Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CA High School Graduation Rates
Transféré par
govandlaw4671Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CA High School Graduation Rates
Transféré par
govandlaw4671Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
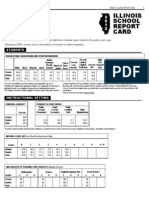
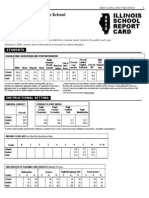
California State Highlights 2010
STATE PROFILE 2006-07
Graduation Profile for the Class of 2007
Graduation Rate
By Student Group
All Students
By Gender
Male
Female
By Race and Ethnicity
American Indian/Alaska Native
Asian/Pacific Islander
Hispanic
Black (not Hispanic)
White (not Hispanic)
By Gender and Race and Ethnicity
Male
American Indian/Alaska Native
Asian/Pacific Islander
Hispanic
Black (not Hispanic)
White (not Hispanic)
Female
American Indian/Alaska Native
Asian/Pacific Islander
Hispanic
Black (not Hispanic)
White (not Hispanic)
California
National
Average
(%)
(%)
62.7
68.8
64.4
71.9
66.0
72.9
51.5
50.7
83.5
57.0
54.0
78.2
80.7
55.5
53.7
76.6
47.0
80.1
52.1
46.4
76.8
50.6
48.2
74.8
46.7
73.7
49.3
85.8
51.1
82.7
61.5
57.2
81.0
59.4
59.4
78.8
Value not calculated because necessary data field(s) not reported in the U.S. Department of Educations Common Core of Data and not provided by state education agency.
Value not reported because of insufficient data for reliable estimate.
Editorial Projects in Education Research Center
www.edweek.org/rc
California State Highlights 2010
How Does the EPE Research Center Calculate Graduation Rates?
The Cumulative Promotion Index (CPI)
The Editorial Projects in Education Research Center uses the Cumulative Promotion Index (CPI) method to calculate graduation
rates. The CPI represents the high school experience as a process rather than a single event, capturing the four key steps a student
must take in order to graduate: three grade-to-grade promotions (9 to 10, 10 to 11, and 11 to 12) and ultimately earning a
diploma (grade 12 to graduation). Each of these individual components corresponds to a grade-promotion ratio.
The equation below illustrates the CPI formula for calculating graduation rates. The class of 2006-07, the most recent year of data
available, is used as an example.
CPI
10th graders, fall 2007
9th graders, fall 2006
11th graders, fall 2007
10th graders, fall 2006
12th graders, fall 2007
11th graders, fall 2006
Diploma recipients, spring 2007
12th graders, fall 2006
Multiplying the four grade-specific promotion ratios together produces the graduation rate, the percent of public school 9th
graders who will complete high school on time with a regular diploma. The CPI counts only students receiving standard high school
diplomas as graduates, following the definition of a graduate established by the No Child Left Behind Act.
We can use a simplified example to further demonstrate how the center calculates the CPI. Let us suppose that a particular school
district currently has 100 students enrolled in each grade from 9 through 12. We will also assume that 5 percent of students
currently in grades 9, 10, and 11 will drop out of school this year and that 5 percent of seniors will fail to earn a diploma at the end
of the year. So, for example, we would count 100 9th graders at our starting point but only 95 10th graders the following fall.
CPI
95
100
95
100
95
100
95
100
.815
Carrying out the calculation (shown above), we arrive at a graduation rate of 81.5 percent for this district. Given conditions in this
hypothetical district (an effective 5 percent annual attrition rate for students at each grade level), only about 82 out of every 100
9th graders would be expected to finish high school with a diploma.
The CPI can be calculated for public school districts that have students enrolled in the secondary grades (9 through 12). State and
national statistics are generated by aggregating the district-level data upward.
Notes on the Methodology
The EPE Research Center calculates graduation rates using data from the Common Core of Data (CCD), an annual census of public
schools and school districts in the United States conducted by the U.S. Department of Education. Detailed methodological
descriptions of the CCD can be found in technical documentation published by the National Center for Education Statistics
(available online at nces.ed.gov/ccd). The District of Columbia, Kentucky, and Oregon did not report 2006-07 diploma counts for
student subgroups to the CCD. The EPE Research Center was able to obtain additional graduation data directly from the state
education agencies of Kentucky and Oregon.
The centers goal is to provide a direct measure of the graduation rate for each of the roughly 11,000 school districts in the nation
that enroll high school students. It was possible to do this for districts serving the vast majority (97 percent) of all public school
students nationwide. But in a small number of casesfor example, if a particular piece of information needed to calculate the CPI
indicator was missingthe center could not directly compute the graduation rate.
To avoid the unintentional disclosure of information about individual students, the EPE Research Center does not report results
for very small demographic subgroups, those with fewer than five students in a given category. Additional procedures are
employed to ensure that results are only reported in situations where sufficient data are available for a reliable calculation.
Editorial Projects in Education Research Center
www.edweek.org/rc
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Washington State Report Card 10 11Document2 pagesWashington State Report Card 10 11api-213684902Pas encore d'évaluation
- Leslie State Report Card 11 12Document2 pagesLeslie State Report Card 11 12api-206158968Pas encore d'évaluation
- WMS Report Card 2010 - 2011Document2 pagesWMS Report Card 2010 - 2011tmlittle3038Pas encore d'évaluation
- CA HS GraduationDocument15 pagesCA HS Graduationgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Highland Elementary SchoolDocument25 pagesHighland Elementary SchoolParents' Coalition of Montgomery County, MarylandPas encore d'évaluation
- Illinois School Card: Stark County Elem SCH Wyoming, ILLINOIS Grades: Stark County CUSD 100Document12 pagesIllinois School Card: Stark County Elem SCH Wyoming, ILLINOIS Grades: Stark County CUSD 100ttalbot6801Pas encore d'évaluation
- RMS DPI 2011-2012 Report CardDocument2 pagesRMS DPI 2011-2012 Report Cardtmlittle3038Pas encore d'évaluation
- District 2015-2016Document2 pagesDistrict 2015-2016api-305626840Pas encore d'évaluation
- EDLD 5333 Week 1 Assignment-1Document9 pagesEDLD 5333 Week 1 Assignment-1tmartinez82996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report Car Dhs 2012 AspxDocument10 pagesReport Car Dhs 2012 Aspxttalbot6801Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bonduel Elementary 2015-2016Document2 pagesBonduel Elementary 2015-2016api-305626840Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cherry Road School's National Blue Ribbon School ApplicationDocument25 pagesCherry Road School's National Blue Ribbon School ApplicationCharleyHannagan100% (1)
- Bonduel Middle 2015-2016Document2 pagesBonduel Middle 2015-2016api-305626840Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bonduel High 2015-2016Document2 pagesBonduel High 2015-2016api-305626840Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amador Valley High School: Principal's MessageDocument8 pagesAmador Valley High School: Principal's MessageyurahdPas encore d'évaluation
- CHS School Report Card 2012-13Document3 pagesCHS School Report Card 2012-13clementsrangersPas encore d'évaluation
- Oak Grove k-8Document15 pagesOak Grove k-8ezexitteamPas encore d'évaluation
- Oregon Report Card Middle School RecommendationDocument3 pagesOregon Report Card Middle School RecommendationStatesman JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Averaged Freshman Graduation Rate For Public High Schools From The Common Core of Data: School Years 2002-03 and 2003-04Document18 pagesThe Averaged Freshman Graduation Rate For Public High Schools From The Common Core of Data: School Years 2002-03 and 2003-04Sherman100% (2)
- Illinois School Card: Stark County Junior High School Toulon, ILLINOIS Grades: Stark County CUSD 100Document12 pagesIllinois School Card: Stark County Junior High School Toulon, ILLINOIS Grades: Stark County CUSD 100ttalbot6801Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newbrook Elementary School: I. Student Performance On The Most Recent State Assessment (Sbac)Document2 pagesNewbrook Elementary School: I. Student Performance On The Most Recent State Assessment (Sbac)api-98197056Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report CardDocument2 pagesReport Cardgke6116Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edtc 630 School Technology PlanDocument20 pagesEdtc 630 School Technology Planapi-653474004Pas encore d'évaluation
- CTGradRates Web 08Document28 pagesCTGradRates Web 08Alfonso RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Wallace Year OneDocument1 pageWallace Year Onelps2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- School Report: Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics, 2013-2014Document34 pagesSchool Report: Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics, 2013-2014Karen KrisfalusiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dss F Presentation State Board 111915Document18 pagesDss F Presentation State Board 111915KevinOhlandtPas encore d'évaluation
- Yonkers City SnapshotDocument2 pagesYonkers City SnapshotWestchester Children's AssociationPas encore d'évaluation
- BT ElementaryDocument18 pagesBT Elementaryapi-308493334Pas encore d'évaluation
- NC School Report Card 2011-12Document2 pagesNC School Report Card 2011-12api-249780077Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oregon Report Card High School RecommendationDocument4 pagesOregon Report Card High School RecommendationStatesman JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- School Report Card 12 13Document2 pagesSchool Report Card 12 13api-271885581Pas encore d'évaluation
- Illinois District Card: Stark County CUSD 100 Wyoming, ILLINOISDocument21 pagesIllinois District Card: Stark County CUSD 100 Wyoming, ILLINOISttalbot6801Pas encore d'évaluation
- ReportDocument5 pagesReportapi-314221761Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Economic Benefits of International Education To The United States For The 2009-2010 Academic Year: A Statistical AnalysisDocument5 pagesThe Economic Benefits of International Education To The United States For The 2009-2010 Academic Year: A Statistical AnalysisMuhammad MotaweaPas encore d'évaluation
- Texas Education Agency 2014-15 School Report Card SPRING BRANCH EL (101920114)Document2 pagesTexas Education Agency 2014-15 School Report Card SPRING BRANCH EL (101920114)api-317039196Pas encore d'évaluation
- EPSL 0706 236 EPRU AppgDocument10 pagesEPSL 0706 236 EPRU AppgNational Education Policy CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- WJC Report CardDocument10 pagesWJC Report Cardapi-282666502Pas encore d'évaluation
- School and Community ProfileDocument31 pagesSchool and Community Profileapi-253260591Pas encore d'évaluation
- State Education TrendsDocument60 pagesState Education TrendsCato Institute100% (1)
- RTT Goal Area or Performance Measure TargetsDocument22 pagesRTT Goal Area or Performance Measure TargetsJulian A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Delaware Dropout Summary Statistics 2011 - 2012: State of Delaware Department of EducationDocument22 pagesDelaware Dropout Summary Statistics 2011 - 2012: State of Delaware Department of EducationJohn AllisonPas encore d'évaluation
- BT Mid HiDocument18 pagesBT Mid Hiapi-308493334Pas encore d'évaluation
- Original Performance MatrixDocument6 pagesOriginal Performance Matrixenm077486Pas encore d'évaluation
- School and Community ProfileDocument32 pagesSchool and Community Profileapi-251392528Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wallace Year FourDocument1 pageWallace Year Fourlps2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Connecticut Department of EducationDocument7 pagesConnecticut Department of EducationHelen BennettPas encore d'évaluation
- School and Community Profile Assignment Zoe Romero OhsDocument23 pagesSchool and Community Profile Assignment Zoe Romero Ohsapi-253803594Pas encore d'évaluation
- College Corner: What You Need To Know by NOW!!!Document4 pagesCollege Corner: What You Need To Know by NOW!!!EricPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-2011 Special Education ReportDocument2 pages2010-2011 Special Education ReportStatesman JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- EPSL 0509 109 EPRU AppDocument19 pagesEPSL 0509 109 EPRU AppNational Education Policy CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- Setting and ContextDocument14 pagesSetting and Contextapi-257586514Pas encore d'évaluation
- Public High School Four-Year On-Time Graduation Rates and Event Dropout Rates: School Years 2010-11 and 2011-12 2014391Document35 pagesPublic High School Four-Year On-Time Graduation Rates and Event Dropout Rates: School Years 2010-11 and 2011-12 2014391Latinos Ready To VotePas encore d'évaluation
- Fraser Report 2010Document12 pagesFraser Report 2010Parker BradyPas encore d'évaluation
- School and Community ProfileDocument17 pagesSchool and Community Profilevirginia.philbrookPas encore d'évaluation
- A Real Mom's Guide To Saving Money on College TuitionD'EverandA Real Mom's Guide To Saving Money on College TuitionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Missing the Mark: Why So Many School Exam Grades are Wrong – and How to Get Results We Can TrustD'EverandMissing the Mark: Why So Many School Exam Grades are Wrong – and How to Get Results We Can TrustPas encore d'évaluation
- Uc Field Research Safety Manual 2017 18 Final 082318Document49 pagesUc Field Research Safety Manual 2017 18 Final 082318govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 6 Gow and Rookwood Vol 2 2009Document12 pagesPaper 6 Gow and Rookwood Vol 2 2009govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Improv For DI1Document3 pagesImprov For DI1govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Free-Response Question Tasks: OtherDocument24 pagesFree-Response Question Tasks: Othergovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Must Know These CasesDocument3 pagesMust Know These Casesgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- AMS Workshop HandoutDocument5 pagesAMS Workshop Handoutgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual: Maxpower 802.11N/G/B Usb 2.0 AdapterDocument19 pagesUser Manual: Maxpower 802.11N/G/B Usb 2.0 Adaptergovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Challenge Day OprahDocument21 pagesChallenge Day Oprahgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1 In-Class Reading AP GovDocument2 pagesDay 1 In-Class Reading AP Govgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Making Miracles Happen: The Gratitude GameDocument8 pagesMaking Miracles Happen: The Gratitude Gamegovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circle of Change Start-Up Guide: 2520 Stanwell Drive, Suite 160 Concord, CA 94520 USA (925) 957-0234Document27 pagesCircle of Change Start-Up Guide: 2520 Stanwell Drive, Suite 160 Concord, CA 94520 USA (925) 957-0234govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Youth Needs AssessmentDocument63 pagesYouth Needs Assessmentgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Empowerment Through Learning in A Global World - Conference 2012Document2 pagesEmpowerment Through Learning in A Global World - Conference 2012govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lot Near Florida State University With City Water Sewer and Power - LandCentralDocument1 pageLot Near Florida State University With City Water Sewer and Power - LandCentralgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of Constitutional InterpretationDocument6 pagesTheories of Constitutional Interpretationgovandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Resource For Equitable Classroom Practices 2010Document40 pagesA Resource For Equitable Classroom Practices 2010govandlaw4671Pas encore d'évaluation