Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Vectors Quiz
Transféré par
Sumant SumantCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
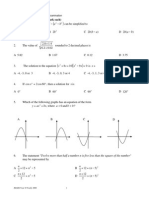
Vectors Quiz
Transféré par
Sumant SumantDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Math SL Quiz
1.
2 1
A line L passes through A(1, 1, 2) and is parallel to the line r = 1 + s 3 .
5 2
(a)
Write down a vector equation for L in the form r = a + tb.
(2)
The line L passes through point P when t = 2.
(b)
Find
(i)
OP ;
(ii)
OP .
(4)
(Total 6 marks)
2.
Find the angle between the following vectors a and b, giving your answer to the nearest degree.
a = 4i 2j
b = i 7j
Working:
Answer:
.......................................................................
(Total 4 marks)
1
3.
Points A, B, and C have position vectors 4i + 2j, i 3j and 5i 5j. Let D be a point on the xaxis such that ABCD forms a parallelogram.
(a)
(i)
Find BC .
(ii)
Find the position vector of D.
(4)
(b)
Find the angle between BD and AC .
(6)
The line L1 passes through A and is parallel to i + 4j. The line L2 passes through B and is
parallel to 2i + 7j. A vector equation of L1 is r = (4i + 2j) + s(i + 4j).
(c)
Write down a vector equation of L2 in the form r = b + tq.
(1)
(d)
The lines L1 and L2 intersect at the point P. Find the position vector of P.
(4)
(Total 15 marks)
4.
2
3
The points A and B have the position vectors and respectively.
2
1
(a)
(i)
Find the vector AB .
(ii)
Find AB .
(4)
d
The point D has position vector
23
(b)
Find the vector AD in terms of d.
(2)
D is 90.
The angle BA
(c)
(i)
Show that d = 7.
(ii)
Write down the position vector of the point D.
(3)
The quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle.
(d)
Find the position vector of the point C.
(4)
(e)
Find the area of the rectangle ABCD.
(2)
(Total 15 marks)
1.
(a)
correct equation in the form r = a + tb
A2
N2
1 1
r = 1 + t 3
2 2
(b)
(i)
attempt to substitute t = 2 into the equation
2
e.g. 6 ,
4
1 1
1 + 2 3
2 2
3
OP = 5 3
2
(ii)
(M1)
A1
N2
correct substitution into formula for magnitude
e.g.
A1
3 2 + 5 2 + (2) 2 , 3 2 + 5 2 + 2 2
OP = 38
A1
N1
4
[6]
2.
cos =
=
=
a.b
ab
4 + 14
20 50
10
(M1)
(A1)
10 10
1
=
(= 0.3162)
(A1)
10
= 72 (to the nearest degree)
(A1) (C4)
Note: Award (C2) for a radian answer between 1.2 and 1.25.
[4]
3.
(a)
(i)
BC = OC OB
= 6i 2 j
(ii)
(A1)(A1) (N2)
OD = OA + BC
= 2i + 0 j (= 2i )
(b)
(A1)(A1) (N2)
BD = OD OB
= 3i + 3 j
(A1)
AC = OC OA
= 9i 7 j
(A1)
Let be the angle between BD and AC
(3i + 3 j ) (9i 7 j )
cos =
(3i + 3 j ) 9i 7 j
(M1)
numerator = + 27 21 (= 6)
(A1)
denominator = 18 130 = 2340
therefore, cos =
6
2340
= 82.9o (1.45 rad)
(c)
(A1)
r = i 3 j + t (2i + 7 j )
( = (1 + 2t )i + (3 + 7t ) j )
(A1) (N3)
(A1) (N1)
(d)
EITHER
4i + 2 j + s (i + 4 j ) = i 3 j + t (2i + 7 j ) (may be implied)
(M1)
4 + s = 1 + 2t
2 + 4 s = 3 + 7t
(A1)
t = 7 and/or s = 11
(A1)
Position vector of P is 15i + 46 j
(A1) (N2)
OR
7 x 2 y = 13 or equivalent
(A1)
4 x y = 14 or equivalent
(A1)
x = 15 , y = 46
(A1)
Position vector of P is 15i + 46 j
(A1) (N2)
4
[15]
4.
(a)
(i)
(ii)
3 2
AB = OB OA =
1 2
5
=
1
AB = 25 + 1
=
(b)
26 (= 5.10 to 3 sf)
Note: An answer of 5.1 is subject to AP.
(M1)
(A1) (N2)
(M1)
(A1) (N2)
(A1)(A1)
AD = OD OA
d 2
=
23 2
d 2
=
25
(c)
(i)
EITHER
D = 90 AB AD = 0 or mention of scalar (dot) product.
BA
5 d 2
= 0
1 25
5d + 10 + 25 = 0
d=7
(M1)
(A1)
(AG)
OR
1
5
25
Gradient of AD =
d 2
25 1
= 1
d 2 5
d=7
Gradient of AB =
(AG)
(A1)
AD = BC
5
BC =
25
(M1)
OC = OB + BC
3 5
OC = +
1 25
(M1)
2
=
24
(e)
(A1)
7
OD = (correct answer only)
23
(ii)
(d)
(A1)
(A1)
(A1) (N3)
= 130
Note: Many other methods, including scale drawing, are
acceptable.
AD or BC = 5 2 + 25 2 = 650
Area =
(A1)
26 650 =( 5.099 25.5)
(A1)
2
[15]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageD'EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguagePas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY 2012 SA SolutionsDocument22 pagesKVPY 2012 SA SolutionsRachita AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesD'EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesÉvaluation : 1.5 sur 5 étoiles1.5/5 (2)
- E5 AnswersDocument24 pagesE5 AnswersIsrar AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat122 Tutorial QDocument10 pagesMat122 Tutorial QolasunmboPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Name: - Class: - Class No.Document4 pagesName: - Class: - Class No.okuyotasPas encore d'évaluation
- DPP-1 To 4 MathsDocument21 pagesDPP-1 To 4 MathsSanjay VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY Paper Solution XI 04-11-12Document23 pagesKVPY Paper Solution XI 04-11-12muley_jayPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM 2014 Maths T Paper 1 Trial Sem 1 SSIJBDocument8 pagesSTPM 2014 Maths T Paper 1 Trial Sem 1 SSIJBKenneth Chan50% (2)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector AlgebraDocument16 pagesVector AlgebrasudersanaviswanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Distributive Laws N Basics Etc PDFDocument56 pagesVector Distributive Laws N Basics Etc PDFsound05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aieee Paper 2008Document30 pagesAieee Paper 2008Ravi LorventPas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY SA SolutionsDocument24 pagesKVPY SA SolutionsawaninderPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsDocument9 pagesSPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsPatrick PhuahPas encore d'évaluation
- James Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument16 pagesJames Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsRicha Ng50% (2)
- Vectors: The Engineering Universe 1Document10 pagesVectors: The Engineering Universe 1Lokesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths 06Document14 pagesMaths 06Kashish ManochaPas encore d'évaluation
- X-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET A - QPDocument5 pagesX-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET A - QPSAID SAYALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Regional Mathematical Olympiad-2013: Time: 3 Hours December 15, 2013Document4 pagesRegional Mathematical Olympiad-2013: Time: 3 Hours December 15, 2013Surya PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- S4 Maths - Exam (Ans)Document9 pagesS4 Maths - Exam (Ans)Natalie Yeung100% (1)
- Kvpy Paper XiiDocument25 pagesKvpy Paper XiiVishank RustagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument10 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremPas encore d'évaluation
- Kvpy Paper 2010 Class Xii Career PointDocument40 pagesKvpy Paper 2010 Class Xii Career PointSwapan Kumar MajumdarPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Silver 1 - FP1 Edexcel PDFDocument15 pages03 Silver 1 - FP1 Edexcel PDFRyantyler13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acs I Y4 Prelim Em1 2010Document15 pagesAcs I Y4 Prelim Em1 2010math3matics3Pas encore d'évaluation
- WBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument20 pagesWBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh Kumar0% (2)
- George Ayubu 094456Document11 pagesGeorge Ayubu 094456lutubaraca856Pas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDocument10 pagesForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongPas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY 2012 Stream SA Solved PaperDocument22 pagesKVPY 2012 Stream SA Solved PaperKushal Kumar Reddy DPas encore d'évaluation
- Alevel FP1Document35 pagesAlevel FP1nuddin123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2Document5 pagesAnderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2math3matics3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Gold 4 - C2 Edexcel PDFDocument17 pages12 Gold 4 - C2 Edexcel PDFNicholas TehPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Part 1Document12 pagesMaths Part 1Sanjay Verma50% (2)
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT JEE 2006 MathsDocument14 pagesIIT JEE 2006 MathsKainshk GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Geometry Questions and Answers Grade 12Document15 pagesAnalytical Geometry Questions and Answers Grade 12phumucpPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Of: Revision Test (XI Syllabus) Part - I: ChemistryDocument10 pagesSolution Of: Revision Test (XI Syllabus) Part - I: ChemistryBodhisattva BasuPas encore d'évaluation
- SYSS 2019 F6 Maths Mock Paper 2 SolutionDocument11 pagesSYSS 2019 F6 Maths Mock Paper 2 SolutionChun Kit LauPas encore d'évaluation
- 2D Vectors MSDocument11 pages2D Vectors MSgzautanPas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY 2011 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDocument40 pagesKVPY 2011 Stream SB SX Solved PaperAnkitKambojPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 3 1 5 2Document42 pages1 3 1 5 2Himanshu GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- 03comp IDocument5 pages03comp Ialiscribd46Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD CBSE X Mathematics-Standard Paper 2 SolutionsDocument19 pagesCD CBSE X Mathematics-Standard Paper 2 SolutionsPushpakar ChandrakerPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 WMI Grade 11 Questions Part 1Document5 pages2015 WMI Grade 11 Questions Part 1Daffa Ardana100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument4 pagesTrigonometryYash Akhauri100% (1)
- Matrices Exercise Solution PDFDocument3 pagesMatrices Exercise Solution PDFChai Usajai UsajaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev Ex For S4 PDFDocument30 pagesRev Ex For S4 PDFjjPas encore d'évaluation
- Board of Intermediate Education: Mathematics - I (A)Document14 pagesBoard of Intermediate Education: Mathematics - I (A)Sriram_VPas encore d'évaluation
- Pure Maths Unit 1 Paper 1 2013Document10 pagesPure Maths Unit 1 Paper 1 2013KingBee1123100% (1)
- Uuur Uuur: BA BADocument8 pagesUuur Uuur: BA BASaidin AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths-Revision 3QPsDocument15 pagesMaths-Revision 3QPsvhdhanabal3339Pas encore d'évaluation
- MathsDocument22 pagesMathsMeenakshi ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- KVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDocument32 pagesKVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperAnkitKambojPas encore d'évaluation
- Long-Term Planning Template 2: Cambridge Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 7Document5 pagesLong-Term Planning Template 2: Cambridge Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 7Sumant Sumant100% (1)
- Sum1 PDFDocument8 pagesSum1 PDFSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Use The Tools To Enter Your Answer.: Question Details Interval Notation (3258126)Document4 pagesUse The Tools To Enter Your Answer.: Question Details Interval Notation (3258126)Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Review Gimnasio Colombo Britanico Grade 8Document4 pagesExam Review Gimnasio Colombo Britanico Grade 8Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Trimester ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Trimester ExamSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Birthday MagicDocument1 pageBirthday MagicSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Standard ReviewDocument11 pagesCalculus Standard ReviewSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4: Transformations of Functions and GraphsDocument15 pages2.4: Transformations of Functions and GraphsSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- MT 3 June Class 62010Document1 pageMT 3 June Class 62010Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10: Mathematics HL: Trisemester 2:finalDocument4 pagesGrade 10: Mathematics HL: Trisemester 2:finalSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Prime Number Project For KidsDocument1 pagePrime Number Project For KidsSumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- mt4JuneClass10 2010Document1 pagemt4JuneClass10 2010Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- Hrbacek-Introduction To Set Theory PDFDocument308 pagesHrbacek-Introduction To Set Theory PDFhermahuitron100% (2)
- Yr 7 Q2Document3 pagesYr 7 Q2Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- The English School: Instructor: Sumant Quiz 3 Yr 11 Find The Exact Value of Given That (X Is Not Acute)Document1 pageThe English School: Instructor: Sumant Quiz 3 Yr 11 Find The Exact Value of Given That (X Is Not Acute)Sumant SumantPas encore d'évaluation
- F32018 June IALDocument32 pagesF32018 June IALLoh Jun XianPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Chapter 3matrix MultiplicationDocument10 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 3matrix MultiplicationSarah TahiyatPas encore d'évaluation
- NPTEL R Programming Assignments2019 PDFDocument106 pagesNPTEL R Programming Assignments2019 PDFKalyan Ram100% (2)
- Vertical Format - Area of A ParallelogramDocument3 pagesVertical Format - Area of A ParallelogramLu AscencioPas encore d'évaluation
- Y X Sinx ,: 2 Cosec 2x Cosec 2x (2sin X+X Sin X+X Cos X) (2sin X+X Sin X Cos X) (2sin X+X Sin X+cos X)Document17 pagesY X Sinx ,: 2 Cosec 2x Cosec 2x (2sin X+X Sin X+X Cos X) (2sin X+X Sin X Cos X) (2sin X+X Sin X+cos X)ashok pradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions ManualDocument61 pagesLinear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manualmouldywolves086ez100% (27)
- 13.5: Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pages13.5: Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors: Learning ObjectivesanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument8 pagesCurvilinear CoordinatesYang CaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Example of Mutual Impedances: ( Z) Matrix Formulation in The Presence ofDocument8 pagesExample of Mutual Impedances: ( Z) Matrix Formulation in The Presence ofamit77999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix in Computer GraphicsDocument17 pagesMatrix in Computer GraphicsG Vinay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- National Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mathematics MA 1001D: Mathematics 1Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mathematics MA 1001D: Mathematics 1Nanditha APas encore d'évaluation
- Translation of Points: A (-1,1) To B (2,2) by Going To The Right 3 and Up 1 by Applying VectorDocument4 pagesTranslation of Points: A (-1,1) To B (2,2) by Going To The Right 3 and Up 1 by Applying VectorCarl Agape DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Questions - CH 3&4Document5 pagesMCQ Questions - CH 3&4vanshika sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- PCA and Sparse PCA Principal Component AnalysisDocument2 pagesPCA and Sparse PCA Principal Component AnalysisRAVI TEJ AMBATIPas encore d'évaluation
- First Order Linear Systems With Constant Coefficients: Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Shb/SuDocument29 pagesFirst Order Linear Systems With Constant Coefficients: Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Shb/SuakshayPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus SymbolsDocument1 pageCalculus Symbolspcr123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Deterministic and Random Signal AnalysisDocument106 pagesChapter 2 Deterministic and Random Signal AnalysisgrasspackingPas encore d'évaluation
- PLA FoldingDocument23 pagesPLA Foldingkrishnaprasad50% (2)
- Answers Level9-10Pack6Document22 pagesAnswers Level9-10Pack6David TurnerPas encore d'évaluation
- (Brent Nelson) Von Neumann AlgebrasDocument71 pages(Brent Nelson) Von Neumann AlgebrasLUIS QUEZADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ma 7251Document1 pageMa 7251Saba Vijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Equation of A Plane ExamplesDocument1 pageEquation of A Plane ExamplesGlambabes WoozPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Information: Instructor: Serkan Ho StenDocument3 pagesCourse Information: Instructor: Serkan Ho StenkevinPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving A System of Linear Equations by Matrix MethodDocument25 pagesSolving A System of Linear Equations by Matrix MethodGarvit Raj DevangPas encore d'évaluation
- Drawing A Lumley TriangleDocument4 pagesDrawing A Lumley TrianglegoldenthangamPas encore d'évaluation
- For Code Allocation/Blob/53Ef4846/Functionbrbalgorithm - CVX.MDocument19 pagesFor Code Allocation/Blob/53Ef4846/Functionbrbalgorithm - CVX.Mermiascachi kassahunPas encore d'évaluation
- Laplace Development Answers PDFDocument10 pagesLaplace Development Answers PDFNeil Carlo OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- EE263 Homework Problems Lecture 2 - Linear Functions and ExamplesDocument154 pagesEE263 Homework Problems Lecture 2 - Linear Functions and Examplestinozasable100% (1)
- The Cardinality of Hamel Bases of Banach Spaces - Lorenz HalbeisenDocument7 pagesThe Cardinality of Hamel Bases of Banach Spaces - Lorenz HalbeisenGabriel medinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Curriculum PDFDocument6 pagesDetailed Curriculum PDFananda.rudra89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Machinery of the Mind (An Interview)D'EverandMachinery of the Mind (An Interview)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (28)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceD'EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseD'EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldD'EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (64)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesD'EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2193)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayD'EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (125)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidD'EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowD'EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)D'EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (157)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldD'EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessD'EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterD'EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (410)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldD'EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (60)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingD'EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessD'EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (57)
- Mastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicD'EverandMastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (91)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeD'EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseD'EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (126)
- The Cosmos: Exploring the Universe's Biggest MysteriesD'EverandThe Cosmos: Exploring the Universe's Biggest MysteriesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 50 Quantum Physics Questions In Plain Simple English Book 1: Simple And Easy Answers Without Math For BeginnersD'Everand50 Quantum Physics Questions In Plain Simple English Book 1: Simple And Easy Answers Without Math For BeginnersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- Once Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingD'EverandOnce Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (43)