Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Row-Column Major Address
Transféré par
Vinod SrivastavaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Row-Column Major Address
Transféré par
Vinod SrivastavaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
www.vinodsrivastava.
com/Maths
Address Calculation
Row Major Order :
Address of A[R][C]=BA+W[(R-LBR)*N+(C-LBC)]
Column Major Order :
Address of A[R][C]=BA+W[(I-LBR)+(J-LBC)*M]
Where : BA = Base Address W=Size of elements I,J=Find or determine the location LBR=Lower Bound of
row N= Number of columns LBC=Lower bound of column
LBR & LBC=0 and UBR =N and UBC=M : if 2- DEMENSIONAL ARRAY IS IN THE FORM OF
A[N][M]
FOR EXAMPLE -> A[20][30]
BUT IF 2- DEMENSIONAL ARRAY IS IN THE FORM OF A[LBR..N][LBCLBCM] FOR
EXAMPLE -> A[2..20][4..30]
M=UBC LBC+1;
N=UBR - LBR+1;
Solved Examples
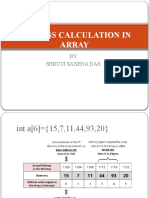
A double dimension array DA[20][40] is stored in computers main storage. Every element of DA
requires 8 bytes of memory. If the base address of DA is 1000 then calculate the address of
DA[20][30] when the array is stored as:
i)Row Major
ii)Column Major
N = 20, M = 40, BA = 2000, W = 8, R = 20, C = 30 LBC=0,LBR=0
Row Major:
Address of DA[R][C] =
BA + W * (R-LBR) * M + (C-LBC))
Address of DA[20][30]=
2000 + 8 * ((20-0) * 40 + (30-0))
=
Col Major:
8640
Address of DA[r][c]
= BA + W * (R-LBR) + (C-LBC)*N)
Address of DA[20][30]=
2000 + 8 * ((20-0) + (30-0)*20)
=
6960
Row Major/Column Major Address Calculation
A double dimension array DD[5..25][7..30] is stored in computers main storage. Every element of DD
requires 4 bytes of memory. If the base address of DD is 1000 then calculate the address of
DD[17][25] when the array is stored as: i)
Row Major
ii)
Column Major
lbr = 5, ubr = 25, N = ubr - lbr + 1 = 25 - 5 + 1 = 21
lbc = 7, ubc = 30, M = ubc - lbc + 1 = 30 - 7 + 1 = 24
Base = 1000, W = 4, r = 17, c = 25
Row Major: Address of DD[r][c]
=
Base + W * ((r - lbr) * M + (c - lbc))
Address of DA[17][25]
=
1000 + 4 * ((17 - 5) * 24 + (25 - 7))
=
2224
Col Major:
Address of DD[r][c]
=
Base + W * ((r - lbr) + (c - lbc) * N)
Address of DA[17][25]
=
1000 + 4 * ((17 - 5) + (25 - 7) * 21)
=
2560
A double dimension array MAT[20][25] is stored in computers main storage as row wise. If the
address of MAT[24][8] is 3932 and address of MAT[33][21] is 4884, then find the base address, width
(W) and also calculate the address of MAT[27][19].
N = 40, M = 25
Base + W * (24 * 25 + 8) = 3932
Or, Base + 608 * W = 3932 (1)
Base + W * (33 * 25 + 21) = 4884
Or, Base + 846 * W = 4884 (2)
Subtracting (1) from (2)
Base + 846 * W = 4884
Base + 608 * W = 3932
238 * W = 952
W = 952 / 238 = 4
Substituting the value of W in (1)
Base + 4 * 608 = 3932
Base = 3932 - 2432 = 1500
Address of MAT[27][19]
= 1500 + 4 * (27 * 25 + 19) = 4276
A double dimension array MAT[20][30] is stored in computers main storage as column major. If the
address of address of MAT[15][23] is 4850 and address of MAT[12][18] is 4232, then find the base
address, width (W) and also calculate the address of MAT[16][25].
ROW = 20, COL = 30
Base + W * (15 + 23 * 20) = 4850
Base + W * (12 + 18 * 20) = 4232
Subtracting (2) from (1)
Base + 475 * W = 4850
Base + 372 * W = 4232
103 * W = 618
W = 618 / 103 = 6
Substituting the value of W in (1)
Base + 6 * 475 = 4850
Base = 4850 - 2850 = 2000
Or, Base + 475 * W = 4850
Or, Base + 372 * W = 4232
(1)
(2)
Address of MAT[16][25] = 2000 + 6 * (16 + 25 * 20) = 5096
C++ 12 @ VKS-Learning Hub
Page 2
Row Major/Column Major Address Calculation
Try Yourself
1. An array x[8][20] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. If the base
address of the array is 2500, calculate the location of x[5][5] when the array x is stored using the column
major order and row major order.
2. An array Arr[1..20][1..20] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 4 bytes of storage. If the
base address of array Arr is 2000, determine the location of Arr[15][9] when the array Arr is stored in (1)
Row wise and (2) Column wise.
3. An array MAT[30][10] is stored in the memory row wise with each element
occupying 8 bytes of memory. Find out the base address and the address of the element MAT[15][5], if
the location of MAT[5][7] is stored at the address 3000.
4. An array MAT[20][25] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. If the base
address of MAT is 4000 MAT[[12][8] when the array stored in (i) RMO and (ii) CMO
5. An array ARR[15][20] is stored in the memory, along the row with each element occupying 4 bytes . Find
out the base address and the address of the element ARR[3][2] if the element ARR[5][2] is stored at the
address 1500.
6.
Each element of an array Data[20][50] required 4 bytes of storage, Base address of data is 2000,
determine the location of Data[10][10] when the array is stored as (a) row major (b) column major
7. An array A[11][21] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. If the base
address of array in memory is 300, determine the location of a[5][31] when the array is A stored by (i)
Row major (ii) Column major
8.
An array VAL[1....15][1...10] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 4 bytes of storage. If
the base address of array VAL is 1500, determine the location of VAL[12][9] when the array VAL is stored
(i)row-wise (ii)column-wise
9.
An array ARR[15][35] is stored in the memory along the column with each of its elements occupying 8
bytes. Find out the bas address and the address of an element Arr[2][5], if the location Arr[5][10] is stored
at the address 4000.
10. An array Arr[35][15] is stored in the memory along the row with each of its elements occupying 4 bytes.
Find the bas address and the address of an element Arr[20][5], if the location Arr[2][2] is stored at the
address 3000.
11. An array arr[15][20] is stored in the memory along the row with each element occupying 4 bytes. Find out
the base address and address of the element arr[3][2], if the element arr[5][2] is stored at the address
1500.
12. An array MAT[30][10] is stored in the memory column wise with each element occupying 8 bytes of
memory. Find out the bas address and the address of element MAT[5][7] is stored at the address 1000.
13. If an array B[11][8] is stored as column wise and B[2][2] is stored at 1024 and B[3][3] at 1084, find the
address of B[5][3] and B[1][1].
C++ 12 @ VKS-Learning Hub
Page 3
Row Major/Column Major Address Calculation
14. An array Arr[50[100] is stored in the memory along the row with each element occupying 2 bytes. Find
out the address of the location ARR[20][50] if location of Arr[20][30] is 1350.
15. An array x[30][10] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 4 bytes of storage. If the base
address of x is 4500, find out memory locations of x[12][8] and x[2][4], if the content is stored along the
row.
16. An array ARR[15][35] is stored in the memory along the column with each of its elements occupying 8
bytes. Find out the base address and the address of an element ARR[2][5] , if the location is stored at the
address 4000
17. An array X[15][10] is stored in memory with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. If the base
address of array is 2000, calculate the location of X [7][8] when the array is stored by (1) row major order
(2) column major order.
18. X [1..6][1.10] is a two dimensional array. The first element of the array is stored at
Location 100. Each element of the array occupies 6 bytes. Find the memory location of X[2][4] when (i)
array is stored row wise. (ii)array is stored column wise
19. Each element of an array A[-20..20,10..35] requires one byte of storage. If the array is stored in column
major order beginning location 500, determine the location of A[0,30].
20. An array S[35][15] is stored in the memory along the row with each of its elements occupying 4 bytes.
Find out the memory location for the element S[20][5], if an element S[2][2] is stored at the memory
location 3000.
21. Given the two dimensional array a[10][20] base address of a is 100 and width of each element is 4
bytes. Find the location of a[8][15] when the array is stored as column-wise and row-wise
22. An array A[-2..8][-2..5] is stored in the memory along the column with each element occupying 4 bytes.
Find out the address of the element A[3][2].
C++ 12 @ VKS-Learning Hub
Page 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideD'EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Array Question 1Document3 pagesArray Question 1Abhishek SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Address CalculationDocument11 pagesAddress CalculationMadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient search and sorting techniquesDocument31 pagesEfficient search and sorting techniquesTheREX IsHerePas encore d'évaluation
- C++ Arrays Chapter 9 Class XiiDocument31 pagesC++ Arrays Chapter 9 Class Xiipranjal75% (4)
- Address Calculation in Arrays (MemoryDocument20 pagesAddress Calculation in Arrays (MemoryDr-Himani MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Address Calculation in ArraysDocument3 pagesAddress Calculation in ArraysAnonymous zrAfrkPOJ7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract Data Type (ADT) : & ArrayDocument26 pagesAbstract Data Type (ADT) : & ArrayAdhara MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Array and AddressDocument3 pagesArray and AddressAkshat RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Arrays Assignment Computer Science: Kendriya Vidyalaya HVF Avadi Chennai 600 054Document1 pageArrays Assignment Computer Science: Kendriya Vidyalaya HVF Avadi Chennai 600 054vikas_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - ArraysDocument23 pages02 - ArraysMuhammad Owais khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 2Document10 pagesPractical 2Temporary UserPas encore d'évaluation
- ArraysDocument71 pagesArraysAbhiraj SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures: Arrays and Stacks ExplainedDocument8 pagesData Structures: Arrays and Stacks ExplainedAyushi KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-5. Two Dimensional Array-1Document48 pages4-5. Two Dimensional Array-1Pratham AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures (2D Array)Document18 pagesData Structures (2D Array)sajjadimamPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchDocument18 pagesLinear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchPratibha BahugunaPas encore d'évaluation
- CALCULATE ADDRESS IN ARRAYSDocument9 pagesCALCULATE ADDRESS IN ARRAYSShahid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Data Structure: Sets ArrayDocument90 pagesTypes of Data Structure: Sets ArrayAmit VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.representation of Arrays in Memory Unit-1Document23 pages5.representation of Arrays in Memory Unit-1v.c cPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Abstract Data TypesDocument51 pagesChapter 4 - Abstract Data TypesTanveer Ahmed HakroPas encore d'évaluation
- CS 211 Lecture 03 - Types of Data StructuresDocument8 pagesCS 211 Lecture 03 - Types of Data StructuresKhia PaghubasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Arrays: Everything You Need to KnowDocument27 pagesArrays: Everything You Need to KnowShibani RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchDocument18 pagesLinear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchAnanth KallamPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchDocument18 pagesLinear Arrays Representation & Traversal Insertion Deletion Linear Search Bubble Sort Binary SearchAnanth KallamPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures & Algorithms: Lecture # 2 Dated: 28-10-2010Document37 pagesData Structures & Algorithms: Lecture # 2 Dated: 28-10-2010Vicky ButtPas encore d'évaluation
- ArrayDocument5 pagesArrayRaja AnsPas encore d'évaluation
- Multidimensional Array1Document16 pagesMultidimensional Array1Sahil NagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Address Calculation of Array Element - Row Major OrderingDocument12 pagesAddress Calculation of Array Element - Row Major OrderingJb SadikPas encore d'évaluation
- BCAC303 notesDocument13 pagesBCAC303 notesGourav JainPas encore d'évaluation
- 8_Double-Subscripted ArrayDocument5 pages8_Double-Subscripted ArrayskewPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear and Binary SearchDocument23 pagesLinear and Binary SearchDatta RajendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Data StructuresDocument32 pagesData StructuresAditya VikramPas encore d'évaluation
- Address Calculation PDFDocument2 pagesAddress Calculation PDFbhasakar naik0% (2)
- Data Structures (2D Array)Document18 pagesData Structures (2D Array)Abdul WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2.1 Linear ArraysDocument15 pages1.2.1 Linear Arraysaksanshukumar1809Pas encore d'évaluation
- 07 DSA PPT Arrays in C-IIDocument19 pages07 DSA PPT Arrays in C-IISayak MallickPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure & Algorithms: ArraysDocument42 pagesData Structure & Algorithms: ArraysBicinPas encore d'évaluation
- Laecture 2:linear Data Structure:ArraysDocument22 pagesLaecture 2:linear Data Structure:ArraysMalik QudoosPas encore d'évaluation
- Class XII Computer Science C++, (083) : Ques.3 (A), (B) 2MM and 3MMDocument14 pagesClass XII Computer Science C++, (083) : Ques.3 (A), (B) 2MM and 3MMsanket singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithm 03606257 Question - Bank 1Document38 pagesAlgorithm 03606257 Question - Bank 1aumvashi04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3&4Document33 pagesLecture 3&4iHamzaMalikPas encore d'évaluation
- DSA - Arrays PDFDocument43 pagesDSA - Arrays PDFArun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Lecture 1: Arrays and StructuresDocument7 pagesData Structures Lecture 1: Arrays and StructuresMUSTAFA BshPas encore d'évaluation
- 56 Lecture 19 - Mutlidimentional DataDocument6 pages56 Lecture 19 - Mutlidimentional DataAbdul RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- DS Unit1 ArraysDocument22 pagesDS Unit1 Arraysnamansehgal3006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2.1 (Arrays)Document19 pagesLec 2.1 (Arrays)SURYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Guide: Arrays, Records, Pointers & AlgorithmsDocument27 pagesData Structures Guide: Arrays, Records, Pointers & Algorithmstowha elahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 ArraysDocument24 pagesChapter 2 ArraysAdil SajjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Information Technology (Academic Year - 2021-22) UNIT-I Question BankDocument37 pagesDepartment of Information Technology (Academic Year - 2021-22) UNIT-I Question BankHarsh ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.arrays IntroDocument16 pages3.arrays IntroUsha PPas encore d'évaluation
- Arraya of XiiDocument4 pagesArraya of Xiihar4sgPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques Bank Unit-1,2 (CAT-1)Document2 pagesQues Bank Unit-1,2 (CAT-1)anmolPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Arrays and StructuresDocument65 pagesChapter 2 Arrays and StructuresAnandReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Dimensional Arrays and SearchingDocument16 pagesTwo Dimensional Arrays and Searchingshashankmehta0205Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSE 109 Lec 9 Array BasicDocument15 pagesCSE 109 Lec 9 Array Basicanisruhan6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dsa Assignment - 3: Tutorial Sheet 2Document11 pagesDsa Assignment - 3: Tutorial Sheet 2PRAVEEN KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionD'EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersD'EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersPas encore d'évaluation
- Section10-Document Production Skills ChecklistDocument15 pagesSection10-Document Production Skills Checklistnalinda medagodaPas encore d'évaluation
- Walkthrough DWT+Practical PDFDocument13 pagesWalkthrough DWT+Practical PDFVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stackqueue WorksheetDocument1 pageStackqueue WorksheetVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vks JavascriptDocument16 pagesVks JavascriptVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- LoopsDocument3 pagesLoopsVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs Sunday Test NotesDocument13 pagesCs Sunday Test NotesVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- LoopsDocument3 pagesLoopsVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Walkthrough DWT+Practical PDFDocument13 pagesWalkthrough DWT+Practical PDFVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- LoopsDocument3 pagesLoopsVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Python Worksheet-1Document8 pagesPython Worksheet-1Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- CS Chapter2Document8 pagesCS Chapter2Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stackqueue WorksheetDocument1 pageStackqueue WorksheetVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- MMWT Xii WT 1 T1 2018Document4 pagesMMWT Xii WT 1 T1 2018Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- MMWT Xii WT 1 T2 2018Document2 pagesMMWT Xii WT 1 T2 2018Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- C++ Basics: Vks-Learning HubDocument17 pagesC++ Basics: Vks-Learning HubVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- VKS Flash 2aDocument48 pagesVKS Flash 2aVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- VKS PythonDocument41 pagesVKS PythonVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class AssignmentDocument8 pagesClass AssignmentVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- PythonworksheetDocument10 pagesPythonworksheetVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- ComputerScience SQPDocument15 pagesComputerScience SQPNirvana Adithya Visiobibliophobiatic GuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Network AssignmentDocument5 pagesNetwork AssignmentVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12: Revision-Web ApplicationDocument8 pagesClass 12: Revision-Web ApplicationVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-qp Model2 MWT 2017Document2 pages12-qp Model2 MWT 2017Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Invigilation Duty 11marchDocument2 pagesInvigilation Duty 11marchVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Python Worksheet 1Document10 pagesPython Worksheet 1Vinod Srivastava0% (1)
- Chapter 1-Networking PDFDocument58 pagesChapter 1-Networking PDFVinod Srivastava100% (1)
- VKS XII Worksheet STackQueueDocument3 pagesVKS XII Worksheet STackQueueVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSS 11 2018Document12 pagesCSS 11 2018Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionbank For q2 10marksDocument14 pagesQuestionbank For q2 10marksVinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mean Ex 1Document2 pagesMean Ex 1Vinod SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Design Recommended Reading ListDocument3 pagesProduct Design Recommended Reading ListSai Prasath100% (1)
- CS-280E Chain Saw: Parts CatalogDocument16 pagesCS-280E Chain Saw: Parts CatalogГоран СтанишићPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Publications: Direction 2190775 100Document21 pagesTechnical Publications: Direction 2190775 100zakaria alhosinyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Conversion Heat TransferDocument5 pagesUnit Conversion Heat TransferFamela GadPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsDocument22 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsMaggie HepditchPas encore d'évaluation
- Schneider LV Switchboard Inspection GuideDocument59 pagesSchneider LV Switchboard Inspection GuideAlp Arslan Ok100% (1)
- Thinking ForthDocument311 pagesThinking ForthCristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer Targeted E-CommerceDocument4 pagesCustomer Targeted E-CommercepriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksDocument71 pagesAnalysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksAnonymous BACdUNvPZ280% (5)
- Oil Analysis - Ruller and MPC TestDocument81 pagesOil Analysis - Ruller and MPC Testmaidul.islamPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsDocument80 pages13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsEdgar Muñoz Fernández50% (4)
- Que Dice Ese Gesto Descargar GratisDocument2 pagesQue Dice Ese Gesto Descargar GratisjavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Calgon Tech SpecDocument4 pagesCalgon Tech SpecDanStratoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: Introduction Introduction To Tribology: Fig. 1.1: Carbon Graphite SealDocument18 pagesModule 1: Introduction Introduction To Tribology: Fig. 1.1: Carbon Graphite Sealbansalmohit01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amphenol Musician Range PDFDocument8 pagesAmphenol Musician Range PDFtrc_wmPas encore d'évaluation
- Operators Manuel International Cub Cadet 72, 104, 105, 124, ZND 125 TractorsDocument44 pagesOperators Manuel International Cub Cadet 72, 104, 105, 124, ZND 125 Tractorsfundreamer1Pas encore d'évaluation
- JDA SCE Standard Release NotesDocument3 pagesJDA SCE Standard Release Notesgolcha_edu532Pas encore d'évaluation
- Variable Geometry Turbine Technology For Marine Gas Turbines-Springer (2022)Document227 pagesVariable Geometry Turbine Technology For Marine Gas Turbines-Springer (2022)miladPas encore d'évaluation
- ITILDocument16 pagesITILelenviegas82Pas encore d'évaluation
- VDP08 Technical CatalogueDocument47 pagesVDP08 Technical CatalogueAdal VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014-6-2 PCED South Hill Coalition Proposed Elements MatrixDocument2 pages2014-6-2 PCED South Hill Coalition Proposed Elements MatrixSpokane City CouncilPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPhysics Lab ReportFelix SonsunPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens-Relee de Timp PDFDocument2 pagesSiemens-Relee de Timp PDFChioibasNicolaePas encore d'évaluation
- Previews AGA XQ9902 PreDocument6 pagesPreviews AGA XQ9902 PreAldrin HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument40 pagesMinor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantArpit Garg100% (1)
- NTP35N15 Power MOSFET Features and SpecificationsDocument7 pagesNTP35N15 Power MOSFET Features and SpecificationsChristine GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Electricity SafelyDocument1 pageUsing Electricity SafelymariaPas encore d'évaluation
- ESD Protection in CMOS: Characterization and Failure AnalysisDocument113 pagesESD Protection in CMOS: Characterization and Failure AnalysisElisavNirolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Feed Water and Boiler Water of Steam GeneratorsDocument2 pagesFeed Water and Boiler Water of Steam GeneratorsIvicaT0% (2)
- TDS2000 Rig Systems DiagramsDocument13 pagesTDS2000 Rig Systems DiagramsBaskar KannaiahPas encore d'évaluation