Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Control System Engineering EC6405 Unit I-Cont Rol Syste M Mod Elin G Part A
Transféré par
Sivaprakasam KarthikeyanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Control System Engineering EC6405 Unit I-Cont Rol Syste M Mod Elin G Part A
Transféré par
Sivaprakasam KarthikeyanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
SUBJECT NAME: Control System Engineering
YEAR/SEM: II/IV
SUBJECT CODE: EC6405
UNIT I- CONTROL SYSTEM MODELING
PART A
1.
2.
3.
4.
Give the comparison between open loop and closed loop system. Nov/Dec.2010&Nov/Dec 2014
Define transfer function of the system. Nov/Dec.2010
Define open loop and closed loop system. Apr/May2011
Write down the transfer function of system whose block diagram is shown
below.Apr/May2011&Nov/Dec 2012
5. What are the advantages of the closed loop control system? May/June 2012& Nov/Dec - 2012
6. What are the prosperities of signal flow graphs? May/June 2012
7. Name any two dynamic models used to represent control systems.May/June 2013
8. Write the masons gain formula of signal flow graph.May/June 2013&May/June 2014&Nov/Dec 2014
9. Define transfer function. Nov/Dec 2013
10. What are the characteristics of negative feedback? May/June 2014
11. What is meant by a system?
12. What is a command input?
13. What is an actuating signal?
14. Define manually controlled systems?
15. Give the important characteristics of open loop control system.
16. Why most of the systems are non-linear in nature?
17. Mention the basic elements of closed loop system
18. What is translational system?
19. Define torque & friction?
20. Give the other names for force voltage analogy, force current analogy
21. List the advantages of block diagram.
22. Define chain node
23. Give the properties of signal flow graph?
24. What do you mean by a node in signal flow graph?
25. List the advantages and disadvantages of feedback systems.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
PART B
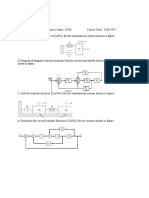
1. Reduce the block diagram to its canonical form and obtain C(s) R(s).(10) Nov/Dec 2010
2. Using Masons gain formula, find C/R of the signal flow graph shown in figure (8) Nov/Dec2010
3. Give the comparison between block diagram and signal flow graph (6) Nov/Dec 2010
4. Obtain C(S)|R(S) using block diagram reduction rules.(8) May/June 2012
5. Write differential equations governing the mechanical rotational system shown in figure below
Draw the torque voltage and torque current electrical analogous circuits and verify by writing mesh and
node equations (16) May/June 2012
6. Construct the signal flow graph for the following set of simultaneous equations.
and obtain the overall transfer function using Masons gain formula.(8) May/June 2012
7. State Masons gain formula using Masons gain formula to find .(16) Nov/Dec 2013
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
8. Use Masons gain formula to obtain C(s)/R(s) of the system shown below. (16) Nov/Dec 2013
9. Give the step by step procedure of determining transfer function using signal flow graph (8) May/June
2013
10. Write the differential equations governing the mechanical system. Draw the force-voltage and force
current electrical analogous circuits and verify by writing mesh and node equations.(8) May/June
2013&Nov/Dec 2014
11. Determine the transfer function Y2(S)/F(S) of the system shown in fig. (16)Nov/Dec 2013
12. Determine the overall transfer function C(S)/R(S) for the system shown in fig.(16)May/June 2013
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
13. Obtain the closed loop transfer function C(S)/R(S) of the system whose blockdiagram is shown in fig.
(16) May/June 2012
14. Write the equations of motion ins domain. Determine the transfer function of the system(16)
15. Write the differential equations governing the mechanical rotational system. Obtain the transfer
function of the system?(16)
16. Obtain the transfer function of the lead network shown(16)
17. Derive the transfer function for Armature controlled DC servo motor (16)
18. Derive the transfer function for Field controlled DC servo motor. (16)
UNIT II TIME RESPONSE ANALYSIS
PART A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What is meant by peak overshoot?Nov/Dec 2010
What is meant by steady state error? Nov/Dec 2010
How a control system is classified depending on the value of damping? May 2011
Why derivative controller is not used in control system? May 2011& May/June 2012
What are transient and steady state response of a control system? Nov/Dec 2012
With reference to time response of a control system, define peak time. Nov/Dec 2012
List the advantages of generalized error coefficients. May/June 2012
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
8. The closed loop transfer function of a second order system is given by
. Determine
the damping ratio and natural frequency of oscillation. May/June2013
9. Give the steady state errors to a various standard inputs for type 2 system. May/June 2013
10. What are the units of Kp, Kv and Ka? Nov/Dec 2013
11. What is the effect of PI controller on the system performance? Nov/Dec2013&2014
12. What are the type 0 and type 1 system? May/June 2014
13. What is meant by rise time? May/June 2014
14. What are the various time domain specifications? Nov/Dec 2014
15. Define settling time.
16. Define peak overshoot.
17. What is time response?
18. What is transient response?
19. What is steady state response?
20. What is meant by transient period?
21. For what purpose standard test signals are used?
22. Define step signal.
23. Define ramp signal.
24. Define parabolic signal.
25. What is positional error coefficient?
26. A system is critically damped. How will the system behave, if the gain of the system is increased?
27. List the advantages of generalized error coefficients.
28. What is the effect of PD controller on the system performance?
29. What is the order of the system?
30. What is called a proportional plus integral controller?
PART-B
1. A unity feedback system is characterized by the open loop transfer function G(s) =
Determine the steady state errors for Unit step, Unit ramp and Unit acceleration Unit. Also determine
damping ratio and natural frequency of the dominant roots.Nov/Dec 2013
2. For a unity feedback control system the open loop transfer function G(S) = 10(S+2)/ S2 (S+1). Find (a)
Position, velocity and acceleration error constants.(b) The steady state error when the input is R(S)
where R(S) =3/S 2/S2 +1/3S3 (16)May/June 2012
3. The open loop transfer function of a servo system with unity feedback system is G(S) =10/ S
(0.1S+1).Evaluate the static error constants of the system. Obtain the steady state error of the system
when subjected to an input given by the polynomial r(t) = a0+a1t +a2 /2 t2 . (16)May/June 2012
4. A second order system is given by
Find its risetime, peak overshoot and settling time if
subjected to unit step input. Also calculate expression for its output response.(16)May/June 2013
5. The unit impulse response of a unit feedback control system is given by c(t) =
(t
find the open loop transfer function.(16) May/June 2013
6. A potential control system with velocity feedback is shown in fig. What is the response of the system
for unit step input? (8)May/June 2014
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
7. What are the various standard test signals? Draw the characteristic diagram and obtain the
mathematical representation of all.(8)Nov/Dec 2014
8. Calculate the following parameters for the system whose natural frequency of oscillations is 10 rad/sec
and damping factor is 0.707(8) Nov/Dec 2014
a. Delay time
b. Rise time
c. Peak overshoot
d. Settling time
9. With the block diagram explain the concepts of PI and PD compensation.(8) Nov/Dec 2014
2
10. Determine the steady state errors for the following inputs 5u(t),5tu(t),5t u(t) to a system whose open
loop transfer function is given by G(s) =
(8) Nov/Dec 2014
11. (a) Derive the expressions and draw the response of first order system for unit stepinput. (8)
(b) Draw the response of second order system for critically damped case and wheninput is unit step
12. Derive the expressions for Rise time, Peak time, and Peak overshoot.
(16)
13. Measurements conducted on a Servomechanism show the system response to be
c(t)=1+0.2 60t-1.2 10 t. when subjected to a unit step. Obtain an expression for
closed loop transfer function.
(16)
14. A unity feedback control system has an open loop transfer functionG(S) = 10/S(S+2). Find the rise
time, percentage over shoot, peak time and settlingTime.
(16)
15. A closed loop servo is represented by the differential equation, where c is thedisplacement of the output
shaft, r is the displacement of the input shaft and e= r-c.Determine undamped natural frequency, damping
ratio and percentage maximumovershoot for unit step input.
(16)
16. (a) Obtain the response of second order underdamped system with unit step input(8)
(b) Derive the response of undamped second order system for unit step input (8)
17. A second order system has 40%r peak overshoot and settling time of 2 sc for unit step input.Find
resonant peak gain and reasonant freq.(16)
18. For servomechanisms with open loop transfer function given below explain what type of input signal
give rise to a constant steady state error and calculate their values. (16)
UNIT III FREQUENCY RESPONSE ANALYSIS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
PART A
List the advantages of Nichols chart? Nov/Dec 2010.
What are the specifications used in frequency domain analysis? Nov/Dec 2010
What is meant by corner frequency in frequency response analysis? May 2011
Draw the circuit diagram of lead compensator and draw its pole zero diagram. May 2011
What is mean by corner frequency in frequency response analysis? Nov/Dec 2012.
What is Nichols chart? Nov/Dec 2012.
Draw the polar plot of G(s) =
. May/June 2012
8. State the uses of Nicholas chart. May/June 2012&Nov/Dec 2014
9. Draw the polar plot of an integral term transfer function. May/June 2013
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
10. Write the MATLAB statement to draw the bode plot of the given system. May/June 2013
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
11. Define Phase margin? Nov/Dec 2013
12. What are the constant M and N circle?Nov/Dec 2013.
13. The damping ratio and undamped natural frequency of a second order system are 0.5 and 5
respectively. Calculate the resonant frequency. May/June 2014
14. What is corner frequency? May/June 2014
15. Define Gain and Phase margin. Nov/Dec 2014
16. Define cut-off rate.
17. Define resonant peak(Mr)
18. Define gain-cross over frequency. (gc).
19. Define phase-cross over frequency. (gc)
20. How the closed loop frequency response is determined from the open loop frequencyresponse?
21. What are the M and N circles?
22. What happens to the damping ratio and rise time if the band width is increased?
23. What are the two methods of specifying the performance of control system?
24. Give the two approaches to the control system design problem.
25. What are the two situations in which compensation is required?
PART-B
1. Plot the Bode diagram for the following transfer function and obtain the gain and phase cross over
2
frequencies. G(S) =KS / (1+0.2S) (1+0.02S). Determine the value of K for a gain cross over
frequency of 5 rad/sec.(16)Nov/Dec 2010
2. The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by G(s) =
Sketch the
polar plot and determine the gain margin and phase margin. (16) Nov/Dec 2010
3. Given G(s) = K
.find K for following two cases.
a) Gain margin equal to 6 db
b) Phase margin equal to 45 . (16)May 2011&Nov/Dec 2012
4. The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system isG(s) =
. Design a
suitable Lead Lag compensator so as to meet the following specifications: Static velocity error
-1
constant
. Phase margin equal to 50 and Gain margin 10db.(16) May 2011
5. For the following transfer function G(s) =
. Sketch the bode magnitude plot by showing slope
contributions from each pole and zero. (8)May/June 2012
6. For an unity feedback system with closed loop transfer functions
derive the expressions for local
constant M circles and constant N circles. (8)May/June 2012
7. Write the procedure to obtain Nichols chart from constant M circles. (8)May/June 2012
8. Write a MATLAB program to examine stability using bode plot for the given transfer function G(s) =
.Explain the code (statements) as to what the variables and numbers mean and also what
action is caused by each statement. State also how you will interpret the result. (8)May/June 2012
9. Draw the pole zero diagram of a lead compensator. Propose lead compensation using electrical
network. Derive transfer functions and Draw the Bode plots.(16) Nov/Dec 2012
10. Consider a unity feedback open loop transfer function G(s) =
. Draw the Bode Plot and
find the phase and gain cross over frequencies, phase and gain margin and stability of the
system.(16)May/June 2013
11. Explain in detail the design procedure of lead compensator using Bode plot.(16) May/June 2013
12. Discuss in detail about lead and lag networks.(16) Nov/Dec 2013
13. For the following transfer function draw bode plot and obtain gain cross over frequency. G(s) =
www.vidyarth.i(p1l6u)s.Ncoomv/oDf e1c1.2013.
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
14. The open loop transfer function of a system is given byG(s) H(s) =
. Draw the Bode plot
and determine Gain margin and Phase margin.(16)May/June 2014
15. Sketch the polar plot of unity feedback system with open loop transfer function G(s) =
find the frequency at which
. Also
.(10) May/June 2014
16. What are the advantages and disadvantages of frequency response analysis.(6) May/June 2014
17. The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is G(S) = 1/ S (1+S)(1+2S) Sketch the Polar
plot and determine the Gain margin and Phase margin.(16)Nov/Dec 2014
18. Describe about Lead Lag compensators design procedure.(8) Nov/Dec 2014
19. Write short shorts on constant M and N circles. (8) Nov/Dec 2014
20. Write short notes on correlation between the time and frequency response? (16)
UNIT-IV STABILITY ANALYSIS
PART A
1. What is meant by BIBO stability? Nov/Dec 2010&2014
2. Using Routh criterion, determine the stability of the system represented by the characteristic
equation
Comment on the location of the roots of characteristics
equation? Nov/Dec 2010
3. State the rule for obtaining the breakaway point in root locus? May 2011
4. Define stability of the system? May 2011
5. State two limitations of Routh stability criterion? Nov/Dec 2012.
6. State the advantages of Nyquist stability criterion over that of rouths criterion? Nov/Dec 2012.
7. What is root locus?May/June 2012
8. State Nyquist stability criterion. May/June 2012&May/June 2013
9. Write the necessary and sufficient condition for the stability in routh stability criterion. May/June 2013
10. Sate the property of Lead compensator? Nov/Dec 2013
11. State Nyguist stability criterion for a closed loop system when the open loop system is stable. Nov/Dec
2013.
12. What is meant by relative stability?May/June 2014
13. Define Phase Margin? May/June 2014
14. What is meant by dominant pole?. Nov/Dec 2014
15. What are the conditions for a linear time invariant system to be stable?
16. What do you mean by asymptotic stability?
17. How the system is classified based on stability?
18. What does the positive ness of the coefficients of characteristic equation indicate?
19. State the conditions under which the coefficients can be zero or negative.
20. How the roots of characteristic equation are related to stability?
21. What is the relation between stability and coefficient of characteristic polynomial?
22. What will be the nature of impulse response when the roots of characteristic equation are lying on
imaginary axis?
23. What will be the nature of impulse response when the roots of characteristic equation are lying on right
half of the S-plane?
24. How will you find the gain K at a point on the root locus?
25. Give the effect of addition of poles on the root locus.
PART-B
1.Sketch the root locus for the open loop transfer function of unity feedback control system given below:
G(S) H(S) =K/S(S+2) (S+4). Find the value of K, so that the damping ratio of theclosed loop system is 0.5.
(16) Nov/Dec 2010&(10) May/June 2012
2.Construct the Nyquist plot for a system whose open loop transfer function is given by G(s) H(s) =
Finwdwthwe.vriadnygarethoifplKusf.coormstaobf i1l1it.y. (16) Nov/Dec 2010
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
3.Draw the Nyquist plot for the system whose open loop transfer function is G(S)H(S) =
Determine the range of K for which closed loop system is stable. (16)May 2011&May 2012
4. Using Routh criterion, determine the stability of the system represented by the characteristic equation is
6
5
4
3
2
S + 2S + 8S + 12S + 20S + 16S +16 = 0(6) May/June 2012& (16) May/June 2013&(8)Nov/Dec 2014
5.Sketch the root locus for the open loop transfer function of unity feedback control system given below:
G(S) = K/S(S+1)(S+2).Also find K of breakaway point.(8) Nov/Dec 2012
6.Determine the approximate root locus diagram for a closed loop system whose loop transfer function is
given by G(S) H(S) =
comment on the stability.(8) Nov/Dec 2012
7.Sketch the Nyquist plot for a system with open loop transfer function G(S) H(S) =
and
determine the range of K for which the system is stable.(16)Nov/Dec 12
8.Sketch the root locus of the system having G(S) =
9.Sketch the root locus for GH(S) =
(16) May/June 2013
(16) Nov/Dec 2013
10.The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by
. By
applying Routh criterion,discuss the stability of the closed loop system as a function of K.(16) Nov/Dec
2013
11.The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by
. Determine
the value of K so that the gain margin is 6dB. (8) May/June 2014
12.Using Routh criterion, determine the stability of the system represented by the characteristic equation is
4
3
2
S5 + S + 2S + 2S + 11S +10 = 0(8)May/June 2014
13. Draw the root locus plot for the system whose open loop transfer function is given by
. Find the marginal value of K which causes sustained oscillations and the
frequency of the oscillations. (16) May/June 2014
14.Draw the root locus plot for the system whose open loop transfer function is given
by
.(16) Nov/Dec 2014
15. Define Nyquist stability criterion and explain the different situations of it. (8)Nov/Dec 2014
16.The characteristic equation of a given system is
what restrictions
must be placed upon the parameter K in order to ensure the system is stable?(16)
17.The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is G(S) =
Determine
the Nyquist stability locus for the system when H(s) = (1+2S). Test the stability.(16)
UNIT-V
STATE VARIABLE ANALYSIS AND DIGITAL CONTROL SYSTEM
PART A
1. What is meant by sampling theorem? Nov/Dec 2010
2. Mention the need for state variables? Nov/Dec2010
3. Name methods of state space representation for phase variables. May 2011
4.What is meant by quantization? May 2011&May/June 2012
5. How the model matrix is determined? May/June 2012
6. Define state and state variables? Nov/Dec 2012&May/June 2013
7. What is meant by sampled data controlled system? Nov/Dec 2012
8. What are the advantages of state space representation? May/June 2013
9. Define state equation? Nov/Dec 2013
10.wGwiwve.vtihdyeacrothnipcelupst.coofmcoonf t1r1o.llability. Nov/Dec 2013
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
11. Draw the circuit diagram of sample and hold circuit. May/June 2014
12. What are the properties of State Transition matrix? May/June 2014
th
13. Define state model of n order system? Nov/Dec 2014
14. What are sampler and hold circuits? Nov/Dec 2014
15. What is the condition to be satisfied for a sampled data system to be stable?
16. What is the characteristic equation of a sampled data system?
17. List the methods used to test the stability of discrete time system.
18. Define sampled data system.
19. When a control system can be called as sampled data control system?
20. Distinguish between sampled data systems and continuous-time systems.
21. List the advantages and disadvantages of sampled data control system.
22. What are sampling and sampler?
23. What is periodic sampling?
24. What is coding?
25. What is pulse transfer function?
PART-B
1. Explain in detail the state space representation for continuous time systems. (8)Nov/Dec 2010
2.Explain in detail the state space representation for discrete time systems. (8)Nov/Dec 2010
3. Determine the state controllability and observability of the system described by
y=
. (16) Nov/Dec 2010
4.The state space representation of a system is given below
y=
Obtain the transfer function.(16)May 2011&Nov/Dec 2012
5. Obtain the state space representation of armature controlled DC motor with load, shown below:
Choose the armature current
, the angular displacement of shaft , and the speed
as output variables. (16) May/June 2012.
6. The State model matrices of a system given below:
A=
,B=
,C=
Evaluate the observability of the system using Gilberts test.(10) May/June 2012
7. Find the controllability of the system described by the following equation:
=
. (6) May/June 2012
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
as state variables and
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
8.
Determine the state controllability and observability of the system described by
y=
. (8) Nov/Dec 2012
9. Obtain the z-transfer function of the system shown below:(8) Nov/Dec 2012
10. A system is represented by the state equation
and C =
= AX+BU; Y=CX where A =
,B=
.Determine the transfer function of the system.(16)May/June
2013
11. A system is characterized by the transfer function
Identify the first state as the
output. Determine whether or not system is completely controllable and observable. (16)May/June 2013
12. For the given state variable representation of a second order system given below find the state response
for a unit step input and
by using the discrete time
approximation. (16) Nov/Dec 2013
13.Consider the system with the state equation.
. Check the
controllability of the system. (16) Nov/Dec 2013
14. Obtain the state model of the system described by the following transfer function
(8)
May/June 2014
15. Obtain the state transition matrix for the state model whose system matrix A is given by A =
(8)
May/June 2014
16.Check the controllability of the following state space system
=
, = , =
(8) May/June 2014
17. Obtain the transfer function model for the following state space system.
A=
B=
C=
D=
(8) May/June 2014
18.Test the controllability and observability of the system whose state space representation is given as
(16)Nov/Dec 2014
y=
19. A discrete system is described by the difference equation, y (k+2) +5y (k+1) +6y (yk) =u (k), y(0) =
y(1) = 0; T = 1 sec. Determine the state model in canonical form. Draw the block diagram. (12) Nov/Dec
www.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
201w4ww.vidyarthiplus.com of 11.
20. Explain sampling theorem and Sample & Hold operation briefly.(16)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 6.control System EngineeringDocument11 pages6.control System EngineeringAnonymous 1Xx4mQcqeTPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec6405 CS QB 2Document16 pagesEc6405 CS QB 2Ananth SettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Engineering Time Response and Frequency AnalysisDocument16 pagesControl System Engineering Time Response and Frequency AnalysisrameshsmePas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems PDFDocument12 pagesControl Systems PDFLakshmi Prabha100% (1)
- Control System Question BankDocument23 pagesControl System Question Bankdr mbaluPas encore d'évaluation
- 208 - EC8391, EC6405 Control System Engineering - Important QuestionsDocument7 pages208 - EC8391, EC6405 Control System Engineering - Important QuestionsSagar Babu NandigamaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSN College Aeronautical Engineering Questions BankDocument8 pagesPSN College Aeronautical Engineering Questions BankNambi RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument12 pagesKings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringLatosha FarrellPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Question BankDocument17 pagesControl System Question BankerrakeshagrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Modelling and Time Response Analysis NotesDocument12 pagesControl System Modelling and Time Response Analysis NotesSaravanan PazapughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemDocument21 pagesControl SystemGAkumari0% (1)
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Question BankDocument12 pagesKings: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Question Banks.reeganPas encore d'évaluation
- IC6501-Control Systems EngineeringDocument16 pagesIC6501-Control Systems EngineeringragupaPas encore d'évaluation
- QB BcsDocument10 pagesQB BcsKrishna Reddy Y.VPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Engineering Question BankDocument9 pagesControl Engineering Question Banksathesh waranPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IDocument18 pagesUnit ILAKSHMI SPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec6405 IV SemDocument10 pagesEc6405 IV SemKaruppu SamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems - Question BankDocument6 pagesControl Systems - Question Bankmadhu balanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece-IV-control Systems (10es43) - Question PaperDocument12 pagesEce-IV-control Systems (10es43) - Question PaperAbdul AzeezPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System (PT)Document7 pagesControl System (PT)MATHANKUMAR.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Mahalakshmi Engineering College Control Systems Question BankDocument16 pagesMahalakshmi Engineering College Control Systems Question Bankjenath1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)Document9 pagesDept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)DeepakLingamoorthyPas encore d'évaluation
- VMU Aarupadai Veedu Institute of Technology Question Bank for Control SystemsDocument10 pagesVMU Aarupadai Veedu Institute of Technology Question Bank for Control SystemsSagaraptor RexPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems IMP QUESTIONSDocument8 pagesControl Systems IMP QUESTIONSHarika HarikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec8391-Control Systems Engineering-947551245-Cse QBDocument18 pagesEc8391-Control Systems Engineering-947551245-Cse QBMr. V. Buvanesh Pandian EIE-2019-A SEC BATCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse Question Bank Part BDocument5 pagesCse Question Bank Part Bbalaji1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- MergedDocument34 pagesMergedmahamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank: Unit I Systems and Their RepresentationDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank: Unit I Systems and Their RepresentationramyakalaPas encore d'évaluation
- EC6405 Syllabus Control Systems Engineering Class III EEEDocument16 pagesEC6405 Syllabus Control Systems Engineering Class III EEEAruna ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajalakshmi Engineering College Control Systems Question BankDocument6 pagesRajalakshmi Engineering College Control Systems Question Bankbramesh_31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems Question BankDocument12 pagesControl Systems Question BankdhayasathishPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester - Iv Control System Question Bank: Unit - 1 Part-I (2 Marks)Document2 pagesSemester - Iv Control System Question Bank: Unit - 1 Part-I (2 Marks)Dina GaranPas encore d'évaluation
- CS Mod1 QBDocument10 pagesCS Mod1 QBthenithyanagrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Engineering Question BankDocument7 pagesControl System Engineering Question BankOhmsakthi Vel RPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemDocument27 pagesControl SystemMookambigai CollegePas encore d'évaluation
- Model Examination: Hindusthan Institute of Technology, CoimbatoreDocument6 pagesModel Examination: Hindusthan Institute of Technology, CoimbatoreParama GuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs ImpDocument5 pagesCs ImpLiki LikithPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE-502 Control Systems Question Bank with SolutionsDocument7 pagesEEE-502 Control Systems Question Bank with SolutionsAvinash ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE University Questions Part ADocument4 pagesCSE University Questions Part Abalaji1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- EEN 407 Sample QuestionsDocument41 pagesEEN 407 Sample QuestionsAbu SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- EC6405 CS Question Bank FULLDocument84 pagesEC6405 CS Question Bank FULLreporterrajiniPas encore d'évaluation
- EC6405-Control Systems EngineeringDocument12 pagesEC6405-Control Systems EngineeringAnonymous XhmybK0% (1)
- CS EsmDocument58 pagesCS EsmsriramrpselvamPas encore d'évaluation
- QUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFDocument12 pagesQUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFMouhanit LimbachiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- TE 2019 MechatronicsDocument6 pagesTE 2019 MechatronicsVishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechtronics QBDocument8 pagesMechtronics QBKarthik Perumal SwamyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3cs EceDocument3 pages3cs Ecekirankumar412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsvpj100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Robotics Home Assignment-1Document3 pagesRobotics Home Assignment-1Ram MPas encore d'évaluation
- IC6501 Iq PDFDocument13 pagesIC6501 Iq PDFKRISHNA VAMSIPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 1402 - Mechatronics PDFDocument6 pagesME 1402 - Mechatronics PDFnagarajancePas encore d'évaluation
- ME2401 Mechatronics QBDocument9 pagesME2401 Mechatronics QBkarthiksubramanian94Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME2401 Mechatronics QBDocument9 pagesME2401 Mechatronics QBkarthiksubramanian94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project MatlabDocument10 pagesProject MatlabAbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 1402 - Mechatronics PDFDocument6 pagesME 1402 - Mechatronics PDFHiru Purushothaman HirudayanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Techniques and Technology of Computer-Aided Feedback ControlD'EverandAdvanced Techniques and Technology of Computer-Aided Feedback ControlPas encore d'évaluation
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesD'EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlD'EverandNonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlPas encore d'évaluation
- Om Shanthi Higher Secondary School Unit Test-1 EVS I.Fill in The Missing Letters 5×1 5Document8 pagesOm Shanthi Higher Secondary School Unit Test-1 EVS I.Fill in The Missing Letters 5×1 5Sivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Transconductance AmplifiersDocument1 pageOperational Transconductance AmplifiersSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- L - G H - N B - T: Vowel SoundsDocument5 pagesL - G H - N B - T: Vowel SoundsSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceDocument27 pages8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- India Shillong GuwahatiDocument1 pageIndia Shillong GuwahatiSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Project PaperDocument6 pagesProject PaperSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- LOOSLEY CoupledDocument10 pagesLOOSLEY CoupledSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phased and Adaptive Array Antennas ExplainedDocument5 pagesPhased and Adaptive Array Antennas ExplainedSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Timer ProgrammingDocument7 pagesTimer ProgrammingSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grover Algorithm in DetailDocument60 pagesGrover Algorithm in DetailSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Flashcards PDFDocument7 pages5 Flashcards PDFSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudiesDocument8 pagesCase StudiesSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Masm Program 11Document22 pagesMasm Program 11Sivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview TechDocument3 pagesInterview TechSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Principles of CountingDocument6 pagesFundamental Principles of CountingSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Type Questions on C Programming Language FundamentalsDocument12 pagesObjective Type Questions on C Programming Language FundamentalsSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- LDFDocument11 pagesLDFSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Type Questions on C Programming Language FundamentalsDocument12 pagesObjective Type Questions on C Programming Language FundamentalsSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- ISCA2002-2Channel ss2Document10 pagesISCA2002-2Channel ss2Sivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Se Qu Ntial CK TDocument10 pagesSimulation of Se Qu Ntial CK TSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assebler DirectivesDocument4 pagesAssebler DirectivesSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- LPC2378 ProcedureDocument10 pagesLPC2378 ProcedureSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio and Proportion Important FormulasDocument2 pagesRatio and Proportion Important FormulasSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor&MicrocontrollerDocument121 pagesMicroprocessor&MicrocontrollerNhu Ngoc Phan TranPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are ZerosDocument1 pageWhat Are ZerosSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Time and Distance Using Speed FormulasDocument29 pagesCalculating Time and Distance Using Speed FormulasRahul Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- LinesDocument1 pageLinesSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- LinesDocument1 pageLinesSivaprakasam KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Forced Oscillations - Pohl's PendulumDocument5 pagesForced Oscillations - Pohl's PendulumJose GalvanPas encore d'évaluation
- LRFD-BASED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF BEARINGS IN BRIDGES 9-24-2010 Compressed PDFDocument370 pagesLRFD-BASED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF BEARINGS IN BRIDGES 9-24-2010 Compressed PDFFrancis Domingo100% (1)
- Vibration Shapes For A Plucked String.Document4 pagesVibration Shapes For A Plucked String.John AlexiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation Model of Hydro Power PlantDocument7 pagesSimulation Model of Hydro Power Plantwoldemariam workuPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock-Response-Spectrum Analysis of Sampled-Data Polynomial For Track-Seeking Control in Hard Disk DrivesDocument6 pagesShock-Response-Spectrum Analysis of Sampled-Data Polynomial For Track-Seeking Control in Hard Disk DrivesjackPas encore d'évaluation
- DYNAMICS OF PHYSICAL SYSTEMSDocument122 pagesDYNAMICS OF PHYSICAL SYSTEMSMahmoud SammyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dielectric Ceramics: Basic Principles IntroductionDocument67 pagesDielectric Ceramics: Basic Principles IntroductionRajveer FandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Vibration CH 3 Harmonically Excited SystemsDocument57 pagesMechanical Vibration CH 3 Harmonically Excited SystemsPutro Adi nugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Vibration IsolationDocument8 pagesBasics of Vibration IsolationSAiTejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Oscillations GuideDocument9 pagesPhysics Oscillations GuideMordecai ChimedzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Mcq-Automatic Control SystemsDocument21 pagesImportant Mcq-Automatic Control Systemsarijitlgsp50% (2)
- How to Pump a Swing in Different ModesDocument17 pagesHow to Pump a Swing in Different ModesVictor PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Marks QA MOMDocument11 pages2 Marks QA MOMvasanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7 OscillationDocument9 pagesModule 7 OscillationGreen BrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Fault Management in Electrical Distribution SystemsDocument41 pagesFault Management in Electrical Distribution SystemsMario MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Degrees of FreedomDocument44 pagesMultiple Degrees of FreedomShafiq Ahmed Shahbaz100% (1)
- Experimental Observation of Wing Rock Phenomenon on Delta WingDocument13 pagesExperimental Observation of Wing Rock Phenomenon on Delta WingChegrani AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Summer 2020 PHY-105 Mid-TermDocument1 pageSummer 2020 PHY-105 Mid-TermMd. Imran AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Stabilizers ABBDocument25 pagesPower System Stabilizers ABBlrpatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to seismic sensors (subject 3.2Document17 pagesIntroduction to seismic sensors (subject 3.2Dhananjai SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems 41Document10 pagesProblems 41Raoul FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Tamu Iws 1982Document461 pagesTamu Iws 1982davih007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oscillations and Simple Harmonic MotionDocument20 pagesOscillations and Simple Harmonic MotionMedal NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- ApgencoDocument10 pagesApgencoSurya RockyPas encore d'évaluation
- OscillationsDocument29 pagesOscillationsTetsuya OkazakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic MotionDocument16 pagesPeriodic MotionAngela MariePas encore d'évaluation
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Transients in RLC CircuitsDocument20 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Transients in RLC CircuitsBrendan BurrPas encore d'évaluation
- IJREI - Vibration Analysis and Response Characteristics of A Half Car Model Subjected To Different Sinusoidal Road ExcitationDocument6 pagesIJREI - Vibration Analysis and Response Characteristics of A Half Car Model Subjected To Different Sinusoidal Road ExcitationIjrei JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Detection of Structural Damage in Building Using Changes in Modal Damping Mechanism (2012) - Paper PDFDocument6 pagesDetection of Structural Damage in Building Using Changes in Modal Damping Mechanism (2012) - Paper PDFJulio Humberto Díaz RondánPas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Stage Mechanical Oscillator Generates Over-Unity EnergyDocument26 pagesTwo-Stage Mechanical Oscillator Generates Over-Unity EnergyErwin BlancoPas encore d'évaluation