Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Vidyakankar Rotational Mechanics PDF
Transféré par
soumyag98Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Vidyakankar Rotational Mechanics PDF
Transféré par
soumyag98Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ds
IIT Advanced - Rotational Mechanics : Worksheet
Multiple Correct Answer Type
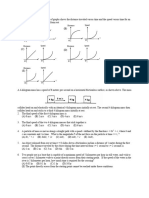
1. Solid sphere, ring and disc of different masses are kept on incline plane such that they start
sliding. When they reach the bottom of plane,
(A) Time taken will be same.
(B) Time taken will be different
(C) Velocities are same
(D) K.E. will be same.
2. A ball moves over a fixed track as shown in the figure.
A
From A to B the ball rolls without slipping. Surface BC
is frictionless. KA, KB and KC are kinetic energies of the
hA
ball at A, B and C, respectively. Then,
(A) hA > hC; KB > KC (B) hA > hC; KC > KA
C
hC
B
(C) hA = hC; KB = KC (D) hA < hC; KB > KC
3. A particle moves in a circle of radius r with angular velocity . At some instant its velocity is v
and radius vector with respect to centre of the circle is r. At this particular instant centripetal
acceleration a c of the particle would be
(A) v
(B) v
(C) ( r)
(D) v (r )
4. A thin uniform rigid rod of length is hinged at one end so that it can move
in a vertical plane by rotating about a horizontal axis through upper end. The
lower end is given a sharp blow and made to acquire a linear velocity v o.
Maximum height attained by lower end of the rod is :
v2
3v 2
(A) 0 for vo < 6g
(B) 0 for vo < 6g
g
3g
(C) 2 for vo
6g
(D) for vo 3g
5. A particle of mass m is travelling with a constant velocity v = v0i along the line
y = b, z = 0. Let dA be the area swept out by the position vector from origin to the particle in time
dt and L the magnitude of angular momentum of particle about origin at any time t. Then
dA 2L
dA
L
(A) L = constant
(B) L constant
(C)
(D)
dt
m
dt 2m
6. A spherical body of radius R rolls on a horizontal surface with
linear velocity v. Let L1 and L2 be the magnitudes of angular
momenta of the body about centre of mass and point of contact P.
Then
(A) L2 = 2L1 if radius of gyration K = R
(B) L2 = 2L1 for all cases
(C) L2 > 2L1 if radius of gyration K < R
(D) L2 > 2L1 if radius of gyration K > R
(Pg.1)
7. A 2 kg mass attached to a string of length 1 m moves in a horizontal
circle as a conical pendulum. The string makes an angle = 30 with
the vertical. Select the correct alternative(s) (g = 10 m/s2)
(A) the horizontal component of angular momentum of mass about the
point of support P is approximately 2.9 kgm2/s.
(B) the vertical component of angular momentum of mass about the
point of support P is approximately 1.7 kgm2/s.
dL
(C) magnitude of
(L = angular momentum of mass about point of support P) is
dt
kg m 2
approximately 10
.
s2
dL
(D)
will not hold good in this case.
dt
Matrix-Match Type
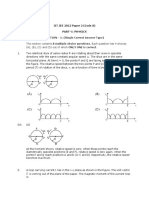
1. In the following column I mass of each object is m and circular of radius R. Column II
represents moment of inertia.
Column I
(A) Full ring
Column II
(p) mR2
(B)
Half ring
(q)
mR 2 / 2
(C)
Quarter ring
(r)
(D)
Arc making an angle at the centre
(s)
mR 2 / 4
mR 2
2
2. Suppose a force F is applied at the top most point of a
rigid body of radius R and mass M.
(A)
Column I
Force of friction will be zero for
(p)
Column II
Solid sphere
(B)
Force of friction will be forward for
(q)
Zero
(C)
Force of friction will be backward for
(r)
Ring
(D)
If a = R then force of friction
(s)
No body
(Pg.2)
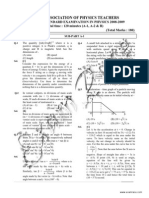
3. A rigid body is rolling without slipping on the horizontal surface
Column I
Column II
(A)
Velocity at point A i.e. VA
(p)
V 2
(B)
Velocity at point B i.e. VB
(q)
Zero
(C)
Velocity at point C i.e. VC
(r)
(D)
Velocity at point D i.e. VD
(s)
2V
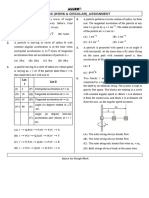
4. A circular body of mass M and radius R, initially spinning about its centre of mass with 0 is
gently placed on a rough horizontal surface. The moment of inertia of body about its C.M is
IC.M = MK2. If the coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is then :
Column I
Column II
(A)
(B)
(p)
(q)
ve
+ ve
(r)
smaller
(s)
(t)
longer
greater
(C)
(D)
Translational work done by the friction
Rotational work done by the friction
Larger the moment of inertia of body, the time required for rolling
motion
Larger the moment of inertia of the body, work done by the friction
5. A rigid body of mass M and radius R rolling without slipping on the inclined plane, then the
magnitude of force of friction.
Column I
Column II
(A)
For ring
(p)
Mg sin /2.5
(B)
For solid sphere
(q)
Mg sin /3
(C)
For solid cylinder
(r)
Mg sin /3.5
(D)
For hollow sphere
(s)
Mg sin /2
(Pg.3)
IIT Advanced - Rotational Mechanics : Worksheet Solutions
Multiple Correct Answer Type
1. (A), (C)
2. (A), (B)
6. (A), (C)
7. (A), (B), (C)
3. (A), (C)
Matrix-Match Type
1. (A) (p); (B) (p); (C) (p); (D) (p)
2. (A) (r); (B) (p); (C) (s); (D) (q)
3. (A) (q); (B) (p); (C) (s); (D) (r)
4. (A) (q); (B) (p); (C) (s); (D) (t)
5. (A) (s); (B) (r); (C) (q); (D) (p)
(Pg.4)
4. (A) , (C) , (D) 5. (A), (D)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Vidyakankar Rotational MechanicsDocument4 pagesVidyakankar Rotational MechanicsVikalp JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics C 1988 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics C 1988 With AnswersjhbmleePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSDocument14 pages11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSharshitsharmasportsPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Aiims PatternDocument7 pagesPhysics Aiims PatternMuhammad YudhistiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsDocument8 pagesSample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsShivam KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1480059572JEE Main Sample Paper 2Document12 pages1480059572JEE Main Sample Paper 2Sohini RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Class TestDocument73 pagesSpecial Class TestSatyam YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Adams-User Guide PDFDocument138 pagesAdams-User Guide PDFPANCHAL SHREYASH HEMANT 16BME1146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive 15BME-1-8Document8 pagesComprehensive 15BME-1-8Prateek srivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit & Dimension & Basic Mathematics (J-Batch)Document6 pagesUnit & Dimension & Basic Mathematics (J-Batch)Raju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Units and DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits and DimensionsSourabh BhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocument7 pagesClass Xi Physics Sample PaperHarekrishna DasPas encore d'évaluation
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 pagesUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Rotational Motion For IIT JEE JEE Main and AdvancedDocument15 pagesRotational Motion For IIT JEE JEE Main and Advancedrish rajPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotation MCQDocument2 pagesRotation MCQAdarsh Dhawan0% (1)
- Aieee 2004.Document52 pagesAieee 2004.NCERT SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- PCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-BDocument16 pagesPCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-BRaju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Mains 2012-1 QuestionsDocument43 pagesJee Mains 2012-1 QuestionsJanaki KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22Document6 pages11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22AJAY SINGH RAGHAVPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Study MaterialDocument164 pagesPhysics Study MaterialgauravPas encore d'évaluation
- NSEP Solved Paper 2008 PDFDocument11 pagesNSEP Solved Paper 2008 PDFapcc1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module Exercise 1 - RotationDocument22 pagesModule Exercise 1 - RotationKrishna PrintsPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main Sample PaperDocument13 pagesJEE Main Sample PaperAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Special Class TestDocument73 pagesSpecial Class TestNautamlal ThakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet of Rotational Motion Student Copy With Ans 30-07-2021 1632047789959Document72 pagesSheet of Rotational Motion Student Copy With Ans 30-07-2021 1632047789959PpPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics DPPsDocument327 pagesPhysics DPPsabhay singhPas encore d'évaluation
- NSEP Solved Paper 2007Document10 pagesNSEP Solved Paper 2007ShubhamKhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- SHMDocument7 pagesSHMSuman SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iitian'S Choice: Mechanics: Iit Jam PhysicsDocument22 pagesIitian'S Choice: Mechanics: Iit Jam PhysicsChunu Physics loverPas encore d'évaluation
- PG Brainstormer - 8c (Mechanics) 635526640000606386Document5 pagesPG Brainstormer - 8c (Mechanics) 635526640000606386mahmood_810357066Pas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 26 February MorningDocument198 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 26 February MorningRahul PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Xi ND Phy NeetDocument7 pagesXi ND Phy NeetDeena chemistPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Paper: (Objective Question Type)Document5 pagesTest Paper: (Objective Question Type)ankit chaturvediPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 01Document212 pagesPhy 01Varsha Dange100% (1)
- Mains Rotational Motion Paper-01Document7 pagesMains Rotational Motion Paper-01Anju MohtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational MotionDocument87 pagesRotational Motionkushagrajoshi69Pas encore d'évaluation
- QP 11 12 P Physics Xi P.M.Document7 pagesQP 11 12 P Physics Xi P.M.Harsh ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aura One Mark Question and AnswersDocument13 pagesAura One Mark Question and Answersmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics - (Work & Circular) - AssignmentDocument9 pagesPhysics - (Work & Circular) - Assignmentmalani.swastikPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Gaurav KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Beware of Negative Marking Have Control Have Patience Have Confidence 100% SUCCESSDocument12 pagesBeware of Negative Marking Have Control Have Patience Have Confidence 100% SUCCESSAYUSH DASPas encore d'évaluation
- P0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsDocument7 pagesP0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsxTERMINATOR007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Samplepape03022024112234 0Document7 pagesSamplepape03022024112234 0bladex605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Document7 pagesRevision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Devansh SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Rotation PDFDocument16 pages08 Rotation PDFAadit Kumar SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Worksheet 1 - ABVPDocument3 pagesPhysics Worksheet 1 - ABVPateefjodamani67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Xi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Document4 pagesXi ND Phy Iit CPT 19.02.24Deena chemistPas encore d'évaluation
- PT 1Document8 pagesPT 1LOVELESH KHATTERPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsDocument32 pagesNEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsSuriyanarayana KPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee-2014-Booklet3-Hwt-system of Particles & Rotational MotionDocument14 pagesJee-2014-Booklet3-Hwt-system of Particles & Rotational Motionvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Scan 04-Aug-2022Document12 pagesScan 04-Aug-2022abhijeetPas encore d'évaluation
- 01ParticleProblems PDFDocument10 pages01ParticleProblems PDFBarbaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have ToDocument1 pagePhysics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have TolohanopiryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Half Yearly (2023-24)Document4 pagesClass 11 Half Yearly (2023-24)shivkarnwal2Pas encore d'évaluation
- C022Document17 pagesC022FATHIMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Easypdf - Best PDF Converter: 1. Tap "Upload" Button and Select The File You Would Like To ConvertDocument2 pagesEasypdf - Best PDF Converter: 1. Tap "Upload" Button and Select The File You Would Like To ConvertSoumya Ranjan GPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 A PolymersDocument19 pagesUnit 3 A PolymersSatyaprakash Goli100% (1)
- Pname VersionDocument66 pagesPname Versionsoumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Easypdf - Best PDF Converter: 1. Tap "Upload" Button and Select The File You Would Like To ConvertDocument2 pagesEasypdf - Best PDF Converter: 1. Tap "Upload" Button and Select The File You Would Like To ConvertSoumya Ranjan GPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument45 pagesIonic Equilibriumsoumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- 22.solutions To ConceptsDocument2 pages22.solutions To ConceptsডৰাজবংশীPas encore d'évaluation
- Pname VersionDocument66 pagesPname Versionsoumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test - 6: Chemistry (Chemical Bonding - 1)Document6 pagesTest - 6: Chemistry (Chemical Bonding - 1)Abhishek Singh100% (2)
- Clinic Class Test 1 M E Sol PDFDocument2 pagesClinic Class Test 1 M E Sol PDFGaurav SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 44 X-Rays PDFDocument5 pages44 X-Rays PDFJayanth VgPas encore d'évaluation
- AIEEE Class XI Chem Structure of AtomDocument64 pagesAIEEE Class XI Chem Structure of AtomVishal_9363% (8)
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistrysoumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dispersion and SpectraDocument3 pagesDispersion and SpectraDhruv KlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio MoleculesDocument55 pagesBio Moleculessoumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 1Document4 pagesChemistry 1soumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- 09.solutions To ConceptsDocument20 pages09.solutions To Conceptssreeramk13Pas encore d'évaluation
- HCV Solutions SssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssDocument3 pagesHCV Solutions SssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssAditi SahaiPas encore d'évaluation
- P-Block Part 4 of 4Document33 pagesP-Block Part 4 of 4soumyag98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics (5 Hours) : PhysicsDocument56 pagesThermodynamics (5 Hours) : PhysicsSaiful Nizam0% (1)
- DSI Mar03 UpdateDocument437 pagesDSI Mar03 UpdateAdel ALkhaligyPas encore d'évaluation
- Volvo Edc III Tad 1241 2 Workshop ManualDocument7 pagesVolvo Edc III Tad 1241 2 Workshop Manualmary100% (55)
- Ficha TensoresDocument4 pagesFicha TensoresedgarPas encore d'évaluation
- Amal Float 691 622069 PDFDocument2 pagesAmal Float 691 622069 PDFjvdkjdlkkPas encore d'évaluation
- SP 1212 Check SheetDocument5 pagesSP 1212 Check SheetDaniel MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEN 200 Homework Problems 1: Problem 1: (3 Marks)Document2 pagesCHEN 200 Homework Problems 1: Problem 1: (3 Marks)Amy MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- RP551Document281 pagesRP551HalotropiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Formula SheetDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics Formula SheetVashish RamrechaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bo-45 Catalogo # 2 PDFDocument957 pagesBo-45 Catalogo # 2 PDFJavier PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet-CF.S10Document1 pageData Sheet-CF.S10nicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ho (V) - 4-1 Side ThrustersDocument125 pagesHo (V) - 4-1 Side ThrustershamzehPas encore d'évaluation
- First Law Applied To Engineering SystemsDocument8 pagesFirst Law Applied To Engineering Systemsguy100% (1)
- Pump & Motor Catalog: Aluminum Bushing SeriesDocument116 pagesPump & Motor Catalog: Aluminum Bushing SeriesMario SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Propellar Design and AnalysisDocument1 pagePropellar Design and AnalysisHarish Kumar SPas encore d'évaluation
- Removing and Installing Toothed BeltDocument12 pagesRemoving and Installing Toothed BeltJulien VasilevPas encore d'évaluation
- Me2151 Engineering Mechanics L T P CDocument1 pageMe2151 Engineering Mechanics L T P CragothsinghramPas encore d'évaluation
- 05-1 N T4 Hydraulic Section Rev1Document128 pages05-1 N T4 Hydraulic Section Rev1Fútbol y más100% (1)
- Mmscience - 2019 12 - Design of CNC Milling Machine As A Base of Industry 4 0 EnterpriseDocument6 pagesMmscience - 2019 12 - Design of CNC Milling Machine As A Base of Industry 4 0 EnterpriseKadir ŞUATAMANPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSPORT PHENOMENA - Unit 1 NotesDocument150 pagesTRANSPORT PHENOMENA - Unit 1 NotesRathi ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- DEE APPLIED PHYSICS - Remedial TestDocument2 pagesDEE APPLIED PHYSICS - Remedial TestMilan SasmolPas encore d'évaluation
- Trajan 712 Owners ManualDocument21 pagesTrajan 712 Owners ManualGIVAN93Pas encore d'évaluation
- CE Test-1 PDFDocument93 pagesCE Test-1 PDFKundan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Raw Mill Patroller Checklist Route 1Document5 pagesRaw Mill Patroller Checklist Route 1AbasiemekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Series 9200 ManualDocument31 pagesSeries 9200 Manualtxlucky80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Dynamic Resonance Ignition For Repetitive StartsDocument8 pagesGas Dynamic Resonance Ignition For Repetitive StartsBrunno VasquesPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Process DiagramDocument3 pagesManufacturing Process DiagramCris Diane G. DatingginooPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Cycle: P-V Diagram T-S DiagramDocument3 pagesDiesel Cycle: P-V Diagram T-S DiagramJJ100% (1)
- HW 1 ForcesDocument2 pagesHW 1 ForcesRebecca LuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On A Control Method With A Ventilation Requirement of A VAV System in Multi-ZoneDocument3 pagesA Study On A Control Method With A Ventilation Requirement of A VAV System in Multi-Zonepsn_kylmPas encore d'évaluation