Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
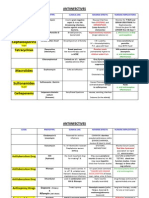
Pharmaceutical Drug Classifications
Transféré par
hiteshchavadaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pharmaceutical Drug Classifications
Transféré par
hiteshchavadaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine or medicament, can be loosely defined as
any substance intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of
disease.Other synonyms include pharmacotherapy, pharmacotherapeutics, and drug
treatment.
Classification
Medications can be classified in various ways[3], such as by chemical properties, mode of
administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. An elaborate and widely used
classification system is the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC
system). The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines.
A sampling of classes of medicine includes:
1. Antipyretics: reducing fever (pyrexia/pyresis)
2. Analgesics: painkillers
3. Antimalarial drugs: treating malaria
4. Antibiotics: inhibiting germ growth
5. Antiseptics: prevention of germ growth near burns, cuts and wounds
Types of medications (type of pharmacotherapy)
For the gastrointestinal tract or digestive system
Upper digestive tract: antacids, reflux suppressants, antiflatulents, antidopaminergics,
proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor antagonists, cytoprotectants, prostaglandin
analogues
Lower digestive tract: laxatives, antispasmodics, antidiarrhoeals, bile acid sequestrants,
opioid...gatartic drugs
For the cardiovascular system
General: beta-receptor blocker or beta blocker, calcium channel blockers, diuretics,
cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmics, nitrate, antianginals, vasoconstrictor, vasodilator,
peripheral activator
Affecting Blood pressure: ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, alpha blocker
Coagulation: anticoagulant, heparin, antiplatelet drug, fibrinolytic, anti-hemophilic factor,
haemostatic drugs
Atherosclerosis/cholesterol agents: hypolipidaemic agents, statins.
For the central nervous system
See also: Psychiatric medication
hypnotic, anaesthetics, antipsychotic, antidepressant (including tricyclic antidepressants,
monoamine oxidase inhibitor, lithium salt, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor), anti-emetic,
anticonvulsant and antiepileptic, anxiolytic, barbiturate, movement disorder drug, stimulant
(including amphetamines), benzodiazepine, cyclopyrrolone, dopamine antagonist, antihistamine,
cholinergic, anticholinergic, emetic, cannabinoids, 5-HT antagonist
For pain & consciousness (analgesic drugs)
Further information: Analgesic
The main classes of painkillers are NSAIDs, opioids and various orphans such as paracetamol,
tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants.
For musculo-skeletal disorders
NSAIDs (including COX-2 selective inhibitors), muscle relaxant, neuromuscular drug
anticholinesterase
For the eye
General: adrenergic neurone blocker, astringent, ocular lubricant
Diagnostic: topical anesthetics, sympathomimetics, parasympatholytics, mydriatics,
cycloplegics
Anti-bacterial: antibiotics, topical antibiotics, sulfa drugs, aminoglycosides,
fluoroquinolones
Anti-viral:
Anti-fungal: imidazoles, polyenes
Anti-inflammatory: NSAIDs, corticosteroids
Anti-allergy: mast cell inhibitors
Anti-glaucoma: adrenergic agonists, beta-blockers, carbonic anhydrase
inhibitors/hyperosmotics, cholinergics, miotics, parasympathomimetics, prostaglandin
agonists/prostaglandin inhibitors. nitroglycerin
For the ear, nose and oropharynx
sympathomimetic, antihistamine, anticholinergic, NSAIDs, steroid, antiseptic, local anesthetic,
antifungal, cerumenolyti
For the respiratory system
bronchodilator, NSAIDs, anti-allergic, antitussive, mucolytic, decongestant
corticosteroid, beta-receptor antagonist, anticholinergic, steroid
For endocrine problems
androgen, antiandrogen, gonadotropin, corticosteroid, human growth hormone, insulin,
antidiabetic (sulfonylurea, biguanide/metformin, thiazolidinedione, insulin), thyroid hormones,
antithyroid drugs, calcitonin, diphosponate, vasopressin analogues
For the reproductive system or urinary system
antifungal, alkalising agent, quinolones, antibiotic, cholinergic, anticholinergic,
anticholinesterase, antispasmodic, 5-alpha reductase inhibitor, selective alpha-1 blocker,
sildenafil, fertility medication
For contraception
Hormonal contraception
Ormeloxifene
Spermicide
For obstetrics and gynecology
NSAIDs, anticholinergic, haemostatic drug, antifibrinolytic, Hormone Replacement Therapy,
bone regulator, beta-receptor agonist, follicle stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone, LHRH
gamolenic acid, gonadotropin release inhibitor, progestogen, dopamine agonist, oestrogen,
prostaglandin, gonadorelin, clomiphene, tamoxifen, Diethylstilbestrol
For the skin
emollient, anti-pruritic, antifungal, disinfectant, scabicide, pediculicide, tar products, vitamin A
derivatives, vitamin D analogue, keratolytic, abrasive, systemic antibiotic, topical antibiotic,
hormones, desloughing agent, exudate absorbent, fibrinolytic, proteolytic, sunscreen,
antiperspirant, corticosteroid
For infections and infestations
antibiotic, antifungal, antileprotic, antituberculous drug, antimalarial, anthelmintic, amoebicide,
antiviral, antiprotozoal
For immunology
vaccine, immunoglobulin, immunosuppressant, interferon, monoclonal antibody
For allergic disorders
anti-allergic, antihistamine, NSAIDs
For nutrition
tonic, iron preparation, electrolyte, parenteral nutritional supplement, vitamins, anti-obesity drug,
anabolic drug, haematopoietic drug, food product drug
For neoplastic disorders
cytotoxic drug, therapeutic antibody, sex hormones, aromatase inhibitor, somatostatin inhibitor,
recombinant interleukins, G-CSF, erythropoietin
For diagnostics
contrast media
For euthanasia
An euthanaticum is used for euthanasia and physician-assisted suicide, see also barbiturates.
Euthanasia is not permitted by law in many countries, and consequently medicines will not be
licensed for this use in those countries.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chemotherapy NDocument28 pagesChemotherapy NFaisal MehboobPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis Nursing OutlineDocument6 pagesSepsis Nursing OutlineSavannah Hayden100% (1)
- STUDENT Sepsis Rapid ReasoningDocument6 pagesSTUDENT Sepsis Rapid Reasoningghodghod123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug CardsDocument17 pagesDrug CardsJoane LacapPas encore d'évaluation
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis Content Concepts MapDocument3 pagesSepsis Content Concepts Mapghodghod1230% (1)
- Nursing and PharmacologyDocument9 pagesNursing and PharmacologyJennifer ViciosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX Medication MnemonicsDocument2 pagesNCLEX Medication MnemonicsGVHHPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Drug CardsDocument33 pagesPharmacology Drug CardsAidenhunter05100% (1)
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocument6 pagesPrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 pagePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug CardDocument1 pageDrug CardPaul AlfonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDocument5 pagesCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMePas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerArianne Pearl PrimeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiDocument59 pagesToxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiTan Geok EngPas encore d'évaluation
- Ati Medication Template CodeineDocument1 pageAti Medication Template CodeineSharee HaywoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Neoplastic and Immunosupressant DrugsDocument29 pagesAnti Neoplastic and Immunosupressant DrugsAshraf Moby100% (1)
- Waiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFmp1757100% (1)
- Antibiotics by class, generic names, uses and side effectsDocument6 pagesAntibiotics by class, generic names, uses and side effectsLinguumPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Exam #3 Review: Diuretics, Heart Failure Drugs, Lipids, ElectrolytesDocument293 pagesPharm Exam #3 Review: Diuretics, Heart Failure Drugs, Lipids, ElectrolytesTrish HồPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocument43 pagesNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- Chapter 18 Common Drugs PDFDocument221 pagesChapter 18 Common Drugs PDFlalallalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- GI NotesDocument19 pagesGI NotesBigBoostingPas encore d'évaluation
- 50 Most Commonly Prescribed Medications 02Document4 pages50 Most Commonly Prescribed Medications 02Jelly BeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Cards EndoDocument12 pagesDrug Cards EndoChristine Schroeder100% (1)
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDocument4 pagesDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Infectives Course #25Document18 pagesAnti-Infectives Course #25Gina Giammalvo100% (2)
- Exam Cram Cheet SheetDocument2 pagesExam Cram Cheet SheetSheila Stenson-Roberts100% (1)
- Introduction to commonly used antibioticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction to commonly used antibioticsAmir AmirulPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1Document96 pagesPharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1gelean payodPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug CardsDocument3 pagesDrug CardsDave HillPas encore d'évaluation
- INFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICSDocument8 pagesINFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICStarun paulPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmacologyDocument35 pagesPharmacologyJan Michael ArtiagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Catagories For NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Catagories For NursingTabatha AustinMomPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Infective Drugs for Bacteria, Viruses and ParasitesDocument28 pagesAnti-Infective Drugs for Bacteria, Viruses and ParasitesMay EvelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotics Study Guide For NursesDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Study Guide For NursesLauren Trotman100% (7)
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDocument11 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Ams 11Document702 pagesAms 11CrazyPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- Drug AdvilDocument1 pageDrug AdvilDiana Laura LeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmournePas encore d'évaluation
- SNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Document5 pagesSNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Whitney Krabbenhoft100% (1)
- Understanding ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Electrolytessurviving nursing schoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology BriefDocument287 pagesPharmacology BriefHu Mihi100% (1)
- Lab Values Chart GuideDocument5 pagesLab Values Chart GuideVanessaMUeller100% (3)
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandPATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Experiment No. 3: Fractional Distillation: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 3: Fractional Distillation: ObjectiveshiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bam Sase StudyDocument4 pagesBam Sase StudyhiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 Toxi-Chromo Kit 2015Document7 pagesLab 5 Toxi-Chromo Kit 2015hiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 Nitrogen Cycle 2015Document8 pagesLab 3 Nitrogen Cycle 2015hiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 Nitrogen Cycle 2015Document8 pagesLab 3 Nitrogen Cycle 2015hiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2b - Bacteria and Actinomycetes - 2015Document6 pagesLab 2b - Bacteria and Actinomycetes - 2015hiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 Dna Extraction PCR Ardra 2015Document9 pagesLab 4 Dna Extraction PCR Ardra 2015hiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2a - Contact Slide AssayDocument8 pagesLab 2a - Contact Slide Assayhiteshchavada100% (1)
- Exp 1 Egg Salad ReportDocument4 pagesExp 1 Egg Salad ReporthiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 1 Egg Salad ReportDocument4 pagesExp 1 Egg Salad ReporthiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient surface and air sampling methods for detecting microbesDocument2 pagesEfficient surface and air sampling methods for detecting microbeshiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bam Sase StudyDocument4 pagesBam Sase StudyhiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Courses For BiotechDocument6 pagesCourses For BiotechhiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bam Sase StudyDocument4 pagesBam Sase StudyhiteshchavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson Planapi-456870847Pas encore d'évaluation
- Insoluble Ions EssayDocument2 pagesInsoluble Ions EssayDarshan Meghji100% (1)
- November 2, 2012 Strathmore TimesDocument32 pagesNovember 2, 2012 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematology: DR - Abhilash Kumar JainDocument1 pageHaematology: DR - Abhilash Kumar Jainseds5anuragPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate of Accreditation: Swift Silliker (Pty) LTDDocument10 pagesCertificate of Accreditation: Swift Silliker (Pty) LTDpham xuan tinh tinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Elbow Joint ConditionsDocument3 pagesElbow Joint ConditionsMarilia FarensenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Keto DietDocument2 pagesKeto DietdewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracy Scroggins LawsuitDocument27 pagesTracy Scroggins LawsuitRobert LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Vol. 2 No. 10Document58 pagesVol. 2 No. 10Lindsey RobbinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alemitu MequanintDocument125 pagesAlemitu MequanintshegawPas encore d'évaluation
- The Disciples of Christ Congo Mission in the 1930sDocument20 pagesThe Disciples of Christ Congo Mission in the 1930sHervé DisadidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Heinz Kohut - Self PsychologyDocument49 pagesHeinz Kohut - Self PsychologyDesiree Pescasio DimasuayPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrients: Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRDDocument19 pagesNutrients: Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRDrandy_27995Pas encore d'évaluation
- The New Super Nutrient Food - Raw Banana FlourDocument5 pagesThe New Super Nutrient Food - Raw Banana FlourSandeep Goud kolalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Dissection Lab Report GuideDocument6 pagesHeart Dissection Lab Report Guideelorenzana0511100% (1)
- CAP Protocol-2016 Thyroid - HighlightedDocument8 pagesCAP Protocol-2016 Thyroid - Highlightedpath2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Procedure Checklist Chapter 22: Providing Denture CareDocument1 pageProcedure Checklist Chapter 22: Providing Denture Caremacs_smacPas encore d'évaluation
- COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate from India's Ministry of HealthDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Vaccination Certificate from India's Ministry of Healthbliss bPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of OesophagusDocument24 pagesAnatomy of OesophagusLia Restimulia DelfitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Behavior and Crisis ManagementDocument46 pagesHuman Behavior and Crisis ManagementkimkimkouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Seri Final NotesDocument179 pagesSeri Final Notesbharath gowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Cardiovascular Physiology: A Laboratory ExerciseDocument70 pagesIntegrated Cardiovascular Physiology: A Laboratory ExercisefireworkrwPas encore d'évaluation
- Witch Hunting in Assam Practices Causes Legal Issues and Challenges by Jehirul Islam and AfruzAra AhmedDocument11 pagesWitch Hunting in Assam Practices Causes Legal Issues and Challenges by Jehirul Islam and AfruzAra AhmedDaisy GoswamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Assessment - 1Document9 pagesAnatomy Assessment - 1Laylee TaghizadehPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition programmes and organizations in PakistanDocument10 pagesNutrition programmes and organizations in PakistanAB DivillierPas encore d'évaluation
- Detoxification of Pesticide Waste Via Activated Carbon Adsorption ProcessDocument11 pagesDetoxification of Pesticide Waste Via Activated Carbon Adsorption ProcessNadia MandasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Praktikum Taksonomi Vertebrata RDocument10 pagesLaporan Praktikum Taksonomi Vertebrata RMuhammad Fahreza Rizky WPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions For Hepatic Disorders - NURS 1028 Nursing TheoryDocument2 pagesPractice Questions For Hepatic Disorders - NURS 1028 Nursing TheoryNicholas ObasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 MilunovicDocument14 pages20 MilunovicReffada YodhyasenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacographia IndicaDocument615 pagesPharmacographia IndicaSatish Vaidya100% (1)