Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
08 Pheno
Transféré par
Utami IndyastutiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
08 Pheno
Transféré par
Utami IndyastutiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
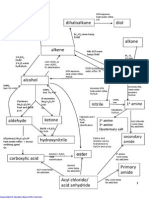
Phenol
F324
PHENOL
OH
Structure
phenol is an aromatic alcohol
the OH group is attached directly to the benzene ring
it is an almost colourless crystalline solid of formula C6H5OH
Uses
production of
plastics
antiseptics
disinfectants
resins for paints
Preparation you cannot put an OH group directly onto benzene by electrophilic substitution
phenol is synthesised in a multi-stage process
Nitration of
benzene
Reduction of
nitrobenzene
Diazotisation of
phenylamine
Substitution
N 2+ Cl
NH2
NO2
OH
reagents
conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid (catalyst)
conditions
reflux at 55C
equation
C6H6
mechanism
electrophilic substitution
reagents
tin and conc. hydrochloric acid
conditions
reflux
equation
C6H5NO2
reagents
nitrous acid and hydrochloric acid (use sodium nitrite)
conditions
keep below 10C
equation
C6H5NH2 + HNO2 + HCl
reaction type
diazotisation
reagents
water
conditions
warm above 10C
equation
C6H5N2+ Cl +
HNO3
>
6 [H]
H2O
KNOCKHARDY SCIENCE 2008
>
C6H5NO2
C6H5NH2
H2O
+ 2H2O
> C6H5N2+ Cl + 2H2O
> C6H5OH
N2 + HCl
Phenol
F324
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF PHENOL
Reactions of the -OH group
Water
phenol is a weak acid
it is a stronger acid than aliphatic alcohols
the aromatic ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion
it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution
C6H5OH(aq)
NaOH
H+(aq)
phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form a salt - sodium phenoxide
it is ionic and water soluble
C6H5OH(aq)
Sodium
C6H5O(aq)
NaOH(aq)
>
C6H5O Na+(aq)
H2O(l)
phenol reacts with sodium to form an ionic salt - sodium phenoxide
hydrogen is also produced
this reaction is similar to that with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol
2C6H5OH(s)
2Na(s)
>
2C6H5O Na+(s)
H2(g)
Reactions of the benzene ring
ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION
Bromine
the OH group is electron releasing
O
electron pair donation takes place
from a p orbital on oxygen
it increases the electron density of the delocalised system
it makes substitution much easier compared to benzene
the electron density is greatest at the 2,4 and 6 positions
substitution takes place at the 2,4 and 6 positions
phenol reacts readily with bromine water WITHOUT A CATALYST
it is so easy that multiple substitution takes place
OH
OH
Br
Br
3Br2
Br
other electrophiles such as NO2+ react in a similar way
KNOCKHARDY SCIENCE 2008
3HBr
OH
Phenol
Q.1
F324
For each of the following compounds...
(a) work out the molecular formula
(b) state its use or importance
(c) classify as 1, 2 or 3 aliphatic alcohols or phenols (or both)
Vitamin A
OH
OH
Estradiol
HO
OH
Testosterone
NH
Paracetamol
O
HO
OH
Picric acid
O2 N
NO2
NO2
Cholesterol
HO
Menthol
OH
OH
4-chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
Dettol
CH3
CH3
Cl
Ethane-1,2-diol
HO
OH
KNOCKHARDY SCIENCE 2008
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaPas encore d'évaluation
- Method For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining ForumDocument11 pagesMethod For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining Forummladen lakic100% (1)
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument9 pagesHydroxy Compoundschong56Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChE461-Course Outline and Teaching ScheduleDocument2 pagesChE461-Course Outline and Teaching ScheduleAl JawadPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDocument78 pagesFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Organic Reaction SummaryDocument8 pagesA2 Organic Reaction SummaryJessie Wu100% (1)
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NotesDocument8 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Notesmajji satishPas encore d'évaluation
- Oisd 142Document55 pagesOisd 142sandeep MPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrochem 10 - SEM 1 12-13Document40 pagesPetrochem 10 - SEM 1 12-13Saifuddin AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning Bones: General GuidelinesDocument4 pagesCleaning Bones: General GuidelinesSaira SepulvidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersPas encore d'évaluation
- Component in Making Fiber Board As Substitute For HardiflexDocument9 pagesComponent in Making Fiber Board As Substitute For Hardiflexxiniac_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- DR FCC PDFDocument7 pagesDR FCC PDFAle SanzPas encore d'évaluation
- Operator Manual BT4500-00ING PDFDocument153 pagesOperator Manual BT4500-00ING PDFquanvh0% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Advanced Chemistry AlcohoDocument17 pagesLesson Plan in Advanced Chemistry AlcohoGlaiza Mapute CaringalPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsPas encore d'évaluation
- PhenolDocument3 pagesPhenolNurul SyuhaidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture# PhenolDocument16 pagesLecture# PhenolRao Wazim AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Xii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSDocument10 pagesXii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSTanmay RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- CHY 32.1 Alcohols and PhenolsDocument37 pagesCHY 32.1 Alcohols and PhenolsMA. NECOLE JEREMIAH GONZALESPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Enolates Enamines-2Document59 pages19 Enolates Enamines-2ronPas encore d'évaluation
- Phenol 203Document47 pagesPhenol 203ajibolaakorede20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 13 Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives-Hannah-PcDocument22 pagesLesson 13 Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives-Hannah-Pcdela2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 22 Reactions of BenzeneDocument51 pages22 Reactions of Benzeneimade100% (1)
- Alcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Document7 pagesAlcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Kaviraj SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolDocument59 pagesHydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- PhenolDocument7 pagesPhenolissraaflower0% (1)
- Organic ReactionsDocument4 pagesOrganic ReactionsRobbing_HoodPas encore d'évaluation
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDocument21 pages20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohols and Ethers CHM457Document51 pagesAlcohols and Ethers CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toluene, Chlorobenzene For HSDocument49 pagesToluene, Chlorobenzene For HSSubhasish SauPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivatesDocument10 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their Derivatesvita iftitahiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Phenol SDocument32 pagesPhenol SBangaloredPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydroxy CompoundDocument37 pagesHydroxy CompoundZuhailimuna MudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesAldehydes and KetonesCamille AdlePas encore d'évaluation
- Alkenes Reactions and SynthesisDocument51 pagesAlkenes Reactions and SynthesisnursenaPas encore d'évaluation
- AreneDocument37 pagesArene'Aqilah ZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsDocument12 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsAmihanPas encore d'évaluation
- Formation of C-C Bonds by Acid-Catalyzed CondensationsDocument21 pagesFormation of C-C Bonds by Acid-Catalyzed CondensationsThabiso GwijiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohol PhenoletherDocument14 pagesAlcohol Phenoletheritsleochandu21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument15 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsSUSHMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17Document35 pagesChapter 17Mohammed FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Drug - 1Document42 pagesSynthesis of Drug - 1'Nurirjawati ElRuri KawangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document39 pagesChapter 6c4.arsyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24Document71 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24jjprakash82chemPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydroxy Compounds: (Alcohols)Document71 pagesHydroxy Compounds: (Alcohols)NorsyazaEdmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesDocument13 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesaqidahPas encore d'évaluation
- PhenolDocument14 pagesPhenolWirda ZafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Groups - Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Learning Question: How Do Functional Groups Affect TheDocument20 pagesFunctional Groups - Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Learning Question: How Do Functional Groups Affect TheemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesOrganic Synthesis Notesgarwade72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17Document74 pagesChapter 17Vasudevan SubramaniyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 pagesMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 25b: Phenols and Quinones: Suggested Problems: 12, 14, 15, 16, 33, 37, 42 (Problems in Bold Face Are HIGHLYDocument4 pagesChapter 25b: Phenols and Quinones: Suggested Problems: 12, 14, 15, 16, 33, 37, 42 (Problems in Bold Face Are HIGHLYaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 Lecture NotesDocument30 pagesChapter 16 Lecture NotesJuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - PhenolsDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Phenolsdr.3nonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument9 pagesCarboxylic Acids and DerivativesDương Thị Ngọc HiềnPas encore d'évaluation
- Tautomeria y Oxido ReduccionDocument44 pagesTautomeria y Oxido ReduccionRoxana PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Org Chem Alcohol Mechanisms From JasperseDocument22 pagesOrg Chem Alcohol Mechanisms From JasperseChloe JazminesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch7Summary AlcoholDocument6 pagesCh7Summary AlcoholdanielmahsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument70 pagesWord Problems in Organic ChemistryreghuuchihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reatividade Carbonilas Chap19Document41 pagesReatividade Carbonilas Chap19darthcaedusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Unit 4Document23 pagesChemistry: Unit 4Ahmad HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- EthersDocument6 pagesEthersCCPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesDocument15 pagesRamabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesFernanda SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Zhang 2022Document10 pagesZhang 2022Statistics LearningPas encore d'évaluation
- HAl 499-500 PDFDocument9 pagesHAl 499-500 PDFPutri AzzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- TIAC TechnologyDocument13 pagesTIAC TechnologyPaul SunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experilab Breinwave: Bubble BlowersDocument4 pagesExperilab Breinwave: Bubble BlowersHirenkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- NESC Diploma - MillwrightDocument2 pagesNESC Diploma - MillwrightjamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochures WSM2-Y PDFDocument16 pagesBrochures WSM2-Y PDFkunkzPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyglykol Declaration On Correlations Between PH - Eur. or USP-NF and Clariant Methods (Version 01 - 2018)Document5 pagesPolyglykol Declaration On Correlations Between PH - Eur. or USP-NF and Clariant Methods (Version 01 - 2018)verpacking pimPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Capacity Lab ReportDocument8 pagesHeat Capacity Lab ReportLiHong Khaw100% (1)
- Clay Notes (4th Sem)Document21 pagesClay Notes (4th Sem)SamPas encore d'évaluation
- (Artigo) - Etching Isothermally Treated Steels - G. F. v. VOORTDocument8 pages(Artigo) - Etching Isothermally Treated Steels - G. F. v. VOORTcandongueiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sofw Thickening AgentsDocument8 pagesSofw Thickening AgentsPulbere NeagraPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Remedial Module PDFDocument185 pagesBiology Remedial Module PDFBetseha Merawi67% (3)
- Pre - Use Inspection Qualification: Date: Equipment Welding Machine Serial Number Model: LocationDocument3 pagesPre - Use Inspection Qualification: Date: Equipment Welding Machine Serial Number Model: LocationEugenio Jr. MatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 11: General Biology IDocument38 pagesGrade 11: General Biology ITEOFILO GATDULAPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report Final-1Document33 pagesProject Report Final-1Sahil ChelatPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissolution GelatinDocument14 pagesDissolution Gelatinايناس ماجدPas encore d'évaluation
- E Shield6421 Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageE Shield6421 Datasheet PDFYo APas encore d'évaluation
- Part 7 StoichiometryDocument59 pagesPart 7 Stoichiometryjasumin91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sum11 Pharma PDFDocument29 pagesSum11 Pharma PDFMostofa RubalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nta Abhyas Test-65 CDocument5 pagesNta Abhyas Test-65 CMIITY EDUPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation Rate of Solvents PDFDocument2 pagesEvaporation Rate of Solvents PDFsyamlokPas encore d'évaluation