Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 3
Transféré par
NotoprosTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 3
Transféré par
NotoprosDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anomalies of Size
1) Microdontia
a) ectodermal dysplasia
b) hemifacial microsomia
c) Down syndrome
d) Peg lateral incisor
2) Macrodontia
a) facial hemihypertrophy
b) otodental syndrome
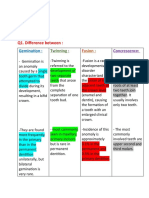
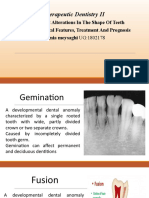
3) Fusion: union of two teeth/tooth buds (primary or permt; more common in primary teeth)
-fused teeth have 2 pulp chambers and 2 pulp canals
-results in large crown
-occurs almost always in anterior teeth
-can be detected by counting teeth b/c fusion results in one less tooth entity in arch
4) Gemination: division of single tooth bud into bifid crown (2 crowns on single root)
-more common in primary teeth
-b/c it occurs on a single tooth, there will be a normal complement of tooth entities
5) Concrescence: form of fusion w/ cementum contact (only cementum is fused)
-usually results from trauma
Anomalies of Shape
1) Dens evaginatus: extra cusp (talon cusp in incisors)
-extra cusp has enamel, dentin, and pulp so must be careful in restorative procedures
2) Dens invaginatus (dens in dente): caused by invagination of inner enamel epithelium
-termed tooth within a tooth
-most common in permt max. lateral incisors
-if enamel and dentin not formed correctly within defect, a direct communication with pulp can occur
-treated w/ small restoration or sealant to prevent pulpal involvement
3) Taurodontism: long vertical pulp chambers and short roots
4) Dilaceration: bent/twisted root occurring as result of intrusive or displacement injury to primary predecessor
-dilaceration also common in congenital ichthyosis
Anomalies of Structure
1) Enamel hypoplasia: refers to deficiency in QUANTITY of enamel
-no interproximal contact btw teeth
-causes: 1) genetic: amelogenesis imperfecta
2) environmental: systemic dx (fever), fluorosis, nutritional defic. (vit A, C, D, Ca, Ph)
2) Enamel hypocalcification: refers to deficiency in QUALITY of enamel
-also has genetic and environmental causes
3) Amelogenesis imperfect (AI): related to enamel only and dependent on stage of enamel formation (enamel
hypoplasia)
-normal root and pulp morphology
1) Type I: Hypoplastic (inadequate QUANTITY of enamel)
2) Type II: Hypomaturation (inadequate MATURATION of enamel)
3) Type III: Hypocalcified (inadequate QUALITY/mineralization of enamel
4) Dentinogenesis imperfect (DI): predentin matrix is defective, resulting in amorphic, atubular dentin
-teeth are reddish-brown to gray color
-slender roots
-small or absent pulp chambers/canals
1) Type I: osteogenesis imperfecta, blue sclera, hearing loss
2) Type II: no osteogenesis imperfecta (most common type)
3) Type III (Brandywine type): multiple periapical radiolucencies
5) Dentin dysplasia
-Shield type I: Normal anatomy. Short, pointed roots. Absent pulp chambers/canals. Multiple periapical
radiolucencies
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Oral Pathology McqsDocument3 pagesOral Pathology McqsAdel Abdel-Azim79% (19)
- Oral Pathology Mnemonics Online Course - PDF versionD'EverandOral Pathology Mnemonics Online Course - PDF versionÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21Document21 pagesNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21amitdineshp78% (9)
- Managing Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors. Part III: Single-Tooth ImplantsDocument9 pagesManaging Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors. Part III: Single-Tooth ImplantsSalma RafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- DriftodonticsDocument2 pagesDriftodonticssweetie0% (1)
- LM InstrumentsDocument76 pagesLM InstrumentsMessaoudi FaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of The ToothDocument22 pagesDevelopment of The ToothJoyce LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Discoloration of TeethDocument5 pagesDiscoloration of Teethريام الموسويPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Anomaly2Document213 pagesClassification of Anomaly2samar yousif mohamed100% (1)
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument32 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of TeethNada SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of TeethSherin ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Anomalies of The TeethDocument5 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of The TeethSaman SadeghiPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Development and Morphology of The Primary Teeth: Bagian IKGA Fakultas Kedokteran Gigi Maranatha 2017Document26 pagesDevelopment and Morphology of The Primary Teeth: Bagian IKGA Fakultas Kedokteran Gigi Maranatha 2017cella bentleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities of TeethDocument74 pagesAbnormalities of Teethzainab.yasinPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyDocument62 pagesDr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyoladunniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomic Anomalies - LectureDocument10 pagesAnatomic Anomalies - LectureKhalid BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- APznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17ZdDocument24 pagesAPznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17Zdclassybrands0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q1. Difference Between:: GeminationDocument3 pagesQ1. Difference Between:: GeminationRadaina NiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Enamel Clinical ConsiderationDocument51 pagesEnamel Clinical ConsiderationBarnali Misra50% (6)
- Pedo2013 14Document189 pagesPedo2013 14Vladimir Argirovic100% (4)
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument97 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of Teethtopuzoglualeyna5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument78 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TeethPauline Joy Cayago CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Disorders and SyndromesDocument77 pagesGenetic Disorders and Syndromesفاطمة الجش.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Isolated Dental Anomalies Class I Angle: Supernumerary Teeth AnodontiaDocument43 pagesIsolated Dental Anomalies Class I Angle: Supernumerary Teeth AnodontiaAdelina IacomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental TeethDocument53 pagesDevelopmental Teethlyli Star AngeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 4 Operative (PART 1)Document14 pagesLec 4 Operative (PART 1)Ahmed YousryPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Science Anatomy of The ToothDocument44 pagesBasic Science Anatomy of The ToothAmmar Al ZoubiPas encore d'évaluation
- ORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensDocument24 pagesORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensPravin PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Dentinogenesis ImperfectaDocument4 pagesDentinogenesis Imperfectamirfanulhaq100% (1)
- Tutorial in English Blok 5Document12 pagesTutorial in English Blok 5Ifata RDPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology of Orthodontic ProblemsDocument85 pagesEtiology of Orthodontic ProblemsShahid Hameed0% (1)
- Oral PathologyDocument184 pagesOral Pathologyyalahopa100% (1)
- Classification of Tooth DiscolourationDocument14 pagesClassification of Tooth DiscolourationSARINAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Anomalies of The ToothDocument14 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of The ToothAman Chowdhry100% (1)
- Dental CariesDocument120 pagesDental CariesSomya Jain100% (5)
- A:Essential RequirementsDocument8 pagesA:Essential Requirementssaged loaiPas encore d'évaluation
- AnamolisDocument11 pagesAnamolisAbood SamoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument65 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Teethisraa0dentist100% (4)
- Dev Dis ToothDocument92 pagesDev Dis ToothVaishnavi ThatiparthiPas encore d'évaluation
- $pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerDocument96 pages$pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerGhadeerHassaanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Development of Dental CariesDocument6 pagesThe Development of Dental CariesHaider F YehyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Pathology ModuleDocument31 pagesOral Pathology ModuleDenee Vem MatorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental AnomaliesDocument108 pagesDevelopmental AnomaliesKrishna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument29 pagesClassification of MalocclusionИскен АдылбековPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Path LecDocument31 pagesOral Path LecJane Krystia TeodoroPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Affection of TeethDocument38 pages7 Affection of TeethAdarshBijapurPas encore d'évaluation
- OralDocument61 pagesOralPragatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aetiology of MalocclusionDocument5 pagesAetiology of MalocclusionSRO oOPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiology Revision 2Document6 pagesRadiology Revision 2Yusnida RahmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Trauma and EndoDocument49 pagesTrauma and EndoKekelwa MutumwenuPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities of Tooth Number: Two TypesDocument28 pagesAbnormalities of Tooth Number: Two TypesKyaw Myo HtetPas encore d'évaluation
- DeepbiteDocument15 pagesDeepbiteagdroubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic IIDocument11 pagesTherapeutic IIkimiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology of MalocclusionDocument46 pagesEtiology of MalocclusionMSA universityPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities in The Development of TeethDocument58 pagesAbnormalities in The Development of TeethAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKAPas encore d'évaluation
- Sakeena Assad PresentationDocument93 pagesSakeena Assad Presentationjenny girlPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental AnomaliesDocument62 pagesDental AnomaliesRanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZD'EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 15Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 15NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 19Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 19NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 17Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 17NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 14Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 14NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 20Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 20NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 18Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 18NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 9Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 9NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 12Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 12NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 21Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 21NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 2Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 2NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 13Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 13NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion: Figure 5: Use of Piezoelectric Inserts To Prepare Implant SiteDocument1 pageDiscussion: Figure 5: Use of Piezoelectric Inserts To Prepare Implant SiteNotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 16Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 16NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 5Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 5NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Dentistry Scientifica: The Scientific World JournalDocument1 pageDentistry Scientifica: The Scientific World JournalNotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 7Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 7NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 6Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 6NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 11Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 11NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 8Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 8NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 4Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 4NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Dentistry Scientifica: The Scientific World JournalDocument1 pageDentistry Scientifica: The Scientific World JournalNotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 7: Second Surgical Phase.: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)Document1 pageFigure 7: Second Surgical Phase.: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 10Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 10NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- NBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 1Document1 pageNBDE Dental Boards Pedo 21 1NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Haaaaa 5Document1 pageHaaaaa 5NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 2: Clinical Situation Before Surgery (Clinical Photo and TC Sections)Document1 pageFigure 2: Clinical Situation Before Surgery (Clinical Photo and TC Sections)NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- N N y N y N y N Y: 4. Technique Description and Case ReportDocument1 pageN N y N y N y N Y: 4. Technique Description and Case ReportNotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Haaaaa 8Document1 pageHaaaaa 8NotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review: 2.1. Materials and Methods. An Electronic Search Was ConDocument1 pageLiterature Review: 2.1. Materials and Methods. An Electronic Search Was ConNotoprosPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard 3 Chapter 1 ScienceDocument5 pagesStandard 3 Chapter 1 ScienceprebasubahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian ObDocument2 pagesUjian ObElsha ZaskiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Logbook Spring 2023Document98 pagesLogbook Spring 2023Horn Dude100% (1)
- Extraction ForcepsDocument8 pagesExtraction ForcepsprasantiPas encore d'évaluation
- LD Implant FailuresDocument152 pagesLD Implant Failureswasim hussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction in Conservative DentistryDocument31 pagesIntroduction in Conservative Dentistryhind shaban100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Assessment of The Impacted Maxillary CanineDocument6 pagesGuidelines For The Assessment of The Impacted Maxillary CanineBarbara AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- ImplantDocument4 pagesImplantSaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior Cross Bites in Primary Mixed Dentition PedoDocument32 pagesAnterior Cross Bites in Primary Mixed Dentition PedoFourthMolar.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. SANATH SHETTY - Philosophies of Full Mouth Rehab 4Document6 pagesDr. SANATH SHETTY - Philosophies of Full Mouth Rehab 4priya100% (2)
- Anterior Open-Bite Treatment With Bonded Vs Conventional Lingual Spurs: A Comparative StudyDocument10 pagesAnterior Open-Bite Treatment With Bonded Vs Conventional Lingual Spurs: A Comparative StudyEmma Alata RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Yusnida FuroidaDocument7 pagesYusnida FuroidahaseosamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue Changes1Document22 pagesTissue Changes1Ishtiaq HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gingival Recession and Root Coverage Up To Date A Liter 2022 Dentistry RevDocument10 pagesGingival Recession and Root Coverage Up To Date A Liter 2022 Dentistry RevDavid ABCPas encore d'évaluation
- HPSC Dental Surgeon Model Question PaperDocument10 pagesHPSC Dental Surgeon Model Question PapergauravkokraPas encore d'évaluation
- Daffa Gemineo Dheona - 31102000017 - Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesDaffa Gemineo Dheona - 31102000017 - Literature ReviewRahmadhani AtmiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hindrance of Tooth Eruption and Orthodontic Tooth Movement by Focal Idiopathic Osteosclerosis in The MandibleDocument3 pagesHindrance of Tooth Eruption and Orthodontic Tooth Movement by Focal Idiopathic Osteosclerosis in The MandiblerachmadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral and Dental TraumaDocument101 pagesOral and Dental TraumaAlex Burde100% (1)
- Abnormalities of TeethDocument24 pagesAbnormalities of TeethRoshni ButalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pepannex1formadulttooth PDFDocument2 pagesPepannex1formadulttooth PDFAnonymous RnuIUjPPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients After ProvidingDocument5 pagesQuality of Life in Pediatric Patients After ProvidingrindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilateral Supplemental Maxillary Central Incisors With Double-Tooth Like AppearanceDocument4 pagesBilateral Supplemental Maxillary Central Incisors With Double-Tooth Like AppearanceSalma FaPas encore d'évaluation
- Overdenture Abutment Under Fix Partial Denture PDFDocument4 pagesOverdenture Abutment Under Fix Partial Denture PDFDeasireePas encore d'évaluation
- Period On TumDocument2 pagesPeriod On TumMa. Antonietta PennisPas encore d'évaluation
- EOrder Template IN69Document6 pagesEOrder Template IN69Uday KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ddslab RX RemDocument1 pageDdslab RX Remdrmohamad drmohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Endodontic Clinical Manual: RES 542 (Endo For Semester 10)Document35 pagesEndodontic Clinical Manual: RES 542 (Endo For Semester 10)Mustafa SaßerPas encore d'évaluation