Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Progress Report Form Nik Abd Hafiidz Bin Nik Abdul Malek
Transféré par
Hafiidz MalekDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Progress Report Form Nik Abd Hafiidz Bin Nik Abdul Malek
Transféré par
Hafiidz MalekDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
Name : NIK ABD HAFIIDZ BIN NIK ABDUL MALEK
ID: 2014688106
Supervisor: MOHAMAD SUFIAN SOA'IB
Title: Enumeration of microbial diversity in naturally fermented Garcinia Mangostana pericarp
Summary of Journal
TITLE
YEARS /
AUTHOR
SOURCE / NAME
OF JOURNAL
PROBLEM STATEMENT
TECHNIQUE /
METHODOLOGY
REMARK/FINDIN
GS
CONCLUSION &
RECOMMENDATION
Investigations
of antimicrobial
activity of
some
Cameroonian
medicinal plant
extracts
against
bacteria and
yeas t with
gastrointestinal
relevance
Emmanuel
Mouafo
Tekwu,
Anatole
Constant
Pieme, Ve
ronique
Penlap
Beng
(2012)
Journal of
Ethnopharmacolo
gy
Aimed to determine the
in vitro antimicrobial
activity of hexane,ethyl
acetate and methanol
extracts from different
parts
(leaves,stembark,entirepl
ant) of five different
plant species against
bacteria and yeast of
gastrointestinal
relevance.
Twenty-one
extracts have
been screened
for their
antimicrobial
activity against
eight bacteria
species using
agar discdiffusion, and
microbroth
dilution assays.
Preparation of
inocula.
Organisms were
subcultured on
agar for bacteria
and yeast follow
by incubation for
24h at 37 C
Study has
demonstrated that
among the plant
species studied, all
of them showed
antimicrobial
activity.The
extracts from N.
latifolia showed
better antibacterial
activity against
Gram-positive and
Gram-negative
bacteria and
antifungal activity.
a-Mangostin
from Garcinia
mangostana
Linn: An
updated review
of its
pharmacologica
l properties
Mohamed
Yousif
Ibrahim,
Najihah
Mohd
Hashim,
Abdalbasit
Adam
Mariod ,
Arabian Journal
of Chemistry
Despite its important
molecular versatility, the
a-mangostin still has
limited clinical
application. In order to
optimize the conditions
of this compound as a
chemotherapeutic and
chemopreventive agent,
Reviews recent
studies on the
central and
potential
pharmacologica
l principles as
well as the
preclinical
Antioxidant
properties of amangostin,
Anticancer and
cytotoxic
properties of amangostin,
Antiinflammatory,
Illustrate
the promising
qualities and
extensive potential
preclinical
application of amangostin which
are largely due to
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
Syam
Mohan,
Mahmood
Ameen
Abdulla,
Siddig
Ibrahim
Abdelwaha
b,
Ismail
Adam
Arbab
(2016)
Tempeh and
fermented
salted fish
Anonymou
s
for instance in diseases
such as cancer, obesity,
diabetes as well as
inflammatory disorders,
the recent tendency is to
limit the range of its
pharmacological
properties
applications of
the amangostin
antiallergy and
analgesic
properties of amangostin,
Anti-parasitic,
anthelmintic
and anti-obesity
properties of amangostin,
Pharmacokineti
c studies of amangostin
its diverse
pharmacological
effects on nearly
all major organ
systems in the
animal models.
To find another fibrinolytic
enzyme source which has
the potential to be
developed for therapeutic
use and investigating
diverse microorganism to
obtain new isolated that
are good protease
producers and increase
productivity
Screening and
isolation of
proteolytic
enzyme
producing
bacteria from
fermented food
tempeh and
Ikan masin, the
second stage is
the
characterization
and
identification of
proteinase
producing
bacteria. Last
stage is the
localization of
the proteolytic
Method of
isolation
microorganism
using dilution
factors with
observation and
method for pure
culture and
characterization
of colonies
Two isolates were
identified as
Enterococcus
feacalis. Three
isolates were also
identified in the
genus Bacillus. A
series of enzyme
purification via
chromatographic
procedures should
be carried out to
purify the enzymes
and characterize
the activity in its
purified form.
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
enzyme whether
it is extracellular
or intracellular
and
measurement of
the qualitative
and quantitative
proteolytic and
fibrinolytic
activity.
Monitoring the
bacterial
population
dynamics during
fermentation of
artisanal
Argentinean
sausages
Cecilia
Fontana,
Pier Sandro
Cocconcelli
b ,Graciela
Vignolo
(2004)
International
Journal of Food
Microbiology
Due to the limitations of
conventional
microbiological methods
such as sugar
fermentation profiles or
other
biochemical/physiological
traits, the identification of
the Lactobacillus and
Micrococcaceae species
involved in meat
fermentation.
resulted ambiguous
LAB and
lactobacilli on
MRS and
acetate agar
media,
respectively,
incubated for 48
h at 30 8C under
restricted
oxygen
conditions;
The isolated
strains, 50 LAB
and 50
belonging to
Micrococcaceae.
Sausage
fermentation
was
characterized by
a rapid increase
in the number of
LAB which
increased from
an initial value of
104 CFU g1 to
107 CFU g1
within the first 5
days of ripening
and remained
stable for the
rest of the
fermentation
period
The ripening
process of
Argentinean
artisanal
fermented sausage
is driven by a
limited number of
strains of
lactobacilli and
staphylococci
selected from
environmental
contamination by
the ability to best
compete under the
prevailing
conditions of the
ecological niche.
The increasing
numbers of large
scale industrial
process are
causing a
continuous loss
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
of microbial
biodiversity,
however the
presence of small
traditional meat
plants in our
country allows the
study of natural
microflora to
prevent the
extinction of
unknown microbial
genotypes
Physio-chemical,
microbiological
properties of
tempoyak and
molecular
characterisation
of lactic acid
bacteria isolated
from
tempoyak
Li-Oon
Chuah ,
Ahamed
Kamal
ShamilaSyuhada ,
Min Tze
Liong,
Ahmad
Rosma,
Kwai Lin
Thong,
Gulam
Rusul
(2006)
Food
Microbiology
The microbial changes of
LAB during tempoyak
fermentation and
the safety aspects of
tempoyak, however, have
not been reported.Thus,
the study the biodiversity
of LAB and microbial
changes taking place
during natural
fermentation of
tempoyak, as well as
highlighting the presence
of multidrug-resistant LAB
isolates involved in the
fermentation of
tempoyak.
Microbiological
analysis of
naturally
fermented
tempoyak, The
PCA and MRS
agar plates were
incubated at 30
C for 24-72 h.
Identification
and
characterisation
of lactic acid
bacteria present
in naturally
fermented
tempoyak
Total plate
count, LAB and
yeast and
mould counts
during
tempoyak
fermentation
and shows the
genotypes and
antibiograms of
representative
dominant LAB
isolated from
naturally
fermented
tempoyak.
incubation
condition for
MRS and PCA
agar
Diverse LAB
species were
involved in the
fermentation and
hence the
organoleptic
properties of
tempoyak. In this
study, the LAB
succession was
monitored and
thus in our opinion
using one batch of
durian sample
from a single
orchard might be
of no consequence
on the final
microflora that is
responsible for the
fermentation of
tempoyak
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
Biodiversity,
dynamics and
antimicrobial
activity of lactic
acid bacteria
involved in the
fermentation of
maize flour for
doklu
productionin
CtedIvoire
N.M.C.Asso
hounDjenia,
N.T.Djenia,
S.
Messaoudi
c, E.L
ommeb,
M.Koussem
onCamaraa,T.
Ouassad,J.M.Chobert
e,B.Onnob,
X.Dousset
(2016)
Food Control
In a framework to
defineand develop starter
culture for controlled
fermentation and
production of doklu with
greater consistency
inquality and safety,
Preparation of
stock solutions,
inoculation of
agar plates and
cultivation and
quantification of
microorganisms
The
antimicrobial
activities of LAB
isolated from
fermented
maize dough
during doklu
production were
assayed against
fungi isolated
The initial stage of
the fermentation
was characterized
by acodominance
of Lb.fermentum,
P.acidilactici, and
P.pentosaceus,but
eventually
gaveway to the
dominance of
Lb.fermentum and
Lb.plantarum
through out the
fermentation.
Microbiological
Study of Lactic
Acid
Fermentation of
Caper
Berries
by Molecular
and CultureDependent
Methods
Ruben Pe
rez Pulido,
Nabil Ben
Omar,
Hikmate
Abriouel,
Rosario
Lucas Lo
pez,
Magdalena
Martnez
Canamero
, and
Antonio Ga
Applied And
Environmental
Microbiology
Caper berries
fermentations has limited
information is available
concerning the microbiota
involved. The
Conventional culturedependent methods of
cultivation can over- or
underestimate the
microbial diversity, as
media may not be
sufficiently selective for
monitoring population
dynamics.
Enumeration of
microorganisms.
MRS agar for
lactic acid
bacteria
McConkey agar
for
enterobacteria;
potato dextrose
agar containing
14 mg of
tartaric acid 50
Changes in
microbial
counts during
the
fermentation of
capers. LAB
counts
increased very
slowly during
the first day of
fermentation,
followed by
rapid increases
at days 2 to 4.
Conventional
methods indicate
that lactic acid
bacteria dominate
this fermentation.
caper fruit
fermentation
shares many
characteristics
with other
vegetable
fermentations,
where L.
plantarum is
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
PROGRESS REPORT FORM FOR FINAL YEAR RESEARCH PROJECT 1 (CHE687 / CBE694)
(EH220, EH221 & EH222)
lvez
(2005)
mg of
chloramphenicol
and 50 mg of
rose Bengal for
yeasts and mol
From day 4 on,
LAB counts
were almost
identical to
counts of total
viable cells,
indicating that
they constitute
the
predominant
group in the
fermentation.
usually the
predominant
species as well,
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Gandhi Was A British Agent and Brought From SA by British To Sabotage IndiaDocument6 pagesGandhi Was A British Agent and Brought From SA by British To Sabotage Indiakushalmehra100% (2)
- Book of Dynamic Assessment in Practice PDFDocument421 pagesBook of Dynamic Assessment in Practice PDFkamalazizi100% (1)
- Optimization of Culture Conditions of Streptomyces Rochei (MTCC 10109) For The Production of Antimicrobial MetabolitesDocument9 pagesOptimization of Culture Conditions of Streptomyces Rochei (MTCC 10109) For The Production of Antimicrobial Metabolitesraj252000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Probiotic Potential of Lactobacillus Paracasei CT12 Isolated From Water Kefir Grains (Tibicos)Document9 pagesProbiotic Potential of Lactobacillus Paracasei CT12 Isolated From Water Kefir Grains (Tibicos)LLUVIA LIZBETH HERNANDEZ JUAREZPas encore d'évaluation
- Articulo Cytotoxic Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of A Selection of MacromycetesDocument9 pagesArticulo Cytotoxic Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of A Selection of MacromycetesLiseth JustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cartagena Filamentus FungusDocument17 pagesCartagena Filamentus FungusLorena Sosa LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Pilihan Hari JugaDocument9 pages1 Pilihan Hari JuganadyasuwayviaPas encore d'évaluation
- tmp7787 TMPDocument7 pagestmp7787 TMPFrontiersPas encore d'évaluation
- Mehmeti Et Al, 2011Document8 pagesMehmeti Et Al, 2011olindacabralPas encore d'évaluation
- 10Document5 pages10Xuân BaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uji Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanolik DAGING BUAH BUNI (Antidesma Bunius (L.) Spreng) TERHADAPDocument9 pagesUji Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanolik DAGING BUAH BUNI (Antidesma Bunius (L.) Spreng) TERHADAPsari ulfiPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Paper MPalelaDocument8 pagesFull Paper MPalelaGSBYGALATIPas encore d'évaluation
- Klaus 2021Document14 pagesKlaus 2021Juan QuitianPas encore d'évaluation
- Fmicb 09 02539Document16 pagesFmicb 09 02539gmanju207Pas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Technologies For Creation of Probiotic Foods: E-Mail: Iliana - Nacheva@abv - BGDocument4 pagesInnovative Technologies For Creation of Probiotic Foods: E-Mail: Iliana - Nacheva@abv - BGFifi Kurnia HidayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Barooah Et Al 2022 Editorial Genomics and Metabolomics of MDocument2 pagesBarooah Et Al 2022 Editorial Genomics and Metabolomics of MAnyela Vanessa Velásquez EmilianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cider Bact PCRDocument6 pagesCider Bact PCRLailatul AzkiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document6 pages2nurul9535Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pan, X., Chen, F., Wu, T., Tang, H., Dan Zhao, Z. 2009. The Acid, Bile Tolerance and Antimicrobial Property of Lactobacillus Acidophilus NIT. J. Food Control. 20 598-602.Document5 pagesPan, X., Chen, F., Wu, T., Tang, H., Dan Zhao, Z. 2009. The Acid, Bile Tolerance and Antimicrobial Property of Lactobacillus Acidophilus NIT. J. Food Control. 20 598-602.AfdhalRuslanPas encore d'évaluation
- BBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-20Document7 pagesBBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-20Dr Sharique AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lactobacillus Plantarium en Kombucha PDFDocument42 pagesLactobacillus Plantarium en Kombucha PDFPAULA ANDREA GUTIERREZ ALVAREZPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Chemistry: A. Sakunpak, P. PanichayupakaranantDocument6 pagesFood Chemistry: A. Sakunpak, P. PanichayupakaranantSamiantara DotsPas encore d'évaluation
- Purification and Characterization of A Bacteriocin Produced by Lactobacillus Lactis Isolated From Marine EnvironmentDocument7 pagesPurification and Characterization of A Bacteriocin Produced by Lactobacillus Lactis Isolated From Marine EnvironmentHoàng-NguyênĐặngPas encore d'évaluation
- Bekasam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesBekasam Bahasa InggrisPurnama WIrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2,4-Di-tert-Butyl Phenol As The AntifungalDocument7 pages2,4-Di-tert-Butyl Phenol As The AntifungalFlorencia IrenePas encore d'évaluation
- Probiotic and Functional Attributes of Probiotic Leuconostoccitreum Strain Mrkak2Document5 pagesProbiotic and Functional Attributes of Probiotic Leuconostoccitreum Strain Mrkak2IJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiological Quality Assessment of A Compost Produced From Animal Waste and VegetablesDocument11 pagesMicrobiological Quality Assessment of A Compost Produced From Animal Waste and Vegetablesjuan carlos CaicedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Inonotus Obliquus Mycelia and Incubated Under Different CultivatingDocument9 pagesInonotus Obliquus Mycelia and Incubated Under Different Cultivatingzalanus13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rios Romero 2018Document8 pagesRios Romero 2018Meitha RizqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Contaminants in Cocoa Powder Samples in South - West NigeriaDocument3 pagesMicrobial Contaminants in Cocoa Powder Samples in South - West NigeriaJorge VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioprospecting of Indigenous Yeasts Involved in Cocoa Fermentation Using Sensory and Chemical Strategies For Selecting A Starter InoculumDocument9 pagesBioprospecting of Indigenous Yeasts Involved in Cocoa Fermentation Using Sensory and Chemical Strategies For Selecting A Starter InoculumOscar Díaz AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Bacteriocin With A Broad Inhibitory Spectrum Produced by Lactobacillus 2009Document6 pagesA Novel Bacteriocin With A Broad Inhibitory Spectrum Produced by Lactobacillus 2009Anonymous OeFSHfybFPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Against Phytopathogenic Fungi Isolated From Cherry TomatoDocument10 pages2021 Antagonistic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Against Phytopathogenic Fungi Isolated From Cherry TomatoEduardo Urbano Moraga CáceresPas encore d'évaluation
- Aktivitas Antibakteri Dari Jamur Endofit Penicillium Oxalicum Hasil Isolasi Dari Spons Homaxinella TanitaiDocument6 pagesAktivitas Antibakteri Dari Jamur Endofit Penicillium Oxalicum Hasil Isolasi Dari Spons Homaxinella Tanitailakatan collectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Antacyd PDFDocument5 pagesAntacyd PDFIra YunrarzPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Cytotoxic Potential of Bacterial Pigments Chapter-2 Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Cytotoxic Potential of Bacterial Pigments Chapter-2 Literature ReviewChanakya ResearchPas encore d'évaluation
- Accepted Manuscript: Food Research InternationalDocument32 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Food Research Internationalbastico2015Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparative GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites Produced by HalotolerantDocument16 pagesA Comparative GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites Produced by HalotolerantAmineJaouedPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation and Characterization of Proteolytic Microorganisms From Fresh and Fermented CabbageDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Proteolytic Microorganisms From Fresh and Fermented CabbageAldair Vergel RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated From Wheat Bran SourdoughDocument20 pagesCharacterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated From Wheat Bran SourdoughTrung HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Antimicrobial and Molecular Characterization of Mortiño Vaccinium Floribundum KunthDocument9 pagesChemical Antimicrobial and Molecular Characterization of Mortiño Vaccinium Floribundum KunthsusanallivisacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Journal of Microbiology 2018Document6 pagesIndian Journal of Microbiology 2018Javier RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal MPN PDFDocument6 pagesJurnal MPN PDFdewi novalitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Composition of Kombucha Determined Using Amplicon Sequencing and Shotgun MetagenomicsDocument10 pagesMicrobial Composition of Kombucha Determined Using Amplicon Sequencing and Shotgun MetagenomicsHiếu Nguyễn TrọngPas encore d'évaluation
- (Allameh, 2012) Isolation, Identification and Characterization of Leuconostoc Mesenteroides As A New Probiotic From Intestine of Snakehead Fish (Channa Striatus) .Document7 pages(Allameh, 2012) Isolation, Identification and Characterization of Leuconostoc Mesenteroides As A New Probiotic From Intestine of Snakehead Fish (Channa Striatus) .José Luis Plaza DoradoPas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro SourdoughDocument11 pagesIn Vitro SourdoughMaryam JameelahPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Article: Molecular Microbial Analysis of Strains Isolated From The Gut of Calves For Potential Probiotic UseDocument8 pagesResearch Article: Molecular Microbial Analysis of Strains Isolated From The Gut of Calves For Potential Probiotic UsevenkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria With High Biological Activity From Local Fermented Dairy ProductsDocument8 pagesIsolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria With High Biological Activity From Local Fermented Dairy ProductsEnkhbaatar BatmagnaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminary Characterization of BacterioDocument9 pagesPreliminary Characterization of Bacteriomanuomar35Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reuteri 2-20B and Pediococcus Acidilactici 0-11A Isolated From FuraDocument9 pagesReuteri 2-20B and Pediococcus Acidilactici 0-11A Isolated From FuramostecocPas encore d'évaluation
- Furlaneto-Maia2020 Article AntimicrobialActivityOfEnterocDocument10 pagesFurlaneto-Maia2020 Article AntimicrobialActivityOfEnterocAmanuel AdugnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Issaas v15n1 POSTER ABSTRACTSDocument28 pagesJournal Issaas v15n1 POSTER ABSTRACTSChai YawatPas encore d'évaluation
- s11274-023-03744-8 E24 LP 16Document13 pagess11274-023-03744-8 E24 LP 16nur rohmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Expanding Knowledge On Russula Alatoreticula, A NovelDocument15 pagesExpanding Knowledge On Russula Alatoreticula, A Novelela.sofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Discrimination of Lactobacilli Isolated From Kefir Grains by FT-IR Spectroscopy. International Journal of Food MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesRapid Discrimination of Lactobacilli Isolated From Kefir Grains by FT-IR Spectroscopy. International Journal of Food MicrobiologyDanielle AlkmimPas encore d'évaluation
- Kjer, 2009 Methods For Isolation of Marine-Derived Endophytic Fungi and Their Bioactive Secondary ProductsDocument14 pagesKjer, 2009 Methods For Isolation of Marine-Derived Endophytic Fungi and Their Bioactive Secondary ProductsMinhHợi100% (2)
- Antimicrobial Activity of Cladosporium Oxysporum Endophytic Fungus Extract Isolated From Aglaia Odorata LourDocument8 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Cladosporium Oxysporum Endophytic Fungus Extract Isolated From Aglaia Odorata LourVzhall El-BryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Chemistry: Analytical MethodsDocument5 pagesFood Chemistry: Analytical MethodsFatehatun NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Protocols For The Isolation and Detection of Lactic Acid BacteriaDocument5 pagesProtocols For The Isolation and Detection of Lactic Acid BacteriaMth RedPas encore d'évaluation
- Identification of Bacterial Strains in Viili by Molecular Taxonomy and Their Synergistic Effects On Milk Curd and Exopolysaccharides ProductionDocument7 pagesIdentification of Bacterial Strains in Viili by Molecular Taxonomy and Their Synergistic Effects On Milk Curd and Exopolysaccharides ProductionDafik A. MasruriPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation, Screening and Partial Purification of Antimicrobial Antibiotics From Soil Streptomyces Sp. SCA 7Document12 pagesIsolation, Screening and Partial Purification of Antimicrobial Antibiotics From Soil Streptomyces Sp. SCA 7Ajzm CompanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Breeding and Genetics of Applied MicroorganismsD'EverandMolecular Breeding and Genetics of Applied MicroorganismsKenji SakaguchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Welded-Joint EfficiencyDocument1 pageWelded-Joint EfficiencyHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Succinic Acid Production PlantDocument102 pagesSuccinic Acid Production PlantHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Assays Can Be Very Diverse, But Generally Involve The Following General StepsDocument3 pagesAssays Can Be Very Diverse, But Generally Involve The Following General StepsHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
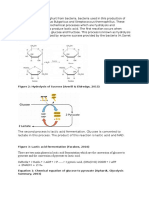
- Figure 2: Hydrolysis of Sucrose (Averill & Eldredge, 2013)Document5 pagesFigure 2: Hydrolysis of Sucrose (Averill & Eldredge, 2013)Hafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Hazard AnalysisDocument74 pagesChapter 6 - Hazard AnalysisHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 Intro N RecommendationDocument6 pagesLab 5 Intro N RecommendationHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- CBE655 Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCBE655 Lab ManualHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 - Section A - Mathcad SolutionsDocument1 pageChapter 16 - Section A - Mathcad SolutionsHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbe682 Separation Processes Ii Tutorial: CrystallizationDocument1 pageCbe682 Separation Processes Ii Tutorial: CrystallizationHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- 8,9,10 Faeez OshaDocument3 pages8,9,10 Faeez OshaHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoppings in MalaysiaDocument1 pageShoppings in MalaysiaHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Saponification KatoDocument24 pagesSaponification KatoHafiidz MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 JPNT Math f4 Modul1Document7 pages07 JPNT Math f4 Modul1Jah RakibPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Thinking PDFDocument7 pagesDesign Thinking PDFFernan SantosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure - Digital Banking - New DelhiDocument4 pagesBrochure - Digital Banking - New Delhiankitgarg13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Win Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsDocument11 pagesWin Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsadetriyunitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Butterfly Valve Info PDFDocument14 pagesButterfly Valve Info PDFCS100% (1)
- Contents Serbo-Croatian GrammarDocument2 pagesContents Serbo-Croatian GrammarLeo VasilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reith 2020 Lecture 1 TranscriptDocument16 pagesReith 2020 Lecture 1 TranscriptHuy BuiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Photograph (Q and Poetic Devices)Document2 pagesA Photograph (Q and Poetic Devices)Sanya SadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- PMS Past Paper Pakistan Studies 2019Document3 pagesPMS Past Paper Pakistan Studies 2019AsmaMaryamPas encore d'évaluation
- Goats & Sheep: What You Need To KnowDocument74 pagesGoats & Sheep: What You Need To KnowAdrian BAGAYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing Global LeadersDocument10 pagesDeveloping Global LeadersDeepa SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus/Course Specifics - Fall 2009: TLT 480: Curricular Design and InnovationDocument12 pagesSyllabus/Course Specifics - Fall 2009: TLT 480: Curricular Design and InnovationJonel BarrugaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2Document6 pagesACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2CATALINA UNDURRAGA UNDURRAGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatrica Indonesiana: Sumadiono, Cahya Dewi Satria, Nurul Mardhiah, Grace Iva SusantiDocument6 pagesPaediatrica Indonesiana: Sumadiono, Cahya Dewi Satria, Nurul Mardhiah, Grace Iva SusantiharnizaPas encore d'évaluation
- CRM - Final Project GuidelinesDocument7 pagesCRM - Final Project Guidelinesapi-283320904Pas encore d'évaluation
- SHS11Q4DLP 21st CentFinalDocument33 pagesSHS11Q4DLP 21st CentFinalNOEMI DE CASTROPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Paper 1 TZ2 HLDocument16 pagesMathematics Paper 1 TZ2 HLPavlos StavropoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Batch 4 PPTDocument20 pagesBatch 4 PPTAbhi ShekPas encore d'évaluation
- Lewin's Change ManagementDocument5 pagesLewin's Change ManagementutsavPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan ADocument29 pagesFunctions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan AsrinivasanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12 Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12Document55 pagesCreative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12 Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12QUINTOS, JOVINCE U. G-12 HUMSS A GROUP 8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaDocument16 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaSubhro ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Hce ReviewerDocument270 pagesHce ReviewerRaquel MonsalvePas encore d'évaluation
- Chpater 2 PDFDocument44 pagesChpater 2 PDFBilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Workplace CommunicationDocument55 pagesLead Workplace CommunicationAbu Huzheyfa Bin100% (1)
- Anindya Anticipatory BailDocument9 pagesAnindya Anticipatory BailYedlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoDocument3 pagesRem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoNoel DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Mix of Van HeusenDocument38 pagesMarketing Mix of Van HeusenShail PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc Quiz 2Document2 pagesEdc Quiz 2Tilottama DeorePas encore d'évaluation