of
hypercalcemia. Has been
used concomitantly with
mannitol for treatment of
severe cerebral edema,
particularly in meningitis.
anuria, fluid and
electrolyte depletion
states; hepatic coma;
pregnancy (category
C), lactation.
increased liver
enzymes, jaundice,
pancreatitis
CNS: tinnitus and
hearing loss,
paresthesias, vertigo,
dizziness, headache,
blurred vision
Hema: aplastic
anemia,
thrombocytopenia,
agranulocytosis,
leukopenia, anemia
from cardiac arrest has
been reported.
Monitor for S&S of
hypokalemia.
Monitor BP during
periods of diuresis and
through period of
dosage adjustment.
Observe older adults
closely during period of
brisk diuresis. Sudden
alteration in fluid and
electrolyte balance may
precipitate significant
adverse reactions.
Report symptoms to
physician.
Lab tests: Obtain
frequent blood count,
serum and urine
electrolytes, CO2, BUN,
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
blood sugar, and uric
acid values during first
few months of therapy
and periodically
thereafter.
Monitor I&O ratio and
pattern. Report
decrease or unusual
increase in output.
Excessive diuresis can
result in dehydration
and hypovolemia,
circulatory collapse,
and hypotension.
Weigh patient daily
under standard
conditions.
Monitor urine and blood
glucose & HbA1C
closely in diabetics and
patients with
decompensated
hepatic cirrhosis. Drug
may cause
hyperglycemia.
Note: Excessive
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
dehydration is most
likely to occur in older
adults, those with
chronic cardiac disease
on prolonged salt
restriction, or those
receiving sympatholytic
agents.
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Nicardipin
e
Blocks the movement of
calcium into the smooth
muscle cells surrounding
the arteries of the body.
Since calcium promotes
contraction of muscle,
blocking calcium entry
into the muscle cells
relaxes the arterial
muscles and causes the
arteries to become
larger.
Indicated for
the short-term
treatment of
hypertension
Chronic Difficulty having a
Bowel Movement, Angina,
Severe Narrowing of the Aortic
Heart Valve, Chronic Heart
Failure, Hemorrhage in the
Brain, Brain Tissue Death from
Decrease in Blood Supply to
Area, Abnormally Low Blood
Pressure, Liver Problems,
Moderate to Severe Kidney
Impairment
Side
Effects/
Adverse
Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
CV: fast or
irregular
heartbeat,
palpitations
1. Establish baseline data
before treatment is started
including BP, pulse, and
lab values of liver and
kidney function.
Resp:
shortness of
breath
2. Monitor BP during
initiation and titration of
dosage carefully.
Hypotension with or
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
G.I: Nausea
without an increase in
heart rate may occur,
especially in patients who
are hypertensive or who
are already taking
antihypertensive
medication.
3. Avoid too rapid reduction
in either systolic or
diastolic pressure during
parenteral administration.
4. Discontinue IV infusion if
hypotension or
tachycardia develop.
5. Observe for large peak
and trough differences in
BP. Initially, measure BP
at peak effect
Drug
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/
Nursing Responsibilities
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Adverse Effects
Diphenhydramin
e
Diphenhydramine
competes with free
histamine for binding
at HA-receptor sites.
This antagonizes the
effects of histamine on
HA-receptors, leading
to a reduction of the
negative symptoms
brought on by
histamine HA-receptor
binding.
For the treatment of
symptoms
associated with
Vertigo/Meniere's
disease, nausea
and vomiting,
motion sickness
and insect bite.
Increased Pressure in
the Eye, Closed Angle
Glaucoma, Chronic
Difficulty having a
Bowel Movement, High
Blood Pressure,
Stenosing Peptic Ulcer,
Blockage of Urinary
Bladder, Enlarged
Prostate, Cannot
Empty Bladder,
Overactive Thyroid
Gland
CNS: Drowsiness,
dizziness, blurred
vision
G.I: constipation,
stomach upset,, or
dry
mouth/nose/throat
1. Monitor
cardiovascular
status especially
with pre-existing
cardiovascular
disease.
2. Monitor for adverse
effects especially in
children and the
older adult.
3. Supervise
ambulation and use
side-rails as
necessary.
Drowsiness is most
prominent during
the first few days of
therapy and often
disappears with
continued therapy.
Older adults are
especially likely to
manifest dizziness,
sedation, and
hypotension.
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Drug
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse
Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
Dobutam
Dobutamine
ine
Produces inotropic
effect by acting on beta
receptors and primarily
on myocardial alphaadrenergic receptors.
Increases cardiac
output and decreases
pulmonary wedge
pressure and total
systemic vascular
resistance with
comparatively little or
no effect on BP. Also
increases conduction
through AV node.
Inotropic support
in short-term
treatment of
adults with
cardiac
decompensation
due to depressed
myocardial
contractility
(cardiogenic
shock) resulting
from either
organic heart
disease or from
cardiac surgery.
History of hypersensitivity to
other sympathomimetic
amines, ventricular
tachycardia, idiopathic
hypertrophic subaortic
stenosis. Safe use during
pregnancy (category C),
lactation, children, or
following acute MI is not
established.
CV: hypotension
INTEG: phlebitis,
cutaneous necrosis
CNS: headache
G.I: nausea
RESP: shortness of breath
HEME: thrombocytopenia
Correct hypovolemia by
administration of appropriate
volume expanders prior to initiation
of therapy.
Monitor therapeutic effectiveness.
At any given dosage level, drug
takes 1020 min to produce peak
effects.
Monitor ECG and BP continuously
during administration.
Note: Marked increases in blood
pressure (systolic pressure is the
most likely to be affected) and heart
rate, or the appearance of
arrhythmias or other adverse
cardiac effects are usually reversed
promptly by reduction in dosage.
Observe patients with preexisting
hypertension closely for
exaggerated pressor response.
Note: Tolerance has been observed
with continuous or prolonged
infusions; adverse reactions are no
different than those seen with
shorter infusions.
Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. Urine
output and sodium excretion
generally increase because of
improved cardiac output and renal
Julius Caesar Francia
BS-N4A
perfusion.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ca ChannelDocument30 pagesCa ChannelKency DoneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIID'EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Drug Dose, Route, Freque Ncy Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageName of Drug Dose, Route, Freque Ncy Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitySherwin Mike QuijotePas encore d'évaluation
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleErickson Caisido GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineMuhammad ArsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsRebecca JoliePas encore d'évaluation
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Effects: AmlodipineDocument8 pagesSide Effects: AmlodipineRobPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart DrugsDocument10 pagesHeart DrugsVanessa FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocument28 pagesAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglintePas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument113 pagesDrugsCARE CATH LABPas encore d'évaluation
- Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesVerapamil HydrochlorideAndrea Huecas TriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilties Patient TeachingDocument1 pageDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilties Patient TeachingLesValenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternDocument12 pagesAntiplatelet Drugs: Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternThomas EipePas encore d'évaluation
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study ICUDocument15 pagesDrug Study ICUJulie Nambatac100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemRegineCuasSulibPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency DrugsDocument21 pagesEmergency DrugsdrsabuegPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Cardio DrugsDocument68 pagesCardio DrugsIconMaicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study For TetanusDocument10 pagesDrug Study For TetanusMei PayumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTrojangBaboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiotonic DrugsDocument67 pagesCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- NorvascDocument1 pageNorvascIsabel Barredo Del MundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meePas encore d'évaluation
- Antianginal & Vasodilating Drugs: Mrs. Davis, MSN/RN 2020Document32 pagesAntianginal & Vasodilating Drugs: Mrs. Davis, MSN/RN 2020HannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalPas encore d'évaluation
- عرض تقديمي2Document18 pagesعرض تقديمي2Sabrina ShalhoutPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of HemodialysisDocument34 pagesComplications of HemodialysisElza GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- VerapamilDocument1 pageVerapamilStephanie PePas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name Brand Name Classificati ON Dosage/ Route Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument3 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classificati ON Dosage/ Route Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationPrincess Gutierrez RositaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kalium Durule Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKalium Durule Drug StudyJustine Garcia100% (1)
- Jerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameDocument4 pagesJerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameSherlyn KirisakiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Drug Study On EpinephrineDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On EpinephrineMaesy Garcia LorenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- EpinephrineDocument2 pagesEpinephrineAlyssa Jade SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- U World Cardiac FinalDocument15 pagesU World Cardiac FinalAcohCChaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs For The Cardiovascular SystemDocument91 pagesDrugs For The Cardiovascular SystemNeisha Halil VillarealPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationArvan SebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabePas encore d'évaluation
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Anime RecommendationsDocument8 pagesAnime Recommendationspauchanmnl100% (1)
- Stardew Valley Community Center ChecklistDocument7 pagesStardew Valley Community Center Checklistpauchanmnl100% (2)
- Sparkle - Kimi No Na WaDocument1 pageSparkle - Kimi No Na WapauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist For Technical CommitteeDocument2 pagesChecklist For Technical CommitteepauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass SongsDocument3 pagesMass SongspauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Insights and Journal - CHANDocument7 pagesInsights and Journal - CHANpauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Competency Appraisal II Respiratory ExamDocument5 pagesCompetency Appraisal II Respiratory ExampauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Handoff: Kurt A. Patton, MS, RPHDocument18 pagesHandoff: Kurt A. Patton, MS, RPHpauchanmnl100% (1)
- Aira Tuliao RationaleDocument1 pageAira Tuliao RationalepauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Stanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionDocument2 pagesStanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionpauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- National Patient Safety Goals Effective January 1, 2015: Hospital Accreditation ProgramDocument17 pagesNational Patient Safety Goals Effective January 1, 2015: Hospital Accreditation ProgrampauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress NotesDocument2 pagesProgress NotespauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- SbarDocument2 pagesSbarpauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- QA Daily Report (Septmeber 9, 2016)Document2 pagesQA Daily Report (Septmeber 9, 2016)pauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Competencies For CliniciansDocument7 pagesCommunication Competencies For ClinicianspauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Stanfield's Supplement StackDocument8 pagesDR Stanfield's Supplement StackKuku KPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Attitude and Practice Outcomes PDFDocument8 pagesKnowledge Attitude and Practice Outcomes PDFGhada ElhassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument18 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndromeshalika42598Pas encore d'évaluation
- Caroline M. Apovian - Body Weight Considerations in The Management of Type 2 DiabetesDocument15 pagesCaroline M. Apovian - Body Weight Considerations in The Management of Type 2 DiabetesFarid RakhmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLyhPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissecting The Interaction Between COVID-19 and Diabetes MellitusDocument11 pagesDissecting The Interaction Between COVID-19 and Diabetes MellitusmehakPas encore d'évaluation
- Loliondo Technical ReportDocument23 pagesLoliondo Technical ReportEvarist ChahaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Anti Diabetic (OAD) : Indwiani Astuti Dept Pharmacology & Therapy Fac of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument34 pagesOral Anti Diabetic (OAD) : Indwiani Astuti Dept Pharmacology & Therapy Fac of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadakikiaprilianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof. Gus Dekker Tox Talks PDFDocument125 pagesProf. Gus Dekker Tox Talks PDFDarameutia obgynPas encore d'évaluation
- Tirzepatide Significantly Reduced A1C and Body Weight in People With Type 2 Diabetes in Two Phase 3 Trials From Lilly's SURPASS ProgramDocument4 pagesTirzepatide Significantly Reduced A1C and Body Weight in People With Type 2 Diabetes in Two Phase 3 Trials From Lilly's SURPASS ProgramJOSÉ CARLOS ÁLVAREZ PAYARESPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Che Writing Correction Oet General NoteDocument139 pagesDR Che Writing Correction Oet General NoteNitesh GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Assignment - Nutrition Assessment and AnalysisDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Assignment - Nutrition Assessment and Analysisoliviachappell13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metformin's Impact On Statin-Associated Muscle SymptomsDocument15 pagesMetformin's Impact On Statin-Associated Muscle SymptomsfromneptunePas encore d'évaluation
- GLIMITAB M-1/GLIMITAB M-2 Tablets: CompositionDocument6 pagesGLIMITAB M-1/GLIMITAB M-2 Tablets: Compositiongaurav7augPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Vildagliptin in Pharmacutical Dosage FormDocument6 pagesA Review On Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Vildagliptin in Pharmacutical Dosage FormEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment With Glp1 Receptor Agonists 2018Document45 pagesTreatment With Glp1 Receptor Agonists 2018فرح الاحمدPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovario Poliquístico/Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDocument14 pagesOvario Poliquístico/Polycystic Ovary SyndromeJosé María Lauricella100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus Treatment ProtocolDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Treatment ProtocolPuja Zarkar100% (1)
- The Following Are Examples of The Audit Criteria For Type 2 Diabetes Recommended by The National Institute For Health and Clinical ExcellenceDocument2 pagesThe Following Are Examples of The Audit Criteria For Type 2 Diabetes Recommended by The National Institute For Health and Clinical ExcellenceHassan Abdullah AL-balushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacodynamics, Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter Type 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors For The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument27 pagesPharmacodynamics, Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter Type 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors For The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes MellituskoolaberPas encore d'évaluation
- METFORMIN - Should Metformin Remain The First-Line Therapy For Treatment of Type 2 DiabetesDocument13 pagesMETFORMIN - Should Metformin Remain The First-Line Therapy For Treatment of Type 2 Diabetessoso jaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Macrosomia ArtDocument14 pagesFetal Macrosomia Artanyka2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced PH Analysis Practical Lab3 MetforminDocument2 pagesAdvanced PH Analysis Practical Lab3 Metforminknowlegebook6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Hyperglycaemia in People With DKD - Final DraftDocument90 pagesManaging Hyperglycaemia in People With DKD - Final DraftRiched LhynePas encore d'évaluation
- Pancreatic Hormones and Anti-Diabetic Drugs: Rosemarie Josue-Dominguez, MDDocument39 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Anti-Diabetic Drugs: Rosemarie Josue-Dominguez, MDJohanna Lindsay CapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific American March 2018Document80 pagesScientific American March 2018faffs100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document19 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1shamma shahulhameedPas encore d'évaluation
- (Req-172) Ficha Tecnica Pavs 2022 PDFDocument10 pages(Req-172) Ficha Tecnica Pavs 2022 PDFJOSUE YALEPas encore d'évaluation
- CARTEProstate Cancer Detection Using A Noninvasive Method For Quantifying miRNAs PDFDocument263 pagesCARTEProstate Cancer Detection Using A Noninvasive Method For Quantifying miRNAs PDFIuliana Florea100% (1)