Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture23 PDF
Transféré par
Ankan GayenTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lecture23 PDF
Transféré par
Ankan GayenDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Leccture--1
MIC
CROST
TRIP ANTEN
A
NNAS
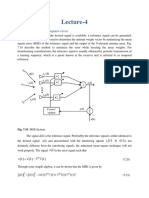
5.1 Intrroduction::
p Antenna (M
MSA) in its sim
mplest config
guration (fig.55.1) consists of a radiatingg patch on onne side
Microstrip
of a dieleectric substratte ( r 10 ), and has a ground
g
plane on the otherr side. The patch conducttors is
normally of copper orr gold. The dielectric
d
consstant of the ssubstrate shouuld be low ( r 2.5 ), so as to
he fringe field
ds which acco
ount for the raadiation.
enhance th
With resp
pect to radiaation properties these anttennas are vversatile in tterms of resoonant frequeencies,
polarizatio
on, pattern and
a impedancce. They allo
ow the use oof additionall tuning elem
ments like piins or
varactor diodes
d
betweeen the patch and
a the groun
nd plane. The choice of thee substrate is very much liimited
by the miccrowave circu
uit coupled to
o the antenna,, which has too be built on tthe same boarrd. The microowave
circuit tog
gether with th
he antenna is usually
u
manufactured by pphoto-etchingg technology.
Fig.5.1 Microstrip
M
anteenna Configurration
5.1.1 Ad
dvantages of
o microstrrip antenna
a:
Microstrip
p antenna has several advantages
a
compared to conventionaal microwavee antennas. T
These
antennas are
a used in many
m
applicatiions over the broad frequeency range froom 100MHz tto 50GHz.
Some of the
t principal advantages
a
off these antenn
nas are:
Lo
ow weight, low
w cost, low profile
p
and con
nformal
Eaasy to fabricatte and can be integrated wiith other micrrostrip compoonents in monnolithic appliccation
lik
ke RFIC and MMIC.
M
Th
he antenna can
n be easily mounted
m
on missiles,
m
rockeets and satellitte without maajor alterationns.
Th
he antenna has low scatteriing cross section.
Du
ual frequency
y antenna can be easily mad
de.
Microstrip antennas are compatible with modular designs (Solid state devices such as oscillators,
amplifiers, variable attenuators, mixer, phase shifters ete. can be added directly to the antenna
substrate board)
5.1.2 Disadvantages:
Narrow bandwidth
Radiation efficiency deteriorates as frequency and antenna array size increases due to an increase
in the feeding network losses.
Lower power handling capacity
Poor isolation between the feed and the radiating elements
In recent years, with the advancement of technology, efforts have been made to minimize these effects
dramatically.
5.1.3 Applications of MSA
For many practical designs, the advantages of MSA far outweigh their disadvantages. With continuous
research and development, the microstrip antennas have been applied in many different and successful
applications. Now a days it is the most popular antenna in the wireless communication market. We can
find applications of MSA in many various fields of high-tech technology which includes:
Satellite communication
Mobile communication
Missile telemetry
Biomedical radiator
Radar system
Radio altimeter
5.2 Microstrip antenna configurations:
Microstrip antennas are characterized by their physical parameters. They may be of any geometrical
shape and any dimension. However all the microstrip antennas can broadly be divided into three basic
categories: (i) microstrip patch antenna, (ii) microstrip traveling-wave antennas, (iii) microstrip slot
antennas.
(i) Microstrip patch antenna
Microstrip patch antenna consists of a conducting patch of any planar geometry on one side of a
dielectric substrate backed by a ground plane on the other side. There are virtually an unlimited umber of
patch patterns for which the radiation characteristics may be calculated. Fig. 5.2 shows some common
patch configuration.
(ii) Microstrip traveling-wave antenna
Microstrip traveling-wave antennas consists of chain-shaped periodic conductors or an ordinary long
TEM line which also supports a TE mode, on a substrate backed by a ground plane. The open end of the
TEM line is terminate in a matched resistive load. As antennas support traveling waves, their structures
may be designed so that the main beam lies in any direction from broadside to endfire. Various
configurations of microstrip traveling-wave antenna are shown in fig.5.3
(iii) Microstrip slot an
ntenna
Microstrip
p slot antennaas comprise of
o a slot in thee ground planne fed by a miicrostrip line. The slot mayy have
the shape of a rectanglee (narrow or wide),
w
a circle or an annuluus as shown iin fig 5.4.
Fig.5.2 Various
V
Micro
ostrip patch an
ntenna config
guration
M
trav
veling wave antenna
a
Fig.5.3 Microstrip
M
slott antenna
Fig.5.4 Microstrip
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- FM 44-2 Light Antiaircraft Artillery (Automatic Weapons) 1956Document206 pagesFM 44-2 Light Antiaircraft Artillery (Automatic Weapons) 1956dieudecafe100% (1)
- Dme ConceptDocument43 pagesDme Conceptkiran bogam100% (1)
- Evolution of Microwave CommunicationsDocument27 pagesEvolution of Microwave CommunicationsStephany Bryan Diez Itao67% (3)
- Network Inter-Working Strategy With GL900M 20160311 (Final Strategy)Document12 pagesNetwork Inter-Working Strategy With GL900M 20160311 (Final Strategy)NaidearBlind50% (2)
- Atoll 3.3.0 LTEDocument139 pagesAtoll 3.3.0 LTESatria86% (7)
- Cell Management Feature Parameter Cell Management Feature Parameter Description DescriptionDocument35 pagesCell Management Feature Parameter Cell Management Feature Parameter Description DescriptionGurpreet Singh MannPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture42 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture42 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture39 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture39 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- MSE Minimization BeamformingDocument3 pagesMSE Minimization BeamformingAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture40 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture40 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture34 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture34 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture43 PDFDocument2 pagesLecture43 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture37 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture37 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture30 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture30 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture26 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture26 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture32 PDFDocument7 pagesLecture32 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture38 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture38 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture24 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture24 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Dolph-Chebyshev Array Design Uses Chebyshev Polynomials to Approximate Array PatternsDocument2 pagesDolph-Chebyshev Array Design Uses Chebyshev Polynomials to Approximate Array PatternsAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture33 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture33 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture36 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture36 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture21 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture21 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture28 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture28 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectangular Patch Cavity Model ExplainedDocument5 pagesRectangular Patch Cavity Model ExplainedAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture20 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture20 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture31 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture31 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- ANTENNA ARRAY LECTURE-1Document4 pagesANTENNA ARRAY LECTURE-1GaneshVenkatachalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture15 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture15 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture17 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture17 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture22 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture22 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture19 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture19 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture13 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture13 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture16 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture16 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture14 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture14 PDFAnkan GayenPas encore d'évaluation
- Icom IC-E208 Instruction ManualDocument92 pagesIcom IC-E208 Instruction ManualYayok S. AnggoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Bizhubc360i C300i C250iQuickGuide PDFDocument61 pagesBizhubc360i C300i C250iQuickGuide PDFHarsha Vardhan Reddy AvulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Profession Broadcast Antennas and Combiner Catalogue Kathrein 2014Document157 pagesProfession Broadcast Antennas and Combiner Catalogue Kathrein 2014Mindaugas PepperPas encore d'évaluation
- IMC UAV ReceieversDocument8 pagesIMC UAV ReceieverssaurabhpachPas encore d'évaluation
- Lps-400 Scale Operation Manual: Contents Subject To Change Without NoticeDocument18 pagesLps-400 Scale Operation Manual: Contents Subject To Change Without NoticeJill MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Point To Point Microwave TransmissionDocument83 pagesPoint To Point Microwave Transmissionfatmirz9448Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anki Vector ManualDocument78 pagesAnki Vector ManualbagasPas encore d'évaluation
- GE 5 Module 2Document12 pagesGE 5 Module 2Glenda RadasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Codan 2110 Series Manpack RadioDocument3 pagesCodan 2110 Series Manpack RadioIvan SungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Low-Cost Outdoor Antenna Radiation Pattern Measurement: Andrian Andaya Lestari Deni YulianDocument4 pagesLow-Cost Outdoor Antenna Radiation Pattern Measurement: Andrian Andaya Lestari Deni YulianSefa KorogluPas encore d'évaluation
- UMTS KPI Formula Counter NamesDocument32 pagesUMTS KPI Formula Counter Namesmebratu teklehaimanotPas encore d'évaluation
- RAN Implementation Workshop GuideDocument58 pagesRAN Implementation Workshop GuideMian Rashid0% (1)
- MODULE 2 Developing The Integrated Marketing Communication ProgramsDocument21 pagesMODULE 2 Developing The Integrated Marketing Communication ProgramsLeslie Ann Elazegui UntalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyDocument86 pagesWireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyRithanathithPas encore d'évaluation
- Improve Atlas Radio with Stable Digital VFODocument16 pagesImprove Atlas Radio with Stable Digital VFOToplician AdrianPas encore d'évaluation
- ПЗ2 GMDSS 3Document4 pagesПЗ2 GMDSS 3ОлегPas encore d'évaluation
- ANT-A104518R05v06-3975 DatasheetDocument6 pagesANT-A104518R05v06-3975 DatasheetoimPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 Q2 Mod1 DifferentFormsOfEMWaves V4Document26 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod1 DifferentFormsOfEMWaves V4Roselyn RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA ComparedDocument22 pagesMultiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA ComparedArun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- OptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description-20100223-ADocument56 pagesOptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description-20100223-AHamid RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- ETSI TetraDocument142 pagesETSI TetramnnoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Mode D'emploi Sony WH-RF400 (2 Des Pages)Document3 pagesMode D'emploi Sony WH-RF400 (2 Des Pages)majdi ben salemPas encore d'évaluation
- IC V8 BrochureDocument2 pagesIC V8 BrochureOngky SajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 84010520Document2 pages84010520marcoPas encore d'évaluation