Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
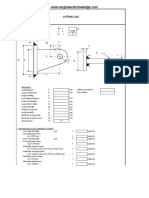
Lifting Eye Design
Transféré par
Fabio OkamotoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
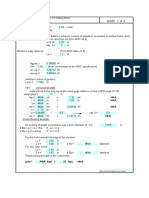
Lifting Eye Design
Transféré par
Fabio OkamotoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Proceedings of the Seventh (1997) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference
Honolulu, USA, May 25-30, 1997
Copyright 1997 by The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers
ISBN 1.880653-28-1 (Set); ISBN 1-880653-29-X (Vol. I)
Lifting Eye Design
Edwin P. Russo and John N. Crisp
University o f New Orleans, New Orleans, LA, USA
William W. St. Cyr
National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Stennis Space Center, MS, USA
Engin A. Egeseli
Avondale Industries, Avondale, LA, USA
ABSTRACT
This paper is an extension of earlier works by the authors on the
design and analysis of lifting eyes (padeyes). The emphasis is on
providing formulas that can be easily incorporated into computer
programs. The paper describes the philosophy of analysis for the
design of lifting eyes. A systematic ordered approach to the design
using simple beam theory is presented. Typical modes of failure for
this connection associated with direct pin action on the padeye are
bearing, pullout, and tension tearing. In the body of the lifting eye
shear, tension, and bending stresses occur. A semi-graphical solution
is also presented for quick order-of-magnitude hand calculations.
Key Words:
Lifting eye, padeye, connection
NOMENCLATURE
Ab
Ac
As
A tl
At2
a
"
"
-
Cc
c
D
De
E
e
F
Fo
Fy h
Ic I~ 12
Minimum pin beating area, in s (ram 2)
Area of hypothetical column, in 2 (mm ~)
Area of pin shear pullout, in 2 (ram 2)
Area of net tearing section at pin hole, in 2 (mm 2)
Area of net tearing section at pin hole, in 2 (ram 2)
Distance from upper edge of padeye to center of pinhole, in
(mm)
Distance from center of pin hole to attachment structure,
in (mm)
Slenderness ratio transition point
Size of cheek plate fillet weld, in (ram)
Diameter of pin hole, in (ram)
Diameter of pin, in (mm)
Modulus of elasticity, ksi (MPa)
Edge distance at pin hole, in (ram)
Load factor
Allowable axial stress, ksi (MPa)
Minimum specified yield stress, ksi (MPa)
Total length of plate at any cross section, in (mm)
Moment of inertia of hypothetical column, in4 (mm 4)
Moment of inertia of main plate, cheek plates in section and
acting stiffeners for in-plane bending, in 4 (mm 4)
Moment of inertia of main plate, cheek plates in section, and
acting stiffeners for out-of-plane bending, in 4 (mm 4)
425
K
L
Ltl
l
Mt
Ms
n
P
Pt
R
Re
r
rc
rg
T
t
W
w
w
'
-
x'
y
z
z'
ct
J3
~b
~'
y~
Y2
~
ow
x~
re
Effective length factor of hypothetical column
Main plate attachment length, in (mm)
Length of plate tearing section, in (mm)
Length of hypothetical column, in (ram)
In-plane bending moment, in-kips (N-mm)
Out-of-plane bending moment, in-kips (N.mm)
Number of padeyes carrying the load
Dynamic design load, kips (N)
Transverse load on padeye, kips (N)
Radius of main plate, in (ram)
Effective radius of main plate, in (ram)
Outside radius of cheek plate, in (mm)
Effective radius of cheek plates, in (mm)
Radius of gyration of hypothetical column, in (ram)
Thickness of main plate, in (ram)
Thickness of cheek plate, in (mm)
Total weight of lift, kips (N)
Size of main plate fillet weld, in (mm)
Effective maximum width of plate for hypothetical column in
compression, in (mm)
Distance from center of pin hole along X axis, in (ram)
(Fig. 1)
Distance from center of pin hole to neutral axis of section, in
(mm) (Fig. 6)
Distance from center of pin hole along Y axis, in (mm)
Distance from center of pin hole along Z axis, in (mm)
Distance from center of pin hole to cross section being
analyzed, in (mm) (Fig. 6)
Angle sling makes with the horizontal, degrees
Angle padeye attachment section makes with load, degrees
Angle between vertical and attachment section, degrees
Angle of taper, degrees
Angle of fight taper of padeye, degrees
Angle of left taper of padeye, degrees
Stress due to combined bending and axial load, ksi (MPa)
Nominal weld electrode tensile strength, ksi (MPa)
In-plane shear stress in main plate, ksi (MPa)
Out-of-plane shear stress in main plate, ksi (MPa)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Bowing Styles in Irish Fiddle Playing Vol 1 - David LythDocument58 pagesBowing Styles in Irish Fiddle Playing Vol 1 - David LythEmma Harry100% (1)
- Design of Crane Runway GirdersDocument22 pagesDesign of Crane Runway GirdersScooby DooPas encore d'évaluation
- Stiffened Plates PDFDocument16 pagesStiffened Plates PDFfarhadmrt6923Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blast Resistant Design of Steel StructuresDocument116 pagesBlast Resistant Design of Steel StructuresPetr KonupčíkPas encore d'évaluation
- #160 Lifting Fixture 38tons 020807Document14 pages#160 Lifting Fixture 38tons 020807halder_kalyan9216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting Lug CalculationsDocument6 pagesLifting Lug CalculationsYash RamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting Lug Design and Stress AnalysisDocument2 pagesLifting Lug Design and Stress AnalysisDarkvader0% (1)
- Design and Verification of Lifting LugsDocument3 pagesDesign and Verification of Lifting LugsFabio Okamoto100% (1)
- Pveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument5 pagesPveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDBruno TrujilloPas encore d'évaluation
- TrunnionDocument7 pagesTrunnionRUDHRA DHANASEKAR100% (1)
- Design of Tail LugDocument34 pagesDesign of Tail LugPrajwal Shetty100% (1)
- Ansi B 16.34Document22 pagesAnsi B 16.34Vinoth Rajendra100% (2)
- Example 02 (Linstatic Angle-Ply)Document7 pagesExample 02 (Linstatic Angle-Ply)Luis HuayaneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting BEAMSDocument90 pagesLifting BEAMSGogyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityD'EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityPas encore d'évaluation
- The Rainflow Method in Fatigue: The Tatsuo Endo Memorial VolumeD'EverandThe Rainflow Method in Fatigue: The Tatsuo Endo Memorial VolumePas encore d'évaluation
- Shear Strength of High-Strength BoltsDocument61 pagesShear Strength of High-Strength Boltsloox600Pas encore d'évaluation
- StrucadTraining Manual v10Document290 pagesStrucadTraining Manual v10Lathesh Janarthanan80% (5)
- Lifting LugDocument39 pagesLifting LugSasikumar JothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue Ocean StructuresDocument65 pagesFatigue Ocean StructureslukmantralalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ITC 215: Data Structure and Algorithm Module ObjectivesDocument3 pagesITC 215: Data Structure and Algorithm Module Objectiveskarthikeyan50700HRPas encore d'évaluation
- Latest Lifting LugDocument8 pagesLatest Lifting Lugjagannadha varmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dupont Design of Trunnions 1979Document26 pagesDupont Design of Trunnions 1979mjjanowski100% (1)
- Calculation Sheet: Padeye Calculations LoadsDocument14 pagesCalculation Sheet: Padeye Calculations Loadsandi_nu0% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Strength Calculation: Shell Side Design Data Tube Side Design DataDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Strength Calculation: Shell Side Design Data Tube Side Design DataSteve MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculo de Brida Segun ASMEDocument29 pagesCalculo de Brida Segun ASMEakarcz6731Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computed TomographyDocument94 pagesComputed TomographyBMT100% (3)
- STRESS ANALYSIS and FATIGUE of Welded StructuresDocument20 pagesSTRESS ANALYSIS and FATIGUE of Welded Structuresmatteo_1234100% (1)
- Welded connection designDocument16 pagesWelded connection designAnkit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Analysis of Pressure VesselDocument9 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Pressure VesselSenguttuvan RaajaahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2400 Tema DCDocument7 pages2400 Tema DCMasoodMiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting Calculation REV ADocument1 pageLifting Calculation REV APohn Myint HanPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Car SeminarDocument24 pagesAir Car SeminarSatyajit MenonPas encore d'évaluation
- Loaded Flat PlatesDocument7 pagesLoaded Flat PlatesGanesh.MahendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Co-Ordinated By: DR Parul Presented By: DR GurneetDocument45 pagesCo-Ordinated By: DR Parul Presented By: DR Gurneetreenujohney100% (2)
- Lifting Lug Calculation: ITEM NO.: 521267876.xls REV. 0Document7 pagesLifting Lug Calculation: ITEM NO.: 521267876.xls REV. 0Steve MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Stress Analysis For Heat Exchanger Channel Head For Protection Against Plastic Collapse and Protection Against Local Failure (FEA)Document8 pagesElastic Stress Analysis For Heat Exchanger Channel Head For Protection Against Plastic Collapse and Protection Against Local Failure (FEA)kingstonPas encore d'évaluation
- Din en 1561 - en - 1997-08Document21 pagesDin en 1561 - en - 1997-08AlissonFernandes17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Analysis of Overhead Cranes - Kine CranesDocument23 pagesSeismic Analysis of Overhead Cranes - Kine CraneshathamphanPas encore d'évaluation
- Load analysis and strength evaluation of vessel lifting lugDocument3 pagesLoad analysis and strength evaluation of vessel lifting lugMudasir MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- BAEK Et Al. Fatigue Life Prediction Based On The Rainflow Cycle Counting Method For The End Beam of A Freight Car BogieDocument7 pagesBAEK Et Al. Fatigue Life Prediction Based On The Rainflow Cycle Counting Method For The End Beam of A Freight Car BogiePPNPas encore d'évaluation
- Study & Analysis of Transportation SkidDocument10 pagesStudy & Analysis of Transportation SkidJay PPas encore d'évaluation
- Anchor ForceDocument14 pagesAnchor ForceAdi Mulyadi100% (1)
- Member Stability CheckDocument3 pagesMember Stability CheckdamindaPas encore d'évaluation
- AB 520 Finite Element Analysis FEA Requirements PDFDocument4 pagesAB 520 Finite Element Analysis FEA Requirements PDFbello imamPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Design and Steel Pole StructuresDocument27 pagesTransmission Line Design and Steel Pole StructuresDanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pin Base ModuleDocument16 pagesPin Base ModuleMd Ahsanul KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Document13 pagesAnsys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Ye Wint ThuPas encore d'évaluation
- Most Applications, F.S. 5.0) : Calculation ReferenceDocument5 pagesMost Applications, F.S. 5.0) : Calculation ReferenceParthibanPas encore d'évaluation
- Flange Leakage Analysis MethodsDocument2 pagesFlange Leakage Analysis MethodsArmandoZacariasAcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6a Padeye Aisc 360 2005Document6 pages6a Padeye Aisc 360 2005mjlazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Padeye Design AnalysisDocument8 pagesPadeye Design AnalysisMyatmyat SwewinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2L5x3x1/2LLBB: #N/A #N/A #N/ADocument1 page2L5x3x1/2LLBB: #N/A #N/A #N/ARaza AidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shackle Stress AnalysisDocument1 pageShackle Stress Analysisarash_mehriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Different Between WSD and LRFDDocument50 pagesThe Different Between WSD and LRFDKhải Nuce100% (1)
- "Lifting - Lug" - Lifting Lug Analysis: Program DescriptionDocument3 pages"Lifting - Lug" - Lifting Lug Analysis: Program DescriptionSung Woong MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt preloading and tensioning notesDocument6 pagesBolt preloading and tensioning notesBishwajyoti DuttaMajumdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding SymbolsDocument12 pagesWelding SymbolsrsrtnjPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME SpreaderBar DWGDocument1 pageASME SpreaderBar DWGInspetor SoldagemPas encore d'évaluation
- Comp 2Document9 pagesComp 2YYo YudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eccentric Column BucklingDocument10 pagesEccentric Column BucklingMukeshChopraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chetan N. Benkar (2014) - Finite Element Stress Analysis of Crane HookDocument5 pagesChetan N. Benkar (2014) - Finite Element Stress Analysis of Crane HookGogyPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002Document13 pagesA New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002RihabChommakhPas encore d'évaluation
- Slab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionDocument7 pagesSlab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionMatteo Dalla Vecchia100% (1)
- PTC 2012 PrandiDocument9 pagesPTC 2012 PrandiFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- System VariableDocument1 pageSystem VariableFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- C 05028Document16 pagesC 05028Fabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) : Environmental Product Declarations of The European Plastics ManufacturersDocument4 pagesHigh Density Polyethylene (HDPE) : Environmental Product Declarations of The European Plastics ManufacturersMuhd AmirfaridPas encore d'évaluation
- Maceio PortDocument4 pagesMaceio PortFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter20 LashingDocument3 pagesChapter20 LashingFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4N4 2012 SDL Talks 2 PDFDocument33 pages4N4 2012 SDL Talks 2 PDFFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Manufacture of PolyethyleneDocument5 pagesThe Manufacture of PolyethyleneGenilson E Neliane SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- XfoilDocument4 pagesXfoilsahit228Pas encore d'évaluation
- Documents Required for Shipping to Banias Terminal, SyriaDocument1 pageDocuments Required for Shipping to Banias Terminal, SyriaFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abs Sts Modelplan101014Document61 pagesAbs Sts Modelplan101014Spiropoulos KostasPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Demands: (One Lifting Point)Document1 pageTechnical Demands: (One Lifting Point)Fabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Banias Terminal HandbookDocument38 pages03 Banias Terminal HandbookFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Banias Berths Layout and Contacts for Shipping in SyriaDocument1 pageBanias Berths Layout and Contacts for Shipping in SyriaFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final ProjectDocument27 pagesFinal ProjectMohit KeshriPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablet ToolingDocument51 pagesTablet ToolingDr. Muhammad Imran Khan100% (2)
- ACEEE - Best Practices For Data Centres - Lessons LearnedDocument12 pagesACEEE - Best Practices For Data Centres - Lessons LearnedtonybudgePas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Analysis of Mooring Hawser of FSO and SPM B PDFDocument10 pagesSafety Analysis of Mooring Hawser of FSO and SPM B PDFORUGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound level meter covers noise applicationsDocument2 pagesSound level meter covers noise applicationsAbigail DextrePas encore d'évaluation
- Formalin MsdsDocument10 pagesFormalin MsdsMank WidhiePas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Raw UpdateDocument3 pagesCamera Raw UpdateHamsharfiPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP-Press - Abap Development For Sap HanaDocument30 pagesSAP-Press - Abap Development For Sap HananicocastanioPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Setup CM Notify SyncDocument2 pagesHow To Setup CM Notify SyncascfsfPas encore d'évaluation
- Blasting and Painting of Sheds, Pipes, Pipe Fittings, Vessels and Tanks DailyDocument3 pagesBlasting and Painting of Sheds, Pipes, Pipe Fittings, Vessels and Tanks DailyEjike Francis ChizobaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Operating Systems Fifth Edition: Memory Management: Virtual MemoryDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Operating Systems Fifth Edition: Memory Management: Virtual MemoryRidzuan DolahPas encore d'évaluation
- JVC TH-M606 - 603 - SMDocument101 pagesJVC TH-M606 - 603 - SMCaillouxPas encore d'évaluation
- Jobber JR DetailsDocument2 pagesJobber JR DetailsUrvish PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyxis SPT HepDocument597 pagesPyxis SPT HepanithaarumallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Easi-Pay Guide via e-ConnectDocument29 pagesEasi-Pay Guide via e-ConnectKok WaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Management: Operating SystemsDocument48 pagesProcess Management: Operating SystemsvidishsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine TimeDocument11 pagesMachine TimeFRANCIS THOMASPas encore d'évaluation
- Sabri Toyyab Resume Spring 2019Document2 pagesSabri Toyyab Resume Spring 2019api-457400663Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blackberry Enterprise Server For Microsoft Exchange: Troubleshooting GuideDocument48 pagesBlackberry Enterprise Server For Microsoft Exchange: Troubleshooting GuideKhaled AjouzPas encore d'évaluation
- B2BDocument31 pagesB2BAjay MaheskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rfid Based Attendance SystemDocument16 pagesRfid Based Attendance Systemhim chauPas encore d'évaluation
- VF1 Technicalspecifications 031997 EN PDFDocument43 pagesVF1 Technicalspecifications 031997 EN PDFelectricistPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Sodium Hyposulfite SolutionDocument2 pagesManufacturing Sodium Hyposulfite SolutionAravind KumarPas encore d'évaluation