Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
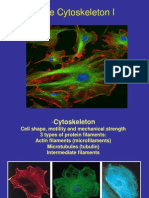
Actin Filaments and Microtubules
Transféré par
JohnCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Actin Filaments and Microtubules
Transféré par
JohnDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
994
PANEL 163: Accessory Proteins that Control the Assembly and Position of Cytoskeletal Filaments
ACTIN FILAMENTS
+
formin
ARP complex
nucleates assembly and remains
associated with the growing
plus end
nucleates assembly
to form a web and remains
associated with the minus end
thymosin
profilin
binds subunits,
prevents assembly
binds subunits,
speeds elongation
actin subunits
actin filament
+
cofilin
binds ADP-actin filaments,
accelerates disassembly
tropomyosin
+
stabilizes filament
gelsolin
capping protein
severs filaments and
binds to plus end
prevents assembly and
disassembly at plus end
filament bundling, cross-linking, and attachment to membranes
plasma
membrane
fimbrin
a-actinin
filamin
spectrin
ERM
Some of the major accessory proteins of the actin cytoskeleton. Except for the myosin motor proteins, to be discussed in
a later section, an example of each major type is shown. Each of these is discussed in the text. However, most cells contain
more than a hundred different actin-binding proteins, and it is likely that there are important types of actin-associated
proteins that are not yet recognized.
995
MICROTUBULES
+
g-TuRC
nucleates assembly and
remains associated with
the minus end
centrosome
+TIPs
stathmin
ab tubulin dimers
binds subunits,
prevents assembly
remain associated with growing plus ends
and can link them to other structures,
such as membranes
microtubule
XMAP215
stabilizes plus ends
and accelerates assembly
kinesin 13
enhances catastrophic
disassembly at plus end
katanin
MAPs
severs microtubules
stabilize tubules by
binding along sides
filament bundling and cross-linking
tau
MAP-2
plectin
links to intermediate filaments
Some of the major accessory proteins of the microtubule cytoskeleton. Except for two classes of motor proteins, to be
discussed in a later section, an example of each major type is shown. Each of these is discussed in the text. However,
most cells contain more than a hundred different microtubule-binding proteins, andas for the actin-associated
proteinsit is likely that there are important types of microtubule-associated proteins that are not yet recognized.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Inigo.j 01109151013Document27 pagesInigo.j 01109151013inigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microfilament: in Vitro Self-AssemblyDocument7 pagesMicrofilament: in Vitro Self-AssemblyABHISHEK RATHODPas encore d'évaluation
- MicrofilamentsDocument4 pagesMicrofilamentsSujan maharjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Microfilament Actin 1Document19 pagesMicrofilament Actin 1DwiRaniPrihandiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 - The Cytoskeleton - 112612Document56 pagesChapter 16 - The Cytoskeleton - 112612Sohan rautPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Motors ExplainedDocument25 pagesMolecular Motors ExplainedDavid HamalalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoskeleton: Structure and Functions of the Cellular NetworkDocument44 pagesCytoskeleton: Structure and Functions of the Cellular NetworkFatma Nadjah MandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 32 - Actin Filaments - Post-LectureDocument47 pagesLecture 32 - Actin Filaments - Post-LectureMuhit ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoskeletal NetworkDocument51 pagesCytoskeletal Networkconan128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Contractile Tissues NotesDocument89 pagesContractile Tissues NotesteePas encore d'évaluation
- Cytology CytoskeletonDocument48 pagesCytology CytoskeletonMitzel Sapalo0% (1)
- Structural ProteinsDocument14 pagesStructural ProteinsAppleDashingPas encore d'évaluation
- CytoskeletonDocument50 pagesCytoskeleton6ypywxdqmkPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoskeleton (Filament Proteins)Document11 pagesCytoskeleton (Filament Proteins)Siyad AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- CollagenDocument8 pagesCollagenkaditasookdeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Myofilaments: A) Thick Filaments - The Thick Filament Is Composed of Myosin. TheDocument3 pagesMyofilaments: A) Thick Filaments - The Thick Filament Is Composed of Myosin. TheMichaelJackson Didnt TouchMePas encore d'évaluation
- The Cytoskeleton I: Actin, Microtubules and Intermediate FilamentsDocument62 pagesThe Cytoskeleton I: Actin, Microtubules and Intermediate FilamentsRebecca ReillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein Structure PredictionDocument52 pagesProtein Structure PredictionMudit MisraPas encore d'évaluation
- The CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesThe CytoskeletonElena OlmedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alberts Chapter 3 NotesDocument3 pagesAlberts Chapter 3 NotesOrielleKlarisseD.OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle Contraction MechanismDocument10 pagesSkeletal Muscle Contraction MechanismLiljana StojkovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoskeleton DADocument35 pagesCytoskeleton DAAnonymous NVBCqKWHPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapte 3 MuscleDocument128 pagesChapte 3 MuscleErmias HadguPas encore d'évaluation
- Sliding Filament Theory ExplainedDocument3 pagesSliding Filament Theory ExplainedMariam DalilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy For Muscle ContractionDocument32 pagesEnergy For Muscle ContractionAndy SkatePunkPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeleton 1Document29 pagesSkeleton 1irajosephsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chripollitt 3 Lamellar AnatomyDocument10 pagesChripollitt 3 Lamellar AnatomyBrandon TaylorPas encore d'évaluation
- Actin Structures Drive Cell MotilityDocument5 pagesActin Structures Drive Cell MotilityRyan CarrollPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 The CytoskeletonDocument7 pages14 The Cytoskeletonsatriamanullang880Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology Slide #1Document18 pagesPhysiology Slide #1anon_974423120Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Recognition Brochure PakistanDocument10 pagesCambridge Recognition Brochure PakistanMuhammad Vaqar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- General-Physiology - Smooth MuscleDocument4 pagesGeneral-Physiology - Smooth Muscledagehi6880Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Leslie HargisDocument24 pagesPresented By: Leslie HargisRhomar GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1Document43 pages2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1m.mansoor3377Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 SummaryDocument11 pagesChapter 16 SummaryCharlottePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Junction ProteinsDocument38 pagesCell Junction ProteinsAndreea SpiridonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Molecular Motor Proteins: Part 1 Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Motor Proteins: Part 1 Lecture Noteskinza888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles 1Document25 pagesMuscles 1Mihaela CosteaPas encore d'évaluation
- البروتيناتDocument54 pagesالبروتيناتYaman HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Bridge CycleDocument14 pagesCross Bridge CycleIdenyi Daniel Ewa EdePas encore d'évaluation
- DJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFDocument43 pagesDJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFNick_989893Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction & Relaxation ExplainedDocument16 pagesMechanism of Muscle Contraction & Relaxation ExplainedShalinie ChittarasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Aps 2005114Document11 pagesAps 2005114sosemir589Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9# Fisiologi OtotDocument25 pages9# Fisiologi OtotfaizalalkharismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument25 pagesMuscle PhysiologyhazelelPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisiologi MusculoskeletalDocument25 pagesFisiologi MusculoskeletalSuardimanAchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tejido MuscularDocument7 pagesTejido MuscularJoaquin Biglia AvanciniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifs 1902 Muscle Lecture #2 2021-1Document109 pagesLifs 1902 Muscle Lecture #2 2021-1KenjiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Quaternary StructureDocument6 pages5 Quaternary StructureShiv KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Cell MembranesDocument44 pagesBiological Cell MembranesMohammed ShaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction: Muscular TissueDocument8 pagesSliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction: Muscular TissueMaryam Nur Azizah RahmahPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 38 Cellular MotilityDocument19 pagesCH 38 Cellular MotilityerichaasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoskeleton MADocument22 pagesCytoskeleton MAsema raraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-3 Muscle Physiology - Class NotesDocument11 pagesCh-3 Muscle Physiology - Class NotesNarelle IaumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Myosin Powered Movement and Contraction in Muscle and Non-Muscle CellsDocument8 pagesMyosin Powered Movement and Contraction in Muscle and Non-Muscle CellsIndranil BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion 1 MMDocument4 pagesDiscussion 1 MMAbhishek LevePas encore d'évaluation
- Motor ProteinsDocument9 pagesMotor Proteinsazazel666Pas encore d'évaluation
- Extracellular MatrixDocument4 pagesExtracellular MatrixElena OlmedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Contraction MechanismDocument14 pagesMuscle Contraction MechanismAlexPas encore d'évaluation
- 508 Lecture 12Document3 pages508 Lecture 12JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT3 091SCF09 SummaryDocument33 pagesMIT3 091SCF09 SummarydavidraaamosPas encore d'évaluation
- The Stock Market Jumpstarter V2.0Document51 pagesThe Stock Market Jumpstarter V2.0Dennis LandichoPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Educational Resources Textbook ListDocument35 pagesOpen Educational Resources Textbook ListJohn100% (1)
- Quimica Organica IIDocument18 pagesQuimica Organica IIvskywokervsPas encore d'évaluation
- Spie Trial ManualDocument9 pagesSpie Trial ManualJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chem NotesDocument45 pagesAP Chem NotesSajiveSivalingamPas encore d'évaluation
- ChimieDocument10 pagesChimieDana CapbunPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 101 Complete NotesDocument323 pagesChemistry 101 Complete NotesEnerolisa Paredes100% (1)
- Semicond LasersDocument23 pagesSemicond LasersurimPas encore d'évaluation
- IPLS Report 2015 v2Document40 pagesIPLS Report 2015 v2JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Statics SlidesDocument35 pagesStatics SlidesHabibullah RadziPas encore d'évaluation
- XML For Software Engineers: Tutorial OutlineDocument47 pagesXML For Software Engineers: Tutorial OutlineJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- X Ray Diffraction 1057Document5 pagesX Ray Diffraction 1057JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- AcDocument44 pagesAcJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Vibrational Excitation of Molecules Involving Methane & NitrogenDocument15 pagesThe Effect of Vibrational Excitation of Molecules Involving Methane & NitrogenRay FraustoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier Problem and AnswerDocument2 pagesFourier Problem and AnswerJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics: Course IntroductionDocument52 pagesThermodynamics: Course IntroductionRodrigo Silveira da SilveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exponential Notation and Physical QuantitiesDocument4 pagesExponential Notation and Physical QuantitiesJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue SystemsJohn0% (1)
- Actin Filaments: 968 PANEL 16-1: The Three Major Types of Protein Filaments That Form The CytoskeletonDocument1 pageActin Filaments: 968 PANEL 16-1: The Three Major Types of Protein Filaments That Form The CytoskeletonJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Flower DevelopmentDocument1 pageFlower DevelopmentJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular MechanismsDocument2 pagesMolecular MechanismsJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- M Phase in An Animal CellDocument2 pagesM Phase in An Animal CellJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Redox PotentialsDocument1 pageRedox PotentialsJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel 11-2Document1 pagePanel 11-2nrf2Pas encore d'évaluation
- PolymerizationDocument2 pagesPolymerizationJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Sequences and Protein TranslocationDocument1 pageSignal Sequences and Protein TranslocationJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Squid Giant AxonDocument1 pageSquid Giant AxonJohnPas encore d'évaluation