Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
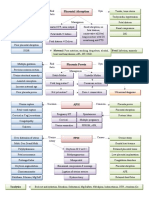
Endometriosis
Transféré par
Ziyad100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
752 vues1 pageObGyn
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentObGyn
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
752 vues1 pageEndometriosis
Transféré par
ZiyadObGyn
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
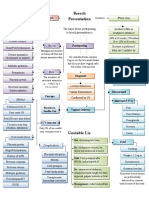
Classical Picture: Ms.
M came to your clinic, a nulliparous woman in her 30’s
complaining of infertility.
Persistence & spread are estrogen 10-15% women presenting
Pathogenesis Endometriosis Incidence
dependent, since it is found almost with gynecological symptoms
exclusively in female reproductive Definition
age group with functioning ovaries. One of the commonest benign gyn.
Presence of endometrial surface conditions
epithelium and/or the presence of Spasmodic, severe dysmenorhoea
Precise etiology unknown, but
unresponsive to analgesia is highly
interaction between one or more of endometrial glands & stroma
these theories occurs outside the lining of the uterine cavity Premenstrual and postmenstrual
spotting is characteristic
Menstrual regurgitation & Implantation
Subtypes symptom of endometriosis,
Coelomic epithelium transformation
Subtype Components Hormonal Response Laparoscopic
Genetic & Immunological factors
appearance
Vascular & lymphatic spread Free Surface Proliferative, secretory and Hemorrhagic
epithelium, menstrual changes vesicle/bleb
glands and
N.B. Minimization of menstrual flow stroma
& suppression of ovarian cycling risk
Enclosed Glands and Proliferative, variable Papule and (later)
stroma Secretory change nodule
Symptoms No menstruation
Healed Glands only No response White nodule or
Site Symptoms
flattened fibrotic scar
Female Dysmenorrhea
reproductive Dyspareunia most Endometrio Variable (Post. Proliferative, secretory and Hemorrhagic
tract (ovaries, common Signs Investigations
broad Infertility
ligament, Lower abdominal &
uterosacral pelvic pain Vaginal Examination (occasionally CA 125 levels (less than ovarian cancer,
lig, post. Rupture/torsion none): useful in evaluation of Rx and recurrence)
cervix) endmetrioma Thickening/nodularity “barbwire”
Low back pain of utereosacral ligaments Ultrasound (limited value, used to assess
(diagnostic). ovarian cyst for endometriomata –
Urinary tract Cyclic hematuria/dysuria Tenderness in pouch of Douglas. homogenous, hypoechoic collection of low-
Ureteric obstruction Ovarian mass or masses (2 out of level echoes within an ovarian cyst)
3).
GIT Dyschezia (triad D’s)
Fixed retroverted uterus MRI (little benefit, better than US for
(rectovaginal Cyclic rectal bleeding
DD also include PID, Ca. of uterus, ovarian cyst or invasion of surrounding
septum) Obstruction
ovary or cevix, hemorrhagic corpus
Surgical Cyclic pain and bleeding luteum, ectopic.). Laparoscopy (Gold Stand., Stag. & Rx)
Scars/umbilicus
N.B. There is no clear relationship between
Lung Rx
Cyclic hemoptysis the stage of endometriosis and the frequency
and severity of pain.
Medical Surgical (if > 3cm)
(aim to suppress estrogen and
progesterone levels to prevents
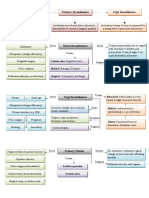
Adenomyosis
Conservative Definition: Extension of endometrial glands & stoma into uterine
NSAIDS musculature > 2.5 cm beneath the basalis layer.
(analgesics±paracetamol/codeine)
Laparoscopy
Combined oral contraceptive (standard) with intra- Patients are usually multiparous and diagnosed in their late 30’s
agents (reduce dysmenorrheal & abdominal lasers. or early 40’s. 15% have associated endometriosis.
1st
menorrhagia)
line Definitive Symptoms: Many asymptomatic, present with secondary
Progestogens
Medroxyprogesterone acetate spasmodic dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia.
Dydrogesterone Hysterectomy and
(Pesudo-decidualization of bilateral salpingo- Signs: Bulky, tender uterus particularly premenstrually.
endometrium) oophorectomy. Invest.: MRI method of choice, image myometrium.
Danazol/gestrinone (weight
gain, acne) N.B. No evidence that Rx Rx: Conservative with NSAIDs and hormonoal control
GnRH Aganoist ( bone density) significantly improves fertility. (amnorrhea) are mainstay Rx (but returns). Hysterectomy only
± HRT definitive Rx.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Endometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersD'EverandEndometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersPas encore d'évaluation
- Associate Professor:Ivan Bonet. Obstetric and Gynecology Associate Professor:Ivan Bonet. Obstetric and GynecologyDocument31 pagesAssociate Professor:Ivan Bonet. Obstetric and Gynecology Associate Professor:Ivan Bonet. Obstetric and Gynecologyivan0% (1)
- Module 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsRenz Francis SasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAbnormal Uterine Bleeding, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Contraception: Science and PracticeD'EverandContraception: Science and PracticeMarcus FilshiePas encore d'évaluation
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 9: GynecologyD'EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 9: GynecologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Clinical Reproductive EndocrinologyD'EverandIntroduction to Clinical Reproductive EndocrinologyÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- ENDOMETRIOSISDocument33 pagesENDOMETRIOSISSusi Indriastuti83% (6)
- Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain: Everything You Need to KnowD'EverandEndometriosis and Pelvic Pain: Everything You Need to KnowPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Diagnostic EndocrinologyD'EverandHandbook of Diagnostic EndocrinologyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Kernicterus, (Bilirubin Encephalopathy) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandKernicterus, (Bilirubin Encephalopathy) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Doctor Will See You Now: Recognizing and Treating EndometriosisD'EverandThe Doctor Will See You Now: Recognizing and Treating EndometriosisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (4)
- Gynecology PDFDocument18 pagesGynecology PDFKatheryn100% (2)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Document23 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Diana Rashid100% (1)
- Pelvic InfectionsDocument56 pagesPelvic Infectionsvein94Pas encore d'évaluation
- GYNE 4.08 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixDocument9 pagesGYNE 4.08 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixGray SnellPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors (Gynaecology)Document70 pagesBenign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors (Gynaecology)Dr Ali MehdiPas encore d'évaluation
- EndometriosisDocument17 pagesEndometriosisapi-383379774Pas encore d'évaluation
- Swatilekha Das (RN, MSN)Document20 pagesSwatilekha Das (RN, MSN)sandeepv08Pas encore d'évaluation
- GynecologyDocument50 pagesGynecologyPhilips55100% (4)
- Gynaecology NotesDocument175 pagesGynaecology NotesNathaniel Mbiu TimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Document14 pagesThe Gynecologic History and Pelvic Examination Up To Date 2016Mateo GlPas encore d'évaluation
- Office Gynecology: Princess Cony CayabaDocument60 pagesOffice Gynecology: Princess Cony CayabaCarla Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometriosis GuidelineDocument44 pagesEndometriosis GuidelineHen DriPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometrial CancerDocument23 pagesEndometrial CancerAlmina RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gynecology Abnormal Bleeding 2014aDocument8 pagesGynecology Abnormal Bleeding 2014aBhi-An BatobalonosPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Gynecologic Lesions FinalDocument11 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions Final2012100% (4)
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument9 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseSohanInduwaraGamage100% (2)
- Progestogens in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2015th Edition (PRG)Document213 pagesProgestogens in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2015th Edition (PRG)amenu_bizuneh100% (4)
- AmenorrheaDocument23 pagesAmenorrheaKarmmanya Razahani PurnamaPas encore d'évaluation
- EndometriosisDocument46 pagesEndometriosisManoj Ranadive0% (1)
- 62 Lecture Menstrual Cycle Abnormalities, Infertility, MenopauseDocument69 pages62 Lecture Menstrual Cycle Abnormalities, Infertility, MenopauseTarek TarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes of GynecologyDocument104 pagesNotes of GynecologyJean Pierre Hitimana100% (1)
- Approach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALDocument56 pagesApproach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALapi-3700579Pas encore d'évaluation
- Short Notes and Short Cases in GynaecologyDocument163 pagesShort Notes and Short Cases in Gynaecologysalah subbahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical CancerDocument36 pagesCervical CancerPro fatherPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Amenorrhea by Ghulam MurtazaDocument14 pagesSecondary Amenorrhea by Ghulam MurtazaDr. Ghulam Murtaza Palh100% (1)
- Fibroid in PregnancyDocument11 pagesFibroid in PregnancyAnonymous UHnQSkxLBDPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 EndometriosisDocument475 pages9 EndometriosisDelviDeavia100% (2)
- Obstetrics MnemonicsDocument9 pagesObstetrics MnemonicsJared Khoo Er Hau100% (2)
- OB Gyne Clinical and Teaching CasesDocument221 pagesOB Gyne Clinical and Teaching CaseszzPas encore d'évaluation
- Gyne History Taking PDFDocument6 pagesGyne History Taking PDFGokul AdarshPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Ovarian ConditionsDocument31 pagesBenign Ovarian ConditionsNur Hanani KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- GYNEPrelims - UrogynecologyDocument18 pagesGYNEPrelims - UrogynecologyRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityDocument23 pagesTreatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityVaisnavi Muthoovaloo67% (3)
- Topic AmenorrheaDocument23 pagesTopic AmenorrheaMohammed AbdulPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual DisorderDocument17 pagesMenstrual Disorderalisaa100% (1)
- Obgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONDocument94 pagesObgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONvalentinemusa218100% (1)
- Amenorrhea: Student HandoutDocument3 pagesAmenorrhea: Student HandoutJc Mae CuadrilleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Fibroid - Viva VoceDocument77 pagesUterine Fibroid - Viva VoceK Haynes Raja100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (1)
- Chronic Pelvic Pain - ACOG Practice Bulletin PDFDocument12 pagesChronic Pelvic Pain - ACOG Practice Bulletin PDFCarlos GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
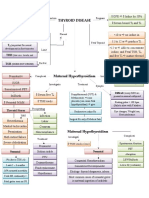
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Secondary Amenorrhea: DR Hanaa AlaniDocument44 pagesSecondary Amenorrhea: DR Hanaa AlaniAakashPas encore d'évaluation
- ObGyn Outline BeckmannDocument85 pagesObGyn Outline Beckmannp4sierra50% (2)
- Menstrual DisordersDocument29 pagesMenstrual DisordersJesse EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual Disorders: Olufemi Aworinde Lecturer/ Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Bowen University, IwoDocument36 pagesMenstrual Disorders: Olufemi Aworinde Lecturer/ Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Bowen University, IwoAkinbani MoyosorePas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of Endometriosis: Petra A.B. Klemmt and Anna Starzinski-PowitzDocument11 pagesMolecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of Endometriosis: Petra A.B. Klemmt and Anna Starzinski-PowitzSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Gyne LesionsDocument133 pagesBenign Gyne LesionsJulie Ann ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyDocument52 pages14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyZiyad100% (4)
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument2 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyad100% (1)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDocument3 pagesFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- "Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyDocument1 page"Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Typical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisDocument1 pageTypical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal Assessment of FetusDocument1 pagePrenatal Assessment of FetusZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
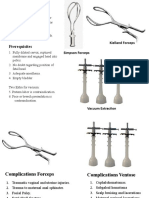
- Instruments & IndicationsDocument11 pagesInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- Thyroid DiseaseDocument1 pageThyroid DiseaseZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetric BleedingDocument1 pageObstetric BleedingZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary IncontinenceDocument1 pageUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- BreechDocument1 pageBreechZiyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Assasination (Partial)Document14 pagesPharmaceutical Assasination (Partial)jamie_clark_2100% (2)
- Rectovaginal FistulaDocument8 pagesRectovaginal FistulaRomi Mauliza FauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Spex Practice Test1Document29 pagesSpex Practice Test1nowPas encore d'évaluation
- ManitolDocument20 pagesManitolkr PadmanabhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kamagra Tablets Are A Outstanding Treatment For EDwmqrm PDFDocument3 pagesKamagra Tablets Are A Outstanding Treatment For EDwmqrm PDFcherryburn67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalence of Abnormal Pap Smear During Pregnancy in A Teaching Hospital in South IndiaDocument4 pagesPrevalence of Abnormal Pap Smear During Pregnancy in A Teaching Hospital in South IndiapebripulunganPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-691127747Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Board IIIDocument7 pagesPre-Board IIIAiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nikkiso Dialysis Machines PDFDocument2 pagesNikkiso Dialysis Machines PDFenricolamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ananth Narayan and Paniker 11th EditionDocument42 pagesAnanth Narayan and Paniker 11th EditionArjun Kandara50% (2)
- Crohns DiseaseDocument21 pagesCrohns DiseaseKasuganti koteshwar raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Svvfuip Brochure VersionDocument16 pagesSvvfuip Brochure VersionViswasukthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Galvano Terapy Topic - 2Document3 pagesGalvano Terapy Topic - 2Gigi CotoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Streptococci and Enterococci and OthersDocument11 pagesStreptococci and Enterococci and OthersthedarkwingPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccination Form (Sample)Document1 pageVaccination Form (Sample)Godfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- D10W (Anything D5W) - 3% Normal Saline ( 0.9% Hypertonic) - Mannitol - Parenteral NutritionDocument6 pagesD10W (Anything D5W) - 3% Normal Saline ( 0.9% Hypertonic) - Mannitol - Parenteral NutritionAlec Anon100% (1)
- Bài Tập Tự Luyện Unit 2: Your Body And You (Lesson 1) #hasuenglishclassDocument4 pagesBài Tập Tự Luyện Unit 2: Your Body And You (Lesson 1) #hasuenglishclassThu Tra NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- G PsumatDocument22 pagesG PsumattimworkmakesthedreamworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Advisor - A Medical Expert System For Diabetes ManagementDocument5 pagesDiabetes Advisor - A Medical Expert System For Diabetes ManagementPrincess LuniePas encore d'évaluation
- New York Imaging Specialists Announces Grand Opening in Port Jefferson StationDocument2 pagesNew York Imaging Specialists Announces Grand Opening in Port Jefferson StationPR.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Medical Use CountriesDocument5 pagesSecond Medical Use CountriesAnonymous AWcEiTj5u0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Male InfertilityDocument38 pagesMale InfertilityPrincessMagnoliaFranciscoLlantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument37 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromePramadya Vardhani MustafizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gra ViolaDocument8 pagesGra ViolaAnthony SullivanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1339-Article Text-24955-2-10-20220330Document6 pages1339-Article Text-24955-2-10-20220330Kevean Kimi LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)Document65 pagesRecent Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)amal.fathullahPas encore d'évaluation
- African Swine Fever: Pesti Porcine Africaine, Peste Porcina Africana, Maladie de MontgomeryDocument52 pagesAfrican Swine Fever: Pesti Porcine Africaine, Peste Porcina Africana, Maladie de MontgomeryDecereen Pineda Rodrigueza100% (1)
- Assignment 3 Suicide Prevention ProgramDocument20 pagesAssignment 3 Suicide Prevention Programapi-696109851Pas encore d'évaluation
- CVA Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesCVA Impaired Physical MobilitycessyannePas encore d'évaluation