Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DSP 2
Transféré par
James Francis0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues3 pagesDSP QP
Titre original
dsp2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDSP QP
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues3 pagesDSP 2
Transféré par
James FrancisDSP QP
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Question Paper Code :
9
21
R. No. :
31145
93
M.E./M.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, JUNE 2011.
Common to M.E. Applied Electronics/M.E. Computer and Communication/
M.E. Communication Systems
First Semester
21
248101 ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
(Regulation 2010)
Time : Three hours
Maximum : 100 marks
Answer ALL questions.
93
PART A (10 2 = 20 marks)
1.
Write Yule-Walker equation.
2.
The power density spectrum of an AR process
xx (w ) =
2
w
A (w )
25
{x (n )}
is given as
where w2 is the variance of the input
1 j2w
e
2
sequence. Determine the difference equation for generating the AR process
when the excitation is white noise.
21
1 e jw +
Define Periodogram? How can it be smoothed?
4.
Compare Parametric and Non-Parametric methods of spectral estimation.
19
3
3.
How do find the ML estimate?
6.
Write the error criterion for LMS algorithm.
7.
Why are FIR filters widely used for adaptive filters?
8.
Express the LMS adaptive algorithm. State its properties.
9.
What are the advantages of multistage implementation in multirate signal
processing?
32
5.
10.
What is purpose of low pass filter before the down sampler?
(a)
(i)
Let x(n) be a stationary random process with zero mean and
autocorrelation rx (k) if the process y(n) = x(n) f(n). where f(n) is the
deterministic sequence. Find the mean my(n) and autocorrelation
ry(k,l) of the process y(n).
(5)
(ii)
State and prove Parsevals Theorem.
93
11.
21
PART B (5 16 = 80 marks)
(5)
(iii) What do mean stationary of a random process? Explain with an
example.
(6)
Or
(a)
Obtain Wiener Khintchines relation.
(ii)
Define power spectral density and list the methods of computing
the power spectral density for stationary random process.
(8)
(i)
Consider the ARMA process generated by the difference equation
x (n ) = 1.6x (n 1) 0.6x (n 2) + w(n ) + 0.9w(n 1)
21
12.
(i)
(1)
(2)
(i)
Determine the power density spectrum of {x (n )} .
(a)
32
13.
(8)
Show that Barlett estimate of the power spectral density is
asymptotically unbiased, the variance of the estimate decrease with
the number of data sections and spectrum estimates are consistant.
(8)
Or
Explain the Levinson Durbin Recursion algorithm for solving
Toplitz system of equations using an AR model.
(8)
19
3
(b)
(8)
Determine the system function of the whitening filter and its
poles and zeros.
21
(ii)
93
(b)
(ii)
How the Levison equation is used to derive the lattice filter
structure for FIR digital filters?
(8)
(i)
What is kalman filter? Explain its features.
(8)
(ii)
Give applications where Kalman filter is used.
(8)
Or
31145
(a)
Explain how AR parameters are obtained using Linear Prediction.
(8)
(ii)
Use the Levinson recursion to find the predictor polynomial
corresponding to the auto correlation sequence R = [2,1,1,2]T . (8)
21
14.
(i)
Justify the use of adaptive filters instead of conventional filters in
applications such as
(i)
Noise cancellation
(ii)
Channel equalization.
(16)
(b)
Obtain Widrow-Hopf LMS algorithm.
(a)
(i)
What is the need of multirate signal processing? Give few
applications.
(4)
(ii)
Explain the interpolation process in time domain and frequency
domain.
(12)
93
15.
21
Or
93
(b)
(16)
Or
(i)
Describe about sub band coding.
(ii)
Design a two-stage decimator for the following specifications.
D = 100 , Pass band : 0 F 50 , Transition band : 50 F 55,
21
(b)
Ripple : 1 = 10 1 2 = 10 3 , Input sampling rate : 10,000 Hz.
(8)
(8)
32
19
3
31145
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
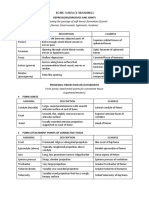
- CH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDocument46 pagesCH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDeepak KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- CH 14. HydrogenDocument14 pagesCH 14. HydrogenDipin Preet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 7. Thermodynamics - Thermo Chemistry (Chem +1)Document51 pagesCH 7. Thermodynamics - Thermo Chemistry (Chem +1)James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- CH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Document43 pagesCH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Mole Concept Motion ClassDocument15 pagesMole Concept Motion ClassJames FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- CH 5. Redox Reaction (Chem +1)Document38 pagesCH 5. Redox Reaction (Chem +1)Dipin Preet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- DSP 3Document3 pagesDSP 3James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- 1-2 - Trueman-Biology-Living World PYQDocument2 pages1-2 - Trueman-Biology-Living World PYQJames FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Swap NilDocument10 pagesSwap NilGaurav Kumar MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- DSP 5Document3 pagesDSP 5James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Degrees To Radians With KeyDocument4 pagesDegrees To Radians With KeyJames FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- M Hayes Statistical Digital Signal Proc Part 2Document200 pagesM Hayes Statistical Digital Signal Proc Part 2James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulink Behavioral Modeling of A 10-Bit Pipelined ADCDocument9 pagesSimulink Behavioral Modeling of A 10-Bit Pipelined ADCbhasin_hemantPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- DSP 1Document3 pagesDSP 1James FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Formal Verification of SystemsDocument11 pagesFormal Verification of SystemsSathish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Bil BODocument12 pagesBil BOJames FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- State Reduction and AssignmentDocument49 pagesState Reduction and AssignmentJames Francis100% (4)
- Diverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesDocument2 pagesDiverging Lenses - Object-Image Relations: Previously in Lesson 5 Double Concave LensesleonPas encore d'évaluation
- National Interest Waiver Software EngineerDocument15 pagesNational Interest Waiver Software EngineerFaha JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Biorefinery Models Towards Sustainable Circular Bioeconomy Critical Review and Future Perspectives2016bioresource Technology PDFDocument11 pagesWaste Biorefinery Models Towards Sustainable Circular Bioeconomy Critical Review and Future Perspectives2016bioresource Technology PDFdatinov100% (1)
- 12 Step Worksheet With QuestionsDocument26 pages12 Step Worksheet With QuestionsKristinDaiglePas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The University of The West Indies: Application For First Degree, Associate Degree, Diploma and Certificate ProgrammesDocument5 pagesThe University of The West Indies: Application For First Degree, Associate Degree, Diploma and Certificate ProgrammesDavid Adeyinka RamgobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Abilash - Subramanian CV - 003 PDFDocument4 pagesAbilash - Subramanian CV - 003 PDFAbilash SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Rsi r2 Super Rsi FaqDocument14 pagesRsi r2 Super Rsi FaqChandrasekar Chandramohan100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Fundasurv 215 Plate 1mDocument3 pagesFundasurv 215 Plate 1mKeith AtencioPas encore d'évaluation
- CE162P MODULE 2 LECTURE 4 Analysis & Design of Mat FoundationDocument32 pagesCE162P MODULE 2 LECTURE 4 Analysis & Design of Mat FoundationPROSPEROUS LUCKILYPas encore d'évaluation
- Expression of Interest (Eoi)Document1 pageExpression of Interest (Eoi)Mozaffar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- CPD - SampleDocument3 pagesCPD - SampleLe Anh DungPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- 2.a.1.f v2 Active Matrix (AM) DTMC (Display Technology Milestone Chart)Document1 page2.a.1.f v2 Active Matrix (AM) DTMC (Display Technology Milestone Chart)matwan29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of Theory in ResearchDocument2 pagesFunctions of Theory in ResearchJomariMolejonPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO Position ToleranceDocument15 pagesISO Position ToleranceНиколай КалугинPas encore d'évaluation
- School Based Management Contextualized Self Assessment and Validation Tool Region 3Document29 pagesSchool Based Management Contextualized Self Assessment and Validation Tool Region 3Felisa AndamonPas encore d'évaluation
- 1188 2665 1 SMDocument12 pages1188 2665 1 SMRita BangunPas encore d'évaluation
- A202 KBK3043 - Assignment Individual (20%) Review LiteratureDocument5 pagesA202 KBK3043 - Assignment Individual (20%) Review LiteratureAlfie AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Wine TourismDocument9 pagesWine Tourismyarashovanilufar1999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1Document5 pagesExploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1api-349870595Pas encore d'évaluation
- JO 20221109 NationalDocument244 pagesJO 20221109 NationalMark Leo BejeminoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensitivity of Rapid Diagnostic Test and Microscopy in Malaria Diagnosis in Iva-Valley Suburb, EnuguDocument4 pagesSensitivity of Rapid Diagnostic Test and Microscopy in Malaria Diagnosis in Iva-Valley Suburb, EnuguSMA N 1 TOROHPas encore d'évaluation
- Peter Szekeres-Solutions To Problems of A Course in Modern Mathematical Physics - Groups, Hilbert Space and Differential Geometry PDFDocument382 pagesPeter Szekeres-Solutions To Problems of A Course in Modern Mathematical Physics - Groups, Hilbert Space and Differential Geometry PDFMed Chouaybi0% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Internal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsiteDocument48 pagesInternal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsitetheodorebayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 1 Company Overview StandardsDocument34 pagesSection 1 Company Overview StandardsChris MedeirosPas encore d'évaluation
- Static Electrification: Standard Test Method ForDocument10 pagesStatic Electrification: Standard Test Method Forastewayb_964354182Pas encore d'évaluation
- Church and Community Mobilization (CCM)Document15 pagesChurch and Community Mobilization (CCM)FreethinkerTianPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Surface MarkingsDocument2 pagesBone Surface MarkingsNurul Afiqah Fattin AmatPas encore d'évaluation
- EPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023Document66 pagesEPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023akashupscmadeeasePas encore d'évaluation
- Scrum Exam SampleDocument8 pagesScrum Exam SampleUdhayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Systems Project: IITB CPUDocument7 pagesDigital Systems Project: IITB CPUAnoushka DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPND'EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsD'EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)