Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet On Kolb: Accommodating Diverging
Transféré par
bbking44Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Worksheet On Kolb: Accommodating Diverging
Transféré par
bbking44Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
National College for School Leadership
National College for School Leadership
Worksheet on Kolb
1/3
When you have read pages 1 and 2 try to complete the grid on page 3.
We may begin a learning process in any of the four phases of the learning cycle and a well-rounded learning
process would cycle through all four phases. However, individuals may sometimes skip a phase in the cycle
or focus primarily on just one. Kolbs theory tells us that to optimise learning we should recognise where this
happens and develop ways of strengthening learning skills that are outside of our own preferences.
Kolb explains that people have different preferences in the way they approach learning based on two pairs
of variables how they approach a task and how they think or feel about it. The combination of these leads
to four distinct preferences or learning styles.
Concrete experience
Accommodating
Diverging
Active
experimentation
Reflective
observation
Converging
Assimilating
Abstract conceptulisation
PB1074/FAC/RES/KOLBWORKSHEET
Resource I Facilitation
National College for School Leadership
National College for School Leadership
2/3
Principles of adult learning
Diverging (feeling and watching CE/RO): These people are able to look at things from different perspectives.
They are sensitive. They prefer to watch rather than do, tending to gather information and use imagination to
solve problems. They are best at viewing concrete situations from several different viewpoints. Kolb called this
style diverging because these people perform better in situations that require ideas-generation, for example,
brainstorming. People with a diverging learning style have broad cultural interests and like to gather information.
They are interested in people, tend to be imaginative and emotional, and tend to be strong in the arts. People
with the diverging style prefer to work in groups, to listen with an open mind and to receive personal feedback.
Assimilating (watching and thinking AC/RO): The assimilating learning preference is for a concise, logical
approach. Ideas and concepts are more important than people. These people require good clear explanation
rather than practical opportunity. They excel at understanding wide-ranging information and organising it in a
clear logical format. People with an assimilating learning style are less focused on people and more interested
in ideas and abstract concepts. People with this style are more attracted to logically sound theories than approaches
based on practical value. This learning style is important for effectiveness in information and science careers.
In formal learning situations, people with this style prefer readings, lectures, exploring analytical models and
having time to think things through.
Converging (doing and thinking AC/AE): People with a converging learning style can solve problems and
will use their learning to find solutions to practical issues. They prefer technical tasks, and are less concerned
with people and interpersonal aspects. People with a converging learning style are good at finding practical
uses for ideas and theories. They can solve problems and make decisions by finding solutions to questions and
problems. People with a converging learning style are more attracted to technical tasks and problems than social
or interpersonal issues. A converging learning style enables specialist and technological abilities. People with
a converging style like to experiment with new ideas, to simulate and to work with practical applications.
Accommodating (doing and feeling CE/AE): The accommodating learning style is hands-on, and relies on
intuition rather than logic. These people use other peoples analysis, and prefer to take a practical, experiential
approach. They are attracted to new challenges and experiences, and to carrying out plans. They commonly act
on gut instinct rather than logical analysis. People with an accommodating learning style will tend to rely on
others for information, rather than carrying out their own analysis. This learning style is prevalent and useful
in roles requiring action and initiative. People with an accommodating learning style prefer to work in teams
to complete tasks. They set targets and actively work in the field, trying different ways of achieving an objective.
PB1074/FAC/RES/KOLBWORKSHEET
Resource I Facilitation
National College for School Leadership
National College for School Leadership
3/3
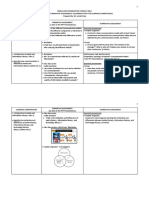
Kolb
Implications for your work with adults
Diverging
(feeling and watching CE/RO)
Assimilating
(watching and thinking AC/RO)
Converging
(doing and thinking AC/AE)
Accommodating
(doing and feeling CE/AE)
PB1074/FAC/RES/KOLBWORKSHEET
Resource I Facilitation
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Learning Styles PDFDocument14 pagesLearning Styles PDFMarione HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Determinants of LearningDocument6 pages3 Determinants of LearningKenPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 107A Pedia Week 5-7 Growth and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesNCM 107A Pedia Week 5-7 Growth and DevelopmentInsatiable CleePas encore d'évaluation
- Johari WindowDocument4 pagesJohari Windowanu000712Pas encore d'évaluation
- Knudtson Personal Nursing PhilosophyDocument11 pagesKnudtson Personal Nursing Philosophyapi-346349076Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conclusion & Recommendations Ewc661Document2 pagesConclusion & Recommendations Ewc661Ruzana MokhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Planning ReportDocument14 pagesPlanning ReportReylan GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Edhp 500 Summary of Learning Theories ChartDocument5 pagesEdhp 500 Summary of Learning Theories Chartapi-254318672Pas encore d'évaluation
- Communication: Dr. Prakashkumar RathodDocument26 pagesCommunication: Dr. Prakashkumar RathodHafiz ShoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership and Management Theories in NursingDocument13 pagesLeadership and Management Theories in NursingAngel Cauilan100% (1)
- Concept Map Part BDocument5 pagesConcept Map Part Bapi-315294234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Format - Health Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesFormat - Health Teaching PlanRichie VilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Health History and Interview GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHealth History and Interview GuidelinesGeraldine GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fowler's Stages of Faith Development SummaryDocument18 pagesFowler's Stages of Faith Development SummaryErin RedPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDimpal ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing Instructional Objectives 6.1 Characteristics of A Useful Objectives 6.2 Criteria of A Well Stated ObjectivesDocument39 pagesPreparing Instructional Objectives 6.1 Characteristics of A Useful Objectives 6.2 Criteria of A Well Stated ObjectivesJamine Joyce Ortega-AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- C CEF Roles, Character, Team PlainDocument10 pagesC CEF Roles, Character, Team PlainConrad C. CatimbangPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature and Scope of EthicsDocument10 pagesNature and Scope of EthicsSreekanth ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Contraception ReportDocument16 pagesContraception ReportJino Onij BolandoPas encore d'évaluation
- King's General Systems Framework ExplainedDocument8 pagesKing's General Systems Framework Explainednyx minaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative ReflectionDocument5 pagesSummative Reflectionapi-346049731Pas encore d'évaluation
- Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesInterview Questionsapi-272836789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Theory: Florence NightingaleDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Theory: Florence NightingaleJo Marchianne PigarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Determinants of Learning: Learning NeedsDocument4 pagesDeterminants of Learning: Learning NeedsFeb NamiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCMA110: 1. Eriksson, Watson and Benner 2. Rogers and Orem 3. Johnson, Roy and NeumanDocument31 pagesNCMA110: 1. Eriksson, Watson and Benner 2. Rogers and Orem 3. Johnson, Roy and NeumanMarian TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Nine Steps To More Effective Parenting: 1. Boosting Your Child's Self-EsteemDocument3 pagesNine Steps To More Effective Parenting: 1. Boosting Your Child's Self-Esteemapi-522213725Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human BecomingDocument3 pagesHuman BecomingCharles DavePas encore d'évaluation
- Physical and Mental AssessmentDocument3 pagesPhysical and Mental AssessmentAlexis FurtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing Learning Needs and ReadinessDocument43 pagesAssessing Learning Needs and ReadinessVince Peliño De MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Learning Theories Implications For Learning and Teaching in Medical Education AMEE Guide No 83Document13 pagesAdult Learning Theories Implications For Learning and Teaching in Medical Education AMEE Guide No 83skyforger8925Pas encore d'évaluation
- Six Reasons For Conducting Research Is CoolDocument2 pagesSix Reasons For Conducting Research Is CoolSareno PJhēaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample ROS, PE PDFDocument4 pagesSample ROS, PE PDFKASIA SyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.5 WorkshopDocument25 pages1.5 WorkshopSweety YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDocument6 pagesSession 14: Common Humanity: Our Lady of Fatima University Veritas Et MisericordiaDarling Rose De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abela - Adult Learning PDFDocument7 pagesAbela - Adult Learning PDFDhiaul IzzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument15 pagesJoyce TravelbeeRaphael SevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceu NSTPDocument45 pagesCeu NSTPAISHAPas encore d'évaluation
- She Believed That in The Nurturing Environment, The Body Could Repair ItselfDocument7 pagesShe Believed That in The Nurturing Environment, The Body Could Repair ItselfMegan N. ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 10 Modern Biotechnology PLMDocument53 pagesChap 10 Modern Biotechnology PLMJosh DumalagPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluating the Teaching ProgramDocument5 pagesEvaluating the Teaching ProgramPerly joy SeguraPas encore d'évaluation
- Health EducationDocument26 pagesHealth EducationALYSSA NICOLE GINESPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP TemplateDocument2 pagesNCP TemplatesoftwareitoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Grooming and Attitude On Professional Life: Affects The Way You ThinkDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Grooming and Attitude On Professional Life: Affects The Way You ThinkHitisha agrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- NUR325-PMHN-ProcessDocument4 pagesNUR325-PMHN-ProcessJayakrishnan P KripPas encore d'évaluation
- The Imago Dei FinalDocument7 pagesThe Imago Dei Finaldpieratt_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of Learning 10237Document4 pagesTheories of Learning 10237soniya josephPas encore d'évaluation
- Stage of Labor Quizlet 1Document5 pagesStage of Labor Quizlet 1Abmil Ching TinggalongPas encore d'évaluation
- Rozzano Locsin TheoryDocument4 pagesRozzano Locsin TheoryCHRISTIAN JAY MANDAC100% (1)
- Health Belief ModelDocument8 pagesHealth Belief ModelRUIZ JAKE CANCILLER. VELARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Jean Watson's Theory of Transpersonal CaringDocument10 pagesJean Watson's Theory of Transpersonal CaringJamaica Ala LauroPas encore d'évaluation
- Spiritual AssessmentDocument4 pagesSpiritual AssessmentCharm ArroyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment - Subjective: Client Verbalized, - "Sobrang SakitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment - Subjective: Client Verbalized, - "Sobrang SakitchelcasumbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowed Theories Used by NursesDocument24 pagesBorrowed Theories Used by Nursesmelaipwu0% (1)
- M&M: Mindfulness and Meditation While On Home Quarantine: An Encounter With The Lord / A Synthesis Paper of Topics DiscussedDocument5 pagesM&M: Mindfulness and Meditation While On Home Quarantine: An Encounter With The Lord / A Synthesis Paper of Topics DiscussedpaulinaveraPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Developmrnt of Nursing ProfessionDocument10 pagesHistory of Developmrnt of Nursing ProfessionHanison MelwynPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurs412 Ethical Issues in Nursing Paper Neuburg IntroDocument2 pagesNurs412 Ethical Issues in Nursing Paper Neuburg Introapi-452041818100% (1)
- Group NCPDocument17 pagesGroup NCPNiña Noreen Torres VallegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assess Math & Science Learning StylesDocument11 pagesAssess Math & Science Learning StylesConcepcion PalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Why Use Batna 2Document3 pages2007 Why Use Batna 2Shishir Kumar KisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fpsyt 09 00389Document18 pagesFpsyt 09 00389bbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Law of Animals Health and Guide and RegulationsDocument57 pagesThe Law of Animals Health and Guide and Regulationsbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Keyboard Shortcuts: in The Help Task PaneDocument16 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts: in The Help Task Panebbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Ideal Self As The Driver of Intentional ChangeDocument19 pagesThe Ideal Self As The Driver of Intentional Changebbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Keyboard shortcuts guide for WordDocument18 pagesKeyboard shortcuts guide for Wordbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taylor BakerDocument5 pagesTaylor Bakerbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- 25 Legendary Leadership ActivitiesDocument186 pages25 Legendary Leadership Activitiesgintanaufal507886% (7)
- Stakeholders Analysis GuidelinesDocument48 pagesStakeholders Analysis GuidelineserangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Excelente-Network Small Group PDFDocument26 pagesExcelente-Network Small Group PDFholeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Procurement LawDocument55 pagesPublic Procurement Lawbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Public Procurement Contracts LawDocument17 pagesPublic Procurement Contracts Lawbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crop Rotation Tasks PDFDocument27 pagesCrop Rotation Tasks PDFbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Design of Training Programme Manual PDFDocument107 pagesGeneric Design of Training Programme Manual PDFbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Docs 120111 RN FINAL PDFDocument17 pagesSample Docs 120111 RN FINAL PDFbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methodologies For The Development of Curriculum in VET PDFDocument37 pagesMethodologies For The Development of Curriculum in VET PDFbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Six Moving Parts: of Correctional Training EffectivenessDocument60 pagesThe Six Moving Parts: of Correctional Training Effectivenessbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dacum Sample Design DocumentsDocument4 pagesDacum Sample Design Documentsbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Standards and Indicators For Cultural Competence in Social Work Practice PDFDocument60 pagesStandards and Indicators For Cultural Competence in Social Work Practice PDFbbking4433% (3)
- The Logical Framework A Managers GuideDocument43 pagesThe Logical Framework A Managers Guidebbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Career & Job SourcesDocument2 pagesCareer & Job Sourcesbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Service Delivery ModelDocument52 pagesIntegrated Service Delivery Modelbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tool 3 - Social Inclusion Assessment 0909Document6 pagesTool 3 - Social Inclusion Assessment 0909bbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capability Azerbaijan enDocument20 pagesCapability Azerbaijan enbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Participation MatrixDocument3 pages11 Participation Matrixbbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20 AsfaDocument4 pages20 Asfabbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESMS+Handbook+General+v2 1Document64 pagesESMS+Handbook+General+v2 1bbking44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Social Inclusion and ExclusionDocument10 pagesSocial Inclusion and ExclusionemiliatodeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Collaborative LearningDocument19 pagesCollaborative Learningbbking44100% (1)
- Action Plan in English: Region I La Union Schools Division Office Bacnotan District Ortega Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesAction Plan in English: Region I La Union Schools Division Office Bacnotan District Ortega Elementary SchoolMaria Crisanta GañolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading and Use of English C1Document2 pagesReading and Use of English C1An Huynh100% (1)
- DLL Feb 19, 2020-Etikal PananaliksikDocument8 pagesDLL Feb 19, 2020-Etikal PananaliksikJeppssy Marie Concepcion MaalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lade Sample ProjectDocument26 pagesLade Sample ProjectOlumide AdebayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ang Filipino Sa Batayang Kurikulum NG Edukasyon Major 3Document10 pagesAng Filipino Sa Batayang Kurikulum NG Edukasyon Major 3Marc Anthony ManzanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pia: Kite:: Quality (Literacy Level) Improvement of Learning EnvironmentDocument8 pagesPia: Kite:: Quality (Literacy Level) Improvement of Learning EnvironmentEunice Joy Cuntapay BalganionPas encore d'évaluation
- CIM Grade 10 MUSICDocument7 pagesCIM Grade 10 MUSICJanine ArmamentoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter I Riskamaulina Listening DictoglossDocument17 pagesChapter I Riskamaulina Listening DictoglossJamil AhPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorful Organic Child Psychology PresentationDocument10 pagesColorful Organic Child Psychology PresentationChaima Ahmed GaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ielts Writing Answer SheetDocument2 pagesIelts Writing Answer SheetVuu CanhhPas encore d'évaluation
- LSP300 Assignment Semester 1 202021Document6 pagesLSP300 Assignment Semester 1 202021Yuyeen FarhanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Educ-30103 (1) (Replica)Document72 pagesEduc-30103 (1) (Replica)Cierly Mae Deguia TantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument8 pagesLearning To Be A Better StudentReyalyn AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- (PDF) Academic Achievement in ChemistryDocument1 page(PDF) Academic Achievement in ChemistryJake FinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Attendance: Camarines Sur National High SchoolDocument3 pagesReport On Attendance: Camarines Sur National High SchoolJames AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Handouts ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING 2Document11 pagesUnit 2 - Handouts ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING 2JenniferPas encore d'évaluation
- TLaC Transition GuideDocument26 pagesTLaC Transition GuideCheveux du FeuPas encore d'évaluation
- 549 Professional Growth 3Document11 pages549 Professional Growth 3api-634716450Pas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Accomplishment Report: Maligaya National High SchoolDocument2 pagesAnnual Accomplishment Report: Maligaya National High SchoolGiancarla Ma. DinglePas encore d'évaluation
- MS SCI 102-Lesson 5Document3 pagesMS SCI 102-Lesson 5Jervyn Guianan50% (2)
- Convince MeDocument3 pagesConvince MeNguyễn Yến NhiPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP Math 2Document6 pagesDLP Math 2Ping PingPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessments Align MIL CompetenciesDocument4 pagesAssessments Align MIL CompetenciesAna Marie SuganobPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching World Englishes - Group4 - AnaDocument26 pagesTeaching World Englishes - Group4 - AnaAntje Mariantje100% (1)
- Enhance speaking skills through drama techniquesDocument74 pagesEnhance speaking skills through drama techniquesAzkar SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- Copyofte 206 Assignment 12 LessonplanDocument4 pagesCopyofte 206 Assignment 12 Lessonplanapi-300926376Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Proven Classroom Strategies To Grab Students' Attention in ClassDocument6 pages10 Proven Classroom Strategies To Grab Students' Attention in ClassNabilversityPas encore d'évaluation
- Mso-Io 2016 028 Conversion Radboud 2016 en Update 2018Document64 pagesMso-Io 2016 028 Conversion Radboud 2016 en Update 2018Igor BarcelosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Indirect InstructionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Indirect InstructionsunshinegrlPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Learner Centered ScriptDocument6 pagesModule 2 Learner Centered ScriptJoey PerezPas encore d'évaluation