Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ermeto
Transféré par
Javier VespaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ermeto
Transféré par
Javier VespaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Function of progressive ring fittings
Before tightening
the nut
P
After tightening
the nut
A
G
E
The EO progressive ring fitting produces a keyed, leak
free connection of tubes and components in fluid systems. The basic function of the EO progressive ring is the
controlled progressive bite of the ring into the tube due to
a unique internal geometry.
The front cutting edge (A) has already started cutting into
the tube before the second cutting edge (B) starts. As
soon as both cuffing edges have cut the tube to the
designed depth further advance is limited by the stop
edge (C).
Owing to the design of both cutting edges and stop edge
all forces arising are equally distributed. This distribution
along with the specially designed interior collar (D) of the
ring guarantees increased safety with regard to flexure
stresses. Thus vibrations are eliminated from the
cutting area.
The stop edge causes a sharp increase in tightening forces which is clearly perceptible. After
assembly a visible collar (E) of cut tube material
must completely fill the space in front of the first
cutting edge. With stainless steel tube and hose
connections made from free cutting steel, the collar is less due to the harder material.
It is absolutely essential that the tube should be
held firmly against the stop in the inner cone of the
fitting otherwise the cutting process cannot take
place satisfactorily. Reassembly can be performed an unlimited number of times.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
General, standards, certificates and materials
General
Standards:
The fittings and components listed are intended solely
for the assembly of connections for fluid applications.
3 series of EO tube fittings and accessories are
manufactured in accordance with DIN 2353 (summary)
on the basis of decades of experience. Designs for
higher operating pressures or specific applications are
on request. In these cases, please specify the precise
operating conditions, intended tube dimensions and
tube quality etc.
Our agencies and technical customer service are
always on hand with advice and practical help.
To ensure functional safety of EO tube fittings, only EO
parts should be used in their assembly. Routing of
tubes to be carried out in accordance with regulations.
Assembly instructions are available.
EO-standard range is in accordance with DIN
2353 (summary)
We reserve the right to make changes brought about
by further technical developments.
Standard range
The part numbering refers to steel fittings. When ordering stainless steel or brass fittings, a short code is to
be added on to the part number specified. Types,
which are not part of the standard range, are denoted by weights in brackets. Series LL fittings and brass
fittings are supplied with cutting rings in place of progressive rings. Standard range fittings are supplied in
factory packaging for practical storage and protection
against contamination. Ordering should be made in
multiples of box quantities.
These box quantities are to be found from the respective price list. For quantities less than a box may be
obtained from an E.O. Distributor.
Tube connection side:
DIN 3861 and ISO
8434
Male studs and port tappings for:
Metric and BSP thread:
DIN 3852, parts
1 and 2
NPT thread:
ANSI/ASME
81.20.1-1983
UN/UNF thread:
SAE J 514
Metric thread with
O-ring seal:
ISO 6149 and DIN
3852, part 3
Swivel nuts and
weld fittings:
DIN 3865
Technical terms for tube
fittings as per:
DIN 3859
Seamless EO-tubes
Steel tube:
2391
Stainless steel tube:
DIN 1630 and DIN
DIN 17458 with
tolerances in
accordance with
DIN 2391.
G
E
Approvals:
Approvals from various acceptance organizations
are available for EO tube fittings, among which
are:
Germanischer Lloyd
Lloyds Register of Shipping
American Bureau of Shipping
Det Norske Veritas
Bureau Veritas
CEGB
BS 4368
TUV
(Documents on request)
Fitting materials:
For steel tube:
EO tube fittings
(steel)
For stainless steel tube:
EO tube fittings
(stainless steel)
For copper tube:
EO tube fittings
(brass)
EO tube fittings
(special materials)
Elastomer seals
- Materials see
DIN 3859
- X6CrNIMoTi
17122 in
accordance with
DIN 17440,
material no.1.4571
- CUZN35Ni2 in
accordance with
DIN 1766660/
17672, material
no.2.0540.
BACK TO
- on request
- NBR
FPM
Special materials
on request.
CATALOGUE
Surface Finish, part numbering, working pressure
developments
Surface Finish - Steel fittings:
Standard
LL Series
Body and Nuts - Zinc plated, clear
bichromated
Rings
- Zinc plated
L+S Series Body and Nuts - Phosphated and oiled
(Znphr5f)
Rings
(Progressive)
- Zinc plated and olive
chromated
Short codes for surface protection procedure in
accordance with DIN 267 part 9 or DIN 50942.
Options
L+S Series Body and Nuts - Zinc plated and yellow
chromated add suffix A3C to
standard part number eg
GE 20 PSR=standard,
GE 20 PSR/A3C=Zinc plated
Part numbers:
All pant numbers in this specification sheet refer to fully
assembled steel fittings, for alternatives the following
applies.
Body only If the basic fitting body only is required, the part number
is prefixed by X and the letter P is omitted eg XGE 20SR.
Less Tube Nuts and Rings only If you require fittings which normally consist of
many pieces i.e. banjos, but without the tube nut
and ring, then the suffix /OMD is to be added to
the standard part number, eg. WH20-SR/OMD. The
P is not required.
Fitted with Weld Nipples If the fitting is to be fitted complete with weld nipples SKA and not progressive ring then add 6 in
front of the tube diameter size in the part number.
Also add the required wall thickness after the tube
diameter. eg. GE 620x3-SR.
Steel, Zinc yellow chromated If you require the fittings zinc yellow chromated,
the suffix /A3C is to be added to the standard
part number, eg. GE20-PSR/A3C.
Stainless Steel and Brass Fittings - If your require
stainless steel or brass fittings add suffix /71
for stainless steel or suffix /MS for brass to the
standard part number, eg. GE20-PSR/71 or GE20SR/MS.
Note:
The letter P is not included as Brass rings
are not of the progressive design.
Sealing material FPM (eg. Viton) If you require fittings with other sealing material
(NBR eg. buna N is standard) the suffix /VI (for
FPM eg. Viton) is to be added to the standard part
number. eg. GE 20-PSR/VI.
P
A
G
E
Development of nominal pressure for progressive ring fittings
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Pressure and temperature load capability
Pressure load capability
Pressure reductions
Definition of pressures specified:
Required pressure reductions (determined by the medium) compared with the specifications for higher temperatures.
a) Nominal pressure NP
The nominal pressure as referred to in DIN 2401,
part 1 draft.
b) Working pressure PB
The permissible working pressure for a component
is based on the material and the operation temperature (TB) during trouble free operation (DIN 2401,
part 1 draft).
Permissible operating temperature (TB) range for
fitting materials:
Steel:
-40 to +1200C
(DIN 3859)
Brass:
-60 to +1750C
Stainless steel:
-60 to +4000C
(DIN 17 440, AD W 10)
The specifications in the Pressure reductions section
are to be observed here.
For sealing materials
NBR (e.g. Perbunan): -35 to +1000C
FPM (e.g. Viton):
-25 to +2000C
PTFE (e.g. Teflon):
-60 to +2000C
(Only with banjo
fittings WH/TH)
POM (e.g. Delrin)
-40 to +800C
(Only with ball valves)
Perbunan = registered trademark of Bayer. Viton,
Teflon and Delrin = registered trademarks of Du Pont.
The temperature limits specified for sealing materials
are approximate values, since the temperature limits
can be greatly influenced by the medium.
When combining the different fitting and sealing materials, the lowest temperature limit in each case is
applicable.
Example: GE 10-PLR made from 1.4571 sealed with
cutting face.
Temperature range: -60 to +4000C
GE10-PRL-ED made from 1.4571 with
EOLASTIC seal made from FPM
Temperature range:
Fittings material
-60 to +4000C
ED seal
-25 to +2000C
Premissible temperature range of fitting:
-25 to +4000C, if the medium permits a temperature of 2000C for the ED seal.
Fitting
material
Temperature range
Steel
-40 to +1200C
Messing
-60 to +1750C
1.4571
-60 to +2000C
1.4571
+500C
1.4571
+1000C
1.4571
+2000C
1.4571
+3000C
1.4571
+4000C
Intermediate values are to be interpolated.
Pressure
reductions
30%
4%
11%
20%
29%
33%
If the tube material used deviates from the fitting material, the tube is to be checked separately with regard to
the permissible temperature range and the possible
pressure reductions required. Male stud fittings may
require additional pressure reductions, due to the mating port material and the sealing system must also be
taken into account. For male stud fittings with cutting
face, additional sealants may be required.
If different stipulations for special applications are made
by standards, regulations or approvals with regard to
permissible pressure reductions to be applied if necessary, then these stipulations made are binding.
P
A
G
E
The nominal pressures NP and operating pressures (PB)
represent the max. permissible operating pressure
peaks, in which the temperature limits and pressure
reductions listed in the above tables must be taken into
account.
Operational safety at static load:
Types with NP specification: 4 x
Types with PB specification: complete fitting min. 2.5 x,
tube connection 4x
(if not otherwise specified).
These pressure and safety specifications are based on
all assemblies being in accordance to Parker-Ermeto
instructions.
It is further assumed that the tube routing will be laid
and clamped in such a fashion that no additional stress,
load or tension may act on the fittings. Tube fixtures are
to be laid with sufficient stability according to the operating conditions and connected with supports. EO tube
clamps are recommended for simple, problem-free
assembly.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Unit Construction System
The basic range of fittings i.e. GE, WE, SV etc. may
be combined with adapters to achieve a construction for fittings not available as a one piece fitting
thus eliminating specials.
Adapters available are:
RI
Reducing thread adaptors
RED
Reducing standpipe with swivel nut
EGE
Straight stud standpipe with swivel nut
EW, ET, EL Adjustable swivel nut fittings
MAVE
Pressure gauge fitting with swivel nuts
Examples of combining fittings together
1) Adjustable male stud fitting-using the EGE
fitting combined with basic tube to tube fittings i.e. W, T, K etc.
2) Tube reducer or step down. For example
smaller tube size on the branch. Ideal part
would be TR 15/12/15-PL. This may be
achieved with T15-PL fitted with RED 15/12L.
3) Male stud with non-standard thread size for
the tube size. Achieved with the standard
stud fitting fitted with the appropriate RE
adapter e.g. required GE 12-PL/R 1/2-ED
use GE 12-PLR plus RI 1/2 ED x 3/8.
4) By combining swivel nut fittings EW,T, L etc.
to basic fittings a multitude of configurations,
adaptions can be achieved simply, cheaply
and in a compact manner. (see diagram
below).
P
A
G
E
Tube recommendations
For steel fittings
Seamless drawn steel tubes made from material St.
35.4 or from conditioned base material St. 37.4 in
accordance with DIN 1630, state of delivery NBK (normalizing, brightly annealed) with tube outer and inner
diameter tolerances in accordance with DIN 2391.
Max. hardness: HRB 75. EO tubes.
For stainless steel fittings
Material no.1.4571
Seamless drawn tubes made from austenitic, stainless
steel material no.1.4571, in accordance with DIN
17458 tube outer diameter tolerances according to tolerance class D4 and wall thickness according to tolerance class T4 DlN 2462, part 1. Max hardness: HRB
90.
EO special steel tubes.
These tubes are particularly recommended for
tube fittings, since the tube outer diameter and
wall thickness, tolerances correspond to those
of steel tubes in accordance with DIN 2391.
For brass fittings:
Seamless drawn copper tube made from material with short code SF-Cu F37 in accordance with
DIN 1786.
Copper tube is not part of the Parker-Ermeto
range.
Tube wall thicknesses:
In order to ascertain the required tube wall thicknesses, the calculation for pressures of steel
tubes and stainless steel tubes can be used.
Strengthening sleeves must be used if necessary
in cases of thin-wall tubes, applications in order
to avoid excessive tube restrictions.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
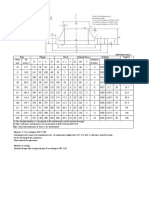
Port tapping for EO tube fittings
Metric ISO thread according to DIN 3852, part 1
BSP according to DIN 3852, part 2
Male studs form A
sealing by metal
sealing washer (DIN 7603)
Male studs form B
sealing by cutting face
Male studs form E
with EOLASTIC-sealing ED
Male studs form C
sealing by taper thread
P
A
Port tapping form X
(for parallel male threads)
tube o.d.
series
LL
L
S
4
6/8
6
8
6
10
8
12
10
15
12
14
18
16
22
20
28
25
35
30
42
38
4/6/8
6
10/12 8/10 6/8
12 10/12
15/18 14/16
22
20
28
25
35
30
42
38
Parallel
thread
d1
M8 x 1
M10 x 1
M12 x 1,5
M14 x 1,5
M16 x 1,5
M18 x 1,5
M20 x 1,5
M22 x 1,5
M26 x 1,5
M27 x 2
M33 x 2
M42 x 2
M48 x 2
G 1/8 A**
G 1/4 A
G 3/8 A
G 1/2 A
G 3/4 A
G1A
G 1 1/4 A
G 1 1/2A
for male stud
form E
+0,4
d4
d7
small small
14
15
17
18
19
20
21,9*
23*
23,9*
25*
25,9*
27*
27
28
31,9*
33*
32
33
39,9*
41*
49,9*
51*
55
56
14
15
18,9*
20*
22
23
26,9*
28*
32
33
39,9*
41*
49,9*
51*
55
56
for male stud
form A
and form B
1)
+0,4
+0,4
d3
d4
d4
a1
small small wide max
14
15
20
1
17
18
25
1,5
19
20
25
1,5
21
22
28
1,5
23
24
30
2
25
26
34
2
27
28
34
2,5
31
32
42
2,5
32
33
42
2,5
39
40
47
2,5
49
50
58
2,5
55
56
65
2,5
14
15
19
1
18
19
25
1,5
22
23
28
2
21
22
34
2,5
32
33
42
2,5
39
40
47
2,5
49
50
58
2,5
55
56
65
2,5
Port tapping form Z
(for taper threads)***
G
E
b
mm
8
12
12
12
12
14
14
16
16
18
20
22
8
12
12
14
16
18
20
22
Taper
thread
d2
M8 x 1
M10 x 1
M12 x 1
M14 x 1
M16 x 1
M18 x 1
M20 x 1
M20 x 1
R 1/8 keg.
R 1/4 keg.
R 3/8 keg.
R 1/2 keg.
-
keg.
keg.
keg.
keg.
keg.
keg.
keg.
keg.
b2
min
5,5
5,5
8,5
8,5
8,5
8,5
10,5
10,5
5,5
8,5
8,5
10,5
-
W
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,2
0,2
0,2
0,2
0,2
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,1
0,2
0,2
0,2
0,2
* Different from DIN 3852
** A does not apply to female threads
*** Complete sealing can only be achieved by using a sealant.
1) For WH/TH fittings with KD sealing.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Port tapping for EO tube fittings
Metric ISO thread according to DIN 3852, part 3 resp. ISO 6149
UNF/UN thread according to SAE J514
NPT thread according to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1-1983
Port tapping form F
with O-ring sealing (DIN 3852,
part 3)
and
Male stud UN/UNF-2A
with O-ring sealing (SAE J514)
Male stud NPT
(ANSI/ASME B1.20.1-1983
P
A
G
Port tapping NPT
(ANSI/ASME B1.20.1-1983
Port tapping form W
DIN 3852 part 3 bzw. ISO 6149
and
Port tapping UN/UNF-2B
for O-ring sealing (SAE J514)
tube o.d.
series
LL
L
4
6/8
6
8
10
12
15
18
22
28
35
42
8/10
12
- 12-18
- 12-22
- 22/28
- 22-35
- 35/42
4/6/8 6
- 6-12
- 10/12
- 12-18
22
28
35
42
S
6
8
10
12
14
16
20
25
30
38
8
10/12
12-20
16/20
20/25
25/30
30/38
6-12
10/12
12-16
20
25
30
38
thread
d1
M8 x 1
M10 x 1
M12 x 1,5
M14 x 1,5
M16 x 1,5
M18 x 1,5
M20 x 1,5
M22 x 1,5
M26 x 1,5
M27 x 2
M33 x 2
M42 x 2
M48 x 2
7/16-20 UNF-2B*
9/16-18 UNF-2B
3/4-16 UNF-2B
7/8 -14 UNF-2B
1 1/16-12 UN-2B
1 5/16-12 UN-2B
1 5/8-12 UN-2B
1/8-27 NPT
1/4-18 NPT
3/8-18 NPT
1/2-14 NPT
3/4-14 NPT
1-11,5 NPT
1 1/4-11,5 NPT
1 1/2-11,5 NPT
D53)
10,9
12,9
16,9
18,9
20,9
22,9
24,9
26,9
30,9
31,9
37,9
47,9
54,9
14,4
17,6
22,3
25,5
31,9
38,2
47,7
Tolerance UNF thread D5 = 0,2/a2 = +0,3
Tolerance M thread
D5 = 0,1/a2 = +0,4
3) Shoulder required, if the across corners of hexagon are larger
than recess d4 UNF-male stud always with shoulder.
d4
min
17
20
22
25
27
29
32
34
37
40
46
56
64
21
25
30
34
41
49
58
d3
11
13
16
18
20
22
24
26
31
32
38
47
53
15
18
23
26
32
39
48
d2
+0,1
9,1
11,1
13,8
15,8
17,8
19,8
21,8
23,8
29,05
29,4
35,4
44,4
50,4
12,4
15,6
20,6
23,9
29,2
35,5
43,5
a1
max
1
1
1,5
1,5
1,5
2
2
2
2
2
2,5
2,5
2,5
1,6
1,6
2,4
2,4
2,4
3,2
3,2
a2
1,6
1,6
2,4
2,4
2,4
2,4
2,4
2,4
3,1
3,1
3,1
3,1
3,1
2,4
2,5
2,5
2,5
3,3
3,3
3,3
b1
min
11,5
11,5
14
14
15,5
16,5
16,5
18
18,5
22
22
22,5
25
14
15,5
17,5
20
23
23
23
11,6
16,4
17,4
22,6
23,1
27,8
28,3
28,3
b2
min
10
10
11,5
11,5
13
14,5
14
15,5
16
19
19
19,5
22
11,5
12,7
14,3
16,7
19
19
19
6,9
10
10,3
13,6
14,1
16,8
17,3
17,3
10
120
120
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
120
120
150
150
150
150
150
BACK TO
*Tolerance class 2A = Male stud thread
Tolerance class 2B = Female thread
CATALOGUE
Assembling in fitting body (for steel and copper tubes)
The use of pre-assembly bodies
VOMO or pre-assembly tools are
strongly recommended for all
assemblies.
Stainless steel tube and fitting as
well as standpipe hose ends must
be preassembled in a VOMO body
or pre-assembly tool.
A) Preparing the tube
1 Maximum height H for straight tube end
The portion of straight tube
H must not deviate from
roundness and straightness
to the extent that the tube
tolerances in DIN 2391 are
exceeded.
Series
Tube o.d.
H min.
L min.
Minimum length L for
short piece of tube
LL
L
S
4 5 6 8 6 8 10 12 15 18 22 28 35 42 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 25 30 38
24 25 25 26 31 31 33 33 36 38 42 42 48 48 35 35 37 37 43 43 50 54 58 65
30 32 32 33 39 39 42 42 45 48 53 53 60 60 44 44 47 47 54 54 63 68 73 82
4 Attention: Do not use tube cutters!
A
G
E
a) tube cut with tube cutter:
heavy burr/bevel cut
Saw off tube square
1/20 angle tolerance to the tube axis.
Cutting the tube square is made easy
with our tube cutting guide (AV).
b) sawn off tube: hardly any burr
B) Preparing fittings parts with lubricants
5
Lightly de burr inside and outside
edge.
Bevel up to 0,2 x 45o permissible.
Is a support sleeve necessary?
Lubricate thread and cone fitting body, also EO-progressive ring and thread of
nut.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Assembly in fitting body (for steel and copper tubes)
C) Components
7
Slip nut and progressive ring over
tube end
D) Assembly
8
Ensure progressive ring and nut are
facing the right way
Screw on nut manually on to fitting
body until fingertight. Hold tube
against the shoulder in the cone of
fitting body.
P
E) Check
10
11
12*
G
E
To measure the prescribed turns of
the nut mark nut and tube
F) Final assembly
Tighten nut 1 1/2 turns (Tube must not
turn with nut). Stop edge limits over
tightening by increasing tightening
torque.
Loosen nut. Remove tube from fitting
and check if a visible collar fills space
in front of 1st cutting edge completely. If not - tighten slightly more. It
does not matter if ring can be rotated
on tube end.
G) Repeated assembly
13
14
Final assembly of all pre-assembled
fittings (EVW, EVT, EVL, EVGE-ED,
MAV-EV and KOR) made in the
appropriate body (well lubricated)
with at least 1/2 turn of the nut
beyond the point of a clearly perceptible resistance.
On remaking joints, nut to be tightened without increased effort. Body
to be held tight.
*After dismantling the tube ends for inspection they
should be refitted into the same inner cone of the fitting body in which assembly was carried out.
Warning:
We warn against using sealing heads, form A, DIN
3868. We recommend the use of swivel nuts, form B
in conformance with DIN 3865. (DKO connections.)
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Assembling in hardened pre-assembly body (VOMO)
with subsequent final assembly
A) Inspection of pre-assembly bodies (VOMO)
For frequent assembly of stainless
steel tube as well as hose standpipe
fittings pre-assembly must take
place exclusively in the pre-assembly bodies VOMO or with preassembly tools/machines.
15
16
The cones of the pre-assembly bodies VOMO are subject to normal wear
and must be checked regularly (after
every 50th pre-assembly) with cone
gauges for trueness. Untrue preassembly bodies must be replaced to
avoid poor quality assemblies.
Use of cone gauges:
The rear of the gauge most protrude
slightly above the top face of the 24o
cone or may be flush with the top
face.
If these conditions are not satisfied,
the pre-assembly body is no longer
dimensionally correct. Bodies must
be checked visually for longitudinal
scoring or other damage which
would not be shown by the gauge.
P
B) Preparing the tube
17
18
19 Attention: Do not use tube cutter!
A
G
E
a) tube cut with tube cutter:
heavy burr/bevel cut
Saw off tube square
1/2o angle tolerance to the tube axis.
Cutting the tube square is made easy
with EO cutting tool (AV).
b) sawn off tube: hardly any burr
C) Treatment with lubricants
20
Lightly de burr inside and outside
edge.
Bevel up to 0,2 x 45o permissible.
Is a support sleeve necessary?
21
Clamp the pre-assembly body-according to tube size and series-in the vice,
coat all parts (VOMO thread and taper, progressive ring, thread of the nut) with
lubricant.
For stainless material we recommend EO NIROMONT FLUID OR PASTE
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Assembly in hardened pre-assembly body (VOMO)
with subsequent final assembly
D) Components
22
Slip nut and progressive ring over
tube end
23
E) Pre-assembly
24
Ensure progressive ring and nut are
facing the right way
Screw on nut manually until fingertight, hold tube against stop in internal cone of pre-assembly body.
To measure the prescribed turns of
the nut mark nut and tube.
Turn nut approx. 1 turn, progressive
ring will have cut into the tube (tube
must not turn).
F) Check pre-assembly
G) Final assembly
25
26
H) Final assembly of preinstalled fittings
P
A
27
G
After the pre-assembly check whether
there is a visible collar in front of the cutting edge
Check the fit of the pre-assembled tube of
the tube stop of a fitting body. Use a partially split fitting for this. The top face of
the pre-assembled tube must touch the
tube stop of the fitting body.
I) Check of final assembly
28
Loosen the nut remove tube and
check whether a clearly visible collar
fills space in front of the first cutting
edge. The collar for stainless tubes
is less than for steel tubes due to the
material hardness. It does not matter if the progressive ring can be
rotated on the tube end.
Put pre-installed tube into fitting
body, tighten by approx. 1/2 turns of
nut beyond point of clearly preceptible resistance.
Final assembly of all pre-assembled
fittings (EVW, EVT, EVL, EVGE-ED,
MAV-EV and KOR) is made in the
appropriate body (well lubricated) with
at least 1/2 turn of the nut beyond the
point of a clearly perceptible resistance.
J) Repeated assembly
29
On remaking joint, nut to be tightened without increased effort, body
to be held tight.
The assembly of stainless steel tube is
made easier by unscrewing the nut a
few times and treating the thread with
lubricant. (This applies for paste and
spray-on lubricants). For liquid lubricants loosening of the nut is sufficient
so that lubricant can get between the
contact surfaces.
It is recommended that test assemblies
should be made before hand with
tubes of a greater rigidity or special
materials. If in doubt, please send us
an approx. 30cm long tube end for test
assembly.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Assembling with support sleeves (VH)
Fig. 1
The thickness of the tube wall is often governed by the requirements of the internal pressure without taking the tube fittings and any
external influences into account. If the tube wall
thickness is relatively low in relation to the
external diameters of the tube this may lead to
greater tube limitations (as a rule, the tube constriction should not exceed 0,3mm for tubes up
to o.d. 16 and 0,4 mm for tubes from o.d. 18
upwards).
When assembling thin walled tubing there is
insufficient cross sectional rigidity where the
progressive ring cuts. This will have a detrimental effect on the sealing efficiency.
For this support sleeves VH are available which
are inserted in tube to prevent constriction and
increase the cross-sectional rigidity respectively.
Their shape allows them to be inserted easily in
the tube. One end of the EO support sleeve is
enlarged on its external diameter by a knurl.
On insertion this knurl forces itself into the inte- Fig. 2
rior wall of the tube and secures the sleeve
against shifting or falling out during assembly
and without widening the tube end.
Steel tubes made of St 35 or soft metal tubes
can be checked in accordance with tables 1
and 2 to see if they require support sleeves; for
plastic tubes stop (support) sleeves are always
necessary.
P
A
G
E
support sleeve
VH
EO fitting completely assembled with support sleeve.
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Assembly of support sleeves
30
Saw off tube square
1/2o angle tolerance to the tube axis.
31
32 Attention: Do not use tube cutter!
Cutting the tube square is made easy
with EO cutting tool (AV)
b) sawn off tube: hardy any burr
P
A
33
34
35
G
E
Lightly de burr inside and outside
edge (Attention: do not chamfer)
Insert support sleeve up to knurl
36
37
Ensure support sleeve is flush with
tube end*
No necking of tube visible after
assembly with support sleeve
Drive knurl edge into tube
BACK TO
*Further assembly
CATALOGUE
Tube fittings (non-adjustable)
The fittings listed in this chapter conform with market
requirements in variety of types, size and nominal pressures.
for male stud fittings in Brass (CuZn 35 Ni), Stainless
Steel (1.4571) on request.
Torque values for taper threads e.g. NPT, and UNF or
ISO 6149 also on request.
Part numbers
Sealing of tapered male stud threads:
The specified part numbers refer to steel fittings. For
ordering stainless or brass fittings /71 or /MS respec- Tapered male stud threads are not self-sealing.
Additional sealant is necessary to achieve a leaktively should be suffixed to the part number given.
proof seal. The use of PTFE (e.g. Teflon) sealing tape
has been proven in practice.
Standard range
Types not readily available in the standard range are
identified by the weights in brackets in the respective
weight column assigned to the material.
Notes:
The specified values apply for steel fittings either
with phosphated and oiled or zinc plated surface
Recommended tightening torques MA:
protection and refer to the port material also of steel.
The table below shows the Nm value required to eliminate thread leakage of male stud fittings with seal form B ( )* values apply for male studs with EOLASTIC seal.
For Ri fittings series S figures are to be used.
(DIN 3852) and EOLASTIC seals. Torque values
P
Series
tube
o.d.
6
8
10
12
15
18
22
28
35
42
6
8
10
12
14
16
20
25
30
38
BSP thread
G 1/8 A
G 1/4 A
G 1/4 A
G 3/8 A
G 1/2 A
G 1/2 A
G 3/4 A
G1A
G 1 1/4 A
G 1 1/2 A
G 1/4 A
G 1/4 A
G 3/8 A
G 3/8 A
G 1/2 A
G 1/2 A
G 3/4 A
G1A
G 1 1/4 A
G 1 1/2 A
Male stud thread
MA (Nm)
Metr. ISO-thread
25
M10 x 1
50
M12 x 1,5
50
M14 x 1,5
80
M16 x 1,5
160
M18 x 1,5
105
M22 x 1,5
220
M26 x 1,5
370
M33 x 2
600
M42 x 2
800
M48 x 2
60
M12 x 1,5
60
M14 x 1,5
110
M16 x 1,5
110
M18 x 1,5
170
M20 x 1,5
140
M22 x 1,5
320 (250)*
M27 x 2
380
M33 x 2
600
M42 x 2
800
M48 x 2
MA (Nm)
25
30
50
80
90
160
285
425
600
800
35
60
95
120
170
190
320 (250)*
500
600
800
A
G
E
BACK TO
CATALOGUE
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanical Properties Min. 0,2 % Yield Strength Values at Increased TemperaturesDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties Min. 0,2 % Yield Strength Values at Increased TemperaturesJarek CieslakPas encore d'évaluation
- PED 2014-68-EU Guidelines EN v4Document235 pagesPED 2014-68-EU Guidelines EN v4Nav TalukdarPas encore d'évaluation
- B Jack Nos For Cs Ss MaterialDocument12 pagesB Jack Nos For Cs Ss MaterialfahadfiazPas encore d'évaluation
- HB D KomplettDocument181 pagesHB D KomplettGabriel BourguignonPas encore d'évaluation
- Knife Gate Valve - AVKCMSDocument2 pagesKnife Gate Valve - AVKCMSjuantamad02Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sa 420Document10 pagesSa 420Widya widyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Contact Molded "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) FlangesDocument5 pagesContact Molded "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) FlangesJosé Luis Sierra100% (1)
- Iso 228 1 2000Document9 pagesIso 228 1 2000Ulvi NebiyevPas encore d'évaluation
- 554 PDFDocument10 pages554 PDFyogiforyouPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2379 Tool SteelDocument8 pages1.2379 Tool Steelsmith willPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm B 729 - 2000 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm B 729 - 2000 PDFLemir LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Drawn Seamless Tube DIN 2391 C ST 37.4 NBKDocument3 pagesCold Drawn Seamless Tube DIN 2391 C ST 37.4 NBKtappannPas encore d'évaluation
- L9 Fastening System PDFDocument6 pagesL9 Fastening System PDFMarcel BaquePas encore d'évaluation
- En 12451 1999Document24 pagesEn 12451 1999victoraghiPas encore d'évaluation
- E91 202006 20orifice 20plate 20 - 20doschDocument6 pagesE91 202006 20orifice 20plate 20 - 20doschiaft100% (1)
- Din 7623Document2 pagesDin 7623Racha Amel100% (1)
- Whitworth Tapered Pipe Thread DIN EN 10226-1, DIN EN 10226-2 Formerly Known As DIN 2999 BSPT (British Standard Tapered Pipe)Document1 pageWhitworth Tapered Pipe Thread DIN EN 10226-1, DIN EN 10226-2 Formerly Known As DIN 2999 BSPT (British Standard Tapered Pipe)LucianNechiforPas encore d'évaluation
- Garlock GYLON Style 3501 - Spec Sheet - (NA) 2016-12 enDocument1 pageGarlock GYLON Style 3501 - Spec Sheet - (NA) 2016-12 ennmosilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Es7 PDFDocument4 pagesEs7 PDFayoungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Steel and StandardsDocument2 pagesTypes of Steel and Standardsewva12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Material Comparisons For Astm and JisDocument2 pagesMaterial Comparisons For Astm and JisNitesh GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Thread Standard BSPDocument7 pagesThread Standard BSPĐạt TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Din 3357-4-1981Document5 pagesDin 3357-4-1981олегPas encore d'évaluation
- Din125 WasherDocument2 pagesDin125 WasherHieu TranvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sae J1231-2011Document14 pagesSae J1231-2011Ace LeePas encore d'évaluation
- ASME B16.47!75!300# Series B Flanges With FLEXSEAL Spiral Wound GasketsDocument5 pagesASME B16.47!75!300# Series B Flanges With FLEXSEAL Spiral Wound Gasketserik aranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Counter Weight Drawing MCT85Document14 pagesCounter Weight Drawing MCT85Nirmalya SenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2520 z000 STD 1780 06 - B Anchor Bolt DetailDocument2 pages2520 z000 STD 1780 06 - B Anchor Bolt Detailabdul mujeebPas encore d'évaluation
- GB T 699 1988 Quality Carbon Structural SteelsDocument17 pagesGB T 699 1988 Quality Carbon Structural SteelsPHUONGPas encore d'évaluation
- 복사본 볼트규격표Document20 pages복사본 볼트규격표임동섭Pas encore d'évaluation
- A276 PDFDocument8 pagesA276 PDFsingaravelan narayanasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 5151Document18 pagesBS 5151Steva76Pas encore d'évaluation
- DIN 2527-1972, Blank FlangesDocument6 pagesDIN 2527-1972, Blank FlangesalfredopinillosPas encore d'évaluation
- Hinge DesignDocument2 pagesHinge Designpare222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Fillet Weld (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, CL 4.5.3) : KN M KN KN M KN KN MMDocument2 pagesDesign of Fillet Weld (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, CL 4.5.3) : KN M KN KN M KN KN MMGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Properties of Bolted JointsDocument5 pagesStructural Properties of Bolted JointsL095244Pas encore d'évaluation
- Low-Pressure Hoselines SN 544: Double Nipple Welding NippleDocument2 pagesLow-Pressure Hoselines SN 544: Double Nipple Welding NippleNaveen Kumar Chauhan100% (1)
- 1 2312 PDFDocument4 pages1 2312 PDFFrancisco CarrascoPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 3799 (74) Specification For Steel Pipe Fittings, Screwed and Socket-Welding For The Petroleum Industry PDFDocument32 pagesBS 3799 (74) Specification For Steel Pipe Fittings, Screwed and Socket-Welding For The Petroleum Industry PDFjodasi300% (1)
- SN756 2005-02 eDocument4 pagesSN756 2005-02 eChristopher Lloyd100% (1)
- VagogyuruDocument856 pagesVagogyurupsnmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sa 299Document3 pagesSa 299Web LogueandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade Chemical Composition (% by Mass - Max Unless Stated) Ferritic SteelsDocument15 pagesGrade Chemical Composition (% by Mass - Max Unless Stated) Ferritic SteelsSenthil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Din 976-1 1995Document6 pagesDin 976-1 1995Charmaine DrafkePas encore d'évaluation
- FDA and 1935 2004 DoC General Food Contact Regulations BU HFH Rev 008Document15 pagesFDA and 1935 2004 DoC General Food Contact Regulations BU HFH Rev 008Gisela ViskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Din 2526 PDFDocument1 pageDin 2526 PDFDaniel TrombimPas encore d'évaluation
- Butterfly ValvesDocument27 pagesButterfly ValvesИгорьPas encore d'évaluation
- Bs7531 Grade y MasterDocument1 pageBs7531 Grade y Masterheena jainPas encore d'évaluation
- PASCAL Check Valves CatalogueDocument19 pagesPASCAL Check Valves Cataloguecrys100% (1)
- DIN580 Eye BoltDocument7 pagesDIN580 Eye BoltReda El-AwadyPas encore d'évaluation
- DIN ArruelasDocument35 pagesDIN ArruelasSigurbjörnBárðarsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Virgo Trunnion Ball ValveDocument16 pagesVirgo Trunnion Ball ValveKamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Din 5401 PDFDocument12 pagesDin 5401 PDFLuciano FontesPas encore d'évaluation
- Din Flange Din 2627: (Dimensions in MM.)Document12 pagesDin Flange Din 2627: (Dimensions in MM.)Wisüttisäk PeäröönPas encore d'évaluation
- BF-PPS As Dismantling Joints - EngDocument3 pagesBF-PPS As Dismantling Joints - EngbikarexpansionjointsPas encore d'évaluation
- Fittings Din11852 Din11850Document14 pagesFittings Din11852 Din11850dingobk1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bottom Failure - Annex K - en 14015 - Rev 3Document3 pagesBottom Failure - Annex K - en 14015 - Rev 3KP SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987D'EverandProceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987W. R. TysonPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME Code Calculations For Companion FlangesDocument9 pagesASME Code Calculations For Companion FlangesKamlesh DalavadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Layout For Fire Sprinkler System PDFDocument5 pagesPiping Layout For Fire Sprinkler System PDFJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- LavavajillasDocument230 pagesLavavajillasJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Mechanical PDFDocument10 pages04 Mechanical PDFsaima shafiPas encore d'évaluation
- AstroFrame AFP 10 758Document1 pageAstroFrame AFP 10 758Javier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASHRAE Journal - The Fundamentals of Expansion TanksDocument7 pagesASHRAE Journal - The Fundamentals of Expansion TanksJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1612 CarbCounter OnlineDocument30 pages1612 CarbCounter OnlineJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1612 CarbCounter OnlineDocument30 pages1612 CarbCounter OnlineJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Smacna Cad StandardDocument149 pagesSmacna Cad Standardilm11280088% (8)
- Fire Hose Friction LossDocument1 pageFire Hose Friction LossJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Pipe Sizes ME303-4.1.1Document5 pagesStandard Pipe Sizes ME303-4.1.1manashbdPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Water SystemsDocument28 pagesHot Water SystemsalejovelPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping DesignDocument2 pagesPiping DesignJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Vertical Ladders 090420Document10 pagesFixed Vertical Ladders 090420Javier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- CropsDocument10 pagesCropsJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump SelectionDocument112 pagesPump SelectionSIVAPATHASEKARAN100% (6)
- FastenersDocument46 pagesFastenerser_lalitgargPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping DesignDocument2 pagesPiping DesignJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump SelectionDocument112 pagesPump SelectionSIVAPATHASEKARAN100% (6)
- Diferenciales Super InmunizadosDocument2 pagesDiferenciales Super InmunizadosJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Esquema Lavadero 1Document1 pageEsquema Lavadero 1Javier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Cyclone Dust CollectorsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Cyclone Dust CollectorsJavier VespaPas encore d'évaluation
- All Product CatalogueDocument22 pagesAll Product CataloguekokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Welch DryDocument6 pagesWelch DryRyanRRPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of PTFEDocument2 pagesProperties of PTFEmister_no34Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polyethylene: Industrial Polymers 1.polyethylene Terephthalate (PET, PETE)Document11 pagesPolyethylene: Industrial Polymers 1.polyethylene Terephthalate (PET, PETE)Muhammad TanweerPas encore d'évaluation
- SSI Catalog-2011 PDFDocument16 pagesSSI Catalog-2011 PDFrafael100% (1)
- Ulrich - A Guide To Chemical Engineering Process Design and EconomicsDocument484 pagesUlrich - A Guide To Chemical Engineering Process Design and Economicsrahadian92% (12)
- Flammability TestDocument6 pagesFlammability TestAlpesh SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- Produktfolder Ensinger Compounds EnglishDocument16 pagesProduktfolder Ensinger Compounds Englishphap thuPas encore d'évaluation
- DLA Cat EUROPE - Multiple Address - English - Low Res PDFDocument18 pagesDLA Cat EUROPE - Multiple Address - English - Low Res PDFAnonymous cVnKDdhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sefar ArchitectureDocument67 pagesSefar ArchitecturecarlosdayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 MeterialsDocument12 pages2 MeterialsthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- General Informaion Box PackingsDocument8 pagesGeneral Informaion Box PackingsJohn TLPas encore d'évaluation
- TLV JA3 Air Drain TrapDocument2 pagesTLV JA3 Air Drain TrapMONAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ProjectDocument32 pagesChemistry ProjectUday Singh RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- KSB MKDocument24 pagesKSB MKDavid MejidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guideline For: Specifications and Salvage For Spacer Plates On 3500 EnginesDocument9 pagesGuideline For: Specifications and Salvage For Spacer Plates On 3500 EnginesStasPas encore d'évaluation
- Technoflex Corporation Profile PDFDocument12 pagesTechnoflex Corporation Profile PDFTuan DangPas encore d'évaluation
- IRECN Bridge Bearing-2Document21 pagesIRECN Bridge Bearing-2vpmohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Tribology of Polymers and Their Composites - Environmental EffectsDocument45 pagesTribology of Polymers and Their Composites - Environmental EffectsJigar M. UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Texfilm1009 ExpJnt DSDocument1 pageTexfilm1009 ExpJnt DSdanny buiPas encore d'évaluation
- PTFE 25% Carbon FilledDocument1 pagePTFE 25% Carbon FilledIan Putra Adita WibisanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Polymer Bearings General CatalogDocument95 pagesMetal Polymer Bearings General Catalogwe427Pas encore d'évaluation
- Additive ComponentsDocument32 pagesAdditive ComponentsmaiatostiPas encore d'évaluation
- Regular Grade Anti-Seize & Lubricating Compound: Never SeezDocument2 pagesRegular Grade Anti-Seize & Lubricating Compound: Never SeezGregory Alan Francisco IIPas encore d'évaluation
- PTEF M - PTFE GBK Sheet, PFA Welding Rod and Cap StripDocument3 pagesPTEF M - PTFE GBK Sheet, PFA Welding Rod and Cap StripmansurudinPas encore d'évaluation
- L Uk PackingDocument24 pagesL Uk PackingBisoyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Packings: Static Applications For Pumps For ValvesDocument9 pagesPackings: Static Applications For Pumps For ValvesИштванPas encore d'évaluation
- Plug Valve FluoroSeal Plug SleevedDocument44 pagesPlug Valve FluoroSeal Plug SleevedbijinlalPas encore d'évaluation
- BRL K21011 02Document35 pagesBRL K21011 02bruno383Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gardco ASTM ThermometersDocument15 pagesGardco ASTM ThermometersmegacobPas encore d'évaluation