Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet No. 1 Design of Gears
Transféré par
sallyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sheet No. 1 Design of Gears
Transféré par
sallyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Department of Mechanical Engineering
University of Mosul
Machines Systems Design
4th Class
Sheet No. 1
Design of Gears
1.
For the gear train illustrated in Fig. (1), determine the output speed and direction
of rotation if the input shaft rotates at 1490 rev/min clockwise. Gears 2 to 5 have
a module of 1.5 mm while gears 6 to 9 have a module of 2 mm.
Fig. (1)
2.
A spur gearset has a module of 6 mm and a velocity ratio of 4. The pinion has
16 teeth. Find the number of teeth on the driven gear, the pitch diameters, and
the theoretical center-to-center distance.
3.
A gearbox is required to transmit 7 kW from a shaft rotating at 2000 rev/min.
The desired output speed is approximately 350 rev/min. Select appropriate
gears. Be sure to avoid an interference problem in the teeth.
4.
A gearbox is required to transmit 5 kW from a shaft rotating at 2650 rev/min.
The desired output speed is approximately 200 rev/min. Specify appropriate
gears.
5.
A gearbox is to be designed with a compound reverted gear train that transmits
25 horsepower with an input speed of 2500 rev/min. The output should deliver
the power at a rotational speed in the range of 280 to 300 rev/min. Spur gears
with 20 pressure angle are to be used. Determine suitable numbers of teeth for
each gear.
6.
Shaft a in Fig. (2) has a power input of 75 kW at a speed of 1000 rev/min in the
counterclockwise direction. The gears have a module of 5 mm and a 20
pressure angle. Gear 3 is an idler.
(a) Find the force F3b that gear 3 exerts against shaft b.
(b) Find the torque T4c that gear 4 exerts on shaft c.
|Page1
Department of Mechanical Engineering
University of Mosul
Machines Systems Design
4th Class
Sheet No. 1
Design of Gears
Fig. (2)
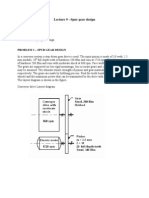
7.
The gears shown in Fig. (3) have a module of 12 mm and a
pressure angle.
The pinion rotates at 1800 rev/min clockwise and transmits 150 kW through the
idler pair to gear 5 on shaft c. What forces do gears 3 and 4 transmit to the idler
shaft?
Fig. (3)
|Page2
Department of Mechanical Engineering
University of Mosul
Machines Systems Design
4th Class
Sheet No. 1
Design of Gears
8.
A
full depth spur pinion is to transmit 1.75 kW at 1200 rev/min. If the
pinion has 18 teeth with a module of 2 mm, determine a suitable value for the
face width based on the Lewis formula if the bending stress should not exceed
75 MPa.
9.
A steel spur pinion has a diametral pitch of 10 teeth/in, 18 teeth cut full-depth
with a
pressure angle, and a face width of 1 in. This pinion is expected to
transmit 2 hp at a speed of 600 rev/min. Determine the bending stress.
10. A
full-depth steel spur pinion with 18 teeth is to transmit 2.5 hp at a speed
of 600 rev/min. Determine appropriate values for the face width and diametral
pitch based on an allowable bending stress of 10 kpsi.
11. A
full-depth steel spur pinion is to transmit 1.5 kW hp at a speed of 900
rev/min. If the pinion has 18 teeth, determine suitable values for the module and
face width. The bending stress should not exceed 75 MPa.
12. A gear drive consists of a 16-tooth
steel spur pinion and a 48-tooth cast-iron
gear having a pitch of 12 teeth/in. For a power input of 1.5 hp at a pinion speed
of 700 rev/min, select a face width based on an allowable contact stress of 100
kpsi.
13. A 20 teeth full-depth,
pressure angle, module 4 mm cast iron spur pinion is
used to drive a 32 teeth cast iron gear. Determine the contact stress if 10.5 kW is
transmitted. The pinion speed is 950 rev/min and the face width is 50 mm.
|Page3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987D'EverandProceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987W. R. TysonPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Health MonitoringD'EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Design of Gear BoxDocument2 pages6 Design of Gear BoxRutvikLathia100% (1)
- Design of CouplingDocument75 pagesDesign of CouplingVatsal BhalaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 Fluctuating LoadDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Fluctuating Loadabhishek chaurasiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knuckle Joints DesignDocument10 pagesKnuckle Joints DesignKvrd Prasad100% (1)
- Machine Design Lec3Document75 pagesMachine Design Lec3sam0415Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report FEADocument15 pagesReport FEAamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Spur Gear Design 1Document16 pagesSpur Gear Design 1Nagu SriramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Document8 pagesGears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Satish Dhandole100% (1)
- ME308 Second Project PDFDocument13 pagesME308 Second Project PDFOzan OzgenPas encore d'évaluation
- Screw Threads: ME354 Albert ClaypoolDocument13 pagesScrew Threads: ME354 Albert ClaypoolfotickPas encore d'évaluation
- Design II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsDocument42 pagesDesign II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsThieroy PelendaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spur Gear Design by IIT MadrasDocument28 pagesSpur Gear Design by IIT MadrasC.S.ABHILASHPas encore d'évaluation
- Meshing of GearsDocument19 pagesMeshing of GearsGovind RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Gear BasicsDocument6 pages2 Gear BasicsMohamed Adel RizkPas encore d'évaluation
- Spur GearDocument11 pagesSpur GearvenkatkavinPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampDocument54 pages3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampKhaled HamdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Spur Gear Theory and Design: Soumitra Bhattacharya, M.Tech (Mech), Professional Member of ASMEDocument16 pagesSpur Gear Theory and Design: Soumitra Bhattacharya, M.Tech (Mech), Professional Member of ASMESyed Shoaib RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tooth ThicknessDocument9 pagesTooth ThicknessPraveen VundrajavarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tolerances As Per en 12493Document5 pagesTolerances As Per en 12493prasad raikarPas encore d'évaluation
- AMTE126 - 10B Wet Sump and Dry Sump LubricationDocument1 pageAMTE126 - 10B Wet Sump and Dry Sump LubricationRebecca Lepon LegaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Bearings & Miscellaneous ElementsDocument14 pagesDesign of Bearings & Miscellaneous ElementsjvanandhPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Fabrication of Bolts (Full)Document26 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Bolts (Full)subinPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-2 Design of Spur GearDocument56 pagesUNIT-2 Design of Spur GearMarthandePas encore d'évaluation
- Contact Stress and Bending Stress Analysis of Spur Gear by Analytical MethodDocument3 pagesContact Stress and Bending Stress Analysis of Spur Gear by Analytical MethodlitonPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Design of Machine Tool GearboxesDocument9 pagesAdaptive Design of Machine Tool Gearboxesأحمد دعبسPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaft LayoutDocument21 pagesShaft LayoutAmmar SafwtPas encore d'évaluation
- Universal Joint and Theory-Basic PDFDocument17 pagesUniversal Joint and Theory-Basic PDFPrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Document21 pagesJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Adib AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- PulleysDocument28 pagesPulleyshelmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cotter JointDocument18 pagesCotter JointritPas encore d'évaluation
- ACD Lab Manual Spur Gear DesignDocument4 pagesACD Lab Manual Spur Gear Designbalaguru780% (1)
- A Crowning Achievement For Automotive ApplicationsDocument10 pagesA Crowning Achievement For Automotive ApplicationsCan CemrePas encore d'évaluation
- Alwasy Step Ahead in TechnologyDocument6 pagesAlwasy Step Ahead in TechnologyDxFx100% (1)
- A-313 - 98Document7 pagesA-313 - 98José Ramón GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Automats and Tool LayoutsDocument20 pagesAutomats and Tool LayoutsAyesha IshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Transmission Systems-Question BankDocument28 pagesDesign of Transmission Systems-Question BankAlfred Franklin V100% (1)
- Design of The Drive Mechanism For A Reciprocating Coal FeederDocument81 pagesDesign of The Drive Mechanism For A Reciprocating Coal FeederemersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Fabrication of Hammering and Grinding Machine-1Document16 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Hammering and Grinding Machine-1Viswaragavan.NPas encore d'évaluation
- Helical Gears: DefinitionDocument29 pagesHelical Gears: DefinitionMuthuvel MPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Design 2Document15 pagesGear Design 2cracking khalifPas encore d'évaluation
- AllowancesDocument4 pagesAllowancesAlok Dubey100% (1)
- Iso 6336 Hohn PDFDocument6 pagesIso 6336 Hohn PDFmgualdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurements & Metrology (English)Document29 pagesMeasurements & Metrology (English)Kumar SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Rack and Pinion Gear DesignDocument32 pagesRack and Pinion Gear DesignmattgrubbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling of Welded Connections in SolidWDocument5 pagesModeling of Welded Connections in SolidWCleyton L. AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- V-Machine Design 1Document37 pagesV-Machine Design 1roamer10Pas encore d'évaluation
- ISO Gear StandardsDocument6 pagesISO Gear StandardsEslam YehiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Production - Technology Lab Manual 181903Document29 pagesProduction - Technology Lab Manual 181903jhpatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Worm Wheel HobsDocument7 pagesWorm Wheel HobsRaul PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Hobbing AplicationsDocument52 pagesHobbing AplicationsMickloSoberanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of PROTECTED FLANGE COUPLING Solidworks 2016 and ANSYS WorkbenchDocument27 pagesDesign and Analysis of PROTECTED FLANGE COUPLING Solidworks 2016 and ANSYS Workbenchamu100% (1)
- LAB REPORT of Gear Hobbing MachineDocument6 pagesLAB REPORT of Gear Hobbing MachineAhtisham AmjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue Design Procedures: Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of the International Committee on Aeronautical Fatigue held in Munich, 16–18 June 1965D'EverandFatigue Design Procedures: Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of the International Committee on Aeronautical Fatigue held in Munich, 16–18 June 1965E. GassnerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39D'EverandThe Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Designn of Tranmission SystemDocument4 pagesDesignn of Tranmission Systemsathiskumar411Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Transmission System-QbDocument5 pagesDesign of Transmission System-QbGanapathi SekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- ME6601.16 MarksDocument6 pagesME6601.16 Markssathiskumar411Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gearing - ProblemsDocument7 pagesGearing - ProblemsmanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas Copco Drilling Solutions: Parts and ServicesDocument28 pagesAtlas Copco Drilling Solutions: Parts and ServicesAbraham HuacasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lattice Boom Hydraulic Crawler Crane SC-50 HDDocument8 pagesLattice Boom Hydraulic Crawler Crane SC-50 HDFelipe HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- DNFT-PRX PoDocument1 pageDNFT-PRX PoSamir ELPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Pump General Functional Test ChecklistDocument4 pagesElectrical Pump General Functional Test ChecklistLouie Raymond Abbas FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- EGB Installation Manual-03113Document16 pagesEGB Installation Manual-03113Maaz BilgramiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shimano Hub Type Maintenance-Manual PDFDocument5 pagesShimano Hub Type Maintenance-Manual PDFArmandSorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel InjectorsDocument2 pagesFuel InjectorsxLibellePas encore d'évaluation
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Monitor Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) and EGR System Module (ESM)Document2 pagesExhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Monitor Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) and EGR System Module (ESM)José AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- 966H and 972H Wheel Loader TA2 Technical InspectionDocument8 pages966H and 972H Wheel Loader TA2 Technical InspectionLaouini GhaithPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Manual, Kurbota EngineDocument364 pagesApplication Manual, Kurbota EngineEl Haji Roku88% (8)
- 2gr TorqueDocument3 pages2gr TorqueDouglasArayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 99759-5M300 Mitsubishi Manual PDFDocument292 pages99759-5M300 Mitsubishi Manual PDFCarlos67% (3)
- DHP85, M65D: Hydraulic Pile Driving RigDocument17 pagesDHP85, M65D: Hydraulic Pile Driving RigNila Mustika100% (1)
- Sanyo Wall Mounted Multi Split System Indoor Units Sell SheetDocument2 pagesSanyo Wall Mounted Multi Split System Indoor Units Sell Sheete-ComfortUSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Sheet 1 OctDocument15 pagesControl Sheet 1 OctM MiftakhPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Tne 106 GeDocument50 pages4 Tne 106 Gezakki ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Actual Crankshaft Manufacturer: Inhouse: Raw Material Production + CNC MachiningDocument16 pagesActual Crankshaft Manufacturer: Inhouse: Raw Material Production + CNC Machiningglobalindospareparts100% (1)
- Serva Pumps Parts Service 113015 LR PagesDocument20 pagesServa Pumps Parts Service 113015 LR Pagesjjjjjj33% (3)
- Ansi-Nema MG 1-2003, Revision 1-2004Document584 pagesAnsi-Nema MG 1-2003, Revision 1-2004maxima10Pas encore d'évaluation
- JP Balancing MachineDocument11 pagesJP Balancing MachineJames JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Robotics - Presentation - IndianDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Robotics - Presentation - IndianMurad QəhramanovPas encore d'évaluation
- Aftermarket CatalogAM802 HelicoilDocument24 pagesAftermarket CatalogAM802 HelicoilDavid OrtízPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancang Bangun Simulator Trouble Shooting Sistem Kelistrikan Ac MobilDocument14 pagesRancang Bangun Simulator Trouble Shooting Sistem Kelistrikan Ac MobilJm'kosongtujuh RudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Corte 2Document5 pagesTaller Corte 2Ayder Fabian Rincón RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- ZWBMD020020Document1 pageZWBMD020020Lucian CostachePas encore d'évaluation
- 500 CedarDocument8 pages500 CedarNicole WuPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Engine Dynamo TestingDocument11 pagesSmall Engine Dynamo TestingKhairil AnuarPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Throttle Switch (TS) : Checking Pedal Switch OperationDocument1 page20 Throttle Switch (TS) : Checking Pedal Switch OperationJuan Manuel Cividanes AlonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solenoid Catalog Nov 2018Document36 pagesSolenoid Catalog Nov 2018Pedro Alberto Benites100% (2)
- Ktta 19 New PDFDocument2 pagesKtta 19 New PDFTC Bengalon100% (1)