Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bipolar Junction Transistors Characteristics
Transféré par
GowthamDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bipolar Junction Transistors Characteristics
Transféré par
GowthamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bipolar Junction Transistors Characteristics
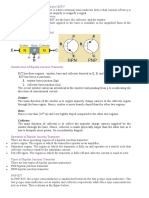
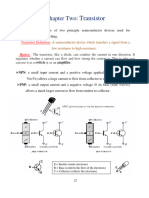
The three parts of a BJT are collector, emitter and base. Before
knowing about the bipolar junction transistor characteristics,
we have to know about the modes of operation for this type of
transistors. The modes are
1.
2.
Common Base (CB) mode
Common Emitter (CE) mode
3. Common Collector (CC) mode
All three types of modes are shown below
Now coming to the characteristics of BJT there are different
characteristics for different modes of operation. Characteristics is
nothing but the graphical forms of relationships among different
current and voltage variables of the transistor. The
characteristics for p-n-p transistors are given for different
modes and different parameters.
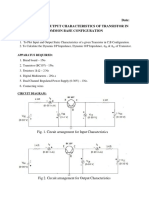
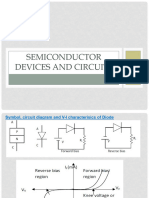
Common Base Characteristics
Input Characteristics
For p-n-p transistor, the input current is the emitter current (I E)
and the input voltage is the collector base voltage (VCB).
As the emitter - base junction is forward biased, therefore the
graph of IE Vs VEB is similar to the forward characteristics of a p n diode. IE increases for fixed VEB when VCB increases.
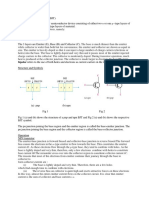
Output Characteristics
The output characteristics shows the relation between output
voltage and output current IC is the output current and collectorbase voltage and the emitter current IE is the input current and
works as the parameters. The figure below shows the output
characteristics for a p-n-p transistor in CB mode.
As we know for p-n-p transistors I E and VEB are positive and IC, IB,
VCB are negative. These are three regions in the curve, active
region saturation region and the cut off region. The active region
is the region where the transistor operates normally. Here the
emitter junction is reverse biased. Now the saturation region is
the region where both the emitter collector junctions are forward
biased. And finally the cut off region is the region where both
emitter and the collector junctions are reverse biased.
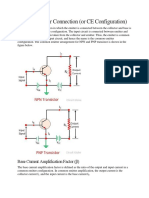
Common Emitter Characteristics
Input characteristics IB (Base Current) is the input current, VBE
(Base - Emitter Voltage) is the input voltage for CE (Common
Emitter) mode. So, the input characteristics for CE mode will be
the relation between IB and VBE with VCE as parameter. The
characteristics are shown below
The typical CE input characteristics are similar to that of a
forward biased of p - n diode. But as V CB increases the base width
decreases. Output Characteristics Output characteristics for CE
mode is the curve or graph between collector current (I C) and
collector - emitter voltage (VCE) when the base current IB is the
parameter. The characteristics is shown below in the figure.
Like the output characteristics of common - base transistor CE
mode has also three regions named (i) Active region, (ii) cut-off
regions, (iii) saturation region. The active region has collector
region reverse biased and the emitter junction forward biased.
For cut-off region the emitter junction is slightly reverse biased
and the collector current is not totally cut-off. And finally for
saturation region both the collector and the emitter junction are
forward biased.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuPas encore d'évaluation
- 15A04802-Low Power VLSI Circuits & Systems - Two Marks Q&A-5 UnitsDocument31 pages15A04802-Low Power VLSI Circuits & Systems - Two Marks Q&A-5 UnitsPallavi Ch71% (7)
- Unit-2 BJT PrintDocument22 pagesUnit-2 BJT PrintAhan TejaswiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction On TransisterDocument36 pagesIntroduction On TransisterMR. DEVESH BHONDWEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : Presented by D.Satishkumar Asst. Professor, Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument36 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : Presented by D.Satishkumar Asst. Professor, Electrical & Electronics EngineeringSiddharth TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 - BJTDocument17 pagesLesson 5 - BJTPavan G MPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document36 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Anuj KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- C.B CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesC.B CharacteristicskrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is BJT and Its ExplanationDocument5 pagesWhat Is BJT and Its ExplanationJerick De LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- BJTDocument34 pagesBJTPratik BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics TransistorDocument11 pagesPhysics TransistorMajid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EDC Course Lect 6 - 10Document31 pagesEDC Course Lect 6 - 10Harsh DeshwalPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ?: EmitterDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ?: EmitterSarika AyyathuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ?: EmitterDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ?: EmitterSarika AyyathuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- EC Chapter 04Document36 pagesEC Chapter 04Muhammad qamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorPadirikuppam PavithraPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistors 1-Introduction To TransistorsDocument27 pagesTransistors 1-Introduction To Transistorsdiya shajiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3Document25 pagesCH 3avishek aviPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document57 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Tooba AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- BE Unit-II PDFDocument21 pagesBE Unit-II PDFJagadeesh KaruturiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Document48 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Oscar BoshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5Document5 pagesLab 5mohanadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 BJT2Document32 pagesLecture 3 BJT2MegaHertz_92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument115 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorVince Silva100% (1)
- Experiment 5Document5 pagesExperiment 5dummy008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp#5: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) DC Characteristics: Eng. Mariam AlfadhliDocument9 pagesExp#5: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) DC Characteristics: Eng. Mariam AlfadhliAyeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Ama Serwaa YeboahPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument16 pagesChapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsGizachew BalchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual Part 2Document9 pagesLab Manual Part 2Mm MPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 BJTDocument5 pagesChapter 4 BJTBRIGHT TZZZY CHINGWENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Document48 pagesSlide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Priyatharshan ViswanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter ThreeDocument38 pagesChapter ThreeTolesa ShorePas encore d'évaluation
- Study Materials - EDC 01Document104 pagesStudy Materials - EDC 01pandaros000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics: TransistorsDocument20 pagesBasic Electronics: Transistorssoumikbh100% (2)
- Experiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsAhmed SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4api-394738731Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taylor & Francis TemplateDocument25 pagesTaylor & Francis TemplateOlatomide OlaosebikanPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document68 pagesUNIT-3 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)laxmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4. BJTPPTDocument52 pagesLecture 4. BJTPPTjthanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewDocument32 pagesUnit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewdevanshhubPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSISTOR - IntroductionDocument23 pagesTRANSISTOR - Introductiongirinandini100% (1)
- Transistors and MOSFETDocument28 pagesTransistors and MOSFETUtkarsh ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)Document17 pagesBJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)matlela92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Document 7 1Document12 pagesDocument 7 1Khaled aliPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT - 2 BJT and Applications & Feedback AmplifiersDocument21 pagesUNIT - 2 BJT and Applications & Feedback AmplifiersakashPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonPas encore d'évaluation
- الفصل 2tDocument23 pagesالفصل 2tmustafaasaad020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - BJTDocument24 pagesChapter 6 - BJTNuyu HasyimiePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeDocument3 pagesExperiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeGREATJUSTGREATPas encore d'évaluation
- Ommon Emitter ConnectionDocument7 pagesOmmon Emitter ConnectionSai NivedhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration of Transistor Circuit: CB, CE, CC Configuration Input and Output CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesConfiguration of Transistor Circuit: CB, CE, CC Configuration Input and Output CharacteristicsRai SenPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT SummaryDocument65 pagesBJT SummaryRutendo SedeyaPas encore d'évaluation
- PHY PROJ - SynopsisDocument13 pagesPHY PROJ - SynopsisPiyush HarlalkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document15 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Ankit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- 22BEE123 Bnmit: Basic BJT ConstructionDocument21 pages22BEE123 Bnmit: Basic BJT ConstructionswathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsD'EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionD'EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of Voltage Regulators With Working PrincipleDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Voltage Regulators With Working PrincipleGowthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction and Woking of BJTDocument3 pagesConstruction and Woking of BJTGowtham100% (1)
- Microwave Devices and Circuits Samuel LiaoDocument545 pagesMicrowave Devices and Circuits Samuel LiaoAkshay Arya100% (8)
- Network Analysis and Synthesis QBDocument11 pagesNetwork Analysis and Synthesis QBGowthamPas encore d'évaluation
- CIBANO 500 Ordering Information ENUDocument19 pagesCIBANO 500 Ordering Information ENUConstantPas encore d'évaluation
- Birwelco HT IgnitionDocument4 pagesBirwelco HT Ignitioncharleselitb92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Ifa 2000 France Uk HVDC Transmission LinkDocument4 pagesCase Study Ifa 2000 France Uk HVDC Transmission LinkTetianaPas encore d'évaluation
- AE8-1384 R6 March 2018: © 2018 Emerson Climate Technologies, IncDocument19 pagesAE8-1384 R6 March 2018: © 2018 Emerson Climate Technologies, IncjoaoPas encore d'évaluation
- VVVF - Working Principle & Its OperationDocument18 pagesVVVF - Working Principle & Its Operationdownload4sumitPas encore d'évaluation
- ME2026 Unconventional Machining - PDF.WWW - Chennaiuniversity.net NotesDocument27 pagesME2026 Unconventional Machining - PDF.WWW - Chennaiuniversity.net NotesSiva Raman100% (1)
- Edc Unit 5 Small Signal Low Freq BJT ModelsDocument61 pagesEdc Unit 5 Small Signal Low Freq BJT ModelsSandeep PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Tele Defender Generation Protection For Telecommunication-SystemsDocument4 pagesThe New Tele Defender Generation Protection For Telecommunication-SystemsLuis PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics - G. AruldhasDocument99 pagesEngineering Physics - G. Aruldhassubho0% (1)
- Sony Klv-22ex300 Klv-26ex300 Klv-32ex300 Klv-32ex400 Klv-40ex400 Klv-46ex400 B L RDocument67 pagesSony Klv-22ex300 Klv-26ex300 Klv-32ex300 Klv-32ex400 Klv-40ex400 Klv-46ex400 B L RDinuka MalinthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Using GigaProbes Agilent TDR D5Document12 pagesUsing GigaProbes Agilent TDR D5yadamyugandharPas encore d'évaluation
- Panasonic Th-37pv8p Th-37px8b Th-42pv8p Th-42px8b Th-42px8e Chassis Gph11deDocument173 pagesPanasonic Th-37pv8p Th-37px8b Th-42pv8p Th-42px8b Th-42px8e Chassis Gph11deYoly Rio RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- PANASONIC Panasonic TH-L32X10M Chassis KM02 Service Manual PDFDocument130 pagesPANASONIC Panasonic TH-L32X10M Chassis KM02 Service Manual PDFAbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.7 Digital Input Module SM 321 DI 32 X DC 24 V (6ES7321-1BL00-0AA0)Document3 pages3.7 Digital Input Module SM 321 DI 32 X DC 24 V (6ES7321-1BL00-0AA0)LanreSKPas encore d'évaluation
- Operacion y Mantenimiento de ReconectadoresDocument5 pagesOperacion y Mantenimiento de ReconectadoresCUAL QUIERAPas encore d'évaluation
- 12v Battery Charger Circuit With Auto Cut Off - Circuits GalleryDocument40 pages12v Battery Charger Circuit With Auto Cut Off - Circuits GalleryRamKumar0% (1)
- Master Cqed Les HouchesDocument155 pagesMaster Cqed Les HouchesmichPas encore d'évaluation
- CSC-121 Breaker Protection IED Engineering and Operation Manual - V1.00Document221 pagesCSC-121 Breaker Protection IED Engineering and Operation Manual - V1.00mentongPas encore d'évaluation
- BEEE (Magnetic Circuits)Document7 pagesBEEE (Magnetic Circuits)Vedu KadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Major PPT Batch 6Document19 pagesMajor PPT Batch 6starboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens Seminario DisjuntoresDocument8 pagesSiemens Seminario DisjuntoresMarcelo RauberPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document24 pagesChapter 9Deivasigamani SubramaniyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6MD86 Complete Wg2Document83 pages6MD86 Complete Wg2daralaketa100% (1)
- 00960a PDFDocument20 pages00960a PDFrosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 BJT AmplifierDocument69 pagesChapter 1 BJT Amplifiernur_azhra90Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Use A Multimeter The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure Electrical Quantities and Make The Most of Your MultimeterDocument23 pagesHow To Use A Multimeter The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure Electrical Quantities and Make The Most of Your MultimeterMohamad Hakimi Bin MakhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- DS276 Low Power Transceiver Chip: Features Pin AssignmentDocument11 pagesDS276 Low Power Transceiver Chip: Features Pin AssignmentJairo PadronPas encore d'évaluation
- QUCS ProcedureDocument559 pagesQUCS ProcedureSailaja DatlaPas encore d'évaluation