Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Muscular System Test
Transféré par
api-335583184Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Muscular System Test
Transféré par
api-335583184Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Name
Progress Test
Muscular
Systems
and
Skeletal
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Multiple Choice Questions (1 Mark each)
Section 1- The muscular system
1. What are the three main functions of the muscular system?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Motion, heat production and movement
Motion, heat production and maintenance of posture
Heat production, support and blood cell production
Maintenance of posture, motion and movement
2. Where in the body is cardiac muscle found?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Lungs
Intestines
Heart
Blood vessel walls
3. Where in the body is smooth muscle found?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Blood vessel walls
Heart
Hamstrings
Quadriceps
4. Which muscle type is found in the walls of the intestines?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Cardiac
Skeletal
Smooth
All of the above
5. Which of the following muscle types has striations?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Cardiac and skeletal
Smooth and skeletal
Smooth and cardiac
All of the above
6. What is the main function of smooth muscle?
a) To contract the heart to pump blood around the body
b) To produce explosive movement of the limbs
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
c) To regulate the diameter of tubular organs and vessels in the body
d) All of the above
7. Which muscle types are controlled involuntarily?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Smooth and skeletal
Cardiac and smooth
Skeletal and smooth
All of the above
8. Which muscle type contracts in an auto-rhythmic nature?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Cardiac
Smooth
Skeletal
All of the above
9. What intensity (power) and duration (time) would occur when type I muscle
fibres contract?
a)
b)
c)
d)
High intensity and short duration
High intensity and long duration
Low intensity and short duration
Low intensity and long duration
10. What intensity (power) and duration (time) would occur when type IIb muscle
fibres contract?
a)
b)
c)
d)
High intensity and short duration
High intensity and long duration
Low intensity and short duration
Low intensity and long duration
11. An athlete running a 100m sprint will predominantly use which muscle fibre
type?
a) Type I
b) Type IIa
c) Type IIb
12. An athlete running an 800m race will predominantly use which muscle fibre
type?
a) Type I
b) Type IIa
c) Type IIb
13. An athlete performing a marathon race will predominantly use which muscle
fibre type?
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
a) Type I
b) Type IIa
c) Type IIb
14. What muscle fibre type predominantly uses fats as an energy source?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Type I
Type IIa
Type IIb
Type IIa and Type IIb
15. What colour are type I muscle fibres?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Red
White
Yellow
Blue
16. What colour are type IIb muscle fibres?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Red
White
Yellow
Blue
17. Which muscle fibre type has the greatest oxidative capacity?
a) Type I
b) Type IIa
c) Type IIb
18. The Gluteals are the largest muscles in the body.
a) True
b) False
19. When a muscle contracts and shortens it is known as what type of
contraction?
a) Concentric
b) Eccentric
c) Isometric
20. When a muscle contracts and lengthens it is known as what type of
contraction?
a) Concentric
b) Eccentric
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
c) Isometric
21. When a muscle contracts but no movement occurs it is known as what type of
contraction?
a) Concentric
b) Eccentric
c) Isometric
22. Which type of muscular contraction will occur when a gymnast holds the
position of a handstand?
a) Concentric
b) Eccentric
c) Isometric
23. Where would you find the deltoid muscle?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Foot
Hand
Leg
Shoulder
24. Where would you find the gastrocnemius muscle?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Calf
Forearm
Shoulder
Arm
25. Where would you find the tibialis anterior muscle?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Arm
Shoulder
Shin
Back
26. Which four muscles make up your quadriceps?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Semimembranosis, semitendinosis, bicep femoris and rectus femoris
Vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, bicep femoris and rectus femoris
Vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and bicep femoris
Vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and rectus femoris
27. Which three muscles make up your hamstrings?
a) Semimembranosis, semitendinosis and rectus femoris
b) Semimembranosis, semitendinosis and bicep femoris
c) Rectus femoris, bicep femoris and vastus lateralis
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
d) Bicep femoris, vastus lateralis and vastus medialis
28. What name is given to a muscle which contracts to initiate movement?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Agonist
Antagonist
Fixator
Synergist
29. What is the name given to a muscle that stabilises and controls the movement
occurring at a joint?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Agonist
Antagonist
Fixator
Synergist
30. What is the name given to a muscle which relaxes and lengthens to allow
movement to occur?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Agonist
Antagonist
Fixator
Synergist
31. What is the name given to a muscle which contracts in combination or
sequence with other muscles to produce a coordinated movement?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Agonist
Antagonist
Fixator
Synergist
32. If the biceps contract to flex the elbow which muscle will act as an
antagonist?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Biceps
Triceps
Deltoids
Pectorals
33. If the biceps contract to flex the elbow which muscle will act as a fixator?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Biceps
Triceps
Deltoids
Pectorals
34. What is the joint action of the Rectus Abdominis?
Progress Test
a)
b)
c)
d)
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Trunk Extension
Elevation
Depression
Trunk Flexion
35. What joint actions do the Hamstrings perform?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Knee Flexion
Hip Flexion
Hip Extension
All of the above
36. A muscles attachment to the more stationary bone is called the
a)
b)
c)
d)
Fixator
Origin
Insertion
Direction
37. What muscle would contract concentrically to extend the knee?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Hamstrings
Quadriceps
Gluteus maximum
Hip flexors
38. What muscle would contract concentrically to abduction the shoulder/arm?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Pectorals
Latissimus dorsi
Deltoids
Biceps
39. What muscle would contract concentrically to plantar flex the ankle?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Gastrocnemius
Tibalis anterior
Quadriceps
Hamstrings
40. What muscle would contract concentrically to extend the elbow?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Deltoids
Biceps
Triceps
Pectorals
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Section 2- The skeletal system
1.
A.
B.
C.
Place where two or more bones meet.
Joint
Marrow
Calcium
2. Which of these is NOT a job of the skeletal system?
A.
Support and give shape to the body
B.
Makes blood cells
C.
Removes wastes from the body
3. These joints are found in the knee and elbow.
A.
Pivot
B.
Ball and socket
C.
Hinge
4. These joints are found in the hip and shoulder.
A.
Hinge
B.
Ball and socket
C.
Pivot
5. The part of the bone where blood cells are made.
A.
Marrow
B.
Joint
C.
Ligament
6.
A.
B.
C.
7.
A.
B.
C.
These connect bones to muscles.
Joints
Tendons
Ligaments
The ribs, sternum and spine protect these.
Kidneys, bladder, urethra
Heart, lungs, blood vessels
Small intestine, large intestine
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Progress Test
8.
A.
B.
C.
9.
A.
B.
C.
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
What do the ilium and spine protect?
Digestive organs
Knee and elbow
Wrist and ankle
What type of joint is the Knee?
Synovial
Cartilaginous
Fibrous
10. There are around how many bones in the adult skeleton?
A.
106
B.
206
C.
66
Section 3- Short answer questions
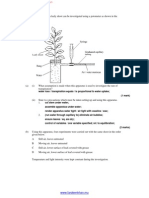
1. 1. Correctly label the major bones of the skeletal system. ( 5 marks)
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
2. Correctly label all elements of this joint
2b. Which classification does this joint belong? (3marks)
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Patella
Patella Tendon
Femur
Tibia
Joint Capsule
Quadriceps
3. What is a joint? And what is its purpose? (2 marks)
4. What are the (3) main classifications of joints? (3 marks)
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Progress Test
Muscular Systems
Mr Collins year 10 P.E
Muscles and Movement (.5 marks each word)
S
L
Q
Q
K
S
G
I
T
F
O
R
C
E
A
T
C
O
F
N
S
T
C
Z
B
H
T
O
N
M
R
U
O
C
D
S
A
D
Y
Q
Q
K
T
T
O
A
V
S
N
O
R
G
W
S
O
L
A
Q
N
D
I
I
E
P
T
M
R
B
X
M
G
J
M
H
V
G
B
I
N
E
E
O
M
L
O
V
O
Q
H
I
H
N
O
O
L
C
Y
T
N
P
L
I
Y
O
K
T
C
E
A
X
D
I
I
E
Y
L
N
S
B
R
E
P
X
B
D
A
S
R
J
S
U
T
R
X
B
N
E
D
K
I
T
P
T
T
E
P
S
S
D
M
S
J
U
P
I
C
S
K
E
L
E
T
A
L
N
Y
H
U
C
F
O
E
A
K
C
P
I
S
Z
U
R
E
T
R
O
H
S
P
D
S
Z
W
N
X
Q
ANTAGONISTIC
PULL
BICEPS
MUSCLES
LOCOMOTE
SHORTER
SKELETAL
FORCE
JOINTS
BENDS
CONTRACT
STRAIGHTENS
TRICEPS
RELAXES
Z
F
U
F
X
H
B
Z
S
U
U
W
F
J
F
U
B
R
G
P
C
K
L
V
M
W
W
Q
W
F
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Tap Yourself FreeDocument134 pagesTap Yourself Freenguyenhavn100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Earthing Substation Earthing Guide Central NetworksDocument12 pagesEarthing Substation Earthing Guide Central Networksshahkhan552000100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- G 26 Building Using ETABS 1673077361Document68 pagesG 26 Building Using ETABS 1673077361md hussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford 1982 3.8L V6Document22 pagesFord 1982 3.8L V6sc100% (1)
- The Study of 220 KV Power Substation Equipment DetailsDocument90 pagesThe Study of 220 KV Power Substation Equipment DetailsAman GauravPas encore d'évaluation
- March 15th 2016Document2 pagesMarch 15th 2016api-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case CommentrayDocument7 pagesCase Commentrayapi-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- At1 - Unit Plan Outline v3Document10 pagesAt1 - Unit Plan Outline v3api-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Year 7 Health UnitDocument5 pagesYear 7 Health Unitapi-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 1 - MicroteachingDocument4 pagesAssessment 1 - Microteachingapi-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Acheivement and Gender FinalDocument12 pagesAcademic Acheivement and Gender Finalapi-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pe Lesson1Document2 pagesPe Lesson1api-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Philosophy and Classroom Management PlanDocument7 pagesTeaching Philosophy and Classroom Management Planapi-335583184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Document16 pagesFajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Jayden ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- District: Surkhet: PopulationDocument13 pagesDistrict: Surkhet: PopulationkarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Navmesh Plus: How ToDocument7 pagesNavmesh Plus: How TobladimirPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagDocument10 pagesGuidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagRaju GawadePas encore d'évaluation
- National Gypsum Purple Book Fire Rated Assemblies in Commercial Construction 1189979Document106 pagesNational Gypsum Purple Book Fire Rated Assemblies in Commercial Construction 1189979alvychuPas encore d'évaluation
- IruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyDocument62 pagesIruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyKhongBietPas encore d'évaluation
- History: Ludwig Hunger: About Us: Home - Ludwig Hunger GMBHDocument3 pagesHistory: Ludwig Hunger: About Us: Home - Ludwig Hunger GMBHPatrizio MassaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Takara 2012Document57 pagesTakara 2012Deepak Ranjan SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- II Unit - End EffectorsDocument49 pagesII Unit - End EffectorsGnanasekarPas encore d'évaluation
- LOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorDocument1 pageLOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorHorizon 99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Names in English and IndonesianDocument7 pagesAnimal Names in English and IndonesianAndi KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques for Studying FossilsDocument11 pagesTechniques for Studying FossilsP. C. PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dahua Pfa130 e Korisnicko Uputstvo EngleskiDocument5 pagesDahua Pfa130 e Korisnicko Uputstvo EngleskiSaša CucakPas encore d'évaluation
- REMEDIATION-Focus BDocument13 pagesREMEDIATION-Focus BCharmaine PerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Semen RetentionDocument3 pagesSemen RetentionMattPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)Document16 pagesEdexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)FardeenKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologyHrituraj banikPas encore d'évaluation
- Vincent Hoa's English 101 PortfolioDocument24 pagesVincent Hoa's English 101 PortfoliovincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Personality Types and Character TraitsDocument5 pagesPersonality Types and Character TraitspensleepePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual Cape Bio Unit 1 2023Document37 pagesLab Manual Cape Bio Unit 1 2023drug123addict25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ninoy Aquino Parks and Wildlife CenterDocument7 pagesNinoy Aquino Parks and Wildlife CenterNinia Richelle Angela AgaPas encore d'évaluation
- EiaDocument14 pagesEiaRamir FamorcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Tub BrochureDocument124 pagesHot Tub BrochureMai Tuan AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- SDE1 V1 G2 H18 L P2 M8 - SpecificationsDocument1 pageSDE1 V1 G2 H18 L P2 M8 - SpecificationsCleverson SoaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NDocument43 pagesPatient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NMercy Anne EcatPas encore d'évaluation