Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Nswers TO: Looh - Kok - Kheong/answers To Rev Ex 6 - AJC
Transféré par
chuasiokleng0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues2 pagesAnswers
Titre original
Answers to Q1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAnswers
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues2 pagesNswers TO: Looh - Kok - Kheong/answers To Rev Ex 6 - AJC
Transféré par
chuasioklengAnswers
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
ANSWERS TO Q6
(b)
-CH3 is an electron donating group. It increases the electron density on N atom.
Hence, lone pair of electrons on N has higher tendency to form a dative bond with
H+.
-OH is an electron withdrawing group. It decreases the electron density on N atom.
Hence, lone pair of electrons on N has lower tendency to accept a H +.
As for C6H5NH2, lone pair of electrons on N is delocalized into the benzene ring and
hence least available to accept H+.
Hence, strength of base of CH3NH2 > NH2OH > C6H5NH2
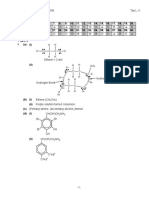
(c)(i)
Enthalpy /
kJ mol-1
4 N2 (g) + 8 H2 (g) + 8 O2 (g)
4 x -367
3(+85) + 7(-286) + 2(-124)
4 NH3OHNO3 (s)
H
3 N2O (g) + 7H2O (l) + 2HNO3 (l)
(ii)
H<0, S<0 hence TS > 0
Hence, at high temperature, TS > H (or TS becomes more positive) and
G becomes more positive
Reaction becomes less spontaneous.
Looh_kok_kheong\Answers to Rev Ex 6_AJC
(d)(i) Cl2 + 2Br- 2Cl- + Br2
Cl2, being more reactive than Br2 (or being a stronger oxidizing agent than Br 2), is
able to displace Br2 from Br(ii)
Br- + H2SO4 HSO4- + HBr
H2SO4 displaces HBr from Br2HBr + H2SO4 Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
H2SO4 oxidises HBr to Br2 and itself is reduced to SO2.
(iii)
Cr2O72- + 6Br- + 14H+ 2Cr3+ + 3Br2 + 7H2O
Cr2O72- oxidizes Br- to Br2 and itself is reduced to Cr3+.
Looh_kok_kheong\Answers to Rev Ex 6_AJC
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Ffi Ffi: P (T: NVDocument14 pagesFfi Ffi: P (T: NVYoruNgPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersPas encore d'évaluation
- Ri h2 Chem p2 AnswersDocument7 pagesRi h2 Chem p2 Answersdragon slayerPas encore d'évaluation
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973D'EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 TJC Promo Exam MCQ Answers CHEMISTRYDocument2 pages2013 TJC Promo Exam MCQ Answers CHEMISTRYgohjwPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsD'EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- J1 Promos 2015 AnswersDocument14 pagesJ1 Promos 2015 AnswersaliciaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 18 SummaryDocument5 pagesCH 18 Summaryalstjq1003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Chemistry One PageDocument2 pagesElectro Chemistry One Pageshankaranand200517Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Document16 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Dishna KarunasekaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bornhaber & Kapustinskii EqnDocument8 pagesBornhaber & Kapustinskii EqnEbsiba Beaula JPas encore d'évaluation
- Preboard - 3 ChemistryDocument3 pagesPreboard - 3 ChemistryvaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hess's LawDocument15 pagesHess's Lawkamal touilebPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionKavitha ThayagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Activity 1Document3 pages04 Activity 1Deocades DexinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 125 08.10.2019: Exam I Will Be Held On Thursday, October 10 at 5:00 PM, Covering CHP 1 - 3Document7 pagesChem 125 08.10.2019: Exam I Will Be Held On Thursday, October 10 at 5:00 PM, Covering CHP 1 - 3nilofar jawadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Dec SolutionsDocument8 pages2012 Dec SolutionsBuyu100% (1)
- Bab 6Document26 pagesBab 6Risna NurhanisaPas encore d'évaluation
- OxnumbersDocument6 pagesOxnumbersmusaasiziannPas encore d'évaluation
- WPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Document3 pagesWPT Xi Centre Che Neet Key 10-12-23Deena chemistPas encore d'évaluation
- Transition Elements: Partly Filed D or F Shells: Why Do We Consider The 1 Row Separately From Others?Document27 pagesTransition Elements: Partly Filed D or F Shells: Why Do We Consider The 1 Row Separately From Others?kaushik bhartiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11Document6 pagesClass 11Anitha SathiaseelanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian 1 STPM t2.2015Document6 pagesUjian 1 STPM t2.2015Bbiesoth AJPas encore d'évaluation
- Very Strong: Carbanions, R Carbocations, RDocument11 pagesVery Strong: Carbanions, R Carbocations, RSandeep ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 9.4 2009 Transition Elements Prelim SolnDocument17 pagesTopic 9.4 2009 Transition Elements Prelim SolndeadbeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sita RamDocument1 pageSita RamSampa MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key HMWK - 1 CHPT 9 - 10Document11 pagesAnswer Key HMWK - 1 CHPT 9 - 10jts399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper-02 Chemistry (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Answers Maximum Marks: 70Document8 pagesSample Paper-02 Chemistry (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Answers Maximum Marks: 70Yt Status WorldPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 11Document5 pagesChem 11Anitha SathiaseelanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chelate Effect 2007Document29 pagesChelate Effect 2007Ragini SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 PDFDocument31 pagesCh1 PDFrashidPas encore d'évaluation
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFDocument18 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFJayant KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- D&F Block Elmt G12 With AnsDocument7 pagesD&F Block Elmt G12 With AnsPadmalaya paloPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes ChemDocument48 pagesRevision Notes ChemUmer Sayeed SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 11th Class NewlyDocument29 pagesChapter 8 11th Class NewlyanujkhotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reoxreaction Quick Revision - 2022Document9 pagesReoxreaction Quick Revision - 2022Hamad FarooquePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesChapter 10 ElectrochemistryPatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Imcho2020s.en 2Document15 pagesImcho2020s.en 2Quốc NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1 (Author Khvalyuk V.N.) : 54th International Mendeleev Olympiad, 2020 1 Theoretical Tour SolutionsDocument15 pagesProblem 1 (Author Khvalyuk V.N.) : 54th International Mendeleev Olympiad, 2020 1 Theoretical Tour SolutionsQuốc NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- N2016 H2 P1 Solns For UploadingDocument8 pagesN2016 H2 P1 Solns For UploadingjkPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument25 pagesOrganic ChemistryhimanisinghbasnalPas encore d'évaluation
- G12 - Sample Paper #1 Chemistry SolutionsDocument9 pagesG12 - Sample Paper #1 Chemistry Solutionsrajprince8818Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Redox ReactionsDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Redox Reactionsapi-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Karnataka CET / KCET 2014 Chemistry Solutions With AnswersDocument14 pagesKarnataka CET / KCET 2014 Chemistry Solutions With AnswersLokesh Kumar78% (9)
- Organic Effect - 15.3.2020Document26 pagesOrganic Effect - 15.3.2020Roban SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Resonance Booklet of Coordination CompoundsDocument39 pagesResonance Booklet of Coordination CompoundsAlok pandey75% (12)
- Bonding in Complexes of D-Block Metal Ions - Crystal Field TheoryDocument22 pagesBonding in Complexes of D-Block Metal Ions - Crystal Field TheoryidownloadbooksforstuPas encore d'évaluation
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3Document6 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3aikubing100% (1)
- Nov 2006 Paper 3 Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesNov 2006 Paper 3 Mark SchemeilnukPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers 1990 Free ResponseDocument5 pagesAnswers 1990 Free Responsetariko11344Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistrynht Examrep17Document12 pagesChemistrynht Examrep17KLPas encore d'évaluation
- Nov 2008Document13 pagesNov 2008dharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Transition Metals1Document12 pagesPre-Transition Metals1YuNeng KhongPas encore d'évaluation
- Iitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsDocument3 pagesIitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsAbhishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- KEAM 2014 Medical Solution - Physics and ChemistryDocument7 pagesKEAM 2014 Medical Solution - Physics and ChemistryAnweshaBose0% (1)
- XII A PT-3 Solution-1059851Document7 pagesXII A PT-3 Solution-1059851ASM CHEPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution 1277533Document8 pagesSolution 1277533subrat swainPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM 2018 Sem 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2018 Sem 2 Mock Anstee hcPas encore d'évaluation
- RJC 2011 Chem Prelim Paper3ANSDocument12 pagesRJC 2011 Chem Prelim Paper3ANSJean HomePas encore d'évaluation
- Comp P1 22Document8 pagesComp P1 22chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Chemistry 9729 P3 - Section BDocument4 pagesH2 Chemistry 9729 P3 - Section BchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- E Lit 22 - 1Document9 pagesE Lit 22 - 1chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Chem Prelim Paper 2Document28 pagesH2 Chem Prelim Paper 2chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- E Lit 22 - 3Document7 pagesE Lit 22 - 3chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- ASR 2020 J2Prelim H2Chem P4 QP PDFDocument20 pagesASR 2020 J2Prelim H2Chem P4 QP PDFchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Chem Prelim Paper 3Document40 pagesH2 Chem Prelim Paper 3chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 QNDocument19 pagesPaper 2 QNchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 ACJC Paper 4 Qns PDFDocument18 pages2020 ACJC Paper 4 Qns PDFchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Chemistry 9729 P3 - Section ADocument9 pagesH2 Chemistry 9729 P3 - Section AchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFDocument19 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 4 QP PDFDocument21 pages2020 JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 4 QP PDFchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult 2244 & Ref - v1Document147 pagesAdult 2244 & Ref - v1chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- S Jc2 C: Chedule FOR HemistryDocument1 pageS Jc2 C: Chedule FOR HemistrychuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Catholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1Document10 pagesCatholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 QNDocument10 pagesPaper 1 QNchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Catholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1Document9 pagesCatholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- A CHEM - 2007 - Paper - 1Document12 pagesA CHEM - 2007 - Paper - 1chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- A CHEM - 2007 - Paper - 2Document14 pagesA CHEM - 2007 - Paper - 2chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- The Chemistry of Food: Proposed Sabbatical Program For Hwa Chong Institution (Year 2)Document2 pagesThe Chemistry of Food: Proposed Sabbatical Program For Hwa Chong Institution (Year 2)chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- S Jc1 C: Chedule FOR HemistryDocument1 pageS Jc1 C: Chedule FOR HemistrychuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- 1530 Specimen Paper & Mark Scheme PDFDocument100 pages1530 Specimen Paper & Mark Scheme PDFchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #14: Preparation of Banana Oil and Characterization Using IR SpectrosDocument8 pagesExperiment #14: Preparation of Banana Oil and Characterization Using IR SpectroschuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemistry Esources: Study GuidesDocument2 pagesHemistry Esources: Study GuideschuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Higher 1 (Syllabus 8872)Document38 pagesChemistry: Higher 1 (Syllabus 8872)chuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Commentaries - Historical BooksDocument3 pagesCommentaries - Historical BookschuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle Strain Torsional Strain Ring StrainDocument6 pagesAngle Strain Torsional Strain Ring StrainchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanistic SummaryDocument2 pagesMechanistic SummarychuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- 7: Reactions of Haloalkanes, Alcohols, and Amines. Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument51 pages7: Reactions of Haloalkanes, Alcohols, and Amines. Nucleophilic SubstitutionchuasioklengPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityD'EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideD'EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdalePas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincD'EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (137)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactD'EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingD'EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (10)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeD'EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsD'EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyD'EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (21)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsD'EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeD'EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodD'EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (20)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsD'EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesD'EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideD'EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersD'EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactD'EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeD'EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (90)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsD'EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsPas encore d'évaluation