Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Foundations of Organizational Structure PDF
Transféré par
ElizaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Foundations of Organizational Structure PDF
Transféré par
ElizaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
4/11/16
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 -1
15
Foundations of
Organization
Structure
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
Learning Objectives
qIdentify seven elements of an organizations structure.
qIdentify the characteristics of the functional structure, the
divisional structure, and the matrix structure.
qIdentify the characteristics of the virtual structure, the team
structure, and the circular structure.
qDescribe the effects of downsizing on organizational
structures and employees.
qContrast the reasons for mechanistic and organic structural
models.
qAnalyze the behavioral implications of different organizational
designs.
1 5 -3
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
4/11/16
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
1 5 -4
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Work specialization: the division of
labor into separate activities.
Repetition of work.
Training for specialization.
Increasing efficiency through invention.
Henry Ford
1 5 -5
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 5 -6
4/11/16
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Grouping jobs together so common tasks can
be coordinated is called departmentalization.
By functions performed.
By type of product or service the
organization produces.
By geography or territory.
By process differences.
By type of customer.
1 5 -7
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Chain of command: an unbroken line of
authority that extends from the top of the
organization to the lowest echelon and clarifies
who reports to whom.
Once a basic cornerstone in organization
design.
Two complementary concepts:
Authority
Unity of command
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
1 5 -8
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
The chain of command is less relevant today
because of technology and the trend of
empowering people.
Operating employees make decisions once
reserved for management.
Increased popularity of self-managed and
cross-functional teams.
Many organizations still find that enforcing the
chain of command is productive.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 5 -9
4/11/16
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
1 5 -1 0
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Centralization and Decentralization
Centralization refers to the degree to which
decision making is concentrated at a single
point in the organization.
Advantages of a decentralized organization:
Can act more quickly to solve problems.
More people provide input into decisions.
Employees are less likely to feel alienated
from those who make decisions that affect
their work lives.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
1 5 -1 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Formalization: the degree to which jobs within
the organization are standardized.
A highly formalized job means a minimum
amount of discretion.
Low formalization job behaviors are
relatively non-programmed, and employees
have a great deal of freedom to exercise
discretion in their work.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 5 -1 2
4/11/16
LO 1
Identify Seven Elements
of an Organizations Structure
Boundary spanning occurs when individuals
form relationships with people outside their
formally assigned groups.
Positive results are especially strong in
organizations that encourage extensive
internal communication; in other words,
external boundary spanning is most effective
when it is followed up with internal boundary
spanning.
1 5 -1 3
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 2
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
1 5 -1 4
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 1
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
Simple structure: the manager and the owner are
one and the same.
Strengths:
Simple, fast, and flexible.
Inexpensive to maintain.
Accountability is clear.
Weaknesses:
Difficult to maintain in anything other than
small organizations.
Riskyeverything depends on one person.
1 5 -1 5
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
4/11/16
LO 2
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
A bureaucracy is characterized by
standardization.
Highly routine operating tasks.
Very formalized rules and regulations.
Tasks grouped into functional departments.
Centralized authority.
Narrow spans of control.
Decision making that follows the chain of
command.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 2
1 5 -1 6
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
Strengths of bureaucracy:
Ability to perform standardized activities in a
highly efficient manner.
Weaknesses of bureaucracy:
Subunit conflicts.
Unit goals dominate.
Obsessive behavior.
Covering weak management.
1 5 -1 7
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 2
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
The matrix structure combines two forms of
departmentalizationfunctional and product:
The strength of functional is putting
specialists together.
Product departmentalization facilitates
coordination.
It provides clear responsibility for all
activities related to a product, but with
duplication of activities and costs.
1 5 -1 8
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
4/11/16
LO 2
Common Organizational
Frameworks and Structures
1 5 -1 9
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 3
Alternate Design Options
The Virtual Organization
The essence of the virtual organization is
that it is typically a small, core organization
that outsources major business functions.
Also referred to as a modular or network
organization.
It is highly centralized, with little or no
departmentalization.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 3
1 5 -2 0
Alternate Design Options
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 5 -2 1
4/11/16
LO 3
Alternate Design Options
The team structure: eliminates the chain of
command and replaces departments with
empowered teams.
Removes vertical and horizontal boundaries.
Breaks down external barriers.
Flattens the hierarchy and minimizes status
and rank.
When fully operational, the team structure may
break down geographic barriers.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 3
1 5 -2 2
Alternate Design Options
In the circular structure: in the center are the
executives, and radiating outward in rings
grouped by function are the managers, then the
specialists, then the workers.
Has intuitive appeal for creative entrepreneur.
However, employees may be unclear about
whom they report to and who is running the
show.
We are still likely to see the popularity of the
circular structure spread.
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 4
1 5 -2 3
Effects of Downsizing on
Organizations and Employees
The Leaner Organization: Downsizing
The goal of the new organizational forms
weve described is to improve agility by
creating a lean, focused, and flexible
organization.
Downsizing is a systematic effort to make an
organization leaner by selling off business
units, closing locations, or reducing staff.
1 5 -2 4
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
4/11/16
LO 4
Effects of Downsizing on
Organizations and Employees
Strategies for downsizing include:
Investment
Communication
Participation
Assistance
Make cuts carefully and help employees
through the process.
1 5 -2 5
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
1 5 -2 6
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
An organizations structure is a means to help
management achieve its objectives.
Most current strategy frameworks focus on
three strategy dimensions:
Innovation
Cost Minimization
Imitation
1 5 -2 7
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
4/11/16
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
1 5 -2 8
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
Organizational Size
Large organizationsemploying 2,000 or
more peopletend to have more
specialization, more departmentalization,
more vertical levels, and more rules and
regulations than do small organizations.
The impact of size becomes less
important as an organization expands.
1 5 -2 9
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
Technology: the way an organization transfers
its inputs into outputs.
Numerous studies have examined the
technology-structure relationship.
Organizational structures adapt to their
technology.
1 5 -3 0
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
10
4/11/16
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
An organizations environment includes
outside institutions or forces that can affect its
performance.
Dynamic environments create significantly
more uncertainty for managers than do
static ones.
To minimize uncertainty:
Broaden structure to sense and respond
to threats.
Form strategic alliances .
1 5 -3 1
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
1 5 -3 2
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 5
Mechanistic vs. Organic
Structural Models
Another factor that shapes organizational
structure is institutions.
Regulatory pressures.
Simple inertia.
Culture.
Fads or trends.
Institutional pressures are often difficult to see
specifically because we take them for granted,
but that doesnt mean they arent powerful.
1 5 -3 3
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
11
4/11/16
LO 6
Analyze the Behavioral Implications
of Different Organizational Designs
An organizations structure can have significant
effects on its members.
Its impossible to generalize!
Not everyone prefers the freedom and flexibility
of organic structures.
Some people are most productive and satisfied
when work tasks are standardized and ambiguity
minimized.
1 5 -3 4
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
LO 6
Analyze the Behavioral Implications
of Different Organizational Designs
Organizational Designs and Employee Behavior
Work specialization contributes to higher employee
productivity.
No evidence supports a relationship between span
of control and employee satisfaction or
performance.
Fairly strong evidence links centralization and job
satisfaction, meaning that less centralization is
associated with higher satisfaction.
National culture influences the preference for
structure.
1 5 -3 5
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
Implications for Managers
1 5 -3 6
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
12
4/11/16
Implications for Managers
Specialization can make operations more
efficient, but remember that excessive
specialization can create dissatisfaction and
reduced motivation.
Avoid designing rigid hierarchies that overly
limit employees empowerment and autonomy.
Balance the advantages of virtual and
boundaryless organizations against the
potential pitfalls before adding flexible
workplace options.
1 5 -3 7
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
Implications for Managers
Downsize your organization to realize major
cost savings, and focus the company around
core competencies, but only if necessary,
because downsizing can have a significant
negative impact on employee affect.
Consider the scarcity, dynamism, and
complexity of the environment, and balance the
organic and mechanistic elements when
designing an organizational structure.
1 5 -3 8
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
Copy right 2 0 1 7 Pe a rs on Educa tion, Inc .
1 5 -3 9
13
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- This Study Resource Was: Unit 705: Leading A Strategic Management ProjectDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Unit 705: Leading A Strategic Management ProjectChathuranga PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pecking Order TheoryDocument2 pagesPecking Order TheoryBijoy SalahuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Differences Between Private, Public & Not For Profit Sectors OrganisationsDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Private, Public & Not For Profit Sectors OrganisationsMohsin Manzoor100% (1)
- CW1 - 1500words AssessmentDocument8 pagesCW1 - 1500words AssessmentarsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Documentation To Select and Recruit A New Member of StaffDocument10 pages1.1 Documentation To Select and Recruit A New Member of StaffsssPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Assignment 1 (You Are The Manager)Document1 pageManagement Assignment 1 (You Are The Manager)Mamoonah Hassan100% (1)
- Merger AcquisitionDocument13 pagesMerger AcquisitionPunitharan Sivanathan100% (1)
- Geography Past PaperDocument56 pagesGeography Past PaperNaim Mokhtar81% (27)
- Nonviolent Communication Lessons 2-20-18Document210 pagesNonviolent Communication Lessons 2-20-18Ice George100% (1)
- Lorie Savage Capital JB 1949Document11 pagesLorie Savage Capital JB 1949akumar_45291100% (1)
- Types of PlansDocument8 pagesTypes of Plansshivani100% (2)
- Role of MisDocument25 pagesRole of MisSantosh Kumar JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizing Adhocracies: Matrix, Collateral, Network & Task Force StructuresDocument43 pagesOrganizing Adhocracies: Matrix, Collateral, Network & Task Force StructuresShilpa N. LendePas encore d'évaluation
- PPM NotesDocument14 pagesPPM NotesNilabjo Kanti PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Henri Fayol's 14 Principles of Management: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument23 pagesHenri Fayol's 14 Principles of Management: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleKabil DevPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVINGDocument26 pagesChapter 11 CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVINGAbdul basit sultani0% (1)
- Economic Factor That Affect BusinessesDocument14 pagesEconomic Factor That Affect Businessessabs1234561080100% (1)
- Performance Management Unit 1Document23 pagesPerformance Management Unit 1Bhuvana GanesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambidextrous OrganizationDocument6 pagesAmbidextrous OrganizationReeya MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module I Intro To IMCDocument31 pagesModule I Intro To IMCalex_daniel81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 4Document27 pagesUnit - 4Ashwin SantokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Plan EvaluationDocument5 pagesStrategic Plan EvaluationCEDRIC JONESPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment IB LeadershipDocument18 pagesAssignment IB Leadershipsasha100% (1)
- Organizational Structure BreakdownDocument25 pagesOrganizational Structure BreakdownKing HeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingredients of A ReportDocument15 pagesIngredients of A ReportAastha JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Management: A Global and Entrepreneurial Perspective by Weihrich, Cannice, and KoontzDocument18 pagesManagement: A Global and Entrepreneurial Perspective by Weihrich, Cannice, and KoontzAbrar Fahim SayeefPas encore d'évaluation
- Sources of Finance SummaryDocument42 pagesSources of Finance SummaryTyson Texeira100% (1)
- Introduction To VC Business ModelDocument3 pagesIntroduction To VC Business ModelMuhammad Shahood JamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Principles for Global SuccessDocument4 pagesManagement Principles for Global SuccessNhàn TháiPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On Investor Behaviour in Systematic Investment Plan of Mutual FundDocument7 pagesStudy On Investor Behaviour in Systematic Investment Plan of Mutual FundSurajPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics NotesDocument17 pagesBusiness Ethics NotesSachin TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hierarchy of ObjectivesDocument14 pagesThe Hierarchy of ObjectivesPushp ToshniwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Research Methods Lecutre Notes ALL UNITSDocument75 pagesBusiness Research Methods Lecutre Notes ALL UNITSshahnilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing For The New Venture Launch: Early Management DecisionsDocument20 pagesPreparing For The New Venture Launch: Early Management Decisionsjawad khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer Bevaivir ARTICLEDocument47 pagesCustomer Bevaivir ARTICLEJavedIqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Talent Management Information SystemDocument7 pagesTalent Management Information SystemAnkita BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Innovation Ready: 25 Ways to Cultivate a Growth Mindset in StudentsDocument4 pagesIT Innovation Ready: 25 Ways to Cultivate a Growth Mindset in StudentsSakthi Vel100% (4)
- Introduction To BusinessDocument7 pagesIntroduction To BusinessRishabh RankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial ManagementDocument15 pagesFinancial ManagementSanjiv Kumar YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Workforce Focus: By: Sherilyn D Maca Raig, MbaDocument33 pagesWorkforce Focus: By: Sherilyn D Maca Raig, MbaSherilyn MacaraigPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1Baby KhorPas encore d'évaluation
- TQMDocument4 pagesTQMMatilda100% (1)
- Consumer Behavior StagesDocument16 pagesConsumer Behavior StagesPriyanka Zalpuri100% (1)
- Visions and Missions of Top Indian and Global CompaniesDocument7 pagesVisions and Missions of Top Indian and Global CompaniesMadhava KamireddyPas encore d'évaluation
- RSMDocument10 pagesRSMregan165Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mba 301Document26 pagesMba 301Akash skillsPas encore d'évaluation
- CB-Unit 02-Internal Influences PDFDocument108 pagesCB-Unit 02-Internal Influences PDFVivek Lal KarnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Employee Training and DevelopmentDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Employee Training and DevelopmentSadaf Waheed100% (1)
- Types of InterviewsDocument2 pagesTypes of InterviewsHamza MunawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Media For HRDocument3 pagesSocial Media For HRVijayPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of A ConstraintDocument9 pagesDefinition of A Constraintrajlaxmi_patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Bridgespan's Organization WheelDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Bridgespan's Organization Wheelmohamud abdirahman hirsi100% (1)
- 1.1 Company Profile: Our VisionDocument5 pages1.1 Company Profile: Our VisionWebhub TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Compensation Management: Components of Compensation SystemDocument9 pagesCompensation Management: Components of Compensation SystemgopareddykarriPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentsptharunPas encore d'évaluation
- The Financial Statements For Armstrong and Blair Companies Are SummarizedDocument1 pageThe Financial Statements For Armstrong and Blair Companies Are SummarizedTaimur TechnologistPas encore d'évaluation
- Management - Learning Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesManagement - Learning Lecture NotesweirdwolfvortexPas encore d'évaluation
- Steps - Oral Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesSteps - Oral Case AnalysisRodolfo Mapada Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- AquarisDocument6 pagesAquarisMahesh DharapPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - ED - 14MBA26Document21 pagesModule 2 - ED - 14MBA26Uday Gowda100% (1)
- Strategic Analysis TechniquesDocument15 pagesStrategic Analysis TechniquesKANNAN MPas encore d'évaluation
- International Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionD'EverandInternational Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- ITM Unit 2 - Tutorial Sheet - StudentsDocument4 pagesITM Unit 2 - Tutorial Sheet - StudentsalexPas encore d'évaluation
- References: International Journal of Nanomedicine 2019:14Document4 pagesReferences: International Journal of Nanomedicine 2019:14Afrah MPas encore d'évaluation
- A Primer in Research Methodology and BiostatisticsDocument163 pagesA Primer in Research Methodology and BiostatisticsAdriana Villarreal100% (3)
- Change The Way You PersuadeDocument19 pagesChange The Way You PersuadeGroundXero The Gaming LoungePas encore d'évaluation
- Modelling Swelling Rock Behaviour in TunnellingDocument5 pagesModelling Swelling Rock Behaviour in TunnellingsuperwxrPas encore d'évaluation
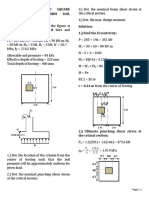
- Eccentrically Loaded Square Footing With Uniform Soil Pressure Solution: 1.) Find The EccentricityDocument14 pagesEccentrically Loaded Square Footing With Uniform Soil Pressure Solution: 1.) Find The EccentricityEarl John LugatimanPas encore d'évaluation
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMDocument3 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAMKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Astrophysics Project Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesAstrophysics Project Reaction PaperEdson DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Differentiation and Integration: By: Habtamu GaromaDocument53 pagesNumerical Differentiation and Integration: By: Habtamu GaromaAmiin HirphoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Human Resource Management TYBBA IBDocument27 pagesInternational Human Resource Management TYBBA IBD SimmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Why NAM remains relevant todayDocument2 pagesWhy NAM remains relevant todaySourabh PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Management Plan - Philippine-Specific AnnexDocument2 pagesRisk Management Plan - Philippine-Specific Annexultimate_2226252Pas encore d'évaluation
- Econ 222 W2012 Assignment 3 Answers PostedDocument9 pagesEcon 222 W2012 Assignment 3 Answers PostedakPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Factors in Second Language AcquisitionDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Factors in Second Language AcquisitionfatemehPas encore d'évaluation
- Beseler 67C EnlargerDocument4 pagesBeseler 67C EnlargerrfkjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Boy and Girl Final Application FormDocument5 pagesHead Boy and Girl Final Application FormboobooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Exemplar Art 6Document3 pagesLesson Exemplar Art 6Arranguez Albert ApawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Admmodule Stem Gp12eu Ia 1Document26 pagesAdmmodule Stem Gp12eu Ia 1Garry GuralPas encore d'évaluation
- Nobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsDocument115 pagesNobilis - UnlikelyFloweringsd7an7pijpkerPas encore d'évaluation
- General Tolerance (From ASME Y14.5M-2009) : Tolerances Can Be ExpressedDocument12 pagesGeneral Tolerance (From ASME Y14.5M-2009) : Tolerances Can Be ExpressedVivek PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Marriage Builders Emotional Needs Questionnaire PDFDocument12 pagesMarriage Builders Emotional Needs Questionnaire PDFPrarthanaRavikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Efland School Art StyleDocument9 pagesEfland School Art StyleinglesaprPas encore d'évaluation
- General Specifications: Ph/redox and Temperature Sensor Model PH20 and FU20Document8 pagesGeneral Specifications: Ph/redox and Temperature Sensor Model PH20 and FU20HolicsPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE(Main) 2023 Answer Key ChallengeDocument9 pagesJEE(Main) 2023 Answer Key ChallengeCHAKRI BABLUPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Method ReviewDocument2 pagesScientific Method ReviewHaneen QamarPas encore d'évaluation
- IUB Admissions Fall Smester 2021Document1 pageIUB Admissions Fall Smester 2021Mudassir RafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Angular Dispersion and Dispersive PowerDocument6 pagesAngular Dispersion and Dispersive PowerShivkant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Yulo, Brittany L. August 15, 2021 FS - 301 WEEK 4: Incised WoundsDocument2 pagesYulo, Brittany L. August 15, 2021 FS - 301 WEEK 4: Incised WoundsBrittany YuloPas encore d'évaluation