Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Concept 1
Transféré par
ccffyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Understanding Concept 1
Transféré par
ccffyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name__________________________________ Class__________________ Date________________
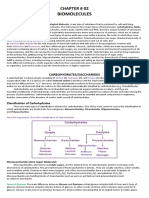
Chapter 1: Molecules of life
[5 major classes molecules which make up the bodies of living organism]
Learning outcome
Water
Explain the structure of
water molecule
Describe the properties
of water and its
importance: universal
solvent, low viscosity,
high specific heat
capacity, high latent heat
of vaporization, high
surface tension,
maximum density at 4
C.
Carbohydrate
Describe various forms
and classes of
carbohydrates such as
monosaccharide,
disaccharides and
polysaccharides
Lipid
State the types of lipid:
fat, oil, phospholipids
and steroids
Describe the formation
and breakdown of
maltose
Describe the formation
and breakdown of
triglycerides.
Describe the structure of
fatty acid and glycerol
Describe the structures
and function of starch,
glycogen and cellulose
1.1 Water
True or False
Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false.
______ 1. Hydrogen bonds form between hydrogen atoms of adjacent water molecules.
______ 2. Nonpolar substances are more soluble in water than are polar substances.
______ 3.Hydrogen bond cause water to be denser as ice than as liquid
______ 4.Hydrogen bonds cause water to absorb heat with maximum change in temperature.
______ 5. Hydrogen bonding cause water molecules to be cohesive.
______ 6. Hydrogen bonds cause water to boil at a higher temperature than expected.
______ 7. Humans are composed of about 95 percent water.
______ 8. Water molecules are released during condensation reaction
Name__________________________________ Class__________________ Date________________
Fill in the Blank
Insert the following statements into the most appropriate column in the following table.
Properties
Explanation
Heat is absorbed or released
when hydrogen bonds break
or form. Water absorbs or
releases a large quatity of
heat for each degree of
temperature change.
Importance
Water column is pulled up
through plant vessels.
High latent heat of
vaporization
Floating ice acts as an
insulator to prevent the water
below it from freezing.
Low viscosity
Polar water molecules
surrround and dissolve ioinic
and polar solutes.
Water molecules is a small is
size, easier to flow, less
resistance.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
High specific heat of capacity
Maximum density at 4oC
Water as universal solvent
High surface tension
Temperature changes in enviroment and organism are moderated.
Hydrogen bonds must be broken for water to evaporate.
Hydrogen bond are hold molecule molecules together and adhere them to hydrophilic
surface.
H. Most chemical reactions in life involve solutes dissolved in water.
I. Water is a suitable medium for transportation in living organism.
J. Hydrogen bonds in ice space water molecules apart, making ice less dense.
K. Evaporation of water cools body surfaces.
Organic Molecule- Carbohydrate and Lipid
True or False
Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false.
______ 1. Carbohydrates contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
______ 2. Table sugar is an example of a monosaccharide.
______ 3. Complex carbohydrates form the external skeleton of some animals.
______ 4. Lipids include substances such as fats and oils.
______ 5. Saturated fatty acids are found mainly in animals.
______ 6. Unsaturated fatty acids form straight chains.
Name__________________________________ Class__________________ Date________________
Critical Reading
Read this passage and answer the questions that follow.
Lipids
Lipids are organic compounds that contain mainly carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They
include substances such as fats and oils. Lipid molecules consist of fatty acids, with or
without additional molecules. Fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general
formula CH3(CH2)nCOOH, where n usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even
number.
Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated. The term saturated refers to the placement of
hydrogen atoms around the carbon atoms. In a saturated fatty acid, all the carbon atoms
(other than carbon in the -COOH group) are bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible.
Saturated fatty acids do not contain any other groups except -COOH. This is why they form
straight chains. Because of this structure, saturated fatty acids can be packed together very
tightly. This allows organisms to store chemical energy very densely. The fatty tissues of
animals contain mainly saturated fatty acids. In an unsaturated fatty acid, some carbon
atoms are not bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible. Double bond is present in
nunsaturaed fatty acid and its occur naturally in bent shapes. This gives unsaturated fatty
acids different properties than saturated fatty acids. For example, unsaturated fatty acids are
liquids at room temperature whereas saturated fatty acids are solids. Unsaturated fatty acids
are found mainly in plants, especially in fatty tissues such as nuts and seeds.
Types of Lipids
Lipids may consist of fatty acids alone or in combination with other compounds. Several
types of lipids consist of fatty acids combined with a molecule of glycerol:
Triglycerides are the main form of stored energy in animals. This type of lipid is
commonly called fat. It is composes by three fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol.
Phospholipids are a major component of the membranes surrounding the cells of all
organisms.
Steroids have several functions. The steroid cholesterol is an important part of cell
membranes and plays other vital roles in the body. Other steroids are male and female
sex hormones.
Questions
1. What are fatty acids?
2. Based on the information in passage, draw the structure of a saturated fatty acid and an
unsaturated fatty acid which have n=3.
3. Compare and contrast saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
4. What are triglycerides?
Name__________________________________ Class__________________ Date________________
Multiple Choice
Circle the letter of the correct choice.
1. Which carbohydrate is not a simple
sugar?
a. fructose
b. sucrose
c. glucose
d. amylose
3.
2. Complex carbohydrates that are used to
store energy include
a. chitin.
b. cellulose.
c. glycogen.
d. all of the above
Which statement is true of all fatty
acids?
a. They are liquids at room
temperature.
b. They can be manufactured by
the human body.
c. They consist of cholesterol and
triglycerides.
d. They contain carbon, hydrogen,
and oxygen.
Terminology
Defination
Match the term with the correct definition.
Term
___________ 1. Carbohydrate
___________ 2. Lipid
___________ 3. Phospholipid
___________4. Steroid
___________ 5. Condensation reaction
___________ 6. Hydrolysis reaction
A reaction in which two molecules become covalently
bonded to each other through the loss of a small
molecule, usually water.
an organic compound with the empirical formula
Cm(H2O)n
An organic substance which is insoluble in water but
soluble in organic solvent.
A process that splits molecules by addition of water
molecule.
A type of lipid containing carbon skeleton consisting of 4
fused rings.
a major component of the membranes surrounding
the cells of all organisms.
Draw a diagram
complete diagram given to outline how two
monosaccharides are converted into a disaccharide
through condensation, producing a glycosidic bond.
Name the glycosidic bond formed.
Write a word equation for the formation of one
triglyceride from fatty acids and glycerol.
Outline how condensation reactions produce one triglyceride molecule (including the name of
the bonds produced):
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Coconut Oil Benefits ForDocument4 pagesCoconut Oil Benefits ForB GirishPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange Lists For DiabetesDocument69 pagesExchange Lists For DiabetesJuan Lopez100% (2)
- DL Industries - Domestic Offering Circular - Nov. 26 2012 - 2Document467 pagesDL Industries - Domestic Offering Circular - Nov. 26 2012 - 2Jake VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalPas encore d'évaluation
- USLP Summary of 10 Years ProgressDocument39 pagesUSLP Summary of 10 Years ProgressRamyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Processing Manual VCO PICT - Chap 7-Annex PDFDocument78 pagesProcessing Manual VCO PICT - Chap 7-Annex PDFjosephine mataPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 - Culinary NutritionDocument28 pagesChapter 11 - Culinary NutritionLIDYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Compendium Packaging Labelling Regulations 22 01 2019 PDFDocument30 pagesCompendium Packaging Labelling Regulations 22 01 2019 PDFDesi BhaiPas encore d'évaluation
- A PositionDocument10 pagesA PositionFernanda DiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional Content and Health Benefits of SeafoodDocument17 pagesNutritional Content and Health Benefits of SeafoodElavarasan KrishnamoorthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Listening Advanced ActivatorDocument205 pagesListening Advanced ActivatorKhảiPas encore d'évaluation
- Roth 10e Nclex Chapter 01Document16 pagesRoth 10e Nclex Chapter 01Jen GatchalianPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Fitness Physical Fitness: A. How Does Physical Activity Help Build Healthy Bones?Document9 pagesPhysical Fitness Physical Fitness: A. How Does Physical Activity Help Build Healthy Bones?Francis Jay EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 MacronutrientsDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Macronutrientsr55fsf75hp100% (1)
- Slow Burn SumaryDocument10 pagesSlow Burn SumarySharizan GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- W A. P F: Eston Rice OundationDocument28 pagesW A. P F: Eston Rice OundationTyler DurdenPas encore d'évaluation
- Healthy FactsDocument2 pagesHealthy FactsAsutosh SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Gelatin Bubbles - ChelsweetsDocument3 pagesGelatin Bubbles - ChelsweetsBintPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015E Updated GuidelinesDocument1 269 pages2015E Updated GuidelinesYipno Wanhar El MawardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Amerman Test BankDocument15 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Amerman Test BankKevinHarrisoncatjn100% (19)
- 7 - Nutrition 1Document24 pages7 - Nutrition 1tamani elkhairPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits and RisksDocument7 pagesBenefits and RisksDanielle LiwanagPas encore d'évaluation
- 45 Tips To Live A Healthier Life Personal Excellence Ebook PDFDocument26 pages45 Tips To Live A Healthier Life Personal Excellence Ebook PDFMarya Fanta C LupuPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Document36 pagesLow Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Alejandro Camargo SanabriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proficiency Test & CRM FapasDocument4 pagesProficiency Test & CRM FapasNierza AlfiannurPas encore d'évaluation
- Bread Enriched With Flour From Cinereous Cockroach (Nauphoeta Cinerea)Document6 pagesBread Enriched With Flour From Cinereous Cockroach (Nauphoeta Cinerea)Rafael Zambelli100% (1)
- Gordon - Small Scale Vegetable Oil Extraction (Book) 1995Document126 pagesGordon - Small Scale Vegetable Oil Extraction (Book) 1995Andres ValderramaPas encore d'évaluation
- These 8 Practical Tips Cover The Basics of Healthy EatingDocument5 pagesThese 8 Practical Tips Cover The Basics of Healthy Eatingprofessor SamPas encore d'évaluation
- Sago Worms As A Nutritious Traditional and Alternative Food For Rural Children in Southeast Sulawesi, IndonesiaDocument10 pagesSago Worms As A Nutritious Traditional and Alternative Food For Rural Children in Southeast Sulawesi, IndonesiaWaRso PapuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unsaturated FatDocument4 pagesUnsaturated FatKaycelyn JimenezPas encore d'évaluation